In a departure from typical travelogues, this video shows a unique picture of Senegal through glimpses into everyday rural life with a focus on the children growing up in this beautiful country. Each clip showcases the diversity in landscape, culture, and lifestyle Senegal’s people experience—all bound together by an enthusiasm for life. After watching this video, you’ll want to dance with the people on screen.
5 of the World’s Most Dangerous Hiking Trails
Everyone loves a good hike, but some trails around the globe stand out due to the intense challenges that they provide. The following five hikes should not be attempted by novice hikers.
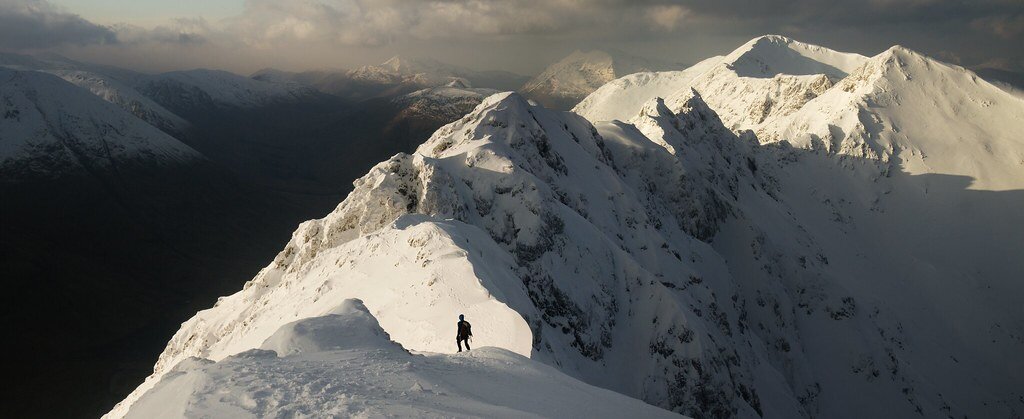
Aonach Eagach, Scotland. Andrew Marshall. CC BY-NC-SA 2.0.
Hiking can test our physical and mental limits, and is a powerful cardio workout that is proven to boost your mood. While it can be fun to test yourself and get your adrenaline flowing and blood pumping, there are some hikes around the world that can cause serious injuries if you are not careful.
These five hiking trails are not for the faint-hearted and should not be attempted by novice hikers.
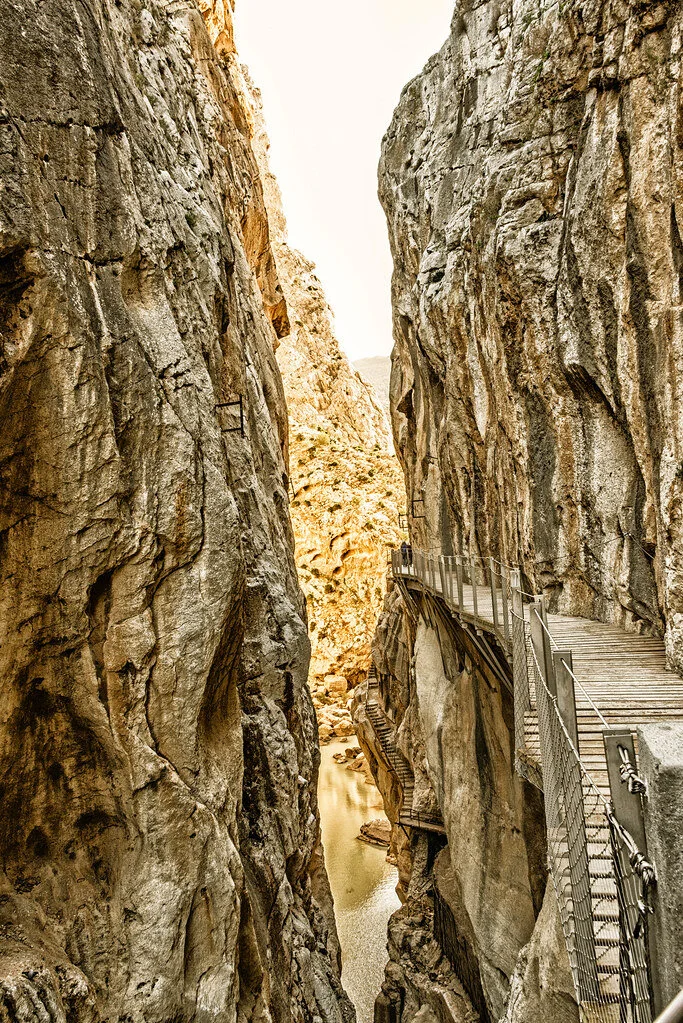
El Caminito del Rey, Spain. Arthur Harrow. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
1. El Caminito del Rey, Spain — 4.8 miles
The name of this hike translates to “The King’s Little Pathway,” and it once was one of the world’s most hazardous footpaths. This aerial path is suspended 100 meters high against the walls of a gorge,. It was originally built from 1901 to 1905 between the waterfalls of Gaitanejo and El Chorro to move materials and workers to the local hydroelectric dam. The trail is named “The King’s Little Pathway” because, in 1921, King Alfonso XIII opened it to visitors and traveled along the walkway to the Conde de Guadalhorce dam.
The Caminito del Rey route runs through cliffs, canyons and large valleys. The area is inhabited by a wide variety of plant and animal species, such as Egyptian vultures, griffon vultures, golden eagles and wild boar. The path takes about three to four hours to walk, starting in the town of Ardales and ending in Álora.
The path closed to hikers in 2001 when five people fell to their demise into the river below. Fences were since built into the renovated path and it reopened in 2015.
Cascade Saddle. Tom@Where. CC BY-NC 2.0.
2. Cascade Saddle Route, New Zealand — 29.9 miles
This trek takes almost two days, or four to five days if you choose the expert route. Built in 1939 and located in the Matukituki Valley area and Mount Aspiring National Park in the Otago region, the route travels through scenery featured in the Lord of the Rings films, so many visitors flock to this route for photo opportunities.
The Cascade Saddle route is an alpine crossing recommended for experienced trampers. It is also recommended to hike it only in good weather during the summer. The Department of Conservation advises hikers to begin from the Matukituki side of the route, since ascending is much safer than descending. There are various different routes to take from there.
However, this route can be very dangerous in some parts, where the ground is slippery and unstable—especially when it is raining. Furthermore, there is danger of avalanches from June to November. Check the New Zealand Avalanche Advisory website before you go.
Several hikers have been injured on this trek, and some have even died. If you go, be sure to have the right skills and experience to make the decisions best for you along the trek—you must also bring the proper equipment.
Aonach Eagach ridge. mr__fox. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
3. Aonach Eagach, Scotland — 6 miles
Located near Kinlochleven in the Scottish Highlands, the Aonach Eagach trail features beautiful wildflowers and mountainous scenery. However, it is also a hard, exposed scrambling ridge between Am Bodach and Stob Coire Lèith. Getting to the summit requires endurance, hard work and lots of climbing. The ridge is 3,126 feet high, making this trail one of the U.K.’s toughest ridge walks.
The trail is only recommended for very experienced hikers in good weather conditions. The rocks can get very slippery in rainy conditions, and side paths are often extremely hazardous and difficult to return from. Over the last 10 years, there have unfortunately been many deaths on the trail, the most recent being in 2017.
The trail is best done east to west, and those who push through the experience are rewarded with the view of a lifetime.
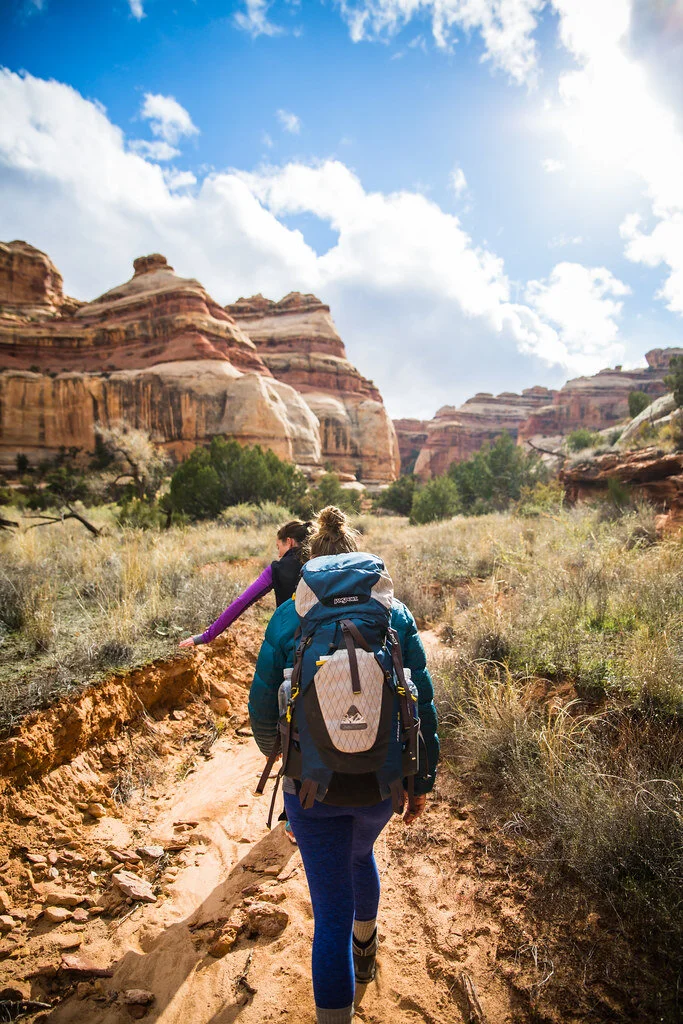
Backpacking in Utah. Zach Dischner. CC BY 2.0.
