Journalist murder cases only continue to rise in Mexico after a federal law was enacted to protect media workers from threats of violence, calling for reforms and increased federal support.
Read MoreHow AI Can Preserve Endangered Languages
As minority native languages worldwide disappear at a rapid rate, Indigenous scientists look to new AI language learning models and community participation as a way of preserving their cultures.
Read MoreBreaking Barriers: 7 International LGBTQ+ Activists
In the face of limited equality for LGBTQ+ individuals across the globe, these activists are dedicating their lives to raising awareness and making change in their home countries.
Read MoreThe Return of Child Marriage to South Asia
Families grappling with post-pandemic economic decline are turning to child marriages, undermining efforts to eradicate the practice.
Read MoreReclaiming the Chagos Islands: Unraveling the Colonial Legacy of Mauritius
The significant return of the Chagos Islands, after centuries of British control, serves as a poignant reminder of the legacy of colonialism and the ongoing hurdles that must be overcome.
Read MoreThe Ongoing Fight for LGBTQ+ Rights in Sri Lanka
As Pride Month approaches, 1.5 million Sri Lankans continue to fight against the longstanding criminalisation of homosexuality.
Read MoreGlobal Pride Amid Rising Hostility Toward LGBTQ+ Communities
LGBTQ+ Pride has grown massively in scale and support since its emergence, but many cities around the world have either maintained or enacted threatening legislation undermining the event.
Read MoreSweeps of Homeless Encampments in the US Intensify After Supreme Court Ruling
Since the Supreme Court ruling, Grants Pass v. Johnson, upended protections for the unhoused, sweeping of homeless encampments has drastically increased.
Read MoreGeneration Z Quits Vaping for the Congo
Rampant child labor in the Congo has ignited an ethical social movement among Generation Z.
Read MoreMexico’s Maquiladoras: The Border Factories Harming Female Workers
While a source of cheap labor, the maquiladora system is fraught with social and environmental issues.
Read MoreDefining Gender and Biology: The Struggle For Transgender Rights
As more global governments define gender and biological sex as a singular identity, transgender communities face a potential loss of rights and social stigma from the U.S. and the U.K. to New Zealand.
Read MoreWhat Happened to Australia’s ‘Stolen Generation’?
Zoe Lodge
A look into the history and consequence of removal practices against indigenous Australian youth, the “Stolen Generation.”
Indigenous Australian children. Mark Roy. CC BY-SA 2.0.
From the early 20th century until as late as the 1970s, Australia carried out a government-sanctioned campaign that forcibly removed Indigenous children from their families in a bid to assimilate them into white society. While much global attention has focused on the legacy of boarding schools for Indigenous children in North America, similar practices were inflicted on Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples under British colonial rule, often with the encouragement of the Roman Catholic Church and other Christian institutions. These efforts left generational scars, contributing to the systemic inequality and social fragmentation that persist into the modern day.
This dark chapter in Australian history is commonly referred to as the “Stolen Generation.” According to a report conducted by the U.S. Department of the Interior, which investigated comparable initiatives across the globe, roughly one in three Indigenous children in Australia were forcibly taken from their homes between 1910 and 1970. These children were placed in church- and state-run institutions or sent to live with white families that exemplified Western values, where they were stripped of their language, culture and identity. The underlying goal, both ideological and colonial, was to “civilize” these children by erasing their cultural roots and integrating them into a white-dominated society.
These practices were grounded in a racist belief system that deemed white Australian culture, rooted in Western European culture, inherently superior. Authorities at the time regarded the removal of Indigenous children as a moral duty and a practical solution to what was referred to as “the Aboriginal problem.” In reality, the result was a trauma that has rippled through generations. Children taken from their families frequently endured physical and emotional abuse, neglect, and, in many cases, sexual assault. They were often treated as cheap labor and denied access to adequate education and healthcare.
Although Australia never formally established a network of Indigenous boarding schools akin to those in the U.S. and Canada, the assimilationist mission was no less destructive. Despite making up only about 6% of Australia’s youth population, Indigenous children account for almost 50% of those in out-of-home care, which includes placement in foster care, group homes and with kinship carers. This gaping disparity emphasizes the lasting effects of these programs, leaving First Nations people to deal with dislocation, cultural loss and intergenerational trauma.
In recent years, the Australian government has taken steps to acknowledge and atone for these policies. A national apology was issued in 2008, followed by reparations exceeding $375 million for surviving members of the Stolen Generation. Additionally, individual states have contributed over $200 million in compensation funds for those affected. However, many argue that financial reparations, while important, cannot undo the profound harm caused by decades of systemic cultural erasure and displacement.
Australia’s history with its Indigenous populations is not unique. As the DOI report highlights, these tactics of domination and forced assimilation are not isolated but part of a broader colonial pattern seen across Canada, the United States and New Zealand. These initiatives, driven by the dual forces of governmental policies and religious institutions, sought to erase Indigenous culture in favor of Eurocentric ideals. From the earliest boarding schools in the United States and Canada to parallel programs in Australia and New Zealand, the common thread was the colonial power’s blatant disregard for the autonomy, culture and humanity of Indigenous communities, particularly through religious messaging and values. These institutions inflicted lasting harm, not only by physically removing children from their homes and subjecting them to abuse but also by obliterating the cultural traditions and languages that sustained Indigenous identities for generations.
GET INVOLVED:
One of the primary organizations focused on bringing justice to the First Nations people of Australia is ANTAR, which offers several ways to get involved, raise awareness and contribute to justice for the Indigenous people of Australia. Locals can volunteer with the organizations, and citizens worldwide can contribute to fundraising efforts or participate in global education and awareness campaigns. Other organizations with similar missions include Pay the Rent, IWGIA and the Aboriginal Legal Service.
Zoe Lodge
Zoe is a student at the University of California, Berkeley, where she is studying English and Politics, Philosophy, & Law. She combines her passion for writing with her love for travel, interest in combatting climate change, and concern for social justice issues.
Colombia: The Deadliest Nation for Environmentalists
Colombia remains the deadliest country for environmental defenders, with 79 of the 196 documented murders occurring there in 2024, largely targeting Indigenous and Afro-descendant communities.
Read MoreChild Slavery in Congo’s Cobalt Mines
The world’s high demand for cobalt mining has led to the exploitation of child labor in the Congo.
Read MoreBarring Basic Rights: Uganda’s Anti-Homosexuality Regulation
Modern anti-gay regulations continue to threaten the lives and safety of Ugandan LGBTQ+ individuals.
