Venetians call their protests a success as the Bezos-Sanchez wedding relocates to the outskirts of the city following the inflatable crocodile threat.
Read MoreIbrahim Traoré: The Making of a Modern Anti-Colonial Icon in Africa
At age 37, Ibrahim Traoré, Burkina Faso’s young leader, is going viral for his pan-African speeches and anti-Western stance. Still, his ties to Russia raise difficult questions about sovereignty and influence in West Africa.
Read MoreSchool Shootings and Gun Violence Spread to Austria
The rare school attack in Austria prompts a reflection on rising violence in the West and debates over firearm policy.
Read MoreSelling Citizenship: A Saving Grace or Path to Corruption?
Numerous programs offering citizenship in exchange for hefty investments have popped up worldwide, bringing problems and questions along.
Read MoreGang Violence: Haiti’s Fight for National Security
Suffering from centuries of economic and political turmoil, Haiti strives for nationwide stability as gang violence worsens humanitarian crises in the country.
Read MoreGreta Thunberg Sets Sail to Gaza to Raise Awareness
As Israel’s blockade threatens famine, Thunberg and other activists launch a civilian flotilla with humanitarian aid, in protest.
Read MoreCartoonists Under Fire: The Fight for Free Expression in India
Political cartoonists in India are facing legal threats and online abuse for criticizing the government, revealing how satire itself is now under siege.
Read MoreInternational Students Put at Risk by Harvard Ban
The Trump administration’s ban on admitting international students to Harvard leaves them in uncertainty amid First Amendment violations and poses concerns to all international students in the US.
Read MoreAnti-American Sentiment Increases Caution for Traveling Americans
Julia Kelley
After introducing controversial war plans and import taxes, Donald Trump’s recent proposals have escalated negative attitudes toward American tourism worldwide.
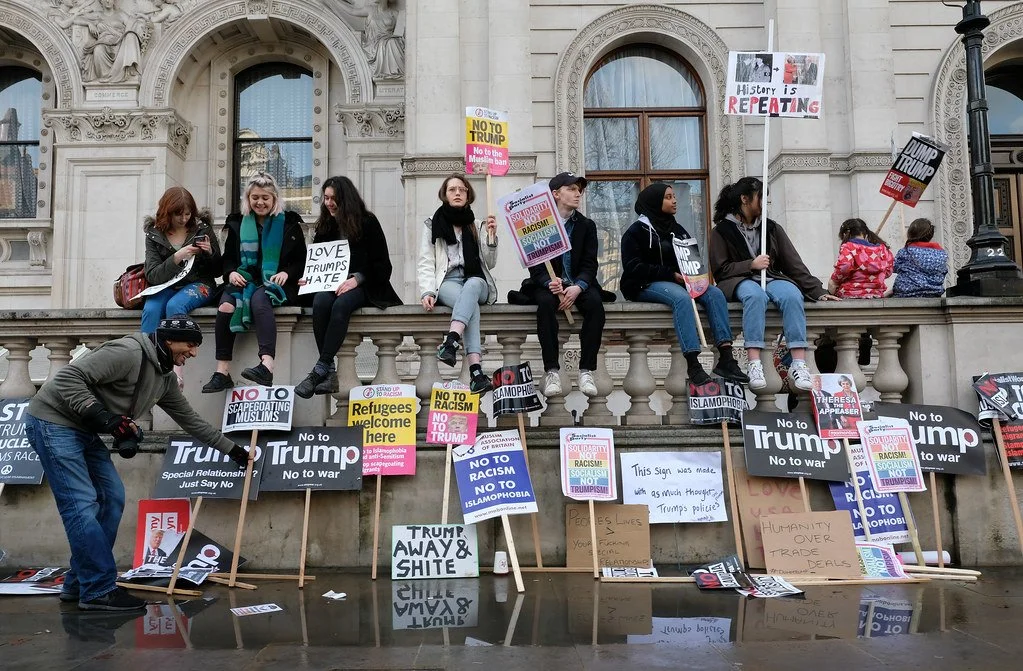
Anti-Trump Protest in London. alisdare1. CC BY-SA 2.0.
During the 20th century, the United States found itself a burgeoning political, economic and cultural world power, gaining increasing international influence. However, since President Donald Trump’s recent inauguration in January 2025, a string of controversial political and economic decisions has seen a subsequent drop in warm foreign sentiments toward the United States. In populations across the globe, those who perceive America as a positive influence number only 46%. Notably, Trump proposed that the U.S. “take over” and “own” Gaza in response to the Israel-Palestine conflict, resettling the population at the same time. These claims were met with widespread condemnation from countries in the Middle East, including Egypt, Saudi Arabia and Jordan, all of whom fiercely rejected the plans and saw them as a violation of the numerous peace agreements between the countries. This contributes to a revival of anti-American views in the Middle East since the beginning of the Israel-Palestine war, as many view the U.S. government as a domineering and pro-Israel force. Despite garnering support from Israel, Trump’s remarks have also been opposed by other powerful countries like China, the United Kingdom, Germany, Australia and Brazil, who consider the proposed relocation of Gaza’s citizens to be an extreme misstep in power.
More recently, Trump has introduced a vast set of tariffs that his administration affirms will secure the economy. Not only did this legislation drastically damage global markets, but many affected countries considered it a threat of global tariff war and an insult to the good relationships between foreign economies. Although the current U.S. tariff plans exclude Canada, an initial tariff placed on Canadian imports increased tensions between the two countries and resulted in a call to boycott American products, naming the U.S. as an enemy. American product boycotts have also been staged in Europe, with U.S. favorability falling across countries such as Denmark, Sweden, Germany and France. For example, the Danish Facebook group Boykot varer fra USA (Boycott products from USA) has amassed over 95,000 followers, while setting fires to Tesla cars has sprung up as part of the “Tesla Takedown” movement in Italy, a protest against Elon Musk’s involvement in international affairs. China has also seen a rise in anti-American perceptions, coinciding with Trump’s decision to place the largest tariff increase on the country at 104%.
In the wake of such turbulent politics, discontent toward America has grown. Overseas travel to the U.S. has declined exponentially in the last few months, seeing an overall drop of 12% in foreign visitors from the previous year. Regions that are usually strong sources of tourism show stark differences, with the number of Canadian tourists dropping by 32% and Mexican tourists by 17% as of March 2025. In many online forums, those from other countries are making their views of Americans known, presenting an overall negative reception of tourists. On a European Reddit forum, user @Iplaymeinreallife from Iceland said, “we want nothing to do with him [President Trump] or a country that would vote him into office a second time,” while user @Mapey from Latvia noted how, despite their initial love for America, they now “hate it to the bone as America stands for absolutely everything” they despise. Americans already face stereotypes while traveling abroad, generally characterized as loud, ignorant or entitled, but such labels are becoming more frequent. More than anything else, countries have replaced an admiration for the U.S. with widespread confusion and antipathy for Trump. In turn, this festering distaste finds itself projected onto American travelers and their experiences, disrupting their hoped-for escapism.