4. The Maze, Utah, USA — 2.9 miles
Although short, trails in the Maze are ancient and lead into various different canyons. Located near Gunlock, Utah, the Maze Overlook Trail requires basic climbing skills in order to navigate steep portions of rock. A 25-foot length of rope also comes in handy to raise or lower packs in difficult spots.
The Maze sees only 2,000 hikers per year since it is so remote and is the least accessible hike in the Canyonlands. The best time to go is in the spring, when temperatures are lower.
The Maze is quite literally a maze of intertwined canyons and dead-ends. The routes do not have beaten trails and they often weave up and over canyons, which are extremely difficult to traverse. Water sources in the Maze are also very limited. Part of the danger comes from how it can take rescuers up to three days to reach hikers because the path is so remote.
The highlight of this difficult and remote path is the view. Hikers will be able to see the Colorado River and Green River converge from atop a massive desert rock in a breathtaking view. Visitors can also see petroglyphs (prehistoric rock carvings) from ancient human history.
Mount Huashan. Jinjian Liang. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
5.Mount Huashan, China — 12.2 miles
Located near Huayin in the Shaanxi province of China, Mount Huashan trails are not very trafficked due to their narrow peaks and dangerous, steep paths. However, the trails feature beautiful wildflowers and scenery, as well as built-in steps and light poles.
Mount Huashan is known to be one of China’s five sacred mountains and one of the most popular pilgrimage sites for Chinese people. It is also considered by many to be the original place of Chinese civilization and is praised as the “Root of Huaxia (China).” The famous plank walk is 7,070 feet high and located on the mountain’s highest peak. There are many different trails to follow in the mountain, but the Changkong Plank Trail is the most dangerous and thrilling. The 700-year-old trail is only 12 inches wide.
The first few miles of the trail are a gradual ascent until Thousand Foot Narrow, and then the trail becomes narrow and steep toward the North Peak. There are many places to stop to experience breathtaking sunrises or sunsets and mountainous scenery. This trail is meant for only very experienced hikers.
Isabelle Durso
Isabelle is an undergraduate student at Boston University currently on campus in Boston. She is double majoring in Journalism and Film & Television, and she is interested in being a travel writer and writing human-interest stories around the world. Isabelle loves to explore and experience new cultures, and she hopes to share other people's stories through her writing. In the future, she intends to keep writing journalistic articles as well as creative screenplays.
Climate Change is Shrinking Italy’s Lake Como
Many major landmarks are now visibly facing the consequences of climate change. Because there is no water from rainfall, ice, or melted snow, water levels in Lake Como are now lower than ever recorded before.
Lake Como, Italy. Harshil Shah. CC BY-ND 2.0.
Lake Como is an extremely popular destination for travelers due to its natural beauty and stunning landscape. However, climate change is threatening its future and hurting the local economy.
The water level in Lake Como is unprecedentedly low due to lack of rainfall and melted ice or snow. There is even a gap of more than three feet between the old waterline and where the water currently sits.
Lake Como has an area of 56 square miles, which means that this low water level is due to the loss of 4.6 billion gallons of water. According to local geologists, the rapidly-shrinking Fellaria glacier is the largest contributing factor to the decreased water levels.
Climate change has greatly affected the glacier, as not much of it remains. Since the late 1800s, the Fellaria glacier has lost two-thirds of its total mass, which translates into an average of more than 20 feet per year.
The lake’s lack of water is enough to cause dangerous erosion and even rockslides. When water recedes, the base of the mountain starts to collapse because the water along the shore can no longer help the rocks stay in place.
Varenna, Lake Como, Italy. Harshil Shah. CC BY-ND 2.0.
Yet another detrimental effect of climate change is that the lack of water in the lake has begun to kill off fish. Many locals rely on fishing for their livelihoods, and they say that the fish level is already 50 percent less than it was 10 years ago.
As one of Europe’s deepest lakes at 1,345 feet deep, Lake Como is not in danger of drying up anytime soon. However, losing its most consistent water source—the Fellaria glacier—will place new pressure on those who rely on the lake. This will have widespread effects, from affecting hydropower reservoirs located upstream to irrigated farms located downstream.Roads and walls that border the lake are also at risk of fracturing or collapsing due to low water levels.
GET INVOLVED
Nonprofits like the Environmental Defense Fund are dedicated to solving environmental challenges from many different angles with the help of scientists and experts. They offer opportunities to make donations, take action, sign petitions and even ways for companies to get involved. Anything helps.
Another nonprofit is Conservation International, which works to protect the land and sea in over 70 countries. They combine fieldwork with innovations in science, policy and finance to secure the benefits that nature provides us with. Conservation International encourages people to donate, fundraise, or become a member.
RELATED CONTENT:
Isabelle Durso
Isabelle is an undergraduate student at Boston University currently on campus in Boston. She is double majoring in Journalism and Film & Television, and she is interested in being a travel writer and writing human-interest stories around the world. Isabelle loves to explore and experience new cultures, and she hopes to share other people's stories through her writing. In the future, she intends to keep writing journalistic articles as well as creative screenplays.
Yemen Experiences World's Worst Humanitarian Crisis
Yemen’s ongoing civil war has left 24 million in need of assistance and more than 100,000 dead since the conflict began in late 2014. Today, Yemen is considered the world’s worst humanitarian crisis and is on the brink of being labeled by the United Nations as the world’s worst famine in 100 years.
A hungry Yemeni child eats a food bag. USAID_IMAGES. CC BY-NC 2.0.
Hunger, malnutrition, famine, displacement and mental health issues are among some of the devastating consequences imposed upon Yemeni civilians by the country’s civil war. Although the conflict between Yemeni President Abdrabbuh Mansour Hadi’s government and the Houthi, or Ansar Allah, armed movement broke out in late 2014, Yemen was already one of the most vulnerable countries in the Middle East.
Following the Arab Spring in late 2011, previous Yemeni President Ali Abdullah Saleh was forced to turn over his power to his deputy, Abdrabbuh Mansour Hadi. Since then, the country has been enthralled in a civil war which has left millions of civilians hungry homeless, or dead. Houthi forces took over Sana’a, the capital of Yemen, in late 2014, instigating the war. By early 2015, Houthi officials declared mobilization to overthrow Hadi’s regime and, only a day later, fighting broke out in Lahij Governorate. Lahij Governorate quickly succumbed to Houthi rule and President Hadi fled the nation.
With the help of the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia created a coalition of mostly Sunni Arab states to combat Houthi forces and the rise of Iranian influence in the Middle East in 2015. Today, much of the conflict in Yemen is a proxy conflict for the power struggle between Iran and Saudi Arabia in the region.
The Arab coalition conducted countless air campaigns to drive out Houthi forces from Yemen and facilitate the return of Hadi’s government, despite the trail of destruction these air strikes leave behind. Funerals, weddings, homes, mosques, schools and hospitals have all fallen victim to these bombs. In response to an attack on Saudi Arabia’s eastern oil fields—which disrupted nearly five percent of the world’s global oil supply—Saudi Arabia spearheaded a bombing campaign. According to the Yemen Data Project, the conflict and air strikes since 2015 left around 17,000 Yemeni civilians dead or injured, as of March of 2019.
According to the United Nations, Yemen remains the world’s worst humanitarian crisis. With over 100,000 people killed and 85,000 children dead from famine, the UN warned that millions of Yemenis could face starvation in what could be “the world’s worst famine in 100 years.” Currently, 16.2 million Yemenis are food insecure while famine continues to rise; child malnutrition there is one of the highest in the world, with two million children in need of acute malnutrition assistance; and at least one child dies of malnutrition or diarrhea every 10 minutes in Yemen.
Displacement is another major consequence of the war in Yemen. With more than five million people estimated to have been forced to flee their homes, four million Yemenis remain displaced today. These displaced families live in camps of makeshift shelters, forcing them to continue moving around and making them vulnerable to severe weather conditions, air strikes and other dangers. In addition to the overwhelming number of displaced and homeless Yemenis, the nation is also home to around 300,000 refugees mostly from the Horn of Africa.
The devastating impacts of Yemen’s ongoing war does not stop at the physical realm—consequences of the violence have affected the mental health of Yemeni youth. According to Columbia Global Centers’ PGIF Project, a 25-year-old living in Yemen today “has already lived through 15 major conflicts and wars,” making depression, PTSD and other mental health disorders common in Yemen’s youth. Considering the lack of infrastructure and medical facilities already in Yemen, mental health concerns are pushed to the backburner. With roughly one psychiatrist per 500,000 people, only three mental health hospitals exist in Yemen. The lack of mental health services and resources has forced individuals who battle with mental health issues to turn to alternate methods of help, such as Quranic healing, while professional help is reserved for more extreme disorders, such as psychosis.
PTSD is one of the most common products of war, and this is evident with Yemeni children. Growing up with bombs dropping all around them, PTSD in Yemeni civilians and children is often triggered by loud noises and the sounds of planes whooshing overhead. Behavioral changes such as bedwetting, isolating oneself and emotional detachment are common consequences of PTSD in children.
Beyond death by air strike or on-the-ground fighting, many Yemenis have lost their lives to hunger and diseases because of restrictions on humanitarian assistance, imports and access to essential services. Because of this, UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres refers to Yemen’s crisis as “man-made.” Many third party nations, organizations and institutions have requested the warring countries involved to improve civilian protection, but have experienced little success. Now, many activists have taken to social media to garner support and aid for Yemen’s children, as well as raise awareness of Yemen’s situation—for being the world’s worst humanitarian crisis, Yemen is often underrepresented in the media.
GET INVOLVED
Despite the restrictions on humanitarian aid in Yemen, there are still ways to help. Save the Children is one of the largest organizations operating in Yemen and is currently aiding children suffering from malnutrition, supporting health facilities in hard-to-reach areas and leading educational programs.