Group Marching in Support of Uganda’s LGBTQ+ Community. Alisdare Hickson. CC BY-SA 2.0.
Known for having one of the world’s harshest LGBTQ+ rights records, the Ugandan parliament has pursued longstanding efforts to diminish same-sex activity within the country. As a result of 19th-century British colonization, the severe criminalization of homosexuality set the stage for modern homophobic sentiments. This culminated in the Anti-Homosexuality Act of 2023, which was later upheld by the Ugandan parliament in April 2024.
The 2023 Anti-Homosexuality Act was signed into law by Ugandan President Yoweri Museveni in May 2023, enforcing strict restrictions against LGBTQ+ individuals. Implementing harsh penalties, the act demands life imprisonment for consensual same-sex activity and the death penalty in cases of “aggravated homosexuality,” a term that denotes any same-sex act that involves people under 18, older than 75, those with a disability, or when consent is not given or cannot be given. This act is not the first attempt to limit LGBTQ+ rights in Uganda. In 2010, the Ugandan parliament passed a bill introducing similarly anti-gay legislation that was eventually ruled illegal by the constitutional court due to its lack of necessary quorum. In 2021, however, the president succeeded in passing a sexual offenses bill that criminalized same-sex relationships and sex work in Uganda.
While the Ugandan government has praised such legislation as acting in the country’s best interest, the persistent condemnation of same-sex actions has negatively impacted the lives of LGBTQ+ Ugandans. This has not only promoted anti-gay views but has also threatened lives through the reduction of HIV prevention and perpetuation of societal abuse. In an interview with Amnesty International, Ugandan activist and founder of the gay and intersex rights organization Freedom and Roam Uganda (FARUG), Jacqueline Kasha described the new law’s impact on her community. She contends that advocacy and visibility for LGBTQ+ individuals have sharply diminished with the aggressive crackdown: “Several LGBTI persons have since gone underground which is now impeding all our efforts, especially in the health sphere in the fight against HIV, mental illness and economic disparities.” The 2023 Act has allowed anti-gay groups to accuse or arrest people with little evidence or reasoning. As such, LGBTQ+ individuals are vulnerable to attack when outside the safety of their homes, forced to hide their identities under the threat of violence. Furthermore, those in need of HIV services have become disproportionately vulnerable to health risks, driven away from receiving care due to fear of criminal punishment or discrimination.
The first case of “aggravated homosexuality” has already come into effect: 21-year-old Michael Opolot was arrested in August 2023 after allegedly participating in public sexual activity with another man reported to have a disability. While the new act permits this arrest, there has not been any evidence submitted by police to substantiate claims that the alleged victim is disabled and therefore could not give consent. Opolot’s case has provoked Ugandan activists to challenge the law's constitutionality, citing the act’s contradiction of citizens’ freedom from discrimination and rights to privacy and health. Moreover, they have noted that Opolot’s case demonstrates the senseless oppression of LGBTQ+ individuals. Ugandan activist Clare Byarugaba affirmed that this mistreatment not only violates human rights but also suppresses advocacy, as “activists, public health workers, and others face long prison sentences and hefty fines” for attempting to voice support.
As a result of such political, social and health persecution, the LGBTQ+ population in Uganda has been left unprotected and endangered by intimidating threats. Although Uganda’s government views the recent passing of anti-homosexual legislation as a “step forward” for the country, many in the LGBTQ+ community have experienced the opposite result in their daily lives. Several international organizations and governments have commented on the bill, with United States President Joe Biden describing the act as a “tragic violation of universal human rights,” and the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) explaining that “criminalizing populations most at risk of HIV, such as the LGBTQ+ communities, obstructs access to life-saving health and HIV services.” Despite such international criticism, anti-homosexuality continues to loom largely over Uganda and LGBTQ+ existence within the country.
TO GET INVOLVED
Those looking to support LGBTQ+ communities in Uganda can do so by getting involved with organizations dedicated to supporting individuals inside the country as well as those who have fled. Such organizations include: Sexual Minorities Uganda (SMUG), an LGBTQ+ advocacy organization, Universal Coalition of Affirming Africans Uganda (UCAA - UG), a human rights organization advocating for human rights and marginalized people, and Global Black Gay Men Connect (GBGMC), a group collaborating with Uganda Key Populations Consortium (UKPC) and SMUG to launch an emergency response fund to support LGBTQ+ Ugandans.
Julia is a recent graduate from UC San Diego majoring in Sociocultural Anthropology with a minor in Art History. She is passionate about cultural studies and social justice, and one day hopes to obtain a postgraduate degree expanding on these subjects. In her free time, she enjoys reading, traveling, and spending time with her friends and family.
4B: Why are American Women Swearing Off Men?
American women are participating in the 4B Movement which originated in South Korea, swearing off dating, marriage and sex.
