With the 2023 Supreme Court case of City of Grants Pass, Oregon v. Gloria Johnson circulating the headlines and threatening the rights of 653,104 unhoused people in the United States, understanding how other countries are addressing the issue of houselessness can help provide perspective.
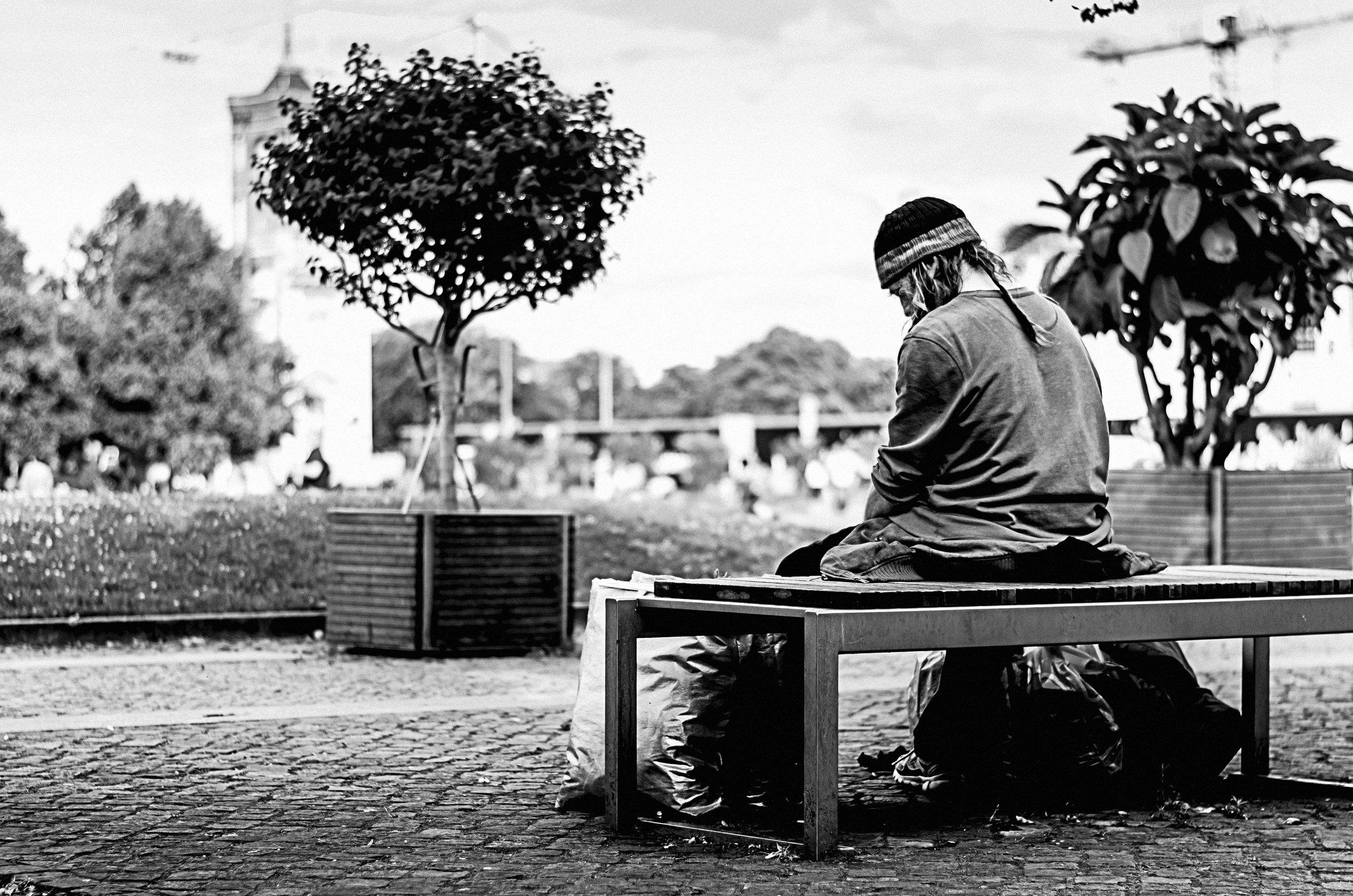
A person sits on a bench with their belongings. Grego. CC0 1.0
In 2020, the world denied an estimated 1.6 billion people the human right to adequate housing. Societies often stigmatize houselessness, leading to discrimination against unhoused people. This stigma often contributes to the criminalization of houselessness.