The international organization, World Food Programme, aims to provide 13 million people with food assistance across Yemen. To accomplish this goal and ensure their efforts are uninterrupted in 2021, the WFP is seeking to raise $1.9 billion.
The Danish Refugee Council offers partnership opportunities to private companies, where partners will have the opportunity to help solve the global displacement crisis. The DNC is a trusted partner of the United Nations, is rated the world’s third best non-governmental organization, and is a Core Humanitarian Standards certified organization.
Mia Khatib
Mia is a rising senior at Boston University majoring in journalism and minoring in international relations. As a Palestinian-American, Mia is passionate about amplifying the voices of marginalized communities and is interested in investigative and data-driven journalism. She hopes to start out as a breaking news reporter and one day earn a position as editor of a major publication.
Meet the Activist and Intersectional Storyteller Developing Data-Driven Humanitarian Tools
Melissa Jun Rowley is a journalist, entrepreneur and activist focused on the intersection of storytelling, technology and social justice.
As the founder and CEO of Humanise, Inc., Melissa Jun Rowley is developing TheToolbox.org, a data-driven humanitarian initiative created by acclaimed musician Peter Gabriel. CATALYST had the chance to catch up with Melissa to learn more about Humanise in Detroit and Melissa’s path to social entrepreneurship.
How did your experience with TheToolbox.org inspire you to develop Humanise, Inc.?
TheToolbox.org is an online destination, founded by Peter Gabriel, that connects people to apps that can help them improve their lives and become everyday activists. I first became involved as an editorial consultant, and was developing stories while curating tools that promote social impact.
For example, there’s an app you can scan over a product’s barcode to see if human trafficking was involved in the product chain. While apps like these are interesting and useful, they’re under-utilized given their lack of commercial and entertainment value.
We came to the conclusion that the site itself is a valuable database of tools, but in order to have an impact, we need to go into the field and get people on the ground using the tools, and providing feedback about how they can be improved. That’s where Humanise comes in: It was created to function as the parent company of TheToolbox.org. The tools we curate are now one of three pillars. We’ve evolved into an organization that promotes human rights through technology, storytelling, AND collaboration with local communities.
Can you describe some of the projects that Humanise has initiated since its founding?
We decided to take Humanise to Detroit, primarily because there’s a lot of data-driven development unfolding in the city. Also, I grew up an hour outside of the D and am in love with the entrepreneurial community there. They’re so spirited. They’re the genuine article.
While money is being directed to development in certain districts, such as downtown, the neighborhoods on the outskirts are tragically deprived of funding and resources. Forty percent of the people in Detroit don’t have Internet access, and 40 percent can’t pay their water bills. It’s a first world city crawling with third world problems!
In the year 2015, there are no excuses for letting people in our own backyard suffer like this. We need to meet them where they are, not where we think they should be, and we need to collectively solve the problems from the ground up — not the top down.
So we started thinking of ways we can work with technology providers to foster digital inclusion. We’ve been working closely with community activists in the Detroit neighborhood of Morningside to understand the neighborhood’s needs and aspirations. We’ve connected them with a smart city advisory to see if the area is eligible for some pretty revolutionary technology. Some of the Detroiters we know are going to use TheToolbox.org as their own citizen journalism platform, where they can publish stories about their neighborhood and discuss the tools they find the most empowering.
If we’re able to provide connectivity for this neighborhood, we may be able to do the same thing in some of Detroit’s other hardest hits zones.
Before developing Humanise, Inc., you spent much of your career as a journalist. How did working in journalism influence your interest in social entrepreneurship?
Being a journalist is the way I became an entrepreneur, really. I worked in TV when I was younger, producing business news updates for CNN and then covering entertainment in Hollywood. The red carpet was my second home. But eventually, I started to feel like I was losing my soul. I became a journalist because I wanted to help connect people through storytelling — not perpetuate the dumbing down of the country, which is what I felt like I was doing half the time, particularly when I was asked to start quoting TMZ in stories. I knew that was the end.
I left Los Angeles, and I started focusing on nonprofits and social responsibility movements. I quickly discovered that I couldn’t make any money that way. Two years later, I began developing content for companies that have a social mission. This was when I started to view myself as more of an entrepreneur. But I’m always going to be a journalist at heart, always looking for the truth and humanity in every story.
Do you have any advice for future journalists or entrepreneurs?
These days, if you’re going to be a journalist, you have to be an entrepreneur. By that I mean, you need to think like an entrepreneur. You need to be constantly thinking of different strategies, who you can connect with, and how you can build your brand and business. It was this mindset that led me to TheToolbox.org and Peter Gabriel.
A second piece of advice is that the best way to develop an idea is to collaborate and find some common core or level of connectivity in the heart of why you’re doing what you’re doing. It’s only through that kind of commitment that you can build a business that has meaning. It’s not easy. But the people you meet along the way will change your life and expand your heart and mind in ways you’ve never dreamed of. I can promise you that.
LEARN MORE ABOUT HUMANISE, INC. HERE.
Sarah Sutphin
Sarah is an undergraduate at Yale University and a content editor for CATALYST. As a traveler who has visited 30 countries (and counting!), she feels passionate about international development through sustainable mechanisms. Sarah has taken an interest in the intersection between public health and theater, and hopes to create a program that utilizes these disciplines for community empowerment. She is a fluent Spanish speaker with plans to take residence in Latin American after graduation.
Congo Couture: “Sapeurs” Bring Europe’s Designer Fashion to Central Africa
The Republic of the Congo’s world-famous fashionistas strut through the streets of Brazzaville wearing outfits from Europe’s most revered designers. But to sapeurs, their fashion savvy is not just style but a lifestyle.
A sapeur in his Sunday best. ilja smets. CC BY-ND 2.0.
Maxime Pivot makes all the ladies scream. Men call him the pride of the town. Children follow him wherever he goes. The Republic of the Congo has never seen a more dashing, debonair, sharp-dressing gentleman. As a modern-day dandy in the streets of Brazzaville, he is a painterly splash of Congo couture amid near-universal penury. He boasts a double-breasted red suit, a pearl-white shirt, pitch-black sunglasses and a pink bowtie, an outfit to amaze the prim and plebeian alike. Rather than envy, his panache inspires pride. Some may call his focus on fashion amid staggering poverty vain, but really, he is preserving a decades-long tradition. He is a sapeur.
That means that he is a member of the Société des Ambianceurs et des Personnes Élégantes—La Sape for short. In English, it translates to the Society of Ambiance-Makers and Elegant People. Every weekend, he and his fellow dandies meet to compare outfits from the hottest European designers, trade notes on color combinations and revel in the pomp of haute couture. They smoke, they dance and they conversate. They escape the squalor in which so many Congolese live—when sapeurs dress up, they feel like the richest men in the world.
No, they are not rich. Quite the opposite. By day, sapeurs are chefs, mechanics, electricians, craftsmen, businessmen, handymen, journeymen, or any other kind of blue-collar worker. 70 percent of people in the Republic of the Congo live in poverty, and most sapeurs are included in that number. What distinguishes them is not wealth but aesthetic distinction, good taste, and a deep knowledge of the latest fashion trends. They aspire to look like a million bucks, not spend it.
The street is a catwalk. Jean-Luc Dalembert. CC BY-SA 4.0.
The tradition began during the Congo’s colonial period. Congolese servants, tired of wearing their Belgian and French colonizers’ secondhand clothes, began saving their wages and purchasing the latest clothes for European dandies. After serving in the French army during World War II, Congolese soldiers returned home bringing closets-worth of European suits, shirts, ties, shoes and accessories. By the time the central African nation gained independence in 1960, many Congolese elites were making pilgrimages to Paris to rack up designer clothes for their wardrobes back home. Although they were accused of relying on white, “Western” traditions, most sapeurs insist on their artistic independence. As Papa Wemba, one of La Sape’s earliest celebrities, said, “White people invented the clothes, but we make an art of it.”
However, investing in clothes instead of, say, property or livestock can be difficult to justify in one of the poorest parts of the world. Many sapeurs hide their expensive lifestyles from relatives to avoid endangering family ties. If a cousin learns that their family member would rather buy an Armani suit or Weston shoes than help put food on the table, they may feel betrayed and break off relations. Furthermore, the wives of sapeurs tend to bear the brunt of the sapeur lifestyle far more heavily than their husbands, as they suffer the financial cost without being able to revel in high fashion.
European style, African art. Opencooper. CC BY-SA 4.0.
La Sape is overwhelmingly male. Overwhelmingly, but not entirely. As the tradition evolves, more women are staking their claim as sapeuses. They, too, don designer suits from Versace, Dior and Yves Saint Laurent and develop mannerisms and gaits to build a persona around their clothes. Even children are beginning to partake in the sapeur culture. Many worry that Congolese tailors lack apprentices to carry on the tradition, so the sight of a child strutting down the streets of Brazzaville in an Armani suit assures them that the legacy of La Sape will continue.
In fact, Maxime Pivot established an organization, Sapeurs in Danger, to preserve the tradition of La Sape, which he asserts is not just about fashion but also is a way of life. When committing to the lifestyle, sapeurs adopt a code of conduct which Ben Mouchaka, another famous sapeur, summed up in 2000. He calls it the Ten Commandments of Sapeology.
1- Thou shalt practise La Sape on Earth with humans and in heaven with God thy creator.
2- Thou shalt bring to heel ngayas (non-connoisseurs), nbéndés (the ignorant), and tindongos (badmouthers) on land, under the earth, at sea and in the skies.
3- Thou shalt honour Sapeology wherever thou goest.
4- The ways of Sapeology are impenetrable for any Sapeologist who does not know the rule of 3: a trilogy of finished and unfinished colours.
5- Thou shalt not give in.
