Sudan is facing what the U.N. has called the world’s largest humanitarian crisis as a result of its ongoing civil war.
Read MoreThe Cage Home Crisis in Hong Kong
Hong Kong's reputation as one of the most expensive housing markets in the world has led to more than 200,000 people living in cage homes, bedspace apartments likened to coffins for the living.
Read MoreThe Impact of Authoritarianism on Food Insecurity in Chad
Food insecurity and the authoritarian regime in Chad have denied many individuals and communities access to fundamental human rights.
Read MoreThe History of Favelas, Brazil’s Impoverished Towns
Since their emergence in the 19th century, favelas have faced continuous struggles with poverty and crime, a symbol of the tension between Brazil’s government and its underrepresented communities.
Favela of Telegrafo. patano. CC BY-SA 3.0.
Scattered throughout Brazil are built-up communities known as favelas. These towns, principally found on the outskirts of large cities like Rio de Janeiro or Sao Paulo, are settlements marked by their unique urban development. While they are often associated with drugs, crime and poverty, these neighborhoods are a symbol of Brazil’s complex history.
Finding their origins in the late 19th century, favelas emerged amid a period of tumultuous political and social change in Brazil. They initially formed after the country abolished slavery in 1888. With a large number of impoverished former slaves left homeless and unemployed, they started forming temporary shelters. These were mainly squatter settlements near their work, which was often found in cities. Over the years, these communities grew in number and size. However, it was only after the Canudos War in 1898 when they became the large settlements we know today. The War on Canudos, a deadly civil war that saw a massacre in the small town of Canudos, left almost 20,000 ex-soldiers homeless after their return from the conflict. With nowhere to live, the group established the first favelas in the federal state of Bahia.
As Brazil’s class divide grew, more favelas popped up from the 1940s to the 1970s, becoming more organized with newly created residents’ associations serving as communicators between the towns and the government. Collaboration between the two led to agreements about water and electricity accessibility and construction investment, playing a large role in the favelas’ maintenance. However, rising politicians during this era also targeted the favelas for political gain, stereotyping their existence as slums breeding disease, illiteracy, crime and moral corruption. Many favelas were “removed” as a result, but other methods were sought out to build up and sustain the communities’ infrastructure. Despite various programs intending to improve buildings, Brazil’s economic crisis led to failed attempts at providing adequate housing in many areas. At the same time, cocaine markets were growing globally, and Brazil became a prominent drug producer and transit point between European and U.S. markets. These criminal groups formed during the 1980s and solidified in the early 2000s, attracting more police attention to the neighborhoods.
In 2022, about 8.1% of Brazil’s population lived in favelas. Because of their densely built-up infrastructure and continuous struggles with crime and drugs, favelas have also become synonymous with slum life. Widespread poverty, in particular, has grown to be favela residents’ largest struggle, with economic hardship producing limits on food, healthcare and education. The government has proposed various methods to help tackle these ongoing issues and support the overall conditions of these communities. Authorities have introduced programs to help residents: setting up training programs, providing low-interest loans or materials to construct accommodations and building facilities such as health clinics or schools. Despite these attempts, favela residents still lack full sociopolitical representation and face police violence. Thus, activism in favela communities remains imperative, as residents continue to search for peace and draw attention to the need for social development and increased rights.
GET INVOLVED:
Residents living in favelas struggle against police brutality, discrimination and stark poverty daily. Those looking to help address these issues can do so in several ways, including through making donations. Outreach organizations include: The Favela Foundation, focusing on the development of sustainable social and educational programs; Catalytic Communities, an NGO based in Rio de Janeiro bringing sustainable programs and legislative support to favelas; and The Gerando Falcões Fund of BrazilFoundation, bringing education and economic development to the favelas. Supporting favela locals in their fight to speak out against systemic violence is also very important. Using social media to follow, share and repost activism can help circulate news and reframe the stereotypes usually associated with favela communities.
Julia Kelley
Julia is a recent graduate from UC San Diego majoring in Sociocultural Anthropology with a minor in Art History. She is passionate about cultural studies and social justice, and one day hopes to obtain a postgraduate degree expanding on these subjects. In her free time, she enjoys reading, traveling, and spending time with her friends and family.
The Ethics of Poverty Tourism in Brazil’s Favelas
Understand the implications of poverty tourism in Brazil, what a favela is, and how the growing tourist rates raise concerns about safety.
Read MoreParadise for Tourists is Hell for Canary Islands Residents
Canary Islands residents are protesting against mass tourism, which they say is making the islands uninhabitable.
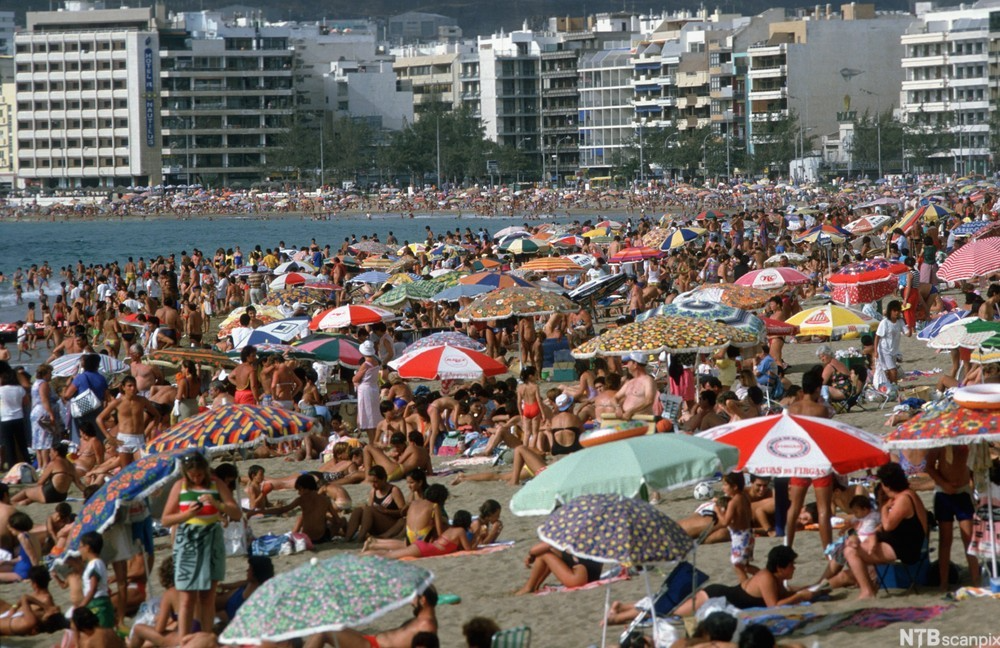
A crowded beach in Las Palmas. Trygve Bølstad. CC BY-NC-SA
The Canary Islands have long been a hotspot for tourism. Vacationers flock to the archipelago in imposing numbers, drawn by the islands’ mild climate, rich cultural history and stunning vistas. In 2023, approximately 14 million international tourists visited the Canary Islands, representing an increase of roughly 13 percent compared to the previous year, and tourism accounts for approximately 35 percent of the islands’ GDP. Unfortunately, not all residents are experiencing the benefits of this influx. In fact, many locals have begun to complain that the massive waves of tourism are actively contributing to a decline in their quality of life.