As a result of this U.S. resentment, international travel has become increasingly risky. In a survey done by Global Rescue, 72% of people noted that Americans traveling abroad will be perceived more negatively, while many had already encountered disputes. One California-based traveler described how they “experienced much more negativity,” while a Wyoming tourist reported having “numerous arguments about American policy” with people they did not know. Some travel agencies are also seeing drops in sales for international travel by Americans, and prospective tourists have begun flooding online travel forums with questions asking if it is safe to travel or if foreign countries will accept them. Many, in an effort to avoid the anti-American attitude altogether, have simply cancelled planned trips and tours. New strategies are being taken by those currently abroad as a way of curbing any possible anti-American sentiment, as noted in Rick Steves’ European forum. One poster, named Emily, describes how she has “made an effort to appear less American” while living in Austria, and another, named Volva, in the UK, says it is important not to start any political discussion. Despite where they are in the world, however, Americans abroad and international citizens alike note that rising political tensions have left a lasting impact on the country’s once-amiable image.
Julia Kelley
Julia is a recent graduate from UC San Diego majoring in Sociocultural Anthropology with a minor in Art History. She is passionate about cultural studies and social justice, and one day hopes to obtain a postgraduate degree expanding on these subjects. In her free time, she enjoys reading, traveling, and spending time with her friends and family.
Tax Incentives Drive Gentrification in Puerto Rico
Kleigh Carroll
Wealthy investors and tech entrepreneurs are buying up land in Puerto Rico, driving up property rates and forcing locals out of their neighborhoods.
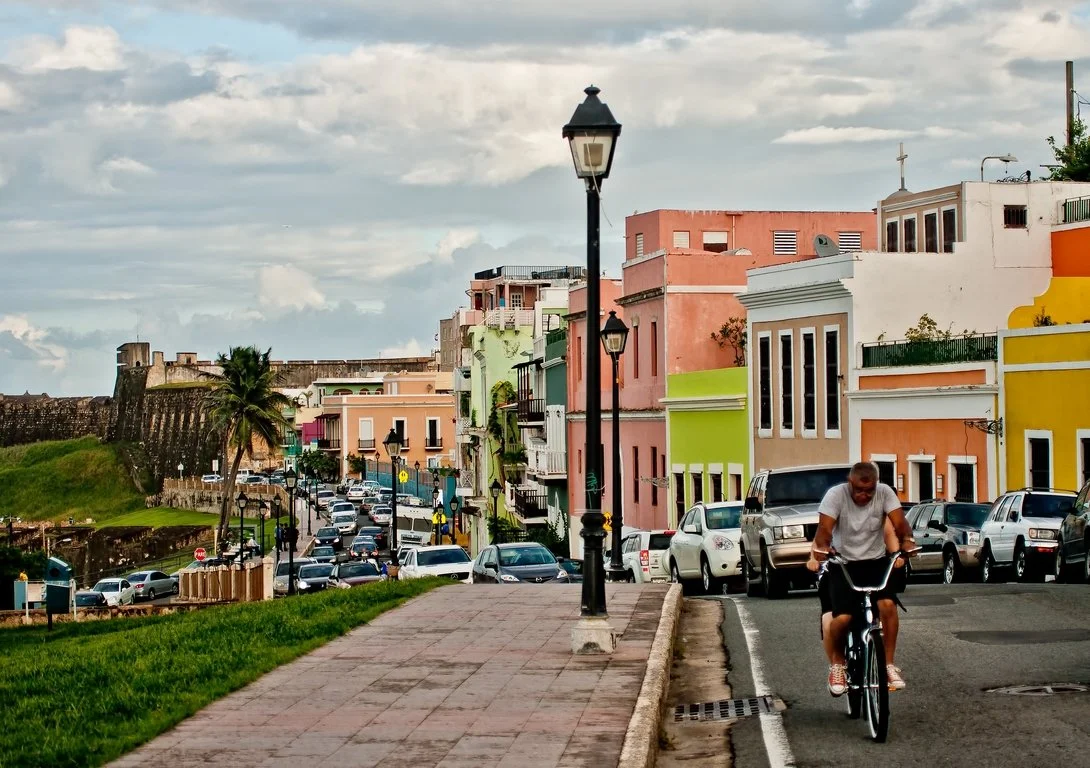
Street in San Juan, Puerto Rico. R9 Studios FL. CC-BY-2.0.
The island of Puerto Rico struggled with an economic recession from 2006 to 2017, during which the economy contracted by 10% and unemployment shot up to nearly 15% at its peak. To draw in foreign investment and stimulate economic growth, the government passed legislation designed to attract tech, finance and wealthy investors to the island. The first of two acts, Act 20, provided tax incentives for companies that establish and expand export services businesses in Puerto Rico. The second, Act 22, provided a total exemption from income taxes on all interest and dividends realized after an individual becomes a bona fide resident. The laws were further revised and repackaged in 2019, now known collectively as Act 60.
Living in a United States territory, residents of Puerto Rico normally benefit from a unique tax status that exempts them from federal income tax. However, Act 60 does not apply to long-time residents of the island. As a result, the incentives have only worsened income inequality and exacerbated a mass exodus of Puerto Ricans to the United States.
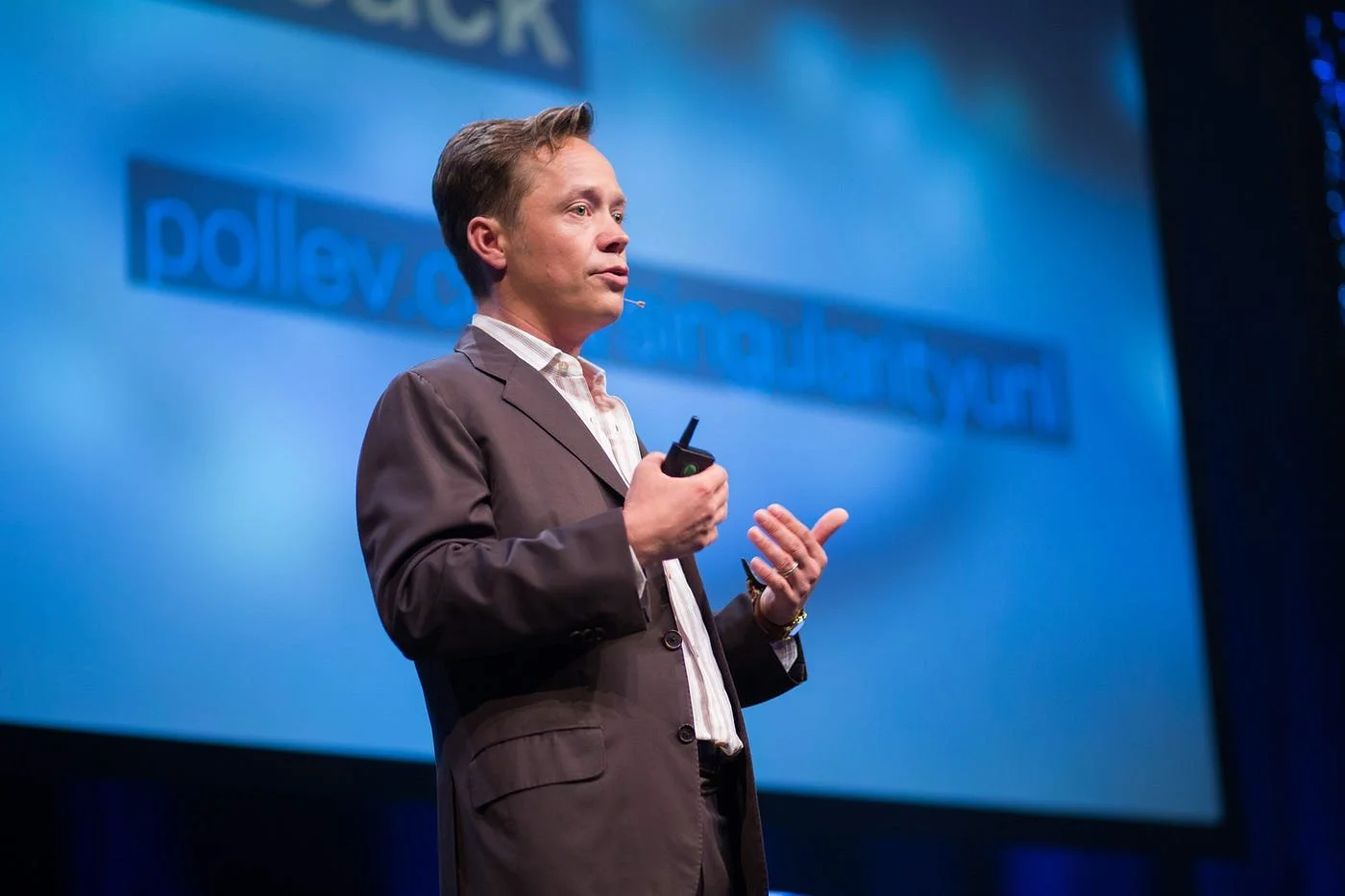
Brock Pierce speaks at a conference. Sebastiaan ter Burg. CC-BY-4.0.