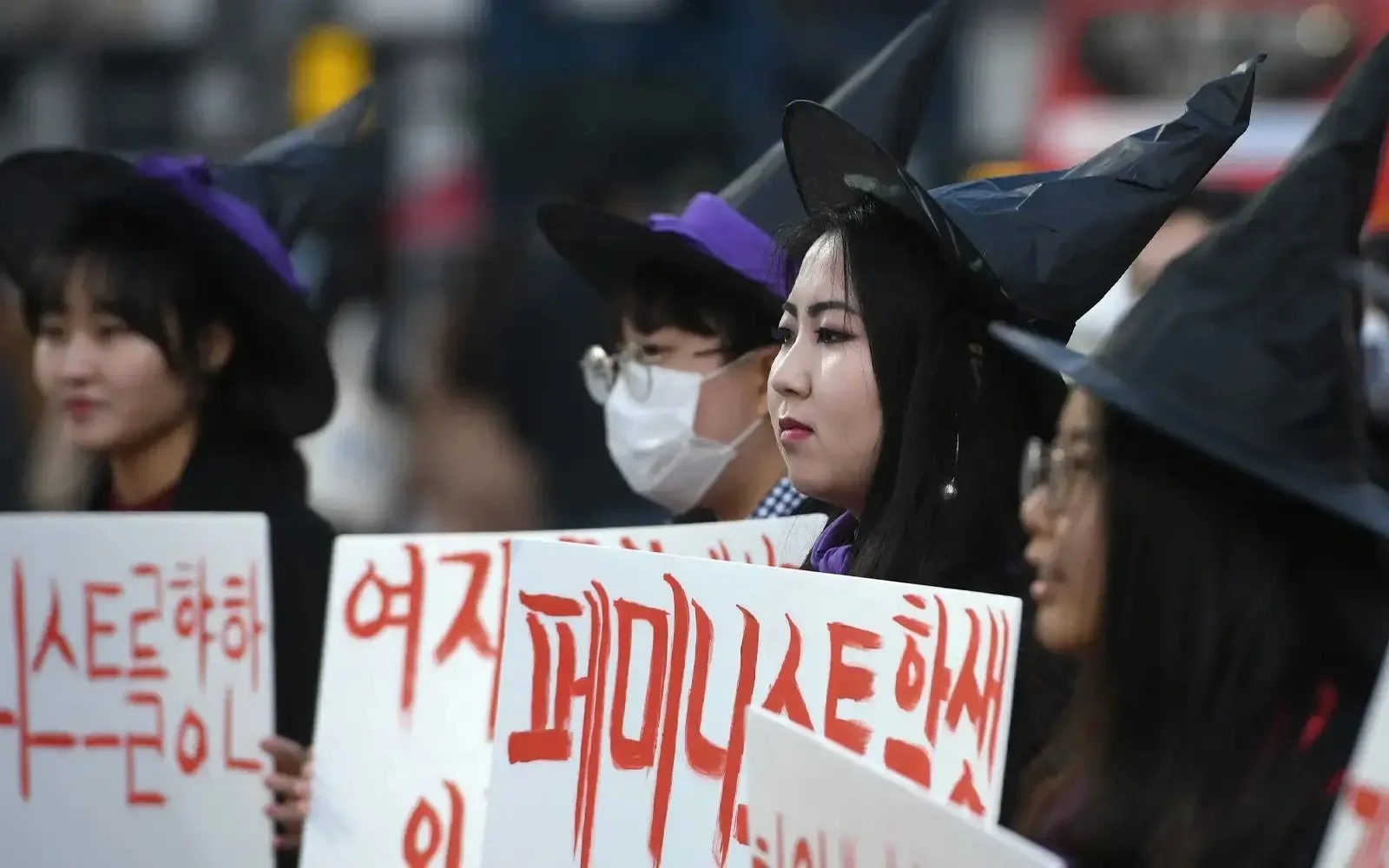
Women in South Korea at a 4B protest. Free Malaysia Today. CC BY 4.0.
In the wake of Donald Trump winning the 2024 U.S. Presidential Election, social media flooded with thousands of posts from women announcing that they were swearing off men as part of the 4B Movement. But what exactly is the 4B Movement, and what does it hope to accomplish?
Originating in South Korea, the feminist 4B Movement derives its name from its four tenets, which all start with the Korean prefix “bi” (or “no”) and denote a denial of something. Indeed, these four “Bs” are: don’t have children (bichulsan), don’t have sex with men (bisekseu), don’t date men (biyeonae) and don’t marry them either (bihon). The movement began in the mid-to-late 2010s as a protest against rising anti-woman sentiments among the nation’s men — especially following the hate-motivated stabbing of a young woman in Seoul in 2016. By withholding heterosexual attachments and exacerbating the nation’s flagging birth rates, South Korean women hope that the movement will provoke the nation’s leadership and male population into caring more about women’s rights. “I think a lot of women, through not participating in marriage and childbearing or relationships with men see a value in dropping the numbers to show through these statistics that women are not going to participate in [any] national agenda unless you listen to where women are coming from,” as Yale sociologist Meera Choi told The Times.
In South Korea, 4B is primarily a fringe movement. Its practices are so elusive and decentralized that the best estimate we have for its total number of participants is anywhere between 5,000 and 50,000, a wide range that highlights researchers’ uncertainty. However, since Nov. 5, 2024, some women in the United States have expressed a desire to introduce the movement mainstream in the West. Immediately following the 2024 U.S. Presidential Election, many expressed shock and fear that Donald Trump — a figure with a well-documented history of sexual misconduct — had again achieved the highest office in the country. Particularly, some were distressed by the sheer number of men that had turned out for Trump, believing their votes to represent endorsements of or even apathy toward Trump’s misogynistic behaviors (“Among men, who made up 47% of the electorate,” NBC News reported, “Trump won 55%”).
For these women, 4B’s appeal of sticking it to the government and an indifferent, if not overtly hostile, male population was immediate. “Young men expect sex, but they also want us to not be able to have access to abortion. They can’t have both,” Michaela Thomas told The Washington Post, referring to Trump’s first-term Supreme Court nominations who helped overturn Roe v. Wade. “Young women don’t want to be intimate with men who don’t fight for women’s rights; it’s showing they don’t respect us.”
4B’s popularity quickly caught on across social media. “Good luck getting laid, especially in Florida! [...] Me and my girlies are participating in the 4B Movement,” user @brielleybelly123 posted to TikTok. User @rabbitsandtea also posted on the platform: “Doing my part as an American woman by breaking up with my [R]epublican boyfriend last night and officially joining the 4B [M]ovement this morning.” Some liberal men have also expressed support for 4B. “The best way to show the importance of taking away women’s rights is to make sure men are affected as much as possible alongside them,” a Buzzfeed commenter wrote. As Instagram user @nosybystanders told her female fanbase: “Why exactly are you going to keep be[ing] subservient to a nation that [literally doesn’t] care about you?”
4B finds footing in an America currently experiencing a widening political gender gap. Young women are becoming more liberal as men drift further to the right and deeper into conservatism. In October 2024, a New York Times/Siena College poll found that “young women — those ages 18 to 29 — favored Vice President Kamala Harris for president by 38 points. And men in the same age group favored former President Donald J. Trump by 13 points. That is a whopping 51-point divide along gender lines, larger than in any other generation.” As Claire Cain Miller reported, this is partly because young women have been “politically galvanized” by “tthe triple punch of Hillary Clinton’s loss to Mr. Trump, the #MeToo movement and the overturning of Roe v. Wade.” On the other hand, young men feel increasingly “unvalued” by young women and “see former President Donald J. Trump as a champion of traditional manhood.” In terms of the 4B Movement, participants know firsthand how this male-harbored resentment can manifest in internet trolls’ hate comments.