While the Canary Islands host large numbers of tourists every year, approximately 15 million, they are home to only 2.2 million native residents. Of those 2.2 million, 33.8 percent are at risk of poverty according to a living conditions survey conducted by the Instituto Nacional de Estadística of Spain in 2023. The same survey designated the Canary Islands as one of the autonomous communities in Spain with the highest percentage of people making ends meet with “a lot of difficulty.”
Canary Islands. PxHere. CC0 1.0
The tourism industry only exasperates the economic challenges faced by residents. The islands’ resources are simply not equipped to sustain the large numbers of tourists, who put pressure on health services, waste management, water supplies and biodiversity. According to reports, tourists use up to six times more water than residents who, as a result of a drought brought on by climate change and rising temperatures, have been subjected to restrictions on water usage. Meanwhile, tourist resorts and golf courses have not been made to comply with the same restrictions.
Biologist Anne Striewe commented on the toll tourism takes on the environment. “There are hundreds of boats and jet skis in our waters every day pumping petrol into the water,” she said, “then there are the boat parties which blast music all day long…this is picked up by whales and other creatures and really confuses and frightens them … Meanwhile, there have been multiple cases of animals being injured or killed by boat propellers, there are often vessels in protected waters but no one is cracking down on the activity.” According to the environmental group Salvar Tenerife (Save Tenerife, the largest of the Canaries), millions of liters of sewage water are being dumped into the sea off Tenerife and other islands every single day, with amounts rising in accordance with the number of visitors.
Sticker against overtourism, 2024. Rasande Tyskar. CC BY-NC 2.0.
Female residents have reported feeling unsafe in the presence of tourists who harass and follow them in public. Trailers park illegally and leave trash in their wake. The number of hotels being built and the amount of housing being converted to short-term rentals to accommodate these tourists has caused a rise in the cost of living. As a result, some locals have been forced to begin sleeping in their cars and in caves. "It is absurd to have a system where so much money is in the hands of a very few extremely powerful groups, and is then funneled away from the Canary Islands," says Sharon Backhouse, who owns GeoTenerife along with her Canarian husband, a program that runs science field trips and training camps in the Canary Islands and conducts research into sustainable tourism.
Thousands of locals took to the streets in April to protest over tourism and defend their right to live in their native land. “We are not against tourism,” Rosario Correo, one of the protesters, clarified to the media, “We’re asking that they change this model that allows for unlimited growth of tourism.”
Protesters are calling for a halt to the construction of a hotel and a beach resort on one of the few remaining unoccupied beaches, a moratorium on all tourism development projects, stricter regulation on property sales to foreigners and a more sustainable model of tourism that will not put the environment or the livelihoods of locals at risk. “I feel like a foreigner here, I don't feel comfortable anymore, it's like everything is made for British and German tourists who just want to drink cheap beer, lay in the sun and eat burgers and chips,” another protester, Vicky Colomer, said. “We need higher quality tourists who actually want to experience our culture and food and respect our nature.”
The protests have motivated the government to introduce measures to limit tourism. The island of Tenerife announced a tourist tax of an undisclosed amount that will go into effect on January 1, 2025 for tourists seeking to visit natural beauty spots. A law that would place harsher regulations on short-term rentals is also expected to pass in 2025.
Rebecca Pitcairn
Whatever it is, the way you tell your story online can make all the difference.
The Global Social Ladder: The Best and Worst Countries for Social Mobility
The World Economic Forum's Global Social Mobility Report 2020 unfolds a gripping narrative.
Read MoreFood Deserts, Food Swamps and Food Apartheid
Around 2.2 percent of all U.S. households live in areas without access to inexpensive healthy foods, leading to higher rates of obesity. These “food deserts” stem from a history of racism and inequality.
Food deserts are areas where residents don’t have easy access to healthy, affordable food. Instead, they may be overrun with fast food options. Mike Mozart. CC BY 2.0
Approximately 23.5 million Americans live in areas with limited or no access to affordable, healthy foods—especially fresh fruit and vegetables. These areas are commonly known as “food deserts” and are disproportionately found in low-income, minority communities.
Food deserts occur when there are few or no grocery stores within convenient distance; for example, a survey by the U.S. Department of Agriculture found that 2.3 million people live more than one mile away from a grocery store and do not have a car. In urban areas, the nearest grocery store might be a long trip away via public transportation, and not everyone is able to take time out of their day to make the trek, especially those in low-income neighborhoods who may be working more than one job.
Despite common misconceptions, living in a food desert does not necessarily mean that a person is food insecure. In fact, food deserts are often flooded with food choices—just not ones that are both healthy and affordable. A food desert may have plenty of smaller stores to buy food from, but these stores typically have limited options compared to grocery stores, specifically in the availability of fresh produce. Without easy access to grocery stores, people living in food deserts must turn to more convenient and affordable options, namely fast food.
Experts have coined the term “food swamp” to describe areas that are oversaturated with unhealthy food options. A study by the University of Connecticut’s Rudd Center for Food Policy and Obesity found that an average food swamp has four unhealthy eating options for every one healthy option.
Because people living in food deserts and food swamps have easier access to unhealthy food than healthy options, these areas also suffer from higher obesity rates. Studies have shown that food swamps may be a more accurate predictor of obesity rates than food deserts. However,food swamps and deserts tend to occur in the same areas, and more often than not these areas are low-income, minority communities.
The USDA has identified over 6,500 of what they refer to as “food desert tracts” based on census data and data about the locations of large grocery stores. In a 2012 study about the characteristics and causes of food deserts, the USDA found that areas with greater levels of poverty were more likely to be—or to become—food deserts. The study also concluded that “food desert tracts have a greater concentration of all minorities” than tracts that are not considered food deserts.
Because of the way that food deserts disproportionately impact minority communities, some food justice activists, like Karen Washington, prefer the term “food apartheid,” as it better captures the racial and economic nuances of the situation. Washington points out that “food desert” brings to mind “an empty, absolutely desolate place” with no food to be found, but this is not what a community with poor access to healthy food looks like. Nina Sevilla, another food justice activist, notes that “desert” implies that these areas are naturally occurring, which is not the case.