In the aftermath of Hurricane Maria, which ravaged the island in 2017, U.S. crypto investors saw an opportunity to take advantage of tax incentives. They hoped to rebuild a part of the capital, San Juan, into what they called “Puertopia” — a modern city run on virtual money and public contracts. Members of this community who flocked to the island included men like Brock Pierce, co-founder of the digital currency Tether, and social media influencer Logan Paul. Upon moving to the island in 2017, Pierce and his partners took over numerous properties, including a beachfront hotel in Vieques and a museum in Old San Juan. They made grand promises to revitalize the economy using blockchain, refurbishing historic neighborhoods and building their own airports and docks.
But there is little evidence that wealthy newcomers like Pierce have done anything to stimulate economic growth on the island. Instead, they have contributed to a surge in housing prices, driving up the cost of living for locals and displacing Puerto Rican families, especially in coastal towns like Rincon, where beachfront property is prime real estate. Housing prices in San Juan increased by 22% between 2018 and 2021 as tax law beneficiaries spent an estimated $1.3 billion on real estate between 2015 and 2019, according to research conducted by Puerto Rico’s Department of Economic Development and Commerce.
Golf resort in coastal Puerto Rico. Your Golf Travel. CC BY-NC-ND 4.0.
According to the 2023 census, the median household income in Puerto Rico is $25,096 — less than a third of the median household income in the United States. Many locals forced to relocate have to commute longer distances and pay expensive tolls. Marina Reyes Franco, an art curator at the Museo de Arte Contemporaneo in Puerto Rico, told the Guardian that she has struggled to find affordable housing in recent years. She blames the tax laws, claiming, “At the end of the day, this is about a new era of colonialism and laws that only benefit the elite.”
Gentrification culturally erodes communities and contributes to a loss of heritage and identity. Not only does it mean that locals can no longer afford to live in the places they call home, but an influx of wealthy newcomers can alter the character of neighborhoods, displacing local businesses, cultural institutions and the unique cultural fabric of Puerto Rican communities.
Solidarity With Puerto Rico Rally in Chicago, Illinois. Charles Edward Miller. CC BY-SA 2.0.
GET INVOLVED:
#AbolishAct60 is a grassroots movement aimed at repealing Act 60. By using social media to raise awareness and inspire collective action, they encourage the Puerto Rican diaspora to put pressure on their representatives. Help amplify their message here.
Diaspora en Resistencia is a nonprofit utilizing social media to mobilize support through online petitions demanding that the Puerto Rican government take action.
You can also petition your representatives to reevaluate Puerto Rican tax policies. U.S. lawmakers, including Chuck Schumer and Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez, have already spoken out against the measure.
Kleigh Carroll
Kleigh is a student at UC Berkeley studying Geography and Journalism. She hopes to integrate her skills in these fields in pursuit of a career in journalism. She is passionate about being outside, exploring, and writing in all of its forms.
Russian Poets and the Risk of Resistance
Kennedy Kiser
From public readings to prison cells, Russian poets are paying the price for speaking against the war.
Protesters march in Moscow against repression and fabricated charges. DonSimon. CC0.
“Kill me, militiaman!
You’ve already tasted blood!
You’ve seen how battle-ready brothers
Dig mass graves for the brotherly masses.
You’ll turn on the television—you’ll lose it,
Self-control has never been your strong suit.”
— Artyom Kamardin, “Kill Me, Militiaman”
In December 2023, Russian poet Artyon Kamardin was sentenced to seven years in prison for reciting anti-war verses during the public “Mayakovsky Readings” in Moscow. Fellow poet Yegor Shtovba, who performed at the same event, received a sentence of five and a half years. Kamardin was reportedly beaten and sexually assaulted during his arrest for reciting poetry in response to Russia’s war in Ukraine.
Daria Serenko at the Moscow International Book Fair in 2019. Sergey Leschina. CC BY 4.0.
Their cases are not isolated. In April 2024, feminist poet and activist Daria Serenko was added to Russia’s federal wanted list. Known for combining poetry with political action, Serenko has faced years of harassment. Her arrest warrant, however, marked a shift in the state’s approach. Where once artists were threatened, they are now hunted.
Literature has long played a role in Russian resistance. During the Soviet era, banned texts circulated underground through samizdat networks. Today, Telegram channels and independent journals continue that tradition, sharing poetry that challenges state narratives. But the stakes are now much higher. Poets are not just being silenced; they are being criminalized. The penalties include imprisonment, forced exile and public brutality.
At the center of this increased repression is the state’s fear of language itself. Poetry distills dissent into a form that is emotionally direct and difficult to contain. It spreads quickly, often through digital platforms, in defiance of Russia’s 2022 censorship laws. Unlike journalism or political commentary, verse can bypass logic and speak directly to the reader’s gut. As poet Osip Mandelstam once wrote, “Only in Russia is poetry respected — it gets people killed. Is there anywhere else where poetry is so common a motive for murder?”
This crackdown is not limited to well-known names. Emerging writers, students and performers with modest online followings have also been detained or investigated for speech-related offenses. In some cases, posting a poem on VKontakte, Russia’s largest social network, has led to criminal charges. The line between art and activism has been effectively erased, especially for those who oppose the war.
International literary organizations have responded by offering emergency grants, publication platforms and legal aid. PEN International, Freemuse and countless other organizations have condemned Russia’s actions, calling for the immediate release of detained artists. Yet the risks persist. For many Russian writers, exile is the only path to safety, though it often comes with the painful cost of losing direct access to their audiences.
Repressing writers like Kamardin, Shtovba and Serenko reveals a broader strategy: to eliminate not just protest but the imagination of a different future. By imprisoning poets, the government also suppresses the potential for alternative visions of the world.
Still, Russian poetry persists. In exile, through online platforms and underground readings, writers continue to speak out. In a regime that fears language, each poem becomes an act of resistance.
GET INVOLVED:
These organizations offer support to writers and artists facing political persecution. From legal aid to international advocacy, their work helps protect freedom of expression and document human rights abuses. Getting involved means helping preserve creative resistance in some of the world’s most repressive environments.
To learn more about PEN International, click here.
To learn more about Freemuse, click here.
To learn more about Memorial International, click here.