Under @brielleybelly123’s video, @user813858060727 commented, “Thanks for not reproducing. You’re doing us all a favor.” Elsewhere, beneath a separate post under the 4B Movement hashtag, TikTok user @feronity commented, “Took a fu—kin new president just to stop being wh—res.” In the context of this vitriolic pushback — coupled with increased threats of “Your Body, My Choice” among young right-wing men — it becomes less surprising that women are joining the 4B Movement.
Some of the online discourses surrounding women’s participation in the 4B movement are likely exaggerations: not every woman who posts about partaking in 4B is likely to completely follow through with its tenets, especially in the long term. For all of the buzz that it’s created in the U.S., 4B has never been among the top 100 trending hashtags on TikTok, signaling that hype for the movement has been largely sensationalized. But so long as Trump continues to campaign on misogynistic rhetoric and policies — and men continue to listen — the underlying sentiments of 4B will remain real, and so will their implications for increasingly fed-up women.
Bella Liu
Bella is a student at UC Berkeley studying English, Media Studies and Journalism. When she’s not writing or working through the books on her nightstand, you can find her painting her nails red, taking digicam photos with her friends or yelling at the TV to make the Dodgers play better. Bella is a student at UC Berkeley studying English, Media Studies, and Journalism. When she’s not writing or working through the books on her nightstand, you can find her painting her nails red, taking digicam photos with her friends or yelling at the TV to make the Dodgers play better.
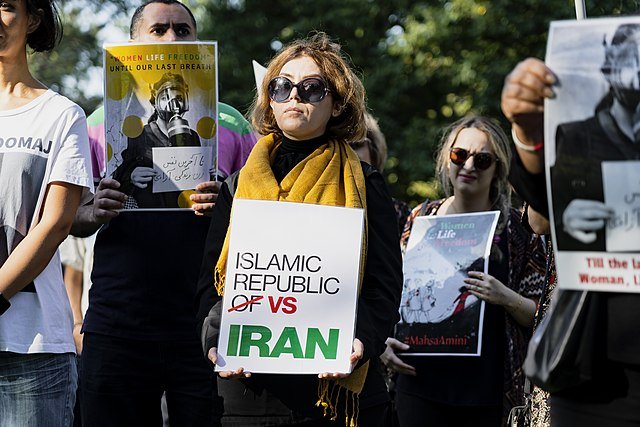
The Direction of Iran’s Woman, Life, Freedom Movement
With tensions high domestically and internationally, women both inside and outside of Iran are cynical that things will change.
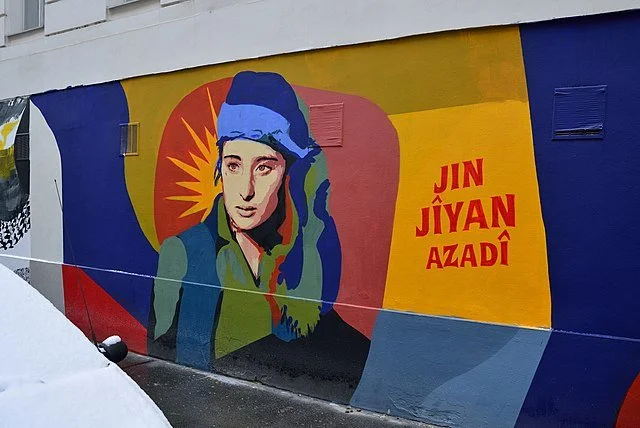
A mural in support of the Jin, Jiyan, Azadi (Woman, Life, Freedom) movement. Herzi Pinki. CC BY 4.0
For many in Iran, history can be broken up into two epochs: before 1979 and after. Women, in particular, find significance in this demarcation because Iran’s 1979 Islamic Revolution brought the expansion — and then constriction — of their rights. These tensions surrounding women’s role in Iranian society came to a head in 2022, when the widespread Woman, Life, Freedom movement put them on global display. But the Woman, Life, Freedom movement didn’t spawn out of nowhere, and it’s important to look at its past when considering its future.
Women at the 1979 International Women’s Day protests in Tehran. Mohammad Sayad. CC0
Prior to the Iranian Revolution, women saw their rights and opportunities gradually expand as part of the country’s modernization efforts. The state wanted to Westernize itself, and this manifested in women being mandated (sometimes violently) to not veil themselves, per a 1936 decree. But the revolution saw the nation shirk its Western influences — thanks in large part to women. While some mobilized public demonstrations, others acted as nurses and first responders. Few fought in guerilla conflicts, but many wore hijabs to protest the monarchy's 1936 ban on veils, linking modest dress with the revolution’s vision of a new Iran.
However, after the revolution succeeded and the pro-Western monarchy was overthrown for an Islamist theocracy, women’s roles became more limited. In an interview I conducted with Iranian Circle of Women’s Intercultural Network steering committee member Ruja Kia, she affirmed, “Adding the religious components of private life to the law of the land never makes things easier for women.”
The revolution placed nearly all Iranian state power in the role of “the supreme leader,” where it still remains today. As both a religious and political authority, the first supreme leader, Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini, sought to curb women’s post-revolution rights and professional opportunities in favor of a return to traditional domesticity. Further, after revolutionaries associated modesty with the new Islamic Republic, Khomeini mandated women to cover themselves with hijabs. What had once been a symbol of dissent and autonomy became a violently imposed law.
The 1979 hijab mandate notably came under international scrutiny in 2022, following the death of Mahsa Amini. Iran’s Guidance Patrol, or morality police, arrested Amini for an “improper hijab.” She died in their custody three days later — officially of a heart attack but allegedly of police brutality (In our interview, Ruja Kia also noted that Amini was Kurdish, an Iranian ethnic minority that often faces discrimination).
A man protests in support of the Woman, Life, Freedom movement following Amini’s death. Ilias Bartolini. CC BY 2.0
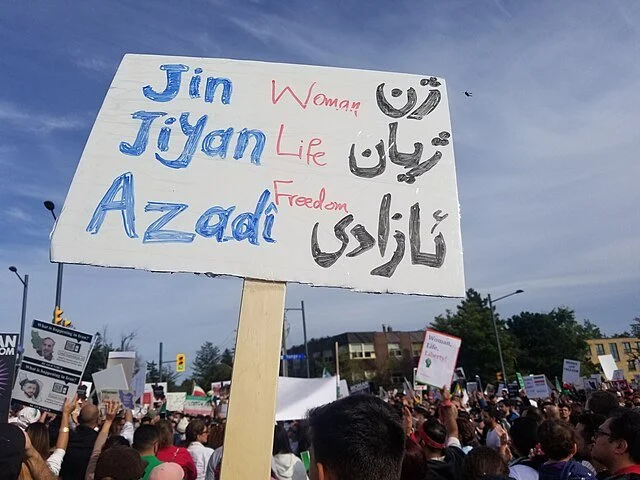
Amini’s death sparked mass protests — not only in Iran but also around the world. Internationally, the rallying cry was “woman, life, freedom,” a translation of the Kurdish feminist slogan “Jin, Jiyan, Azadi.” For its criticisms against the compulsory hijab, the morality police and the Islamic Republic in general, the Woman, Life, Freedom movement has been intensely repressed by Iran’s current supreme leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei. Iranian security forces have killed more than 500 demonstrators and arrested thousands across the country.