“Food deserts” are the result of decades of systemic racism that led to housing segregation; under the Federal Housing Administration starting in the 1930s, middle and lower-class white families migrated to the suburbs while minority families remained in urban housing projects. Redlining policies prevented minority groups from moving into what were seen as white neighborhoods. As white middle-class residents shifted to the suburbs, so did new supermarkets, leaving minority neighborhoods without easy access to a wide variety of food.
The term “food apartheid” highlights how these racist policies shaped low-income minority communities’ access to healthy food.
Since food inequality and so-called food deserts and food swamps are so rooted in racism, they are not an easy problem to address. However, there are many organizations working on different solutions to food apartheid, from championing policy reform to building alternative food systems, such as urban and small-scale farming and affordable organic grocery stores.
To Get Involved:
To learn more about where “food deserts” in the U.S. are located, look at the USDA’s Food Access Research Atlas here.
For a comprehensive policy platform on food, visit the HEAL Food Alliance here.
Rachel Lynch
Rachel is a student at Sarah Lawrence College in Bronxville, NY currently taking a semester off. She plans to study Writing and Child Development. Rachel loves to travel and is inspired by the places she’s been and everywhere she wants to go. She hopes to educate people on social justice issues and the history and culture of travel destinations through her writing.
A Cycle of Dependency: How Donations Worsen Income Inequality
Regardless of the good intentions behind donations, the short-term gain experienced by poor communities often leads to the persistence of income inequality and an endless cycle of dependency.
Secondhand clothing in Haiti. Vanberto. CC BY-NC-SA 2.0
Donations are often associated with a positive image of helping destitute populations get the resources they lack. Yet, this short-term aid often results in far-reaching consequences detrimental to a country’s economy, which leads to the persistence of income inequality.
The donation of money that goes toward buying resources for impoverished communities often creates an endless cycle of dependency, especially if such service is repeatedly conducted through organizations or companies. First, the repeated nature of such service creates a false assumption among receivers that there will always be a supply of that resource without work, making them reliant on such aid. Moreover, the organizations themselves are indirectly relying on marginalized areas to promote their businesses’ charitable work. For instance, back in 2006, when TOMS started its “one for one” program, it would donate a pair of shoes for every pair that was purchased. Although the company’s motive seemed to be pure, it relied on underprivileged populations’ need for shoes to increase its business revenue.
84% of unwanted clothing is thrown into landfills
When donations are consistently provided, those living in poverty often learn to become dependent on the donors as they see less reason to get out of their current situation. Local businesses also shut down, as the need to produce items goes away when high-quality donations are provided at a minimal price from external sources. Although that may come as great news for citizens of developing countries, most of the profit in this exchange goes to the exporters. A 2006 report found that, “textile and clothing employment in Ghana declined by 80% from 1975 to 2000; in Zambia it fell from 25,000 workers in the 1980s to below 10,000 in 2002; and in Nigeria the number of workers fell from 200,000 to being insignificant.” Such statistics imply that despite the good nature of external aid, it often comes at the expense of the receiving countries.
Haiti is a common dumping ground for secondhand clothing primarily from the United States, and due to its regular occurrence, locals have given this process the name “Pepe.” The Netflix documentary “The True Cost” elaborates on how Haiti’s textile industry is suffering due to the widespread popularity of Pepe, leading the country’s local clothing industry to disappear. For this reason, some countries have started to refuse the import of secondhand clothing, and more of it ends up in recycling facilities. Yet according to Newsweek, 84% of unwanted clothing is thrown into landfills.
To combat waste, then, the fast-fashion industry needs to start recycling its own goods, minimize seasonal sales, make more durable products and normalize wearing recycled apparel. Additionally, governments need to start promoting the creation of more jobs for impoverished communities, so that all the necessary resources are available in the market at reasonable prices. Finally, donors should remember that regardless of good intentions, deprived communities may suffer long-term consequences due to misunderstood charity work.
Swati Agarwal
Swati Agarwal is a sophomore at University of California, San Diego, where she is studying Environmental Sciences and Theatre. Although born in India, she was raised in Tokyo, which gave her the opportunity to interact with diverse people from distinct cultures. She is passionate about writing, and hopes to inspire others by spreading awareness about social justice issues and highlighting the uniqueness of the world.
Structural Violence: How Societal Factors Affect Health
Income, race and geographic location are often weaponized against communities, preventing them from accessing and achieving health and wellness.
A routine doctor’s appointment may be rare for those living in poverty, causing them to not seek treatment for incipient medical issues. #PACOM. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Income, geographical location, climate and access to resources all affect people’s health in various ways. Indeed, it is rare to get malaria, a mosquito-borne disease in the Arctic. It is also comparatively easier for a wealthy person who has access to top-notch treatments to recover from cancer than a disadvantaged person who cannot afford a routine doctor’s appointment. These societal factors have a proven link to health outcomes, and they are usually not controlled by individuals. To fully foster public health, it is necessary to eliminate those societal factors that precipitate health concerns.
There are both biological and societal factors that affect health. Biologically, genetics can affect one’s health, as the causal relationship between genetics and diseases such as cystic fibrosis have been demonstrated through medical research. However, biological factors are not the only thing that affects health; societal factors do as well. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines social determinants of health as:
The non-medical factors that influence health outcomes. They are the conditions in which people are born, grow, work, live, and age, and the wider set of forces and systems shaping the conditions of daily life. These forces and systems include economic policies and systems, development agendas, social norms, social policies and political systems.
Sometimes, the system itself is rigged against a substantial part of the population from attaining complete physical, social and emotional well-being. That is called structural violence. These arrangements are ‘structural’ because they are “embedded in the political and economic organization” of society, and they are ‘violent’ because they harm people, whether physically or not.
Lowndes County, Alabama, where the low-income Black population suffers disproportionately from hookworm infections due to structural violence. jimmywayne. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
One example of these biosocial determinants and structural violence in play can be found in rural Alabama, where hookworm, a disease thought to be eradicated years ago, is making a resurgence in Lowndes County. That county is 72% Black and has a poverty rate of 21.9%, almost double the national average of 11.4% in 2020. Low-income Blacks in the county are more prone to hookworm because they live next to pools of raw sewage, the perfect breeding ground for the worms.
Structural violence is also at play here, as the Black population live near the pools of raw sewage because they cannot afford proper sewage systems. The local and state government, in turn, perpetuates this problem by turning a blind eye on the issue and not providing any assistance to the residents. Through no fault of their own, Blacks in Lowndes County have a heightened risk for hookworm due to the circumstance in which society makes them live.
Cultural practices can also precipitate or hinder disease. West African countries that already had fragile healthcare systems were particularly affected by the 2014 Ebola outbreak because of cultural practices regarding funerals. In those cultures, funerals involve washing the dead body by hand before burial and paying respect to the dead through physical contact, both of which are exceptionally high-risk activities with regards to the spread of Ebola, since the virus is still present in the corpse. Controlling the Ebola outbreak must address these cultural issues.