Kennedy Kiser
Kennedy is an English and Comparative Literature major at UNC Chapel Hill. She’s interested in storytelling, digital media, and narrative design. Outside of class, she writes fiction and explores visual culture through film and games. She hopes to pursue a PhD and eventually teach literature!
How Congo and Rwanda Arrived at the Brink of War
In their fight over marginalized peoples and access to rare minerals, the Congolese military and Rwanda-backed rebels risk triggering a broader regional war in southeast Africa.
Read MoreTrump’s USAID Freeze: A Staggering Loss for Humanitarian Aid
Trump’s decision to freeze USAID threatens millions worldwide who rely on humanitarian aid for survival
Read MoreUS Declares Genocide in Sudan
After two years of famine, disease, and misery, the U.S. has given an official deemed the ongoing conflict in Sudan as genocide.
Read MoreA New Dawn for Syrian Refugees
The fall of Assad’s regime has left the world wondering about the future of Syrian refugees abroad who plan to return home.
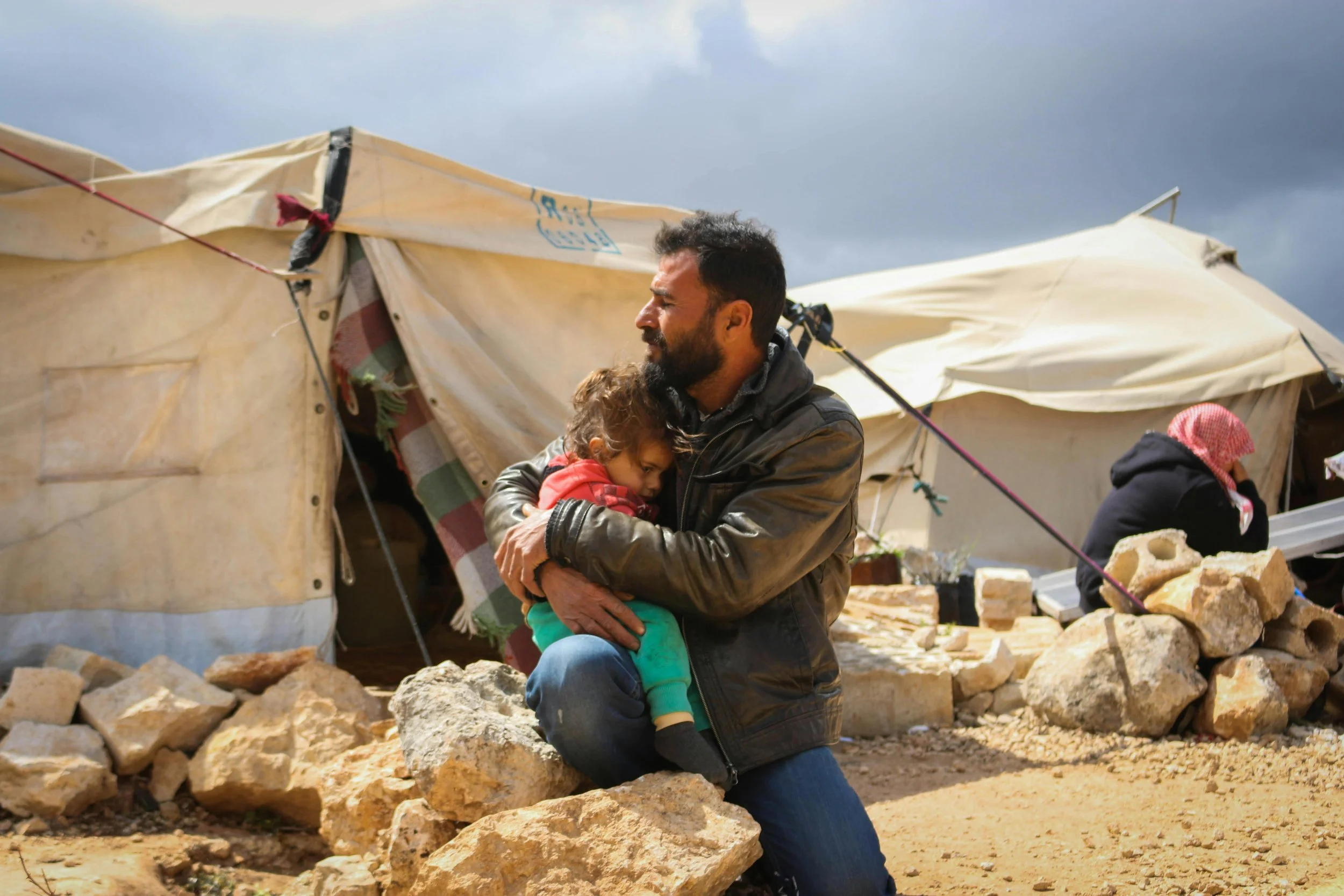
Man and daughter at Syrian refugee camp. Ahmed Akacha. CC0.
The Syrian Refugee Crisis is one of the largest humanitarian crises in history and the largest refugee crisis to date, with over 14 million people both internally and externally displaced. Over six million Syrians fled the country following the civil war that broke out in 2011; the majority of refugees currently live in Turkey, Lebanon, Jordan, Iraq, Egypt and Germany.
President Bashar al-Assad’s violent suppression of pro-democracy protests in 2011 provoked civil conflict, leading to the creation of oppositional militias and rebel groups that began to fight back by 2012. On Dec. 8, 2024, the civil war came to a head when rebel groups seized the Syrian capital, Damascus, forcing Assad to flee to Russia. Assad’s family had ruled Syria under a strict police regime since the 1960s, leading to widespread celebration across the capital as political prisoners were freed.
Despite rebel groups declaring the country free from the autocratic regime, considerable uncertainty remains about the future of the government and Syria’s stability. Some states have expressed a concern that toppling the government may make the country vulnerable to ISIS, whereas others have noted the encroachment of Israeli forces into Syrian buffer zones. The European Union issued a statement claiming that the conditions in Syria have not yet met the conditions for the safe return of refugees, as thousands have continued to flee following the rebel takeover. However, in the days following, videos swept across social media and news outlets featuring thousands of refugees returning home from Turkey, Jordan and Lebanon.
European countries hosting hundreds of thousands of Syrian refugees, including Germany and Austria, have jumped at the opportunity to tighten their asylum regulations. In December 2024, both Germany and Austria paused asylum applications, and Austria announced that they would issue a “return bonus” to Syrians who decided to return to Syria.
Providing incentives or forcing refugees to leave the country could adversely affect host countries, particularly Germany. Approximately two-thirds of employed Syrian refugees in Germany work in critical sectors of the labor force, including healthcare, transportation and food services. Whether forced or voluntary, any kind of mass exodus could negatively affect Germany’s economy by disrupting these industries and causing labor shortages.
Following an outcry from far-right German politicians to close the country’s borders and begin the expulsion of non-naturalized Syrians, current Chancellor Olaf Scholz said that Syrians who are “well-integrated remain welcome in Germany.” However, the Chancellor’s statement may prove unstable, presenting no active policy arrangements if the far-right parties gain control in the upcoming elections and creating further uncertainty for Syrians currently living in Germany.
The United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees advised that countries housing refugees should not forcibly deport them, as Syria is not yet deemed politically stable, and it is estimated that over one million Syrians will return to Syria of their own accord in the first few months of 2025.
Despite this monumental step forward, considerable humanitarian and governmental uncertainty remains surrounding the future of Syrians worldwide, a resolution that may take years to completely unfold.
