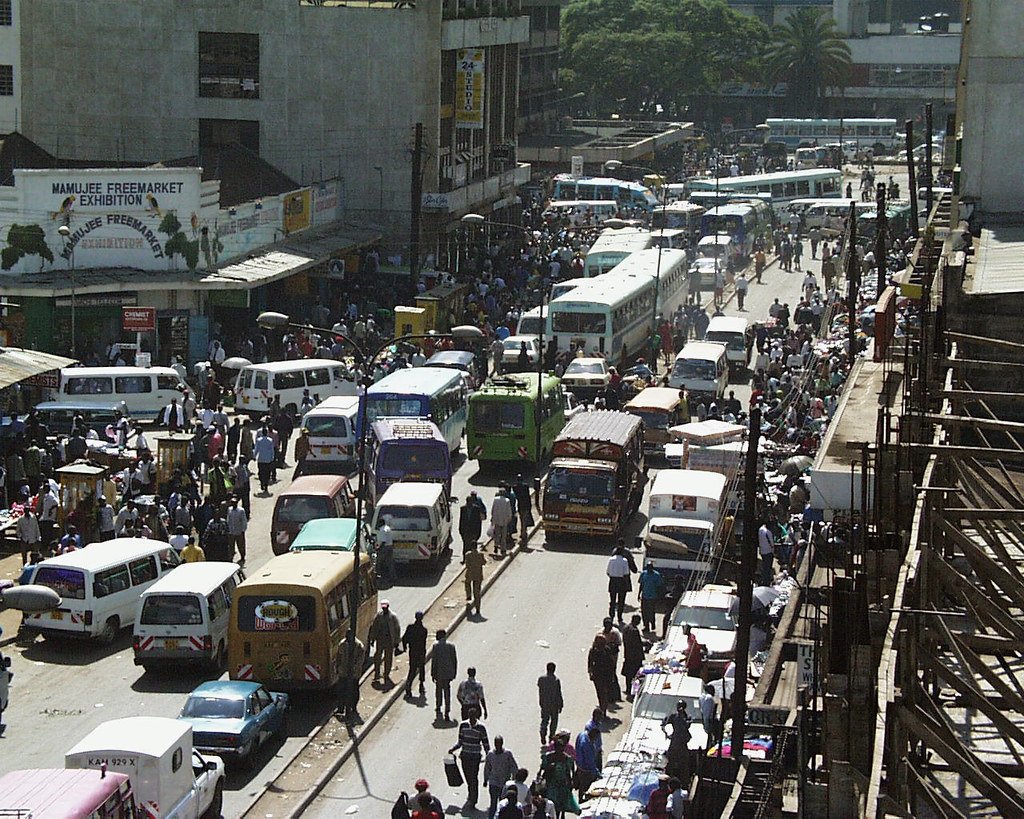
Off the coast of Europe and Africa, the Macronesian islands offer unspoiled landscapes, quaint towns, and stunning coastlines.
The island of La Gomera is located in the Canary Islands, one of the island chains that make up Macaronesia. Jörg Bergmann. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Macaronesia is a group of archipelagos in the North Atlantic Ocean. off the coast of Europe and Africa. It consists of the islands of the Azores and Madeira, (part of Portugal) the Canary Islands (part of Spain) and Cabo Verde (an independent group of islands formerly controlled by Portugal). Some of these islands are only a short flight away from many major cities in Western Europe and becoming more popular, leading to more development on some of them, but unspoiled wilderness remains prevalent.
1. São Miguel, Azores
The Lagoa das Sete Cidades features colorful lakes in the remnants of volcano calderas on São Miguel. energeticspell. CC BY-NC 2.0.
The largest island in the Azores, São Miguel features numerous beautiful natural sights for hikers and/or tourists. Due to minerals in the water, the lakes on the island come in various tints of green and blue. At a more temperate climate than many of the other Macaronesian islands, São Miguel receives more rain, resulting in many waterfalls on the island. Some companies lead rappelling excursions at the waterfalls. The seas around São Miguel are also prime for whale watching.