Finally, around the world, food deserts are scattered around urban centers, usually located in areas of poverty. Food deserts are areas with a dearth of supermarkets and other sources of healthy foods, forcing people living there to travel further for quality foods or to settle for cheaper unhealthy foods. Since many food deserts are in areas of poverty, the people living in those areas usually have no choice but to buy cheap foods with subpar qualities. The unhealthy diet of many in those areas lead to higher rates of obesity and cardiovascular disease.
Structural violence affects food deserts, as the economic disincentives for healthy food sources to serve low-income areas show that society does not provide adequate support to them. In northern Ireland, food deserts are especially pronounced since 32% of households do not have a car. Some food deserts are the result of years of neglect of marginalized communities. Failure of the UK government to provide adequate public transportation in northern Ireland demonstrates that neglect.
Simply treating disease without regard for the underlying causes of it will not eliminate the issue. To eliminate hookworm, proper sanitation services must be implemented. Containing Ebola means educating local communities about safe methods to bury the dead in a way that does not denigrate their culture. To eliminate obesity, focus should be on providing access to healthy foods instead of just telling people to change their diet. It is important to treat diseases as complex issues instead of having a singular focus on the cure. Removing societal barriers to good health is instrumental in ensuring the physical, social and emotional health for all.
To Get Involved
The organization Partners in Health serves to improve healthcare in developing countries through patient-provider partnerships. Partners in Health works to create sustainable healthcare systems that serve all, emphasizing healthcare as a human right.
Often, the best way to remove the societal factors that affect health negatively is by advocacy. Writing to your elected officials is a good way to draw attention to those issues, which may spur them to act on your recommendations. To find your representative in Congress, click here.
Bryan Fok
Bryan is currently a History and Global Affairs major at the University of Notre Dame. He aims to apply the notion of Integral Human Development as a framework for analyzing global issues. He enjoys hiking and visiting national parks.
The Influx of ‘Pisupo’: Food Colonialism in the South Pacific
Globalization has created an influx of unhealthy canned food in the South Pacific region, leading to a dependency on it and increasing health issues associated with an unhealthy diet.
The influx of canned food in the South Pacific has led to a variety of problems. Salvation Army USA West. CC BY 2.0.
The legacy of colonialism has a lasting impact on the island of the South Pacific. Many of those islands have been colonized by Western powers, and some of them are still under the control of foreign countries. Due to this, Western influences are still pervasive throughout the region.
One lasting legacy of Western imperialism in the South Pacific is the introduction of canned and processed food. The first canned food to be brought to the region was pea soup, and therefore, Samoan and a few other languages of the region, the word for canned food in general is “pisupo.” Today, the predominant type of canned food in the region is corned beef.
The prevalence of canned food in the South Pacific has changed the diets of the people living there and has caused a dependence on them. The new diets of the South Pacific Islanders are not necessarily an improvement from their traditional diets. However, as canned and processed foods are generally unhealthy and lacking in nutrients. That has resulted in an increase of obesity, diabetes and heart disease. Between 1990 and 2010, the total disability-adjusted life years lost to obesity also quadrupled in the region.
The traditional diets of South Pacific Islanders provide the nutrients needed for a healthy life. whl.travel. CC BY-NC-SA 2.0.
In order to provide these new foods, livestock such as cattle and pigs have been introduced to the islands, causing ecological damage. The island ecosystems are fragile, and large-scale ranching can easily destroy them. The dependence on canned food introduced by the West has resulted in not only harm to health, but also harm to the environment.
The proliferation of packaged and processed food has affected other parts of society as well, not just the typical diets. In marriage and birthday ceremonies in traditional South Pacific cultures, people often exchange gifts. While in the past, common gifts included fine mats and decorated barkcloths, but today, canned corned beef is one of the more popular gifts at those events. The introduction of canned foods has even changed traditional practices and contributed to the prevalent unhealthy diets of the South Pacific Islanders.
“Pisupo Lua Afe (Corned Beef 2000)” is a piece of art by Michael Tuffery that critiques the food dependency of the South Pacific. Sheep’R’Us. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
The neocolonial nature of these developments has its critics. One of them, Michael Tuffery, offers a unique interpretation through his artwork, with one of the most notable being “Pisupo Lua Afe,” a sculpture of a bull made from canned corned beef. He says that his art addresses the impact that the “exploitation of the Pacific’s natural resources has wrought on the traditional Pacific lifestyle.” His choice of subject matter and the material show his thoughts on the influx of canned food in the South Pacific. Bulls were a common presence at the aforementioned ceremonies, and the fact that the bull is covered in canned corned beef represents the fact that more traditional practices. Tuffery laments the changes that globalization has brought to his traditional Samoan culture, which has led to a “decline of indigenous cooking skills.”
With so much waste being created in the making of “Pisupo Lua Afe,” Tuffery calls into question whether the physical and cultural costs of food dependence are worth it. Could the South Pacific do better without the influx of canned food? Tuffery argues that it could. But even if the South Pacific Islanders decide to shun the prevalence of canned food, hurdles remain to improve the health of both the land and people of the region.
Bryan Fok
Bryan is currently a History and Global Affairs major at the University of Notre Dame. He aims to apply the notion of Integral Human Development as a framework for analyzing global issues. He enjoys hiking and visiting national parks.
VIDEO: Growing Up in a Megaslum in Kenya
Joseph Djemba grew up in Kibera, Kenya, the largest urban slum in Africa. Djemba found himself there when his mother became unable to support her eleven children after the death of her husband. Djemba describes his childhood sleeping outside and begging for food, detailing the psychological impacts of living in poverty. He also notes the large gap between the rich and the poor in Kenya and discusses how impoverished people help each other survive. Djemba is the main character in “Megaslumming,” a book by Adam Parsons. In his work, Parsons explores how the settlement of Kibera came into existence and documents what life is like for those who live in slums.
Get Involved:
Touch Kibera Foundation is a non-profit organization devoted to uplifting children who live in Kibera, Kenya through sports programs, sexual health programs, education support and mentorship opportunities. Donations are accepted online, and more information can be found here.
Polycom Development Project is a foundation which seeks to provide educational and athletic opportunities to girls and women in Kibera. The organization is also devoted to promoting sanitation and public health. Donations are accepted online, and more information can be found here.
St. Vincent de Paul Community Development Organization aims to provide support to orphaned and other vulnerable children in Kibera. The organization supports families and seeks to intervene on behalf of children at an early stage in their development. Donations are accepted online, and more information can be found here.
Half of South Korean Elderly Are Living in Extreme Poverty
The pension retirees receive is only a quarter of the amount needed for single households, causing many elderly to return to work.