“I say explicitly that these [Woman, Life, Freedom] riots and this insecurity were a design by the US and the occupying, fake Zionist regime [Israel],” Khamenei said in 2022, as reported by Al Jazeera. On a broader scale, Khamenei believes that the hijab is a religious and therefore, moral obligation. He further contended that gender equality is a Western plot designed to weaken Iran: “[The West] feel[s] that [Iran] is progressing towards full-scale power and they can’t tolerate this.” Because of and in spite of Khamenei’s deadly response, the Women, Life, Freedom movement gained international prominence, making the future of women’s rights in Iran an unavoidable and salient issue in the recent election.
Two women attend a Woman, Life, Freedom protest wearing past versions of the Iranian flag. Taymaz Valley. CC BY 2.0
Masoud Pezeshkian, Iran’s newest president, campaigned on a reformist platform, asserting a desire to steer the nation toward greater peace. Now, after taking office in July, he has a chance to do so. For many nations that have tensions with Iran, having the moderate Pezeskian in office is cause for cautious optimism. Inside Iran’s borders, however, women are still reeling from the pushback Woman, Life, Freedom received two years ago and are thus more cynical about the promise of Pezeshkian’s election. “Although we might see more moderate approaches in bigger metropolitan areas, women across the rest of Iran will stay controlled by family customs and norms,” said Ruja Kia.
As the only reformist in a field of six candidates, Pezeshkian’s positions on women’s rights stood out as the most progressive. Frequently invoking his daughter, a chemist, and the memory of his late wife, a gynecologist, he spoke of increasing women’s presence in the professional sector: “A woman is not a servant at home,” Pezeshkian wrote on X.
Regarding the mandatory hijab, Pezeshkian has expressed support for relaxing the mandate: “The behavior of Iranian girls will not change. Just as the previous [1936 laws] could not forcibly remove the hijab from the heads of our women, you cannot force them to wear the hijab by passing a law,” he wrote in another X post. But some, like Kimia Adibi, the President of UC Berkeley’s Iranian Students’ Cultural Organization, believe that Pezeshkian’s words are empty promises. “[Pezeshkian’s] not actually pushing for women’s freedom and change because if he were, he never would’ve been allowed to run,” Adibi said to me. “Anyone who’s an actual radical reformist and believes in women’s freedom and not forcing the mandatory hijab… like, they’re not even going to make it to the candidacy level.”
A woman at a Woman, Life, Freedom protest. Matt Hrkac. CC BY 2.0
Pezeshkian’s parliamentary record shows that he’s supported restrictions on women’s rights in the past, and alongside the posts he made calling for women’s rights, he also posted to X, “All of us move towards dignity and power according [...] to the general policies of the supreme leader.”
For Iranian feminists, the zeitgeist has not shifted. While it’s not impossible, they say, for Pezeshkian to achieve some reform — “little shifts,” as Adibi put it — so long as religion and politics remain married to an ultimate authority who violently rejects gender equality, women’s rights in Iran will not improve much under the new president.
A Woman, Life, Freedom protest sign in Kurdish, English and Persian. Pirehelokan. CC BY 4.0
“I’ll speak for myself,” Adibi said, “but I think most Iranians are not super optimistic about the direction of women’s rights under this president. And they won’t be under the next president, or the next president, under however many presidents until the supreme leader is removed from power.”
When speaking with an admin from the Instagram account @irans.feminist.liberation, I found this feeling re-affirmed. “The future for women and minorities in Iran remains bleak,” she said, “unless there is significant internal pressure for change.
Bella Liu
Bella is a student at UC Berkeley studying English, Media Studies and Journalism. When she’s not writing or working through the books on her nightstand, you can find her painting her nails red, taking digicam photos with her friends or yelling at the TV to make the Dodgers play better.
Stopping AAPI Hate: Checking in on the Lead Asian Hate Prevention Group
With Anti-Asian hate on the rise, see what Stop AAPI Hate is doing to combat it and how you can help.
A Stop Asian Hate demonstration in Washington, DC. Elvert Barnes. CC BY 2.0
In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, the United States saw a dramatic increase in anti-Asian hate crimes and attacks. According to the FBI’s data reports, the number of recorded hate crimes exploded to 424 in 2020, up almost 175% from 2019. A survey by the Pew Research Center showed 1 in 3 Asian Americans knew someone who had been attacked or threatened because of their race. Many believed that Sinophobic rumors placing the origin of the COVID-19 virus in China fueled this sharp increase in violence.
Out of this crisis arose the organization Stop AAPI Hate. Initially meant to document anti-Asian hate in the US, Stop AAPI Hate has become a full-fledged advocacy group. The organization has several ongoing campaigns, such as the wildly successful No Place for Hate movement. The group also advocates for policy changes (such as a law in California that aims to prevent harassment on public transit), working to strengthen civil rights protections across the board. In 2023, Stop AAPI Hate fought to stop a potential Texas law that would prevent AAPI (Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders) immigrants from purchasing houses.
More recently, Stop AAPI Hate has moved towards bolstering the confidence and security of AAPIs across the country. In May 2024, a national survey by the organization showed the value of pride and supportive narratives in combating the fear spread by hate crimes. In response to this data, Stop AAPI Hate has announced a new program, Spread AAPI Love, which aims to foster supportive and celebratory connections between AAPIs across the country.
Stop AAPI Hate’s progress has been somewhat restricted by a seemingly unending rise in anti-Asian hate. The organization’s annual survey this year revealed that almost half of all AAPIs in the US were subject to some form of racism or hate. In 2024, there have been a number of reports documenting anti-Asian violence. In February, a man assaulted a Filipino woman on the street in New York. In April, a Massachusetts man ran over a Vietnamese man with his car. In August, a 26-year-old Korean girl calling for medical assistance was instead shot dead by police. The government has acknowledged these crimes and the systems preventing them from being properly reported, but bureaucracy has prevented true justice.