Zoe Lodge is a student at the University of California, Berkeley, where she is studying English and Politics, Philosophy, & Law. She combines her passion for writing with her love for travel, interest in combatting climate change, and concern for social justice issues.
Israel and Palestine: Divergent Histories of Travel and War
One year after the Oct. 7 attacks, Israel and Palestine’s respective travel landscapes reveal just how differently the two countries are experiencing the ongoing war.
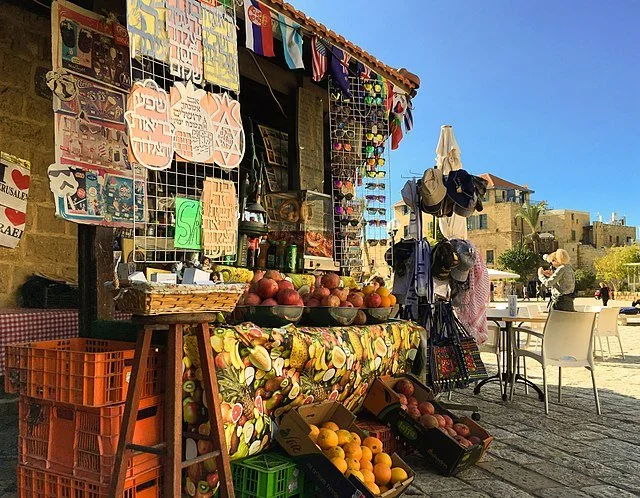
A street vendor in Jerusalem. Ronen Marcus. CC BY 4.0
Boasting ancient holy sites like the Western Wall and natural attractions like the Dead Sea, Israel brands itself as a popular travel destination for both the spiritual and the secular tourist. In 2023, the Israeli Ministry of Tourism reported over 32 million travelers. Palestine, meanwhile, saw 2.5 million visitors between January and early October 2023, according to the Palestinian Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities. While disparate, these numbers reflect a larger pattern in the long history of travel to the region.
Before the Zionist movement (an effort to create a Jewish state through colonization) emerged in the late 19th century, trips to historic Palestine, “the Holy Land,” were almost exclusively religious in nature. After several failed attempts to create a Jewish state, Zionists set their sights on historic Palestine due to the area’s alignment with the biblical land of Israel. To bolster their efforts, Zionists turned to tourism, recognizing that travel to Palestine could help boost immigration and help establish a Jewish presence in the majority-Arab region. Further, Zionists gathered that if they kept promoting tourism, they could perhaps convince secular visitors that this Jewish presence was inherently more valuable and historic, thereby granting it a perception of legitimacy and therefore protection. Desiring to entrench themselves in Palestine, Zionists spent the early 20th century advertising access to biblical Jewish sites, propaganda that continues to prove effective even after Israel’s establishment in 1948.
Posters promoting travel to historic Palestine. (L) 1936. (R) 1940s. CC BY 4.0
Israel enjoys a lucrative tourism industry, seeing more than 32 million travelers and $5 billion in revenue in 2023 alone, according to the Israeli Ministry of Tourism. However, following the immediate aftermath of the Oct. 7 attacks, these numbers plummeted. Flights to Israel were canceled as international airlines and government officials raised safety and security concerns. Traveler rates dropped accordingly. “When the war began, everything stopped,” Israeli tour guide Moshe Benishu said, as reported by The Jerusalem Post. “Not a single tourist arrived in Israel.” Reuters reported 99,000 traveler entries to Israel for the rest of October 2023 and just 39,000 that November. To put this slump into context, the number of monthly entrants into Israel before Oct. 7, 2023, averaged above 300,000.
In recent months, Israel has seen its traveler rates partially recover, tallying 68,100 tourist entrants in February 2024 and 79,500 in March. “Since the beginning of 2024, 400,000 tourists entered the country,” Keren Setton reported for The Media Line in May 2024. During the same January-May period in 2023, Israel saw two million entrants. But still, the monthly rates of 2024 so far mark an increase compared to the last quarter of 2023. “We Israelis are good at reinventing ourselves,” Benishu said. Slowly but surely, things are returning to form in Israel. The same cannot be said for Palestine.
Since the onset of the war, Palestine’s territories, the Gaza Strip and the West Bank, (both occupied by Israel since 1967) have been devastated with next-to-no reprieve. As of Sep. 29, 2024, Palestinian health authorities have attributed more than 41,500 Palestinian deaths to Israel’s air and ground campaign in Gaza alone, though violence in the West Bank has spiked as well.
Casualties in Gaza. Saleh Najm and Anas Sharif. CC BY 4.0
Infrastructure, too, has been decimated in Palestine. With hospitals, water/electric systems, houses and schools reduced to rubble, entire Palestinian communities have been destroyed and families killed in scores. As David Leonhardt summarized for The New York Times, “Israel has dropped 2,000-pound bombs on densely populated neighborhoods” with little consideration for less fatal alternatives.
Destruction in Gaza. Saleh Najm and Anas Sharif. CC BY 4.0
As mentioned previously, the West Bank enjoyed a burgeoning tourism industry before Oct. 7. Despite Israel’s control over the flow of travelers, the Palestinian Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities still reported 2.5 million visitors to the occupied enclave between January and early October 2023. Since then, however, the West Bank has not been able to recoup even 1% of this number, with the region’s tourism sector currently experiencing losses of around $2.5 million every day. In Bethlehem especially, where “tourist dollars” are “the cornerstone” of the economy, according to Haaretz, the financial hit has severely strained people’s livelihoods. “Life has been hell,” said Palestinian merchant Mahmoud Falah Sleiman. “The situation was bad even before the war started, but it was better than now. We were able to pay for electricity, food, water.”
In the Gaza Strip, tourism has been virtually nonexistent since 2007 — a consequence of Israel’s land, air and sea blockade imposed after Hamas took root there. Before Israel’s occupation of the region in 1967, Gaza was a hotspot for traveling Egyptians and Lebanese merchants. But after 1967, and especially since the 2007 blockade cut off food, water and humanitarian aid from Gaza’s two million citizens, (conditions some have likened to “collective punishment” and an “open air prison”) there’s been next-to-no tourism. Given the mass destruction of life and infrastructure in Gaza since Oct. 7, there won’t be anytime soon.
Bella Liu
Bella is a student at UC Berkeley studying English, Media Studies and Journalism. When she’s not writing or working through the books on her nightstand, you can find her painting her nails red, taking digicam photos with her friends or yelling at the TV to make the Dodgers play better.