6- Thou shalt demonstrate stringent standards of hygiene in thy body and clothes.
7- Thou shalt not be tribalistic, nationalist, racist or discriminatory.
8- Thou shalt not be violent or insolent.
9- Thou shalt abide by the Sapelogists’ rules of civility and respect thy elders.
10- Through prayer and these 10 commandments, thou, as a Sapeologist, shall conquer the Sapeophobes.
Maxime Pivot aims to pass down the tradition of La Sape to any man, woman, or child willing to devote themselves to the lifestyle. He operates a school of La Sape where he teaches aspiring sapeurs how to combine colors tastefully and craft a swaggering gait. His classes teach that La Sape needn’t sap their wallets. As the sapeur life and style spread, he hopes that dandies will don local brands, not just expensive European ones.
Innovating a classic style. Makangarajustin. CC BY-SA 4.0.
Then, La Sape could be truly independent from European designers. Fashion trends have been increasingly moving in that direction, thanks to Maxime Pivot’s efforts, especially now that La Sape has moved into the mainstream. Every August 15, the Republic of the Congo’s independence day, sapeurs march alongside the military, indigenous tribes and even the President in the largest parade of the year. Their flashy clothes and sauntering stride draw cheers from the crowd. Their tradition provides an example of how the country can emerge from an oppressive European past and spring into a liberated African future.
Michael McCarthy
Michael is an undergraduate student at Haverford College, dodging the pandemic by taking a gap year. He writes in a variety of genres, and his time in high school debate renders political writing an inevitable fascination. Writing at Catalyst and the Bi-Co News, a student-run newspaper, provides an outlet for this passion. In the future, he intends to keep writing in mediums both informative and creative.
Despite Economic Crisis, Lebanon's Landscape Stands Strong
Lebanon is in one of the world’s worst economic depressions since 1850; however, the nation continues to stand strong with its beautiful landscapes and soulful culture.
Lebanon—former French colony and home to the “Paris of the Middle East,” Beirut—has stood strong between nations riddled with tragedy. With Syria on its Northern and Eastern borders, Israel and Palestine on its Southern border and the Mediterranean Sea to the West, Lebanon was frequently extending a helping hand to its war-torn neighbors. However, in recent years, Lebanon has plunged into a deep economic depression and is riddled with tragedy itself.
With 18 state-recognized religions in Lebanon, it is the most religiously diverse country in the Middle East. However, because religious leaders and political leaders are not mutually exclusive in the sectarian society, this diversity has led to public animosity toward the corrupt government. Although tensions have been brewing for years, the former government’s WhatsApp tax in late 2019 was the tipping point for Lebanese nationals and residents. Protests provoked by the tax broke out across the country and world, calling for a reformed Lebanese government.
Ambushed by the coronavirus a few months later, the Lebanese people experienced immense tragedy in 2020 when one of the world's largest non-nuclear explosions shook the Port of Beirut, leaving more than 200 dead and thousands injured. Lebanon is still haunted by the blast and is struggling to rebuild its destroyed neighborhoods amid COVID-19 and, according to the World Bank, one of the world’s worst financial crises in more than 150 years. To top it off, Lebanon has yet to create a new government since the government of Prime Minister Hassan Diab resigned due to public pressure following the explosion.
Currently, the U.S. State Department advises against traveling to Lebanon due to the large presence of COVID-19 in the nation, the threats of violence and the U.S. Embassy in Beirut’s limited ability to support U.S. citizens. Despite these warnings and Lebanon’s current crises, the people still hold their flag up high and are proud of the beautiful scenes and experiences their country has to offer.
Mountains, beaches, city lights—not only are all these scenic views found in Lebanon, but they are all less than an hour-long drive from one another. Lebanon’s landscape is especially unique because of the country’s small size. Residents and tourists alike can enjoy in a single day these three entirely different scenes and the activities associated with each of them.
There are two main mountain regions in Lebanon—Mount Lebanon and the Anti-Lebanon Mountains. Mount Lebanon extends across the entire country, while the Anti-Lebanon Mountains form the border between Lebanon and Syria, seeping more into Syrian territory. Snow-peaked year-round, Faraya, a village in the Keserwan District of the Mount Lebanon Governate, is one of the best ski spots in the country. Faraya, positioned at an elevation of 3,900 feet to 7,000 feet, is around 25 miles northeast from Beirut and around 23 miles southeast from Byblos, one of the oldest cities in Lebanon which sits on the Mediterranean coast.
“Miracle Monk of Lebanon,” Saint Charbel. DerekL. CC BY-NC-SA 2.0.
Populated primarily by Maronite Christians, Faraya holds the largest statue and church of Saint Charbel in the world, standing 75 feet tall and around 30 feet wide. It is said that St. Charbel resided in this former monastery for over 20 years and those who visit and ask for assistance hear back. Since 1950, the “miraculous healings” of St. Charbel have been tallied and, as of mid-2019, the number lies above 29,000. Miracles were verified by priest witnesses before 1950; however, since 1950 and the advancement of medical technology, all “miracles” require medical proof for verification.
With Mount Lebanon paralleling the Mediterranean sea, the mountains are never too far away from the beaches. Along Lebanon’s coast lies hundreds of public and private beaches. One of the most famous public beaches in Lebanon is Joining Beach in the coastal city Batroun. With water so clear and blue it looks like it was dyed, Joining Beach is the perfect place to explore marine life. Underwater activities like snorkeling and scuba diving are common at this Lebanese shore.
Jeita Grotto. kcakduman. CC BY-NC 2.0.
Beyond swimming and sunbathing at the beach, Lebanon’s coastal towns show off wonders of nature. In Jeita Grotto, located 11 miles from the capital city in Jeita, exists a system of two interconnected caves that are around five and a half miles long. The upper galleries of Jeita Grotto is home to the world’s largest known stalactite—a mineral formation that hangs from the ceilings of caves—and was one of the top 14 finalists for the New 7 Wonders of Nature competition in 2011.
Beirut, Lebanon. marviikad. CC BY-SA 2.0.
Beirut, the heart of Lebanon, has its own natural wonders to show for as a big city in all its glory and flashing lights. Populated with restaurants, clubs and bars, Beirut’s nightlife is like none other in the Middle East. Alive all night, Lebanon’s pride and joy offers an experiential party scene. With clubs like Sunrise Beirut, partygoers start their outing as early as 10:30 p.m. and dance to techno until the sun lights up the sky. Mar Mikhael, named after the Maronite Catholic Church of Saint Michael, is a neighborhood in Beirut that is known for its aesthetic dining options—restaurants, cafes and bars are all fashionable outings in Mar Mikhael, the art hub of Beirut. Stationed on the marina, Zaitunay Bay is another classy area to shop, eat and be mesmerized by Beirut’s soulful city lights.
It’s true, Lebanon is still in crisis; however, the soul of the country lies within its people and landscape—both of which are beautiful, strong and resilient.
RELATED CONTENT:
PODCAST: Social Entrepreneurship in Lebanon
Mia Khatib
Mia is a rising senior at Boston University majoring in journalism and minoring in international relations. As a Palestinian-American, Mia is passionate about amplifying the voices of marginalized communities and is interested in investigative and data-driven journalism. She hopes to start out as a breaking news reporter and one day earn a position as editor of a major publication.
Cubans Protest Government’s Response to Economic Crisis
Political turmoil, severe economic struggles and lack of freedom have pushed Cubans to take a stand against their government.
People walking the streets of Havana, Cuba. Tiago Claro. Unsplash.
Thousands of Cubans marched the streets of Havana on Sunday, July 11 in protest against the poor economic conditions and governmental response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Among other hardships, many demonstrators have faced long-term hunger and medicine shortages due to the Cuban government's lack of action to address the struggles of its people. These protests have led to the damaging of police equipment, the detainment of a journalist and the death of a civilian.
Besides having a mere 15 percent vaccination rate, due to shortages, pharmacies and hospitals lack even the most basic medicines such as penicillin and aspirin. According to Cuban healthcare authorities, on Sunday there were almost 7,000 new reported COVID-19 cases, with a total of nearly 240,000 COVID-19 patients across the country. Many Cubans have also reported having to wait hours in line to purchase food, if they even have access to food to begin with.
These cruel living conditions have pushed many Cubans to a breaking point—in fact, these protests mark the first large-scale acts of defiance that Cuba has seen since the fall of the Soviet Union in the 1990s. The main difference since then is the easy accessibility of the internet, which has been used to spread the word about the protests and inspire a larger turnout. In an attempt to silence protesters on social media, internet access across Cuba was cut off for roughly 30 minutes amidst protests on July 11, with shutdowns intermittently continuing. This makes the stories from activists who were arrested or beaten by police difficult to corroborate due to lack of evidence.
Despite suppression efforts, protesters have managed to maintain a far reach, with Cuban communities such as Little Havana in Miami gathering in solidarity with Cubans. The Cuban protest movement has also garnered international support on social media with the hashtag #SOSCuba, and many celebrities have gotten involved to raise awareness about the protests.
In response to the unrest, the Cuban government has directed the blame toward the American trade embargo, which they believe is responsible for the nationwide shortages. While some activists agree with this point, others have argued that the issue goes far beyond the American embargo, and that it is more due to governmental financial mismanagement and a lack of tourism revenue.
Zara Irshad
Zara is a third year Communication student at the University of California, San Diego. Her passion for journalism comes from her love of storytelling and desire to learn about others. In addition to writing at CATALYST, she is an Opinion Writer for the UCSD Guardian, which allows her to incorporate various perspectives into her work.
The Shamanistic Significance of the Mother Tree in Shaamar, Mongolia
This spiritual landmark represents the intersection between Buddhism and Shamanism within Mongolia.
Sunrise over a cluster of Yurts in Mongolia. Vince Gx. Unsplash.