Elderly South Korean woman. Mctrent. CC BY-NC 2.0
South Korea is known for high rise buildings, luxury skin care and high tech devices. Yet with all of these advances, it has the worst senior poverty rate among developed nations. The population has been struggling to stay off the streets with only 35% of seniors receiving a monthly pension. Fewer than half of seniors receive government assistance and it is only a quarter of the amount needed to cover basic necessities.
The Confucian tradition of children taking care of their parents is fading in South Korea. In previous generations the elderly turned to their children for financial assistance, often living with their children until their passing. However, the Census has shown that one in three Korean seniors live alone today and six out of ten elderly are supporting themselves. It has become difficult for children to help aging parents due to the expensive cost of living and the high unemployment rate. The country’s legal retirement age is 60, but many employees at private companies are pressured to leave around age 50 due to scarce executive or high-ranking jobs. When they retire at such a young age, they realize their pensions or severance packages are far below the cost of living and that the social safety net is insufficient. They are forced to re-enter the working world, but often in positions that are temporary or day-to-day, offering very low pay.
Retiree collecting cardboard boxes. Mariej55quebec. CC PDM 1.0
In order to make a living, many retirees collect anything that can be recycled and transported to the local junk yard using makeshift handcarts. Cardboard boxes are what they tend to collect most because they are the easiest to come across. Although prices vary, the average income per kilogram (2.2 lbs.) is 40 won ($0.33). On a 12 hour day, retirees earn about $6.68: a salary that’s far below the poverty line. South Korea is expected to become a “super-aged society” with more than 20% of its population aged 65 years and older by 2026. A fall in the fertility rate and rising longevity are the two fundamental contributors to the country’s growing ageing population.
Pre-pandemic, soup kitchens were a social gathering place for many retirees. A popular one among the elderly was Angel Soup Kitchen. On average, they served more than 350 free meals three times a week: operating 26 centers across South Korea. Retirees would line up in the early hours of the day to guarantee a spot in line. It was a place where they could be among other seniors enjoying a meal. However, with the pandemic and the elderly being the most vulnerable, Angel Soup Kitchen closed and now distributes take home meals. With so many soup kitchens closing, Warm Chaeumteo was one of the few that remained open. They provide three meals a day, seven days a week. Due to the temporary closure of other soup kitchens, the center is getting approximately 100 more visitors a day, compared with the normal turnout before the outbreak. They receive just under 1,000 people per day. It is becoming harder to keep soup kitchens open with the decline in volunteers, many deciding they want to avoid face to face interactions.
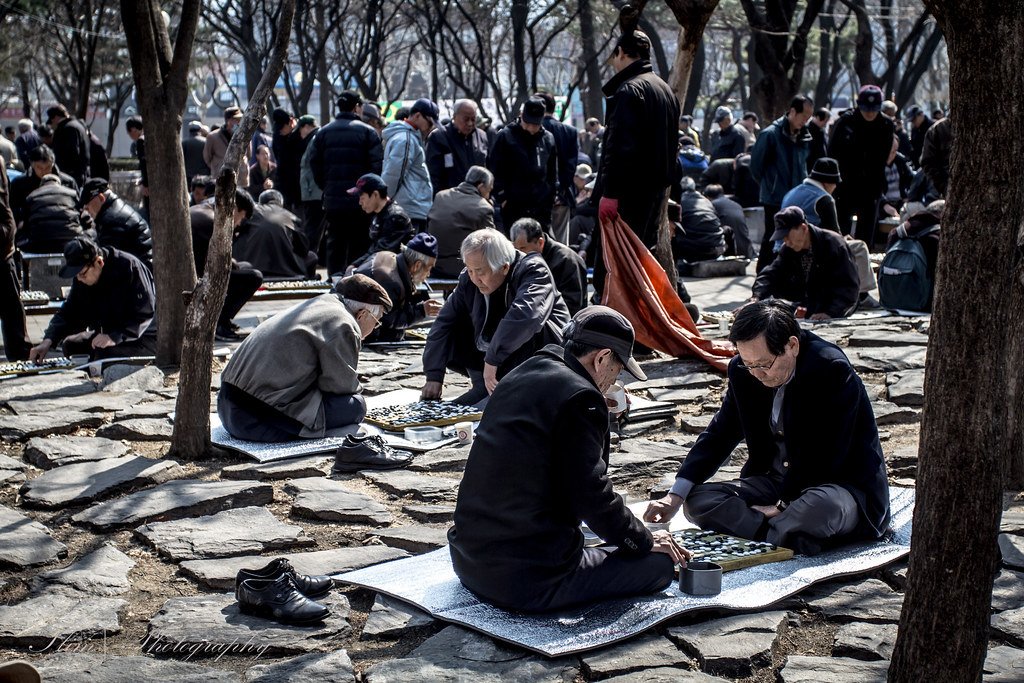
Senior Koreans Playing Chess at a Park. Terence. CC BY-ND 2.0
The mental health of retirees has seen a spike in recent years. The disruption of the traditional family unit is a large reason why. Children often lose contact with their parents, leaving the retired elderly to feel lonely and isolated. A long term effect of these feelings will trigger depression, anxiety and loneliness. To socialize, retirees frequent parks and public areas, but with the restrictions of the pandemic, most areas are now closed. This forces the elderly into further isolation and a toll on their mental health. Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service reported that about 40% of the 684,000 Koreans diagnosed with severe depression were over age 60. With an aging population that will only continue to grow, countries with large elderly populations are facing an unprecedented issue: how to properly care for a large influx of elderly people, while still moving towards the future. Living longer is usually associated as being a hallmark of success, but current societal structures in many countries are not equipped to provide the social services needed.
As South Korea and the globe try to figure out how to care for this large wave of retirees living longer, there are startups like EverYoung. A company that only hires employees aged 55 and older. Employees monitor blog content and detect sensitive information, as well as perform other IT tasks. There are 420 seniors from a variety of career backgrounds employed. Moreover, a mandated 10-minute break for every 50 minutes of work, and staff are rostered on four-hour shifts. Manager Kim Seong-Kyu told ChannelNews Asia that older employees have detail-oriented skills not common in the younger workforce, with distracting cell phones stored away during work time. Kyu said, “they are full of passion. The time that they have, and their interest in this work, are primarily why they come to work”.
To Get Involved:
The Korea Legacy Committee and Asian Boss have partnered to provide free meals every Sunday for the South Korean elderly. They aim to become a safe haven for impoverished seniors and expand the meal program around the country.
To learn more about Korea Legacy Comittee click here.
To support the South Korean elderly during the pandemic click here.
Jennifer Sung
Jennifer is a Communications Studies graduate based in Los Angeles. She grew up traveling with her dad and that is where her love for travel stems from. You can find her serving the community at her church, Fearless LA or planning her next trip overseas. She hopes to be involved in international humanitarian work one day.