Houselessness is criminalized when laws can punish people for partaking in life-sustaining activities in public spaces. Examples of these laws include prohibitions on panhandling or allowing the confiscation of personal property, often referred to as “sweeping.”
The Supreme Court's decision in the City of Grants Pass, Oregon v. Gloria Johnson case will determine whether it is constitutional for states to fine or arrest people for sleeping outside, even when adequate shelter is unavailable. This comes at a time when houselessness is on the rise across the U.S., with a 12 percent increase between 2022 and 2023. Los Angeles and New York City are home to about a quarter of America's unhoused population.
In the U.S., houselessness is a highly politicized issue. The 2020 Democratic platform endorsed a Housing First policy that prioritizes accessible permanent housing, stating that, “Having a stable and safe place to live is essential to helping a person tackle any other challenges.” In contrast, Republicans on the Joint Economic Committee released a report in 2022 criticizing Housing First policy for failing to “to address deeper problems that often drive homelessness”. The lawmakers proposed that Housing First policy be replaced with policy that prioritizes health and employment resources. The debate over solutions persists as houseless populations rise.
The City of Grants Pass, Oregon v. Gloria Johnson case is not the first time laws explicitly criminalizing houselessness have been on the global radar. In 2018, Hungary enacted a new constitutional provision that put houseless people sleeping in public spaces at risk of fines or arrest. Since the passage of this law, the number of houseless people in Hungary has not changed, with an estimated 30,000 houseless people in both 2018 and 2024.
Hungary is far from the only country to combat houselessness with criminalization. Many governments have turned to this strategy, from the forced institutionalization of houseless children in Brazil to laws authorizing the arrest of people loitering in Sierra Leone and Nigeria.
Other countries have taken a different route in tackling this crisis by increasing accessible housing and resources. Finland’s Housing First Policy focuses on providing people with housing and addressing underlying conditions and factors contributing to their houselessness. Since the Housing First policy began in 2008, the number of long-term houseless people in Finland decreased by more than 35 percent. Some policies combine punitive and welfare measures. The government in Tokyo, Japan has combined these strategies by punishing people for residing in public spaces while redirecting them to welfare resources.
Beyond policy, technological innovations present potential solutions for this issue. In India, Tvasta Manufacturing Solutions collaborated with Habitat for Humanity to create 3D-printed homes. These homes can be built in five days or less, are about 30 percent cheaper than traditional construction and create less waste. The 3D-printed homes industry is now present across the globe from Africa to Mexico.
Beyond the world of policy and technology, everyday people can directly take action to help address houselessness. Destigmatization is an important step in addressing this issue. Experts recommend advocacy and creating public education campaigns to help people understand and empathize with unhoused people. Attending educational opportunities such as events hosted by the UN Working Group to End Homelessness is a great way to learn and engage with people fighting for the right to adequate housing.
For those looking to make an impact on a local scale, there are many volunteering opportunities with organizations such as CaringWorks or the National Coalition for the Homeless. With an estimated 1.6 billion people expected to be impacted by the housing crisis in 2025 and an estimated two billion people fearing climate-related displacement, the time to act is now.
Madison Paulus
Madison is a student at George Washington University studying international affairs, journalism, mass communication, and Arabic. Born and raised in Seattle, Washington, Madison grew up in a creative, open-minded environment. With passions for human rights and social justice, Madison uses her writing skills to educate and advocate. In the future, Madison hopes to pursue a career in science communication or travel journalism.