The Mother Tree is a spiritual landmark located in Shaamar, Mongolia that holds deep significance to those who practice Shamanism. Also known as the Eej Mod, the tree is believed to act as a gateway between the human and spiritual worlds. Many make the trek to the tree in hopes of having their prayers answered.
Shamanism is a religious practice that is centered around a shaman, an individual believed to communicate with the souls of the dead and heal others. A large part of shamanistic practices revolve around one’s profound connection to the abstract and spiritual. Thus, the Mother Tree serves as a means to channel and amplify that energy.
While Buddhism is the most commonly practiced religion in Mongolia today, Shamanism is one of the oldest, and still holds deep cultural significance in modern times. Many of those who practice Shamanism believe that the Mother Tree became a gateway to the spiritual world after being struck by lightning. It is believed that the Mother Tree marks the intersection between modern Buddhism and traditional Shamanism, like many monuments and sites in Mongolia tend to do. Rather than ignore the past, Mongolian traditions preserve it.
Trees have a profound significance in the Shamanism tradition—Sacred Trees were often placed in the center of a Shaman’s house to allow their spirits to be freed from the body. This was believed to send a Shaman into a deep trance that would let them ascend in spirit flight, or spiritual ecstasy.
The original Mother Tree was surrounded by a yurt, and it was very common for visitors to leave incense sticks near the site. However, in 2015, one visitor lit an incense stick too close to the tree, causing it to catch fire. Only a stump of the original tree was salvaged. Today, this stump is still visited by many and covered in ceremonial blue scarves to signify honor and respect and is soaked with milk and vodka
Finding the Mother Tree is no easy feat; it is located off of a main road in Shaamar with nothing but a small sign that reads “Eej Mod” to guide visitors. The Tree is located a few kilometers along tracks which split from the main road, but most visitors end up traveling with locals to ensure that they find it. Every year, visitors from as far as Japan, Korea and China make the trek to the Mother Tree to experience its spiritual powers and have their prayers answered.
Zara Irshad
Zara is a third year Communication student at the University of California, San Diego. Her passion for journalism comes from her love of storytelling and desire to learn about others. In addition to writing at CATALYST, she is an Opinion Writer for the UCSD Guardian, which allows her to incorporate various perspectives into her work.
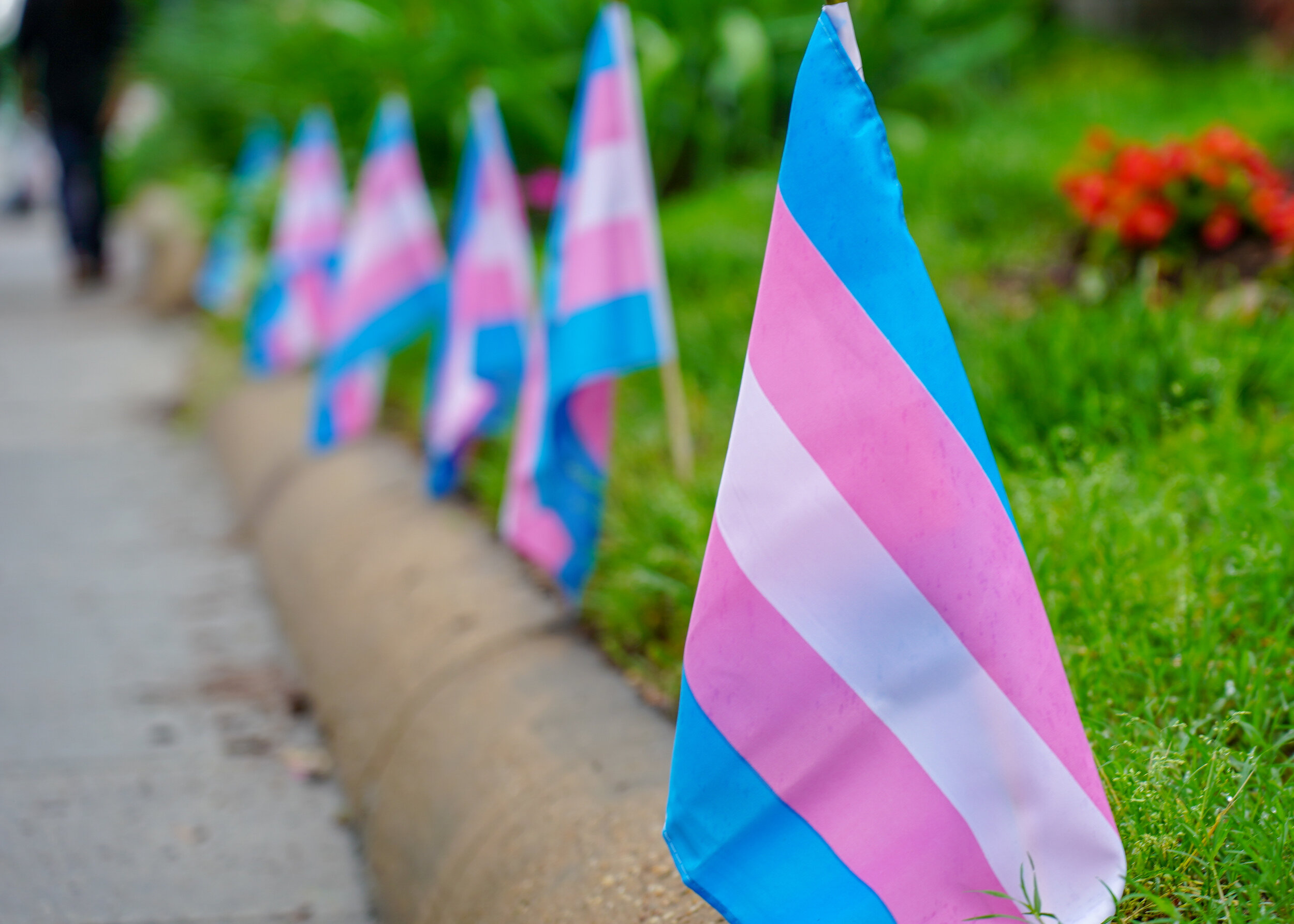
International Human Rights Court Rules in Favor of Trans Rights
The Inter-American Court of Human Rights ruled that the government of Honduras was responsible for the 2009 murder of a transgender woman. Today, Honduras is one of the largest contributors to anti-trans violence in Latin America.
Transgender pride flags. Ted Eytan. CC BY-SA 2.0
On June 26, the Costa Rica-based Inter-American Court of Human Rights delivered a landmark ruling in a transgender rights case. The court held that the government of Honduras was responsible for the 2009 murder of trans woman and trans rights activist Vicky Hernández, stating that the government had violated Hernández’s rights to life and fair trial.
Hernández was 26 years old when she was killed by a single gunshot to the head. No one was ever charged for the crime.
The Court’s ruling stated that Honduran authorities did not sufficiently investigate Hernández’s death. Her murder was dismissed quickly as a “crime of passion,” and police failed to interview anyone from the scene or examine the bullet casing. It is unclear whether a postmortem examination was performed.
Lawyers acting on behalf of Cattrachas, the LGBTQ+ rights organization that brought forward the case, argued that this incomplete investigation was a result of Hernández’s gender identity. Robert F. Kennedy Human Rights reports that during the investigation, authorities continuously identified Hernández as male and referred to her on documents and records by her birth name, which she did not use. In 2009, shortly before Hernández’s killing, Human Rights Watch published a report which found that police in Honduras routinely failed to investigate reports filed by trans people. The report also detailed the harassment and beatings that trans people had endured at the hands of the police.
Hernández’s murder occurred on June 28, 2009, the first night of a military coup against then-President Manuel Zelaya. Zelaya was taken into custody, and the military imposed a 48-hour curfew, leaving the streets closed to everyone but military and police forces. Hernández was a sex worker, and was still on the street after curfew arrived, along with two other trans women. The three women saw a police car approaching and scattered, fearing violence. The next morning, Hernández’s body was found in the street.
Due to the circumstances surrounding her death, lawyers for Hernández’s case posited that she was the victim of an extrajudicial killing, meaning that state agents were responsible for her death. Robert F. Kennedy Human Rights points to the execution-style way in which Hernández was shot and the fact that the streets were closed to everyone but police and military forces, as well as the lack of effort put into the criminal investigation.
In its ruling, the Court found evidence that state agents had participated in Hernández’s death.
Hernández’s murder was the first in a wave of anti-trans violence that followed the 2009 coup. Cattrachas documented 20 deaths of LGBTQ+ people in the 15 years before the coup, and 31 deaths in the eight months directly afterward. 15 of these 31 people were trans women, like Hernández.
Today, Latin America is still a deadly area for LGBTQ+ people. Research released in 2019 showed that four LGBTQ+ people are murdered every day in Latin America and the Caribbean, with Honduras, Columbia and Mexico accounting for nearly 90 percent of these deaths. In 2020, Human Rights Watch published a follow-up to their 2009 report, which found that LGBTQ+ Hondurans still face rampant discrimination and violence from police and other authorities, as well as from non-state actors.
Twelve years after Hernández’s murder, Honduras is finally being held accountable for its anti-LGBTQ+ violence and being made to implement reforms. Activists hope that the ruling will encourage other Latin American countries to address their own issues with violence against the LGBTQ+ community.
The Court’s ruling included orders for the Honduran government to pay reparations to Hernández’s family, restart its investigation into her murder and publicly acknowledge its own role in the event, train security forces on cases involving LGBTQ+ violence, and keep a better record of cases motivated by anti-LGBTQ+ sentiment. The Court also ordered the Honduran government to allow people to change their gender identity in documents and public records, which is a major step forward. The next step is ensuring that Honduras’ new LGBTQ+ legislation is actually enforced.