A Cage Home Away from Being Homeless in Hong Kong
Cage homes have become the dangerous solution to living in the most expensive housing market in the world: Hong Kong.
Man Living in a Cage Home. Pondspider. CC BY-NC-SA 2.0
Hong Kong is considered one of the most expensive cities to live in the world. The population of 7.4 million people live in a metropolis 110 times smaller than New York City. Many struggle with the mounting housing prices which seem to keep rising. As a dangerous solution, low income individuals have developed "cage homes'' or “coffin homes” in which they reside. It consists of a bed-space, usually made of wood or wired boxes, large enough to only fit a bed and one or two personal items. An estimated 200,000 people, including 40,000 children live in cage homes in Hong Kong. The poor and elderly are the ones experiencing the effects the housing crisis Hong Kong has caused.
Out of desperation, many people are deciding to live out of these cage homes in order to avoid living on the streets. These barbed wire “homes” were created in the 1950’s due to an influx of refugees coming from mainland China. They provided cheap labor for Hong Kong and, therefore, a demand for low cost bed space apartments. The apartment operators decided to make more profit by stacking bunk beds known as cages on top of each other, and the term “cage home” was created. Since then, the inhabitants have grown from immigrant workers to elderly men and women and children.
An average home in Hong Kong is about $1.28 million USD and a tiny “nano” apartment is on average $500,000 USD. Cage homes are approximately $230-$300 USD a month. They are the size of a parking space in the US, 7.5 feet in width and about 10 feet in length. They’re stacked on one another and there are approximately 30 cage homes in one room. All of the renter’s personal items are locked away at night or when renter’s go out for the day. Bathrooms are mostly communal and often there are no kitchens, just electric portable burners. While living in these homes, renters usually have no privacy or natural light coming in. Most windows are away from where the cage homes are placed. Many of the cage homes are in older urban districts, such as, West Kowloon, Sham Shui Po and Mongkok.
The mental and physical effects of living in a cage home are concerning. The people who live in these spaces are dealing with depression, anxiety and stress due to their financial situation and cramped living space. Although they live among others, they often feel isolated and alone. Hygiene is also a big issue when living in these confined spaces. Up to a dozen people share bathrooms and kitchen areas, which are at times both in one room. In addition, there are poor safety regulations due to the buildings’ age and the number of people living in these tight spaces. The inadequate fire protection is a big risk many face when choosing to live in constricted spaces like these. Renters often have to deal with the infestation of rodents, roaches and bed bugs, which in turn affects their sleep and adds to health issues. There is poor air quality and no ventilation systems, with summer temperatures making it unbearable. Some elderly people have described their lives in their cage homes as “waiting for death.”
The new coronavirus pandemic has made it extremely difficult to live in these confined spaces. The cage home inhabitants find it impossible to quarantine safely as they do not have any walls or personal space. Most of them have to wear masks to sleep in order to avoid contracting the virus from others in their room. Many who live in the cage homes used to escape their reality by spending the day in parks, librairies or jungle gyms, however the pandemic has forced all public areas to close. Now cage home dwellers pass the time by, napping, listening to music or watching TV. Volunteers visit the people living in these spaces and bring food to donate, while also spending time with the residents to ease their loneliness.
Panorama of Hong Kong. CC BY-NC 2.0
The reason for the rising costs in the housing market is Hong Kong’s dense population, in which only seven percent of the city’s land is used for residential living. The pace of land supply and creation has slowed down in recent years. With low supply and high demand for living space, Hong Kong’s housing prices have no chance to come down. Chief Executive of Hong Kong Carrie Lam has proposed a variety of measures to boost the number of homes in the residential market. Her plan includes an aggressive target to turn the remote northern part of the city into a “metropolis” for 2.5 million people, a project that will take decades to complete. In July, Director of the Hong Kong and Macau Affairs Xia Baolong set a city goal to eliminate its ‘infamously small apartments’ by 2049. This refers to less than 500 square foot apartments many residents live in. The Hong Kong government legally recognised cage homes, but did so under the label “bedspace apartments,” which are defined as “any flat in which there are 12 or more bed spaces occupied or intended to be occupied under rental agreements.” The United Nations has taken notice and calls the poor conditions present “an insult to human dignity”.
Jennifer Sung
Jennifer is a Communications Studies graduate based in Los Angeles. She grew up traveling with her dad and that is where her love for travel stems from. You can find her serving the community at her church, Fearless LA or planning her next trip overseas. She hopes to be involved in international humanitarian work one day.
Africa Faces Higher Food Insecurity Due to COVID-19
Africa experiences food insecurity due to poverty, conflict, climate change and a lack of access to food. When COVID-19 hit, it made all of these matters much worse.
A man inspects failed corn crops in Mauritania. Oxfam International. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Although made significantly more severe by COVID-19, food insecurity has been a serious concern worldwide for decades, mostly caused by economic shocks, climate change and conflict. According to the U.N. Food and Agriculture Organization, 239 million people in sub-Saharan Africa were undernourished as of 2018.
The COVID-19 pandemic has heightened food insecurity across the world by reducing incomes and disrupting food supply chains. The United Nations warns that about three dozen countries—Ethiopia, Nigeria and South Sudan included—could experience major famines this year, pushing 130 million more people to starvation. East Africa’s biggest locust invasion in 70 years combined with the impact of COVID-19 threatens to drive 25 million people into hunger. Research from a series of high-frequency phone surveys shows that over 105 million adults have been affected by some degree of food insecurity across Uganda, Nigeria, Malawi, Ethiopia and Burkina Faso following the onset of the pandemic. Devastated food sources and billions of dollars in crop damage may push residents over the edge.
In addition, preventive measures like border closures, lockdowns and curfews intended to slow the spread of COVID-19 are disrupting supply chains that struggled to keep markets well-stocked even before the pandemic. At least 60% of the African population is dependent on agriculture for their livelihoods and access to food, and disruptions to this system caused by COVID-19 are threatening this group’s food security.
A man tending to his crops in Uganda. Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade. CC BY 2.0.
Most African countries rely heavily on food imports; between 2016 and 2018, Africa imported about 85% of its food from outside the continent. Heavy reliance on world markets is extremely detrimental to food security, and export bans imposed by major food exporters due to COVID-19 made the region even more vulnerable. If trade blockages persist, agricultural production in Africa could decrease by between 2.6% and 7%.
African countries are also reporting shortages and price spikes for some domestic food crops, such as millet, sorghum and maize. In addition, the disruption of marketing and trade activities, combined with panic-buying during the pandemic, intensified food price increases and caused both rural and urban consumers to lose purchasing power.