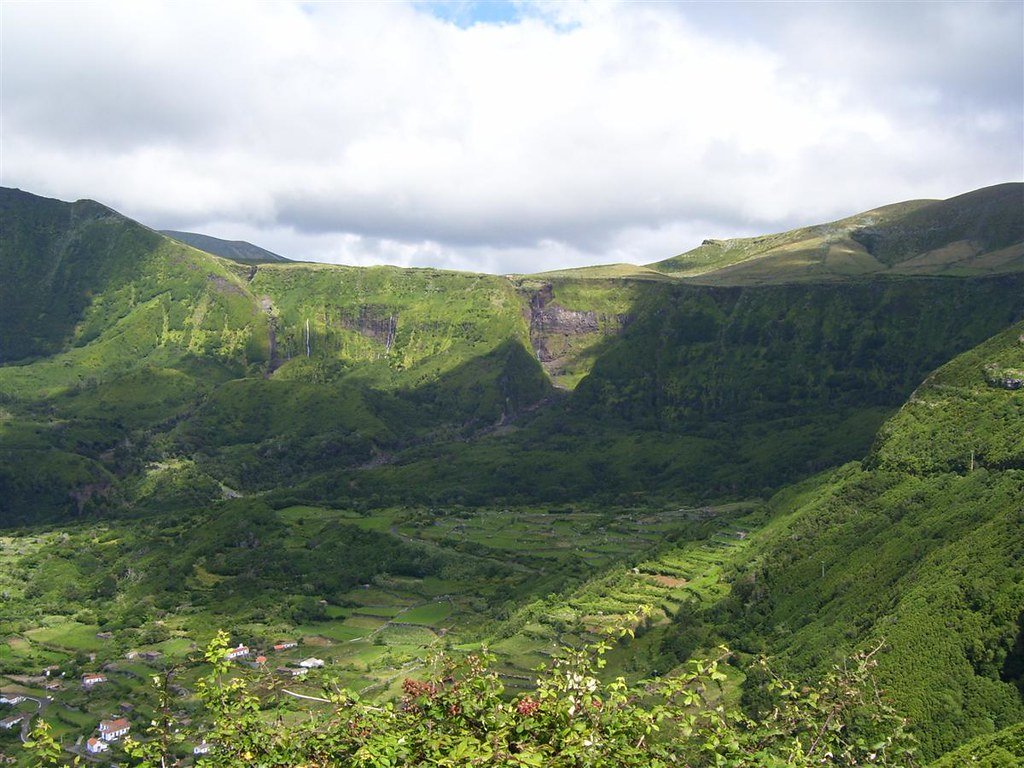
2. Flores, Azores
Lush, green cliffs characterize the island of Flores in the Azores archipelago. Paulo Corceiro. CC BY-ND 2.0.
One of the more remote islands in the Azores archipelago, Flores literally translates to “flowers” in English. Its stunning lush mountains are well-suited for hiking and canyoneering, with trails leading to some unique geological formations. Some places on the island to visit include the village of Fajã Grande, which is tucked in between cliffs and the Atlantic Ocean, and the 7 lagoons, the remnants of ancient volcanoes.
3. Madeira
The cliffs of Madeira. Kacper Gunia. CC BY-NC 2.0.
After a thrilling landing at one of the most challenging airports for pilots in the world, visitors step into a green oasis with dramatic mountains and steep drop-offs. In the past, Madeira was a maritime center with Christopher Columbus and James Cook making stops there on their voyages. Later, rich landowners built ornate summer estates on the island, such as the Monte Palace Madeira, which is a present-day vast botanical garden. Hiking trails criss-cross the island, with many built on the remnants of levandas, irrigation canals used to feed water to drier areas of the island. A strenuous hike to Pico Ruivo, the highest point on the island, rewards intrepid hikers with vast views.
4. La Palma, Canary Islands
The volcanic landscape of the island of La Palma. weberpal. CC BY-NC-SA 2.0.
The island of La Palma in the Canary Islands is fully operational again after the Cumbre Vieja volcano stopped erupting in December 2021. While it is still advisable to exercise caution around the eruption area, the rest of the island is free to be explored. Past volcanic eruptions have created unique rock formations underwater, making diving a popular activity off the coast of the island. Watersports such as kayaking and canoeing are also popular, especially along the sheltered coast of Fuencaliente. There is also an extensive network of hiking paths on the island, leading to a variety of unique landscapes.
5. Fuerteventura
Popular beaches and desert landscapes combine on the island of Fuerteventura. xavipat. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
The more southern islands of Macaronesia have a more arid climate, leading to more desert-like landscapes. Less than 100 kilometers from the coast of Africa, Fuerteventura consists of many popular beaches but also has quaint towns and rolling hills. As the first of the Canary Islands to be settled by Europeans, its first capital city of Betancuria was founded in 1404 and remains to this day and is a great place to learn about the island’s pre-Hispanic history. The island is also famous for its cuisine featuring majorero cheese and papas arugás with mojo (wrinkly potatoes with a local sauce).
6. Sal, Cabo Verde
The barren landscape of Sal is much more than what it seems. Phil Thirkell. CC BY-NC 2.0.
Another desert-like island, Sal is located in the northeast of the Cabo Verde archipelago and used to be the least populous island of the country until recent developments that have caused rapid growth. Like Fuerteventura, Sal has many beaches which are known as prime kiteboarding areas. Away from the beaches and resort areas lies what seems like a barren landscape, but tours on jeep and horseback can bring visitors to the remote interior to secluded areas. The island also has a legacy of salt mining, and it is possible to visit the Pedra de Lume area, which preserves the remnants of salt extraction operations.
Bryan Fok
Bryan is currently a History and Global Affairs major at the University of Notre Dame. He aims to apply the notion of Integral Human Development as a framework for analyzing global issues. He enjoys hiking and visiting national parks.