Rachel Lynch
Rachel is a student at Sarah Lawrence College in Bronxville, NY currently taking a semester off. She plans to study Writing and Child Development. Rachel loves to travel and is inspired by the places she’s been and everywhere she wants to go. She hopes to educate people on social justice issues and the history and culture of travel destinations through her writing.
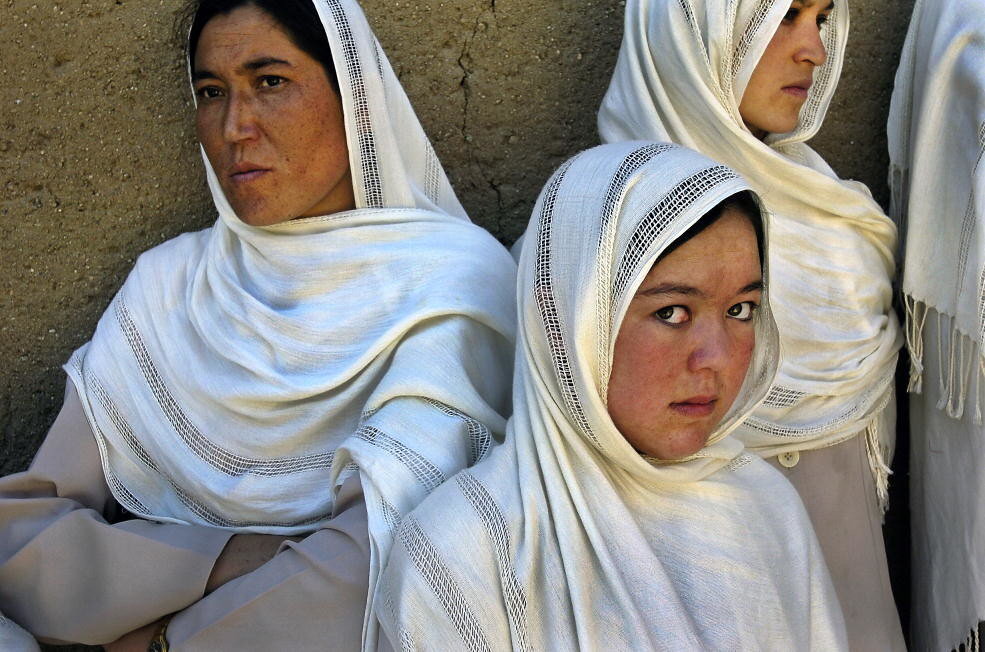
Future of Afghan Women in Limbo after U.S. Troops Leave
After U.S. troops recently left the largest American base in Afghanistan, Bagram Air Base, the future of Afghanistan remains unknown. In particular, the lives of Afghan women are now at stake due to the gender inequality that still exists in the country.
Midwifery students in Afghanistan. United Nations Photo. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Due to the Taliban’s strict rules restricting women’s rights, gender inequality remains a threatening reality in Afghanistan. Countries retreating from Afghanistan—the U.S. included—are leaving behind a dark future for Afghan women and girls, who face serious crises of health, education and violence. The U.S. left Bagram Air Base, its largest base in Afghanistan, on July 1.
Afghanistan has a history of violence within the country after foreign forces have retreated their troops. For example, when the Soviets withdrew from Afghanistan in 1988, the U.S. looked away, and Afghanistan erupted in a factional war that killed thousands. During this conflict, Afghan women were raped by fighting forces.
Photos of Afghan women cowering under the whips of Taliban members haunt history, and they were the cause of feminist sympathies that emerged across the U.S. Those activists hoped that American involvement in the area would bring relief to a tortured country.
Since the Taliban were ousted in 2001, Afghan women have not wasted one minute in fighting for their rights. Today, many women serve in important governmental roles, like as parliament members and ambassadors. Many women are also musicians, artists, entrepreneurs, or inventors. In fact, during the pandemic, the Afghan girls robotics team created low-cost ventilators to treat COVID-19 patients.
Women on the job in Afghanistan. United Nations Photo. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
In more good news, infant mortality has decreased and life expectancy has increased. Foreign involvement has had a big hand in accomplishing this. However, now that international troops are withdrawing, aid has been shrinking and pledges to help Afghanistan are less frequent.
Along with the U.S., several other embassies have also withdrawn their troops from Afghanistan, including Australia.
In an interview with Human Rights Watch, Afghan women said that they now face obstacles in accessing care due to costs, insecurity, and scarcity of providers. Furthermore, as countries withdraw from Afghanistan, the unknown future of the country could mean further violence that would produce even more problems for women and families.
GET INVOLVED
To help the fight for women’s rights in Afghanistan, consider working, interning, or volunteering with Women for Afghan Women WAW. WAW was founded to advocate for women then living under the brutal rule of the Taliban in Afghanistan. Now, it is the largest organization for Afghan women and girls globally and the largest women’s organization in Afghanistan. Afghan Women’s Educational Center also focuses on Afghan women’s rights—they are a non-profit women-led national organization that reduces vulnerability among marginalized communities with a special focus on women and children. They offer various jobs and projects to get involved with.
Isabelle Durso
Isabelle is an undergraduate student at Boston University currently on campus in Boston. She is double majoring in Journalism and Film & Television, and she is interested in being a travel writer and writing human-interest stories around the world. Isabelle loves to explore and experience new cultures, and she hopes to share other people's stories through her writing. In the future, she intends to keep writing journalistic articles as well as creative screenplays.
VIDEO: The World’s Longest Railway
Two continents, seven time zones, 9,288 kilometers. These are all features of the Trans-Siberian railway’s journey, which takes commuters from Moscow to Vladivostok, highlighting the diverse landscape and natural beauty of Asia. In this video, travelers spend 16 days on the railway, covering about 5,000 miles from Beijing to Moscow. Their route, deviating from the standard line, takes them — and viewers — through the Gobi Desert, along Lake Baikal, and into cities such as Kazan and Ulaanbaatar. This video highlights not only the underappreciated features of central Asia, but provides a sneak peak into the future of trans-continental travel.
Beyond Ice Cream, 7 Frozen Treats From Around the Globe
Ice cream is an ancient dessert, dating back to the second century B.C.. Since that time, countries around the world have developed their own versions of ice cream, from Indian kulfi to Ecuadorian Helado de paila.
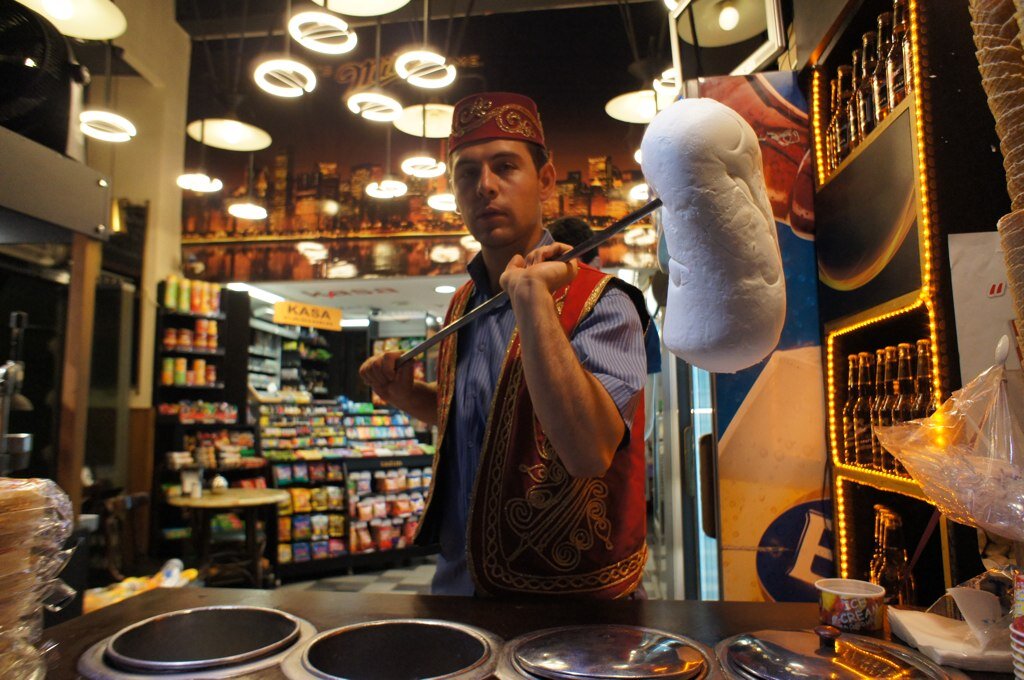
Turkish dondurma is often served on a plate. tuhfe. CC BY 2.0
Ice cream is one of the most popular desserts in the United States. 6.4 billion pounds of ice cream were produced in the US in 2019 alone., The International Dairy Foods Association reports that, on average, each American consumes over 22 pounds of ice cream and other frozen desserts annually. But ice cream is not an American invention. The frozen dessert dates back to the second century B.C., when records show that leaders like Alexander the Great enjoyed ice and snow flavored with honey or nectar as a delicacy. Ice cream as we know it today likely derives from a recipe collected from the Far East by Italian explorer Marco Polo in the 16th century.
The ancient confection made from snow or ice flavored with honey, nectar, or fruit is present in historical records from around the world. While in England and America this treat evolved into the milk and cream based ice cream which we know today, other countries developed different versions of frozen desserts. Here are 7 frozen treats from around the globe, all impacted by the cultures that created them.