Stop AAPI Hate is doing its best to call attention to these cases as instances of anti-Asian violence continue to rise since the COVID-19 pandemic. Although they have made great progress, their mission is far from complete.
How You Can Help
Stop AAPI Hate is always accepting donations and support, both in general and for their specific campaigns. Many other organizations also dedicate themselves to stopping the spread of hate, including Asian Americans Advancing Justice, Red Canary Song, and the National Asian Pacific American Women’s Forum.
Ryan Livingston
Ryan is a senior at The College of New Jersey, majoring in English and minoring in marketing. Since a young age, Ryan has been passionate about human rights and environmental action and uses his writing to educate wherever he can. He hopes to pursue a career in professional writing and spread his message even further.
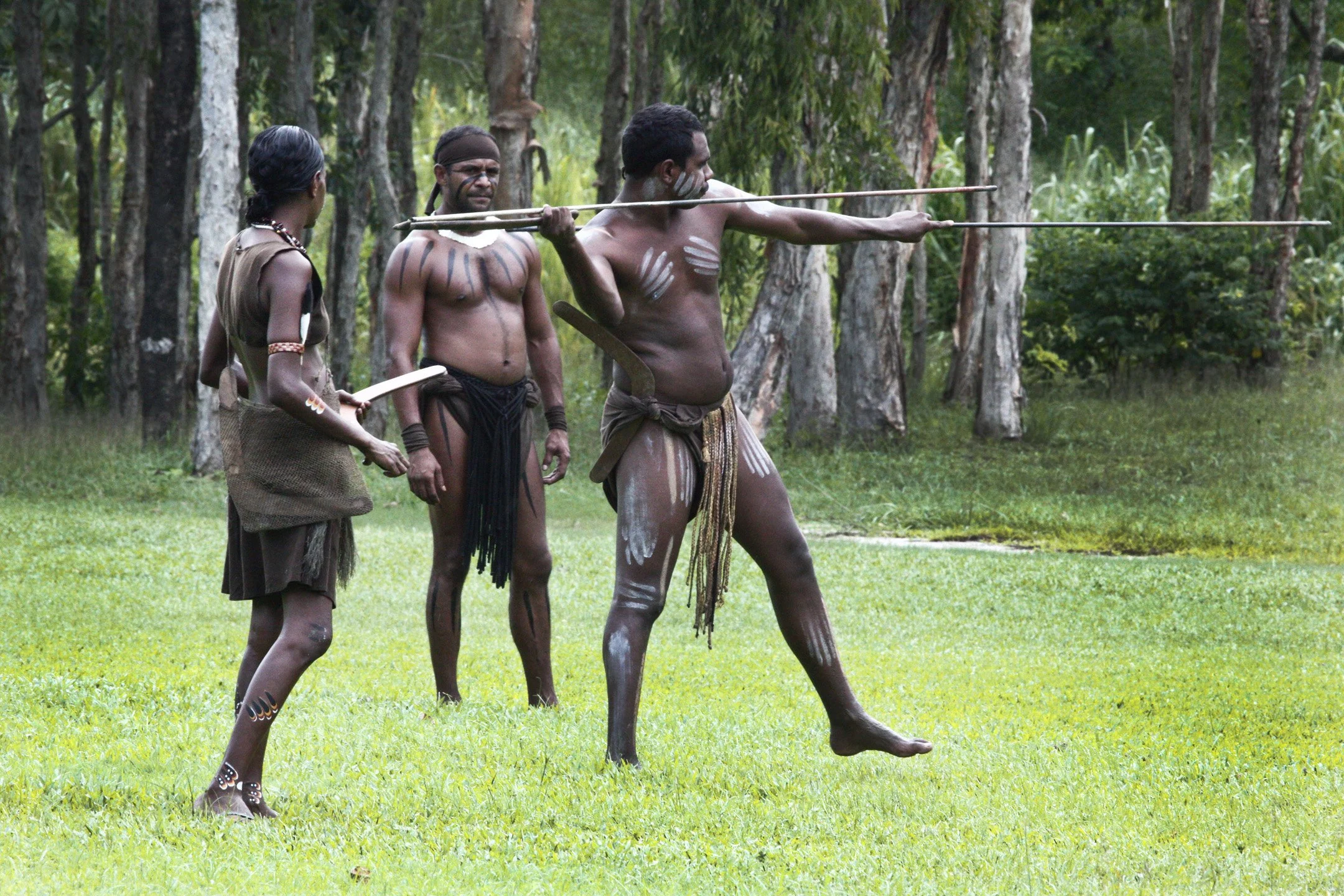
Aboriginal Australians: Ancient Roots and Modern Struggles
Centuries after British Settlement and mass destruction of their culture, Aboriginal Australians continue to be discriminated against by the Australian government.
Aboriginal Men in 2011. Steve Evans. CC BY 2.0
Aboriginal Australians have experienced systemic disadvantages throughout Australia’s history. Noted as one of the oldest Indigenous communities living outside of Africa, Aboriginal Australians led an advanced lifestyle in precolonial times. According to an article in The Conversation, Indigenous Australians are noted for “establishing complex religions, burying their dead with elaborate rituals, engaging in long-distance trade, making jewelry, and producing magnificent works of art” when Europe was still home to Neanderthals.
The ancestors of Indigenous Australians migrated to the continent from Southeast Asian countries like Malaysia, Singapore, Brunei, Indonesia and the Philippines. Numerous studies investigating the Indigenous group conclude that Aborigines have lived in Australia for approximately 65,000 years. Across the country, Aborigines speak more than 250 distinct languages. There are two classifications of Indigenous people in Australia—the Aboriginal peoples and the Torres Strait Islanders. Aboriginal Australians are those whose ancestors lived in mainland Australia before the arrival of European colonists, while Torres Strait Islanders have traditionally lived in an archipelago between the continent and Papua New Guinea to the north.
Over time, Australia’s Aboriginal presence has fallen to just 3% of the national population due to colonization and legal restrictions. When British Settlement began in 1788, 750,000 to 1.25 million Aboriginal Australians were living in the country at the time. The British brought epidemics, land seizures, and violent conflict, subjecting most Aboriginal Australians to poverty and massacres. According to National Geographic, “[t]hough the term ‘genocide’ remains controversial, people related to the continent’s first inhabitants are widely considered to have been wiped out through violence.”