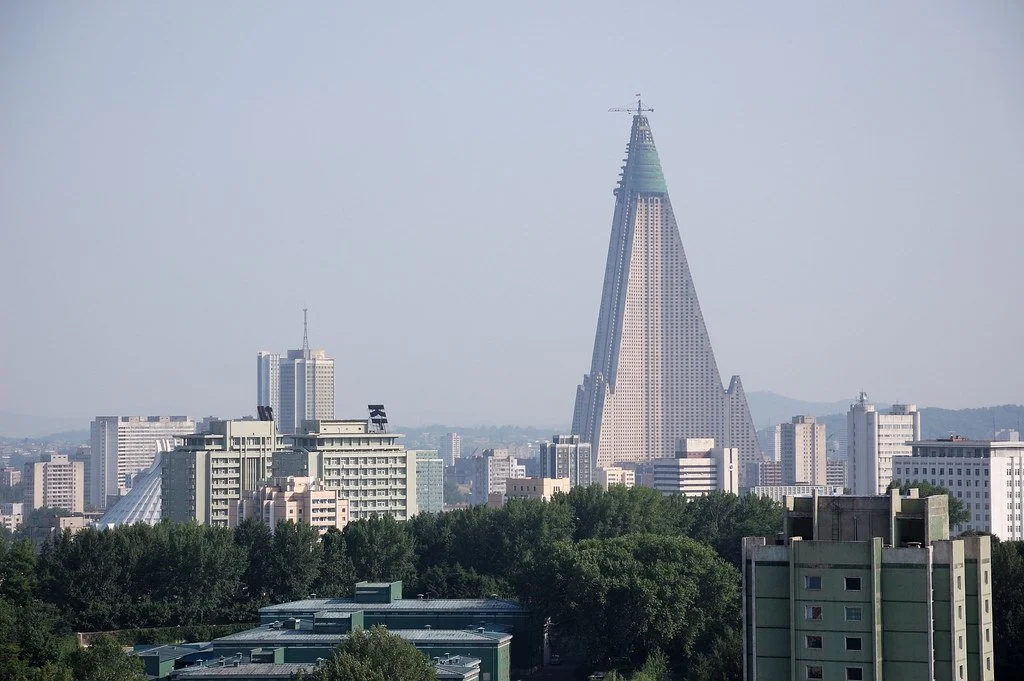
Tourism Set to Reopen in North Korea
The controversial and most isolated country plans to resume tourism this December.
Panoramic view of Pyongyang. Joseph Ferris III. CC BY 2.0
After five years, North Korea is set to reopen its doors to foreign tourists. The country closed its borders in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic but plans to welcome visitors again starting in December. Currently, only the northern city of Samjiyon will be open. Known for its winter activities, Samjiyon is still undergoing reconstruction. Located near the Chinese border and close to Mount Paektu—a sacred mountain claimed to be the birthplace of Kim Jong-Un’s father—Samjiyon was established in 2019. The town, which Kim describes as an “idealist socialist village”, was likely built with forced labor disguised as “volunteers”, given North Korea’s history of enslavement and trafficking. While Samjiyon is reopening, the capital city of Pyongyang has remained closed to tourists.
U.S. tourism to North Korea has been prohibited since 2017, following the death of Otto Warmbier, a University of Virginia student who was imprisoned in North Korea for stealing a propaganda poster. Warmbier traveled to North Korea with a tour group in 2016 and was sentenced to 15 years of hard labor. He was released 17 months later and died in a U.S. hospital just six days after returning home in June 2017. U.S. law reserves the right to revoke citizens’ passports upon attempted entrance into North Korea. While everyday citizens are forbidden from entering North Korea, visitation is not entirely banned, as the U.S. occasionally grants validation passports to professional journalists, Red Cross representatives and other citizens whose jobs serve national interests. South Koreans are the only nationality directly banned from North Korea, as the neighboring countries have been in a state of war since 1950. Today, approximately 5,000 Western tourists visit North Korea each year. Tourists from Russia and China—countries harboring more “friendly” relations with North Korea—are expected to make up the majority of foreign tourists.
Between 2010 and 2017, Americans could travel to North Korea year-round. Many have shared their experiences in Pyongyang through YouTube videos, articles and blog posts. As noted by several American tourists, self-guided tours are not an option in North Korea; itineraries are strictly followed. A recurring theme throughout these tours is the guides’ continual stress on their solidarity to the country's leaders, particularly Kim Jong-Un. The North Korean government uses tourism as a tool to showcase the country’s self-reliance, prosperity, talent and citizen happiness by guiding visitors through monuments, schools and museums.
View of Ryugyong Hotel in Pyongyang. (stephan). CC BY-SA 2.0
Increased tourism could potentially lead to heightened political tensions. Many countries discourage travel to North Korea, not simply due to the inherent dangers, but because tourism revenue supports Kim Jong-Un’s regime rather than the local population. As of 2020, it was estimated that 60% of North Korea’s population lived below the poverty line. If tourism resumes, North Korea could earn nearly $200 million—a significant amount for a country with an economy largely isolated from international trade and exports. Koryo Tours, the most popular gateway to North Korea, is a travel agency based in Beijing that provides group tours to the country, sharing its history, politics, and culture. The tours are capped at twenty people per group, and tour leaders are claimed to have a “passion and interest for the country.” The debate surrounding the ethics of traveling to North Korea remains ongoing. As of now, we are left to observe what the future holds for one of the world’s most isolated countries.
Agnes Volland
Agnes is a student at UC Berkeley majoring in Interdisciplinary Studies and minoring in Creative Writing, with a research focus on road trip culture in America. She currently writes for BARE Magazine and Caravan Travel & Style Magazine. She is working on a novel that follows two sisters as they road trip down Highway 40, from California to Oklahoma. In the future, she hopes to pursue a career in journalism, publishing, or research.
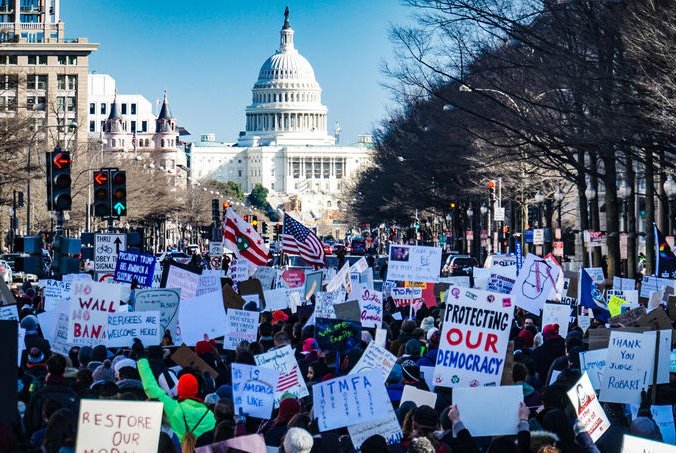
Political Tourism in America’s Swing States
Volunteers play a crucial role in mobilizing key electorates by traveling to swing states, whose voters will ultimately decide the presidential election.
Protestors rally in front of the Capitol in DC. Ted Eytan. CC BY-SA 4.0
With the U.S. presidential election fast approaching, politically minded Americans are turning their attention to swing states, where Democratic or Republican victory often hinges. Volunteers play a crucial role in these states, engaging in grassroots efforts to sway voters and educate communities on policies and candidates. This is often achieved by speaking with locals directly, typically through door-to-door visits, made possible through non-profits.