1. Dondurma, Turkey
Dondurma—the Turkish word for “freezing,” and sometimes referred to as Turkish ice cream—is often eaten with a knife and fork. Dondurma differs from American ice cream in several ways, the most obvious being the texture. While American ice cream is soft and creamy, dondurma is stretchy, chewy and does not melt easily, hence why it is most often served on a plate with a knife and fork. Dondurma is made from a milk and sugar base and added Arab gum, or mastic, a resin that gives the ice cream its chewiness. In addition to mastic, dondurma is thickened with salep, a flour made from the root of a purple orchid which grows in the mountains. The creation of dondurma is credited to the town of Kahramanmaraş, located at the foot of the Ahir Mountain in southern Turkey. The town has been producing dondurma for over 150 years, but the origins of the treat date back even further. Over 300 years ago, the people of the area mixed clean snow from the mountain with molasses and fruit extracts, creating an early form of ice cream. Today, dondurma is frequently served sprinkled with pistachios and can be found at restaurants as well as street vendors, where it is served in cones.
Colorful mochi ice cream. jpellgen (@1179_jp). CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
2. Mochi Ice Cream, Japan
Traditionally a dessert sold and eaten during the Japanese New Year, mochi has recently soared in popularity, especially in the United States. The term mochi refers to a unique Japanese delicacy dating back to 794 A.D., which is made from sticky rice dough. In Japan, mochi is most often enjoyed in small, round balls filled with red bean paste—a treat known as daifuku. In ancient times, mochi was made to be presented as an offering to the gods at temples and was also served to the Emperor and other nobility. Although mochi itself has been around for centuries, mochi ice cream was not developed until the 1980s. And, despite its Japanese roots, mochi ice cream is actually an American invention. It was created by Frances Hashimoto and her husband, Joel Friedman, who ran a Japanese-American bakery in Los Angeles during the 1980s. During a trip to Japan, the couple was inspired by the traditional daifuku to create their own mochi treat using ice cream. Today, mochi ice cream is sold at almost all major grocery stores and is available in a wide variety of flavors, like green tea, chocolate, mango and red bean.
Chocolate, Kesar, and Mango flavored kulfi. richardclyborne. CC BY 2.0
3. Kulfi, India
While often categorized as an Indian ice cream dish, kulfi is denser and creamier than ice cream, more closely resembling frozen custard. Kulfi is made from boiling milk until it solidifies, which is called khoa. Sugar is then added to the milk and the mixture is flavored as desired, typically using natural flavoring ingredients. Popular kulfi flavors include saffron, pistachio, mango, avocado and cardamom. After the kulfi mixture is flavored, it is poured into molds and frozen until the treat has set. Kulfi is thought to have originated in northern India during the 16th century Mughal Empire. Traditional desserts in that area already included condensed milk, and the Mughals added pistachios and saffron for flavoring and then froze the mixture in metal cones using a combination of ice and salt, giving rise to the kulfi dessert served today. Kulfi is popular not only in India but in Bangladesh, Myanmar, Pakistan and the Middle East as well. The dish can also be found in many Indian restaurants around the world.
Different flavors of Italian gelato. arsheffield. CC BY-NC 2.0
4. Gelato, Italy
Gelato is an Italian delicacy which differs from traditional American ice cream in its silky, creamy texture, as well as being denser. Gelato and American ice cream both contain milk and cream, but authentic gelato uses more milk than cream and does not usually contain egg yolks, which are a common ingredient in many ice creams. Gelato typically contains less butterfat as well, which makes the flavors more intense. It is also served at a temperature 10-15 degrees warmer than ice cream, so it melts more easily in one’s mouth. Modern gelato dates back to the Renaissance when Cosimo Rugierri, an alchemist, created a dessert from fruit, sugar and ice that delighted the powerful Medici family in Florence. Other accounts of modern gelato credit architect Bernardo Buontalenti, who is said to have prepared an ice cream dish from milk, egg yolks, wine, fruit and honey and served it to King Charles V of Spain. Whatever its origins, gelato quickly spread out of Italy, becoming a delicacy in other countries as well. Until 1686, however, gelato was mainly served in private residences of the wealthy, as ice and salt were expensive. Then, Italian Francesco Procopio Cutò opened a cafe in Paris where he sold gelato to the public. Since then, gelato has become a wildly popular treat that can be found on nearly every street in Italy and in restaurants and shops around the world.
5. Helado de paila, Ecuador
Helado de paila, literally “ice cream from a pot,” is a sorbet-like treat from Ibarra, Ecuador. The story goes that, 122 years ago in Ibarra, a teenage girl named Rosalía Suárez had nothing to give her friend as a 15th birthday gift. So, she decided to make her a dessert. Rosalía and a friend put natural fruit juice in a container and placed it on a wooden tray, where the container was surrounded by ice and straw to preserve it. They began to spin the container and beat the fruit juice, which turned into a form of ice cream. Rosalía perfected her recipe by adding sugar to the fruit juice and salt to the ice and began to sell her ice creams. Today, helados de paila are prepared in a way very similar to the technique that Rosalía Suárez first used. A blend of fruit and sugar is poured into a wooden bowl sitting in a larger bowl, or paila, which is already prepared with a layer of straw and a layer of ice and salt. The fruit mixture is stirred and eventually cools into the creamy helado de paila. Popular flavors include strawberry, blackberry, coconut, tree tomato and passionfruit.
Spaghettieis is made to look like a bowl of spaghetti. Joshua Shapiro. CC BY-NC-SA 2.0
6. Spaghettieis, Germany
This popular German sundae is made from vanilla gelato, strawberry sauce and white chocolate shavings. The dish sounds innocuous enough, but what makes this treat unique is its presentation: the sundae is made to look just like a bowl of spaghetti. Spaghettieis was invented in 1969 by Dario Fontanella, whose father had moved from Northern Italy to Mannheim, Germany, in the 1930s. In an attempt to honor his Italian roots at the German ice cream parlor his family owned, Fontanella decided to create a bowl of spaghetti entirely from ice cream. Spaghettieis is made by putting vanilla gelato through a chilled spaetzle press (a machine to make German egg noodles) to achieve the spaghetti-noodle shape. The gelato is then topped with strawberry sauce to mimic tomato sauce, and shaved white chocolate curls to mimic parmesan. Apparently, when spaghettieis first began being served at ice cream parlors, it made children cry in disappointment that they were being served pasta rather than a dessert. Despite its tearful start, the dessert is widely popular today. Fontanella never patented his creation, so a variation of spaghettieis is served at nearly every ice cream parlor in Germany.
7. Akutaq, Alaska
Named after the Inupiaq word for “to stir,” Akutaq is an Indigenous Alaskan treat made by mixing fat, oil, berries and sometimes water or fresh snow together into a sweet dessert with a whipped texture. While berry-based akutaq is more similar to an American sorbet, there are also meat-based akutaqs in which the fat and oil are mixed with ground caribou or dried fish to create a more salty, gamey and savory dish. Traditionally in indigenous communities, the dish was made by women after the first catch of a polar bear or seal, and shared with members of the community. Akutaq varies by region depending on what types of flora and fauna are available to add. Indigenous people near the Alaskan coast used saltwater fish, while those inland used freshwater fish, and those in the north used bigger game like caribou, bear and musk-ox. Indigenous Alaskans have been making akutaq for thousands of years. Up until the 20th century, indigenous Alaskans held akutaq cooking contests during annual trade fairs, where members of various communities would compete to create new flavors. While akutaq can still be found today, in modern recipes the traditional caribou fat and seal oil are often replaced with Crisco and olive oil.
Rachel Lynch
Rachel is a student at Sarah Lawrence College in Bronxville, NY currently taking a semester off. She plans to study Writing and Child Development. Rachel loves to travel and is inspired by the places she’s been and everywhere she wants to go. She hopes to educate people on social justice issues and the history and culture of travel destinations through her writing.
Study Predicts African Great Apes Will Lose 94% of Their Territory
A new study about the effects of climate change, land use and human population growth on African great apes found that they may lose up to 94% of their habitat by 2050.
A mountain gorilla in Uganda. Rod Waddington. CC BY-SA 2.0
Great apes are humanity’s closest relatives. They are also a highly endangered group of animals, and experts believe that this status will likely worsen in the coming years. A new study published in the journal Diversity and Distributions predicts that the combined pressures of climate change, human land use and human population growth will lead to immense territory losses for African great apes in the next 30 years.
There are four types of great apes: gorillas, bonobos, orangutans, and chimpanzees. Africa is home to a number of species of great apes, including Cross River and Eastern and Western gorillas, as well as bonobos and chimpanzees. The situation for these species is already critical. All are listed as either endangered or critically endangered on the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources Red List of Threatened Species, a comprehensive list detailing the conservation status of animals around the world. And, as wild areas are destroyed for timber, minerals and food; the human population expands; and climate change alters the land where great apes can comfortably live, experts warn that African great apes could lose a devastating portion of their range by 2050.
The study was conducted by nearly 60 scientists from different research institutions, universities and conservation organizations. The scientists used data about African great ape populations from the IUCN database and then modelled the future effects of climate change, land use and human population growth. Using this data, the scientists analysed a best case scenario, where action is taken to protect the environment , and a worst case scenario where nothing is done. There is little difference in the two outcomes. Both result in massive range loss for African great apes, with 85% range loss by 2050 in the “best case” scenario and 94% by 2050 in the “worst case”.
Half of this lost range will be territory inside national parks and other protected areas, the study predicts. Although these areas are safe from human land use, they will still be affected by climate change, which will make the habitat unsuitable for great apes. Most great ape species prefer to live in lowland habitats, but climate change will make them hotter and drier. In areas where there is no higher lands, apes will be left with nowhere to live. In areas where there are uplands, however, experts suggest that great apes will attempt to migrate upward, following the climate and vegetation they prefer.
Yet, even apes that have the ability to migrate as their range decreases may not have enough time to do so. Apes reproduce slowly, have a low population density and require a very specific diet. All of these factors mean that apes are generally not efficient migrators compared to other species; to fully acclimate to a new habitat would take great ape species longer than the 30 years the study predicts they have left.