As a direct result of rising food prices, the availability and affordability of nutritious food has plummeted. Nutrient-rich foods like eggs, fruit and vegetables are 10 times more expensive than staple foods like rice or wheat in sub-Saharan Africa, so vulnerable families were forced to buy cheaper and less nutritious food to survive, adding to a rise in malnutrition and obesity.
In addition, school closures in South Africa have stopped a national feeding program that provides nutritious meals to 9 million poorer children.
Restrictions imposed by governments—lockdowns, travel bans and social distancing measures included—have increased the risk of food insecurity, and many low-income households have lost their livelihoods and ability to access markets.
A fruit and vegetable stand in Kampala, Uganda. World Bank Photo Collection. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
COVID-19 has clearly had a detrimental effect on food security in Africa, with 43% of households that were not severely food insecure in 2018 estimated to be severely food insecure as of June 2020.
However, there are ways to help, and many government programs have already started to alleviate some of the hunger in Africa. In Chad, a government project is providing food kits, establishing cereal banks and distributing seeds for future harvests so that households can survive the rest of the pandemic. In East Africa, the U.S. Agency for International Development’s Feed the Future program is supporting measures to keep food and agricultural inputs moving across borders and from ports to inland countries.
Although many efforts to help Africa are already in place, it is imperative that African countries take the necessary steps to build resilient, climate-friendly and competitive food systems so that they can survive COVID-19 and any future challenges.
To Get Involved:
Donating to Oxfam South Africa or Action Against Hunger will help to provide essential care to hungry families in Africa. Additionally, the U.N. World Food Program uses donations to deliver lifesaving food to those in need, wherever they may be located.
Another great way to help is by giving to The Hunger Project, which uses donations to implement programs that mobilize rural communities to achieve sustainable progress against hunger. These are just a few of the many ways to get involved to help end the crisis. To learn more, visit the United Nations’ website on hunger in Africa.
Isabelle Durso
Isabelle is an undergraduate student at Boston University currently on campus in Boston. She is double majoring in Journalism and Film & Television, and she is interested in being a travel writer and writing human-interest stories around the world. Isabelle loves to explore and experience new cultures, and she hopes to share other people's stories through her writing. In the future, she intends to keep writing journalistic articles as well as creative screenplays.
Video: Devastating Impacts of COVID-19 in India
Although much of the world is beginning to overcome some of the impacts of COVID-19, India remains very much in need due to widespread infection and unemployment. The surge in cases means that many people are staying at home, hurting industries that depend on in-person interaction, such as hospitality. Those that can’t afford to stay home find themselves scrambling, only to make extremely low wages amidst a spike in poverty. To explain the situation, this report puts a spotlight on Netrapal Yadav, a former taxi driver trying to find work to support his family. Through Yadav’s struggles, we see the massive impact COVID-19 has had on India’s economy and the daily struggles of its lower-income citizens to survive during this unprecedented time.
Just How Successful Is China's War on Poverty?
China announced in February that it has eradicated extreme poverty. Yet, how should extreme poverty be defined, and is the Chinese government really doing enough in the fight?
A dilapidated building in a rural area of Guangxi autonomous region in southeastern China. President Xi’s poverty eradication program targeted China’s rural poor. Edwin Wisse. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
On Feb. 25, Chinese President Xi Jinping announced that China has successfully eliminated extreme poverty. The declaration comes after a lengthy campaign initiated by the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) that claims to have lifted an estimated 100 million people out of poverty in just eight years. President Xi's announcement is a major victory for the CCP, which is celebrating its centennial later this year.
If true, China’s poverty alleviation campaign could become a model of success for developing nations on how to eradicate extreme poverty in rural areas. However, just how comprehensive the program was in fully eliminating extreme poverty is debated, with critics questioning China’s measure of poverty itself. The World Bank defines extreme poverty as living on less than $1.90 a day; China’s threshold is slightly lower at about $1.52 per day. Regardless, China has made immense progress in the past 30 years in reducing the number of people living in poverty, even by World Bank standards. In 2016, the percentage of Chinese people living below $1.90 a day was only 0.5% of the population, compared to 66% in 1990.
While impressive, China’s declaration has garnered criticism for using a metric of poverty that does not adequately reflect the level of deprivation that remains. China has experienced rapid growth since the country introduced market reforms back in the late 1970s. Since 1978, China has averaged 9% real growth per year, higher than other rapidly developing Asian economies, according to the International Monetary Fund. Due to this rapid growth, China is now considered an upper-middle-income country by the World Bank. Under this classification, extreme poverty would be measured as living on under $5.50 a day, which accounts for 14% of the population, or roughly 200 million people.
Chinese President Xi Jinping meeting with World Bank President Jim Yong Kim in 2014. World Bank Photo Collection. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
With continued economic growth, a relatively successful battle against the coronavirus, and now at minimum a vast reduction in extreme poverty, Chinese officials hope to argue that their system of governance is more successful for international development than the West. China exports more than just commodities. As its rise to global superpower status becomes imminent, its influence outside of Asia continues to grow. In 2018, China announced the Global Poverty Reduction & Inclusive Growth Platform, providing a basis for developing countries to fight their own wars against poverty.
Whether or not President Xi was actually successful in eradicating extreme poverty in China remains to be seen. With the COVID-19 pandemic causing global poverty to rise for the first time in 20 years, the CCP hopes that its model inspires other countries to follow its path. In the meantime, China may bring the world one step closer to finally solving the puzzle of poverty.
Aerex Narvasa
Aerex is a current student at Occidental College majoring in Diplomacy and World Affairs with a minor in East Asian Studies. He is passionate about sharing people’s stories through writing, and always strives to learn about new places and cultures. Aerex loves finding new music and exploring his hometown of Los Angeles in his free time.
Iran’s Shoddy ‘Satellite Cities’ Test Citizens’ Patience
Thanks to high rent prices and overpopulation, thousands of Iranians have been forced out of their hometowns. But the “satellite cities” built to hold them leave much to be desired.
An aerial view of Tehran, Iran. Hansueli Krapf. CC BY-SA 3.0
In the 1980s, Iran intentionally tried to grow its own population, aiming to increase its military strength amid the Iran-Iraq war. The 1979 Islamic Revolution had seen Iran’s old monarchy overthrown and a new republic built on Shiite Islam take shape. Student groups and leftist organizations rejoiced at the new rights promised to women; Islamist groups lauded the fact that their country was now a theocracy. But the new government wanted to ensure that the ideas of the revolution would last beyond one generation. So it encouraged polygamy, made birth control nearly impossible to find and lowered the age of marriage to 9 for girls and 15 for boys.
The plan worked—Iran’s population grew enormously. Forty years after the revolution, there are almost 50 million more people living in Iran. But these newcomers are not a new generation of happy, loyal citizens. They are people who the nation was not built to hold.