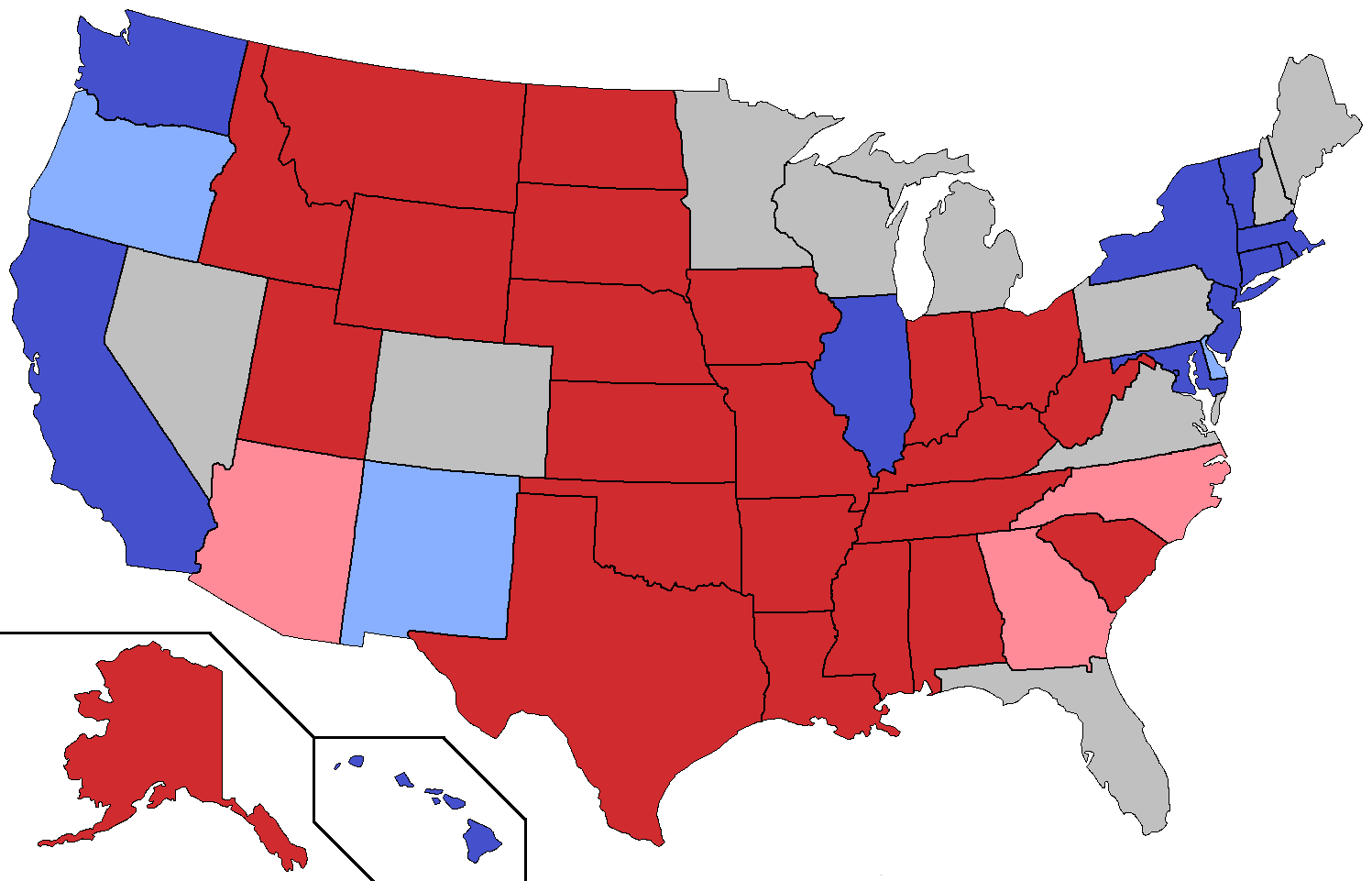
Organizations such as Common Power and the Swing States Action Fund aim to mobilize Democratic voters by providing clear information on when, where and why to vote. Common Power, based in Seattle, allows volunteers to either travel to swing states or contribute remotely through activities like writing postcards and making calls. Common Power allows you to choose volunteer opportunities based on location, activity or date. For the 2024 general election, their tentative travel dates are from September to November, with most trips lasting five days. You can sign up for State Teams here, and the volunteer travel guide is available here. Volunteers travel in teams and take part in a virtual training event before their trip. The estimated total cost for a five-day State Team trip is $2,500 (includes lodging, meals, and transportation). However, volunteers are typically responsible for their own transportation, so the final cost can vary depending on their starting location. The Swing States Action Fund operates a little differently; the organization specializes in encouraging recent graduates or retirees to relocate to swing states. They then connect these individuals with a network of volunteers involved in outreach efforts like voter drives and postcarding. These organizations are crucial in combating voter suppression, especially in historically BIPOC communities, ensuring fair access to the democratic process. Organizations like the Progressive Turnout Project pay volunteers, offering up to $125 for completing a door-knocking list, which typically takes about three hours. The Progressive Turnout Project organization operates in key swing states such as Arizona, Georgia, Michigan, Pennsylvania, North Carolina and Wisconsin.
Map of swing states (in gray and light colors) in the 2020 U.S. Presidential Election. A Red Cherry. CC BY 4.0
Overcoming voter suppression has roots tracing back to the 1950s. During the Civil Rights Movement, volunteers traveled to Southern states to confront segregation and rally Black community members to participate in voting. In the South, Black individuals faced barriers such as poll taxes, rigged literacy tests and fraud when attempting to register. In June 1964, the Freedom Summer Project aimed to register a significant number of Black voters in Mississippi. This effort eventually led to the enactment of the Voting Rights Act of 1965, a landmark legislation that outlawed racial discrimination in the electoral process. Despite this progress, however, voter suppression continues to persist in the South today. In 2021, Georgia and Florida enacted SB 202 and SB 90 respectively, imposing stricter voter identification requirements, particularly for those voting by mail.
Following Kamala Harris's nomination as the Democratic presidential candidate, her campaign claims a recent surge in support, particularly in key swing states such as Florida, Pennsylvania and Georgia. Volunteers will take direct action through advertisements, demonstrations, and fundraising, as well as by encouraging individuals to submit opinions to government officials.
Agnes Moser Volland
Agnes is a student at UC Berkeley majoring in Interdisciplinary Studies and minoring in Creative Writing, with a research focus on road trip culture in America. She currently writes for BARE Magazine and Caravan Travel & Style Magazine. She is working on a novel that follows two sisters as they road trip down Highway 40, from California to Oklahoma. In the future, she hopes to pursue a career in journalism, publishing, or research.
Big Brother is Watching: China’s Social Credit System
The nuanced nature of China’s social credit system has sparked global debate.
People walking through crowded streets in Shanghai. Rawpixel. CC0 1.0
Amid social and political turmoil, many are fascinated by order, hierarchy and control. One of China’s long-term goals is technological self-reliance, reflected in the country’s controversial social credit system. Millions of citizens are defined by and reduced to a numeric value, which is generated as their daily interactions and purchases are closely monitored. The system was predominantly economic—similar to a FICO score—until 2004, when President Jian Zemin expanded the system by adding a social aspect. The current social credit system was formally introduced in 2014, and by 2022, 80% of China’s cities, counties and regions had instituted some version of it.
The social credit system varies geographically. Some citizens receive a numeric score between zero and 1,000, while others are marked by a letter score from A to Z. The system is divided into four categories: business, social, government, and judicial. It operates punitively, rewarding citizens for good behavior and punishing them for bad behavior. A drop in one's score can come from traffic violations, littering and gossiping, while good deeds like donating to charity and assisting the elderly can increase it. The more points accrued, the more preferential treatment one receives, including discounts and travel perks. However, if a citizen's score is too low, they can be prevented from traveling or landing work. In 2019, millions of Chinese citizens were banned from buying plane tickets due to low social credit scores. China’s social credit system has been compared to the Black Mirror episode "Nosedive," which depicts dystopian society in which one’s worth is defined in relation to their portrayal on social media.
Surveillance equipment. Rawpixel. CC0 1.0
The government claims that the social credit system was instituted to “build trust” amongst citizens. However, the lack of privacy and blacklist perpetuated by the system has sparked global concern. Even by criticizing the government, your social credit score is lowered, and in some cities, the government pays citizens to report good or bad behavior. Recent studies suggest that the portrayal of China’s social credit system in the media is exaggerated. According to the MIT Technology Review, the system primarily functions as a comprehensive record of data, documenting companies’ financial histories. It is therefore less important as a single score than as a record.