From 1910 to 1970, the Australian government created assimilation policies for Aboriginal Australian children, resulting in the Stolen Generations. Successive administrations took Indigenous children away from their families and put them into adoptive families or institutions, forbidding them from speaking their native languages or even keeping their original names.
Today’s Aborigines still face various hurdles as a result of settlement, one being accessible maternal healthcare. Edie, an Aboriginal woman interviewed by BBC, explains her recent involvement with a movement called Birthing on Country following the birth of her fourth child and observations about the dearth in Indigenous mother healthcare in Australia. Her colleague and co-director of the Molly Wardahuha Research Centre Yvette Roe explains that the organization is, “a concept with key elements: when we talk about ‘Country,’ we’re talking about ancestral connection to the country where we’re born. We’re talking about 60,000 years of connection to the land and sky.” Lack of proper maternal care for Indigenous mothers results in them being three times more likely to die during childbirth than non-Indigenous mothers, and their babies almost twice as likely to die in the first year. The maternal health crisis reflects general disparities that exist for Australia’s Indigenous population. Aboriginal Australians and Torres Strait Islander people face high levels of discrimination, unemployment, poor housing and poor education compared to their counterparts. Concentration in remote locations has also limited access to life-saving services.
Additionally, Aboriginals continue to fight for general recognition and restitution by the Australian government. As the only country in the Commonwealth of Nations country to not make a treaty with its Indigenous population, Australia's Parliament attempted to recognise Aboriginals in its Constitution and create an Indigenous advisory board that would weigh in on national, relevant issues along with Parliament. In the fall of 2023, Australia rejected the referendum. While most of the Indigenous voters were in favor of the referendum, 60% of Australian voters said no. The Aboriginal community took a week of silence and reflection following the decision. In the Queensland Parliament, the "Path to Treaty Act 2023" was legislated with an 88 out of 92 member majority. Truth and Treaty Queensland described it as a, “Historic piece of legislation … the Act provides the legislative framework for the Truth-telling and Healing Inquiry and the First Nations Treaty Institute to be established.”
Since the late 1700’s, Aboriginal Australians have struggled at the hands of foreign settlers. Whether it is maternal healthcare or incorporation into Australia’s Constitution, their rights and needs have been and continue to be disregarded in numerous ways across the country.
TO GET INVOLVED
Australians are encouraged to get involved with their local Aboriginal communities by attending community events and participating in local Aboriginal tours. Residents can also explore local Aboriginal Land Councils to learn about what actions are currently being taken in their communities. Creativespirits.info explains what land councils do to help Indigenous Australians and has a comprehensive list of Aboriginal land councils in Australia. Activist groups such as Australians for Native Title and Reconciliation (ANTaR) and Stop the Intervention Collective Sydney (STICS) are actively working to help remediate the injustices Aboriginals are facing across Australia.
Aanya Panyadahundi
Aanya is a student at the University of Michigan studying sociology and journalism on a pre-law path. She loves to travel the world whenever she can, always eager to learn more about the different cultures and societies around her. In her free time, she likes to play the violin, ski, and listen to podcasts.
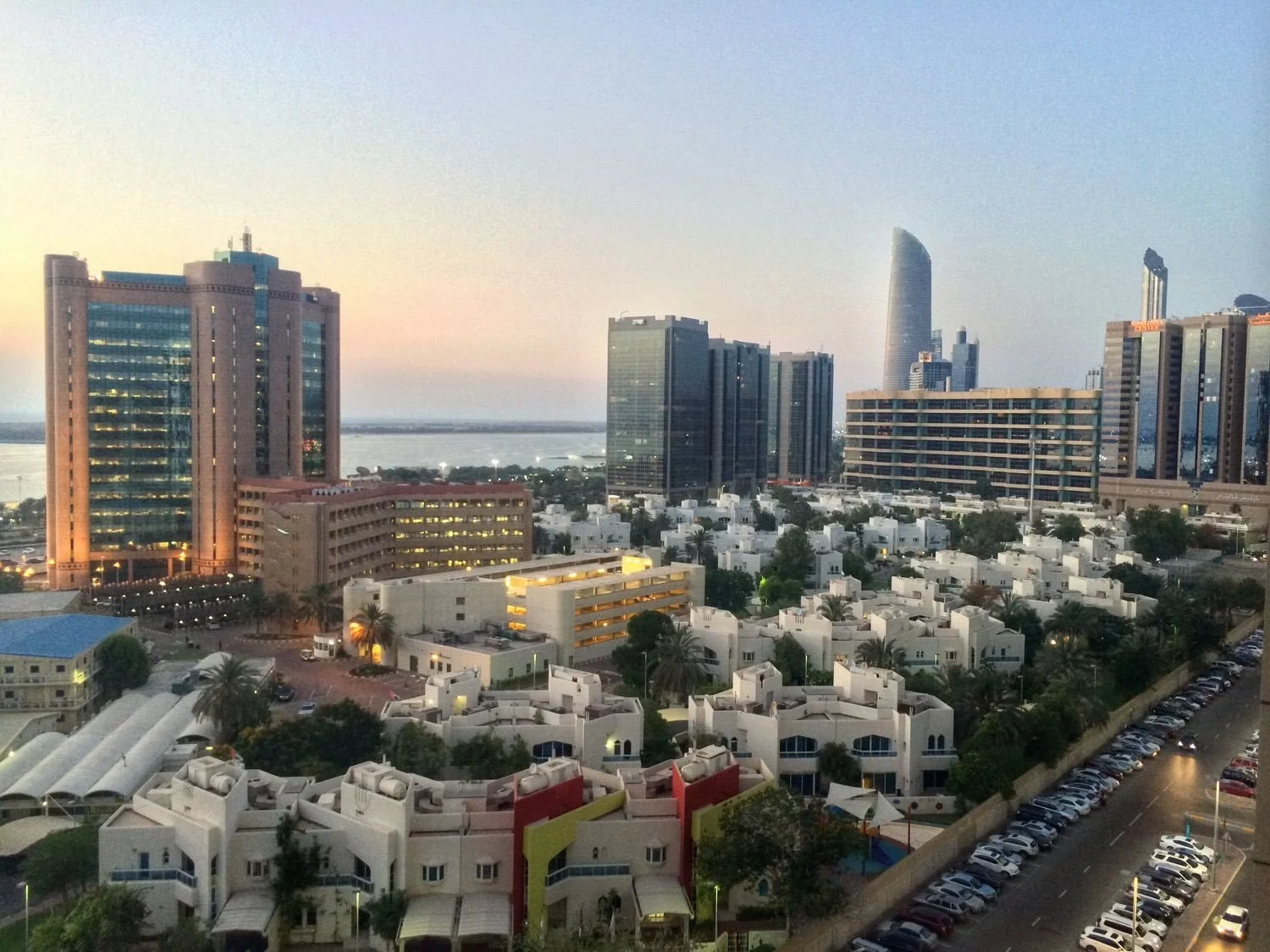
UAE Activists Sentenced on Terrorism Charges
The United Arab Emirates has sentenced 43 activists to life in prison for their alleged participation in terrorist organizations.