Overpopulation was not something Iran was completely unprepared for. Soon after the revolution, 17 new “satellite cities” were planned on the outskirts of the country's major cities. They had names like Pardis (“paradise” in Persian) and Parand ("silk"). They were to provide affordable places to live for people that the larger cities could not hold. But as Iran struggled with unrest and war, these cities wouldn’t begin to be built for decades. They remain half-finished even today.
The Mehr housing project in Nishapur, Iran. Sonia Sevilla. CC BY 1.0
In 2007, the Iranian government developed a scheme it hoped would solve the overpopulation problem and make the satellite cities more livable: contract out free land to real estate developers who were willing to build low-income housing units. In this way around 2 million homes were planned to be built throughout Iran. But the Mehr housing project, as it was called, failed to deliver in the cities that needed housing the most. The 400,000 units built were poorly constructed and lacked essential utilities, like plumbing and clean water. The sterile white color that all the high-rises were painted with in Pardis says it all. These buildings didn’t seem like they were meant to be lived in, only passed through.
But the satellite cities are indeed lived in. In recent years, the overpopulation that plagues Iran’s largest cities has only gotten worse. The Financial Times reported in 2017 that the population of Tehran, Iran’s capital and largest city, “exceeds the optimum level by more than 70%.” The air is full of pollution, and the city’s roads are packed with traffic. But the last straw for many Tehranis is the cost of housing, which according to the New Yorker has more than doubled in the last three years. U.S. sanctions have contributed to this, as did former President Donald Trump’s decision to withdraw from the Iran nuclear deal. With nowhere else to go, droves of Iranians have moved to the satellite cities, where houses are cheaper. In 2019, the population of Parand was 100,000; a year later, that number had doubled.
The unfinished cities have been unable to provide jobs for their populations. Most of the people who make up Pardis must commute each day to work in Tehran. And, as the city lacks most forms of public transport, this means driving—sometimes up to three hours each way. The cities lack recreational areas, stores and the capabilities to provide health care and schooling to their growing populations. It’s no surprise that drug abuse and suicides are common in the cities.
Real estate prices remain high in congested Tehran, and more and more people are expected to leave. The people who make up these satellite cities, despite the lack of basic amenities, are grateful that they have a place to go at all. The Mehr housing project is not finished, and it is possible that in five years the livability of Tehran’s satellite cities will improve. But it is up to the Iranian government to ensure that these improvements do happen, and soon. The well-being of many Iranians depends on it.
Finn Hartnett
Finn grew up in New York City and is now a first-year at the University of Chicago. In addition to writing for Catalyst, he serves as a reporter for the Chicago Maroon. He spends his free time watching soccer and petting his cat.
Video: The Amazing Perseverance of Girls in Kibera, East Africa’s Largest Slum
Kibera is a slum in the heart of Nairobi, Kenya, and is rife with poverty, economic inequality, and gender disparities. However, the future is far from dark for young girls living in Kibera, many of whom dream of getting an education and improving their communities. The path out of poverty is incredibly difficult, but as more awareness is being given to communities in need, young people are beginning to receive the resources they need, such as safe housing and free education. This video shows the daily life of Eunice Akoth, a fourth grader at the Kibera School for Girls who aspires to one day become a doctor. Eunice has faced many obstacles throughout her life, especially due to the preferential attention given to the education of boys. However, her fun-loving spirit and determination to succeed have helped her overcome these challenges, inspiring hope not just in her, but in the community she calls home.
The Immense Impact of COVID-19 on Global Poverty
A pair of boys carry water near a refugee camp in Jowhar, Somalia. The COVID-19 pandemic has made conditions for marginalized groups such as refugees more dire. World Humanitarian Summit. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
For the past 30 years, the world has been able to make immense progress in international development, with the amount of people living in extreme poverty (making below $1.90 a day) declining from 36% in 1990 to just 10% in 2015. The COVID-19 pandemic is reversing that. For the first time in three decades global poverty is on the rise, and up to half a billion people are now at risk of falling into poverty due to the coronavirus. Even more concerning is the matter of where the economic impacts of the virus are being felt the hardest, with the “global south” countries facing the highest risk of increased poverty for what could be years to come.
In 2015, the U.N. adopted the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, which included 17 goals acting as guidelines for the sustainable and equitable development of all member states. Known as the “sustainable development goals” (SDGs), the international community hoped that they would act as a framework for reducing inequality and promoting economic development. Poverty reduction is at the forefront of this initiative, with SDG 1 calling for the end of global poverty. That goal will most likely not be achieved by 2030.
Even before the spread of the coronavirus, countries were not on track to completely eliminate poverty, with the U.N. estimating that 6% of the world population will still live in extreme poverty in 2030. Furthermore, the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic have made that goal even more difficult. In 2020 alone, more than 71 million people have fallen into extreme poverty, and millions more worldwide will likely fall into the same trap as the economic disruptions of the pandemic linger for years to come.
(T)he number of school-age children facing food insecurity has increased by more than 320 million
The aggregate numbers do not portray the full extent of the impacts of COVID-19 on international development. Regions already susceptible to extreme poverty are being hit hardest by the economic impacts of the pandemic. According to the United Nations University, a 10% contraction in global per capita income would cause between 180 and 280 million people to fall into extreme poverty. However, the situation becomes more dire when one considers where people are expected to face increased rates of extreme poverty. Again assuming a 10% contraction, it is estimated that up to 85% of those newly living in poverty would be located in sub-Saharan Africa or South Asia alone. These regions already face disproportionate levels of poverty relative to their populations. For example, the African continent accounts for only 13% of the world population yet makes up over half of those living in extreme poverty.
Those who were already at an increased risk for poverty, such as refugees, informal workers and those living in underdeveloped rural communities, are especially vulnerable to economic disruptions caused by the virus. The International Labor Organization estimates that between 5 and 25 million people could lose their jobs, which would create severe impacts for marginalized workers such as women and migrants. Additionally, the number of school-age children facing food insecurity has increased by more than 320 million according to the World Food Program.
The data shows a worrying trend that the international community must contend with to eliminate global poverty. Since the 1990s, the world has worked together to lift billions of people out of poverty and increase the global standard of living. Now, the COVID-19 pandemic has once again created a barrier to making a poverty-free future possible. The full extent of the virus’s impact has yet to be seen. However, what is already known is its effect on human livelihood, especially for those who are most at risk. The pandemic has created a new challenge for the international community if it wants to make extreme poverty a thing of the past. Yet, what can be achieved with global cooperation is immense, and the world’s vision for a sustainable future is still possible; it just might take a little bit longer than hoped for.
Aerex Narvasa
Aerex is a current student at Occidental College majoring in Diplomacy and World Affairs with a minor in East Asian Studies. He is passionate about sharing people’s stories through writing, and always strives to learn about new places and cultures. Aerex loves finding new music and exploring his hometown of Los Angeles in his free time.