The social credit system is only one aspect of government surveillance in China. The country’s firewall limits internet searches, and there are at least 200 million surveillance cameras installed that can use facial recognition software. China’s government operates without rule of law, leading to the abuse of power. Surveillance capitalism ultimately poses a threat to individual autonomy and democratic governance. The question remains as to how far it will spread in the coming years.
Agnes Volland
Agnes is a student at UC Berkeley majoring in Interdisciplinary Studies and minoring in Creative Writing, with a research focus on road trip culture in America. She currently writes for BARE Magazine and Caravan Travel & Style Magazine. She is working on a novel that follows two sisters as they road trip down Highway 40, from California to Oklahoma. In the future, she hopes to pursue a career in journalism, publishing, or research.
2024 Paris Olympics: Challenges, Protests and Controversies
From transportation and public safety concerns in Paris to discontent in Tahiti, the 2024 Paris Olympic Games are riddled with contention.
The Eiffel Tower with the logo of the Olympic Games. Ibex73. CC BY 4.0 via Wikimedia Commons
As the countdown to the 2024 Olympic Games in Paris reaches its final days, anticipation is building among the estimated 15 million visitors set to descend upon the city. However, this year’s games are not without their share of controversies. Unrest and protests have begun to surface, not just from within the borders of France but also among the vast number of international travelers and athletes. These contentious issues are casting a shadow over the upcoming Games, adding a layer of uncertainty and complexity to an event traditionally associated with unity and the celebration of athleticism.
Security Concerns, Congested Transportation, Unhoused Parisians
The opening ceremony, scheduled to take place in the open air along the historic Seine River, has raised a number of security concerns. These concerns are particularly acute because of the memory of the terrorist attacks in Paris in 2015. Furthermore, ongoing geopolitical unrest, notably the war between Gaza and Israel and Russia’s continued aggression towards Ukraine, adds to the apprehension. In anticipation of potential protests, the French government has reduced the number of tickets for the public from 600,000 to 300,000 and plans to deploy around 45,000 French police and security forces. During the opening ceremony, an additional 35,000 security agents are expected to be on duty alongside the military to safeguard against security threats. The recent stabbing of a French counter-terrorism soldier over a week before the games are set to begin has only increased tensions.
Along with security concerns come concerns over the expected additional congestion of the city’s already packed public transport system. Many Parisians believe the transportation is largely underprepared for the influx of tourists as they already deal with poor frequency of trains, overcrowding, and general uncleanliness. Those who are financially able are electing to leave the city for the period of the games, while others will be forced to turn to alternative modes of transport and access such as biking, walking or telecommuting. Those who are unable to consider alternative transportation will have to endure long commutes with few alternatives. In response to criticism over transportation concerns, the French president of the Ile-de-France region, Valérie Pécresse, made a statement to worried citizens, "Don't be afraid to walk a little, it's good for your health".
The Olympics have also brought the plight of the city’s unhoused population to the forefront. The Olympic Village has been constructed in one of Paris’s most impoverished suburbs, an area where thousands of individuals reside in street encampments, shelters and derelict buildings. In a controversial move, the French government transported thousands of these unhoused individuals on buses to other French cities such as Marseille and Lyon. They were removed from the city under the pretext of promising housing elsewhere, only to find themselves living on unfamiliar streets far from their original homes. This action has drawn widespread criticism as it is in no way a permanent solution, but rather a means to conceal the city’s homelessness issue and present a more idyllic image of Paris. While the government denies any connection between this relocation and the Olympics, an email obtained by the New York Times and initially reported by L’Equipe reveals a government housing official stating the objective to “identify people on the street in sites near Olympic venues” and relocate them prior to the Games.
Water Sport Events
The Seine River, the chosen venue for the opening ceremony, will also host the triathlon and marathon swimming events. This decision has ignited controversy, as many Parisians view the river as polluted and unsafe. Swimming in the Seine has been illegal for over a century. In an effort to clean the river, Paris has invested $1.5 billion in infrastructure to prevent bacteria-laden wastewater from entering the river. Despite the clean up, experts are still uncertain if the river’s E. coli levels will be safe for swimming in time for the events, and no backup plan has been announced. In a show of confidence, President Emmanuel Macron and Paris Mayor Anne Hidalgo have vowed to swim in the river themselves to demonstrate its safety. Just this past Saturday, French Sports Minister Amélie Oudéa-Castéra took the plunge into the river.
In an unusual display of public anger, a distinctive form of protest seemed to be in the works for several weeks. Known colloquially as the ‘poop protest’, it called for citizens to deposit their waste into the Seine on June 23, 2024, strategically timed to coincide with the President’s original planned swim. Remarkably, an unidentified engineer had developed a website that calculates the exact moment for the waste drop-off, ensuring it aligns with the President’s swim based on the individual’s distance from the river. This protest concept was not merely a reflection of skepticism regarding the cleanliness of the Seine, but also a broader expression of French dissatisfaction with the President’s recent election gambit and the anticipated disruptions the Olympic Games are expected to bring to the city. The protestors seem to have been more bark than bite, however, because after Macron canceled his originally planned dip Oudéa-Castéra's swim took place nearly without incident; the Sports Minister slipped while getting in the water.
Meanwhile, in French Polynesia, Tahiti is set to host this year’s Olympic surfing events. Tahiti is a well-known destination for surfing competitions, and has been so for many years. The International Surfing Association (ISA) voiced its opposition to the construction of a new aluminum judges’ tower for the 2024 Olympics in Tahiti, amid concerns from locals and environmentalists about potential damage to the local coral reef. Despite the continued use of a wooden tower at Teahupo’o, one of the world’s most famous surf breaks, for the past 20 years, Olympic organizers and government leaders greenlit construction on a new tower due to safety concerns. The ISA had proposed more environmentally friendly solutions, such as building the tower on land and using digital cameras on the wooden tower, but these were rejected in favor of the new structure.
The controversy escalated from the first peaceful protest in October, with over 200,000 people signing an online petition against the tower and prominent surfers lending their support. An incident where a barge being used in the construction got stuck on the offshore reef further fueled local anger. Despite apologies from the president of French Polynesia, Moetai Brotherson, and assurances from Barbara Martins-Nio, general manager of the 2024 Paris Olympic committee based in Tahiti, that the barge incident was a mistake, the new tower was still deemed necessary for the competition. However, many locals, including the mayor of Taiarapu Ouest, stood by the belief that building the tower outweighed the costs. The protests failed, and the tower has since been completed.
As the 2024 Olympic Games in Paris approach, they carry the weight of numerous controversies and the hopes of millions of spectators, eager to participate in a global event of this magnitude for the first time since the COVID-19 pandemic. From security concerns and transportation issues to the treatment of the city’s unhoused population and environmental concerns, these Games are a testament to the complex interplay of sports, politics and society. Despite the controversies, the essence of the Olympics remains—unity, athleticism and global camaraderie. As the world tunes in, these Games will be a reminder of our shared love for sport and competition, and the collective challenges we need to address.
Julz Vargas
Julz is a student at Wellesley College studying Anthropology and Spanish. She grew up in Los Angeles, CA, and has studied all around the world in places such as Costa Rica, Greece, Iceland, and Spain. She is passionate about employing writing as a tool to explore human connection and diversity. Julz aspires to foster cross-cultural connections through community-based research, amplifying inclusive and diverse media about global cultures, foods, and people, to encourage individuals to engage more wholly with the world.