Khalidiya, Abu Dhabi. Thomas Galvez. CC BY 2.0
In 2024, the UAE tried 84 defendants for terrorism charges for "co-operating with al-Islah" and money laundering, individuals human rights groups have determined are activists and not terrorists. Al-Islah is considered to be the Emirati version of the Muslim Brotherhood, a pan-Islamic organization declared a terrorist group by the Emirates. In 2014, the UAE passed Terrorism Law No. 7. The law defines terrorism as, among other things, “stirring panic among a group of people” and “antagonizing the state,” a broad definition that makes it possible for peaceful dissent to be labeled terrorism. “Terrorist organizations” are defined as groups that act to create “direct or indirect terrorist outcome regardless of the … place of establishment of the group or the place where it operates or exists, or the nationality of its members or places.” Along with the passage of the law, the UAE state news agency announced that the cabinet had “approved a list of designated terrorist organizations and groups in implementation of Federal Law No. 7 for 2014.” Muslim organizations that operate legally in the United States and Norway were included on the list.
On July 10, 43 of the defendants were sentenced to life in prison, while 10 received 10 to 15 years in prison. Human rights organizations, including Human Rights Watch and Amnesty International, insist that the defendants are innocent and that the UAE is abusing its justice system to punish activists, government critics and democracy advocates for forming an independent advocacy group in 2010. In the UAE, these groups mainly advocate for freedom of expression and assembly, the right to a healthy environment and workers' rights, as well as an end to arbitrary detention, torture and the death penalty.
The indictment, the charges, the defense lawyers and the defendants' names have all been kept secret by the government. They are known only partially through leaks. One of the known defendants, Ahmed Mansoor, is on the Board of the Gulf Centre for Human Rights (GCHR) and the MENA Division Advisory Committee for Human Rights Watch, and was arrested on charges relating to his human rights activities. Another, Mohammed al-Roken, is a human rights lawyer who was arrested on charges related to his peaceful criticism of the Egyptian and Emirati authorities. Yet another three, Nasser bin Ghaith, Abdulsalam Darwish al-Marzouqi and Sultan Bin Kayed al-Qasimi, are academics.
The mass sentencing marks the UAE’s second-largest trial of this nature. The proceedings and the verdict were criticized for the lack of transparency and fairness, along with various other allegations of violations of justice, including but not limited to torture, solitary confinement, withholding evidence from lawyers and the removal of key witnesses. Joey Shea, a UAE researcher at Human Rights Watch, called the sentencing a “mockery of justice”, saying, “The UAE has dragged scores of its most dedicated human rights defenders and civil society members through a shamelessly unfair trial riddled with due process violations and torture allegations.”
Authorities launched the new mass trial during COP28, the international climate gathering held in Dubai in 2023. The case had been ongoing since 7 December 2023, yet the UAE only acknowledged the trial was taking place a month after human rights groups and journalists first uncovered and reported it. A number of the defendants had already spent ten years behind bars after being convicted in 2013 for their alleged involvement with the Justice and Dignity Committee, a branch of the al-Islah movement. This has sparked protests that the Emirati authorities are violating the principle of double jeopardy, which prohibits trying people twice for the same offense after receiving a final verdict.
The mass trial reflects a broader trend of the UAE using its anti-terrorism laws to stifle dissent and suppress political opposition. Devin Kenney, Amnesty International’s UAE Researcher, said in a statement, “Trying 84 Emiratis at once, including 26 prisoners of conscience and well-known human rights defenders is a scarcely disguised exercise in punishing dissenters…This case should be the nail in the coffin of the UAE’s attempts to disguise its horrendous human rights abuses behind a progressive façade.”
The UAE government, however, has staunchly defended its judicial process, maintaining that the convictions were based on solid evidence of terrorism-related activities. Officials have argued that the country’s stringent laws are necessary to combat extremism and ensure national security. The court ruled that those convicted “have worked to create and replicate violent events in the country, similar to what has occurred in other Arab states—including protests and clashes between the security forces and protesting crowds—that led to deaths and injuries and to the destruction of facilities, as well as the consequent spread of panic and terror among people.”
Critics argue that the country’s use of anti-terrorism laws to quash political dissent is part of a wider pattern of repression. They point to other cases where activists, journalists and opposition figures have been detained and sentenced under similar charges, calling for greater scrutiny of the UAE’s legal practices and human rights record. The recent trial is a stark reminder of the ongoing struggle for human rights and justice in the UAE and the broader Arab world. The international community’s response to this case will likely shape the future of human rights advocacy in the region and beyond, as activists continue to call for greater transparency, accountability and fairness in the UAE’s judicial system.
TO GET INVOLVED
Emirates Detainees Advocacy Center: Emirates Detainees Advocacy Centre (EDAC) is a non-profit organization founded in 2021 by a group of human rights activists to support detainees of conscience in the UAE and shed light on their cases. Their website contains important information on cases in the UAE.
Amnesty International: Amnesty International is a global organization whose mission is to undertake research and action focused on preventing and ending grave abuses of these rights. Their website provides information on their projects and how to join their organization.
Human Rights Watch: Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an organization that investigates and reports on abuses happening in all corners of the world. They work to protect the most at risk, from vulnerable minorities and civilians in wartime to refugees and children in need. They direct their advocacy toward governments, armed groups and businesses, pushing them to change or enforce their laws, policies and practices. HRW's website provides information on their projects and how to join the organization.
Rebecca Pitcairn
Rebecca studies Italian Language and Literature, Classical Civilizations, and English Writing at the University of Pittsburgh. She hopes to one day attain a PhD in Classical Archeology. She is passionate about feminism and climate justice. She enjoys reading, playing the lyre, and longboarding in her free time.