The authors of the study urge that their findings be used to guide conservation efforts for African great apes in order to prevent irreversible population losses. Their findings suggest that the range loss can be mitigated through specific conservation efforts that focus on new and existing protected areas, as well as connecting habitats that are predicted to still be suitable for great apes in the future.
Rachel Lynch
Rachel is a student at Sarah Lawrence College in Bronxville, NY currently taking a semester off. She plans to study Writing and Child Development. Rachel loves to travel and is inspired by the places she’s been and everywhere she wants to go. She hopes to educate people on social justice issues and the history and culture of travel destinations through her writing.
Amid Pandemic, Japan Faces an Epidemic of Loneliness
Japan has a Minister of Loneliness to address skyrocketing rates of suicide and isolation, some stemming from COVID-19 among other reasons. The elderly and hikikomori, modern day hermits, seem most affected.
Read MoreA Glimpse into Oaxaca City’s Guelaguetza Festival
The annual Guelaguetza festival is one of the largest Indigenous celebrations in Mexico, preserving Oaxaca culture and tradition.
Read MoreGlobal Warming Blankets Turkey’s Waters in “Sea Snot”
Turkey’s Sea of Marmara is covered in a thick blanket of mucus that is suffocating marine life. Global warming is likely the reason.
An aerial view of phytoplankton blooming in the Sea of Marmara in 2015. Right now, the sea is covered with a layer of “sea snot” that is harming marine life. NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. CC BY 2.0
Turkey’s Sea of Marmara is covered in a thick layer of a beige, viscous substance known as “sea snot” that is clogging fishing nets, killing corals and disrupting the breeding grounds of fish.
Sea snot—officially known as marine mucilage—comes from phytoplankton, with high levels occurring as a result of prolonged warm temperatures, calm weather and abundant nutrients in the water. An abundance of nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus lead to a boom in the phytoplankton population. In normal amounts, phytoplankton are an important part of the ocean’s ecosystem; they are microscopic organisms that exude oxygen. During a population boom, however, phytoplankton can become harmful; under conditions of stress they expel mucus that can accumulate on the surface, creating sea snot that can grow to cover many square miles of ocean.
Typically, sea snot on its own is not harmful. In fact, research shows that some deep-sea organisms depend on sea snot to stay alive. It only becomes dangerous when sea snot of large amounts begins to host E. coli and other bacteria and viruses, or forms a layer that covers the surface of the ocean, as in Turkey.
When the sea snot is thick enough to cover the water’s surface, it can act as a blanket, suffocating the marine life below. Immobile organisms like corals are especially vulnerable to damage from sea snot because it can wrap around them, cutting off their ability to breathe or feed. Blankets of sea snot such as the one in Turkey can set off a cyclical chain of events wherein the sea snot suffocates sea creatures, leading to mass die-offs. This in turn leads to mass decomposition, a process that sucks even more oxygen out of the already depleted water, making it more inhospitable for marine life.
Sea snot is not a new phenomenon; it has been periodically blooming in the Mediterranean Sea since the 18th century. However, the frequency and extent of sea snot occurrences along Turkey’s coast since 2007 are unusual, and scientists suggest that global warming may be to blame. Phytoplankton thrive in warmer waters. The average seawater temperature in the Sea of Marmara has increased by 2-3 degrees C since preindustrial times. While that may not seem like a lot, the warmer waters are enough to make a major difference in the phytoplankton populations of the sea, which is already rife with nutrients from wastewater. The higher temperatures make the sea even more hospitable to phytoplankton, which leads to disruptive sea snot events like the one Turkey is currently experiencing.
While the sea snot problem has recently gotten international attention, it has been negatively impacting Turkey’s fishing industry since December, when the bloom began. Fishers have been unable to cast their nets without them getting caught in the sticky mucus, and many of the creatures they do manage to catch are dead, their gills clogged with sea snot.
Dr Neslihan Özdelice, a marine biologist at Istanbul University, urged for a focus on preventing overfishing and limiting waste water discharges into the sea, two factors that scientists have identified as contributing to the sea snot phenomenon. Ultimately, the layer of sea snot that is currently covering the Sea of Marmara, disrupting fishing and threatening biodiversity, is a symptom of a problem that needs to be addressed globally. Major sea snot blooms are an easily visible example of climate change. Global cooperation is necessary to address the root of the problem by working towards mitigating climate change and global warming.
Rachel Lynch
Rachel is a student at Sarah Lawrence College in Bronxville, NY currently taking a semester off. She plans to study Writing and Child Development. Rachel loves to travel and is inspired by the places she’s been and everywhere she wants to go. She hopes to educate people on social justice issues and the history and culture of travel destinations through her writing.
Sexual Assault Prevention: How to Help Yourself and Others
Sexual assault prevention campaigns have been circulating on social media, giving tools to women and men around the world to remove themselves from threatening situations and ward off sexual predators.
Naval Hospital Bremerton's 'Chalk the Walk' display on a visual reminder that April is Sexual Assault Awareness and Prevention Month. Official U.S. Navy Imagery. CC BY 2.0.
Sexual assault is a major issue across the world. From childhood bedrooms and college parties to first dates and marital beds, both women and men alike experience unwanted sexual attention and violence. According to the World Health Organization, 1 in 3 women experience physical or sexual violence from a partner or non-partner in their lifetime. Similarly, at least 1 in 6 men have experienced sexual abuse or assault.
In the past, survivors and allies frequently shied away from speaking about sexual assault; however, in recent years, the topic that was considered taboo is beginning to be spoken about more frequently and openly. Today, workplaces require sexual assault education courses, educational institutions encourage victims to utilize the resources available to them, and social media keeps the conversation alive with its various sexual assault resources, prevention and discussion accounts. People are now more aware of the severity of sexual assault and the long lasting psychological implications it can have on victims, as well as how to report a sexual attack, cope with an unwanted sexual experience or escape situations in which sexual abuse feels imminent.
In recent years, many sexual assault prevention campaigns have been created, often utilizing social media to share these life-saving tactics. One campaign that gained global traction online is “Ask For Angela,” which was launched in Lincolnshire, England by Hayley Child in 2016. The campaign is named in memory of Angela Crompton, a woman who was abused and killed by her husband in 2012 when an argument about redecorating spiraled out of control. Ask For Angela was created to help people escape uncomfortable and potentially threatening situations. By asking a bartender, waiter or employee of an establishment, “is Angela working tonight?” the employee will be alerted that the patron is uncomfortable and would like to be safely and discreetly escorted home. However, Ask For Angela is only effective if the establishment is aware of the phrase and has trained its staff to respond appropriately.
Not only did this campaign gain a lot of traction, but it even encouraged another code word system based on Ask For Angela. The spin-off exists in the United States where, rather than asking if Angela is working, a customer will ask for an “angel shot” when they feel unsafe. Additional setting-appropriate phrases exist to secretly and specifically identify what type of help the person needs. If the person wants the shot “neat,” they want to be escorted to their car; if they want the shot “on the rocks,” they want the establishment to call a taxi for them; and if they want the shot “with a lime,” they are requesting police assistance.
While #AskforAngela recently resurfaced on social media, it is just one of many sexual assault prevention tactics that exist. TikTok is more than an app to share Gen Z’s trendy short dances, comedy skits and shopping hauls—many people have posted videos that mimic real-time phone calls as a way to ward off threatening Uber drivers or escorts when played aloud. According to Uber’s safety report, out of 1.3 billion trips in 2018, over 3,000 sexual assaults and nine murders occured. These TikTok videos typically include a fictitious friend subtly stating that they have your live location, are tracking your ride and are awaiting your arrival, alerting the driver that whatever potential predatory plans they had in mind will not go uncaught. These videos are especially helpful and reassuring because they can be used at times when friends and family members cannot be reached.
Beyond campaigns like these, there are many social media accounts dedicated to sexual assault awareness and discussion. While there is no evidence to suggest that these social media campaigns are effective in deterring sexual violence, at the very least, these initiatives reassure men and women that they are not powerless in those situations. It is important that these posts continue to circulate on social media and inform people how to help others in danger, as well as how to get help when necessary.
TO GET INVOLVED
While it may seem hard to combat sexual assault as an ally, there are many ways to get involved. The Rape, Abuse & Incest National Network—an American non-profit that aims to raise awareness about sexual assault and provide resources and support for sexual assault survivors—is always looking for volunteers to help with it’s 24/7 live chat and hotline, as well as to lead fundraising efforts for research and support programs.
Similarly to RAINN, NO MORE works toward ending sexual violence by spreading awareness, selling products, accepting donations and spearheading various sexual assault prevenetion campaigns. To support NO MORE in their efforts to prevent sexual violence, take the pledge, buy their products and wear their merchandise to show allyship and raise awareness of their organization and cause.
Ending Rape on Campus is an organization that works to prevent sexual assault by providing educational resources in school environments. Help EROC by signing up for its “Action Alerts,” and stay informed about what petitions to sign, events to attend and protests to support.
Mia Khatib
Mia is a rising senior at Boston University majoring in journalism and minoring in international relations. As a Palestinian-American, Mia is passionate about amplifying the voices of marginalized communities and is interested in investigative and data-driven journalism. She hopes to start out as a breaking news reporter and one day earn a position as editor of a major publication.
Sri Lankan Journalists Revive the #MeToo Movement
Female journalists in Sri Lanka have united under the #MeToo movement to foster change within the newsroom.
An overhead view of Colombo, Sri Lanka. Jalitha Hewage. Unsplash.
The Sri Lankan government has called for an investigation of several media outlets following allegations of sexual harassment from female journalists. This resurgence of the #MeToo movement was sparked on June 18 when Sri Lankan journalist Sarah Kellapatha spoke up on Twitter about her experience with a male colleague who threatened to rape her during her time at a publication from 2010-2017.
Encouraged by Kellapatha’s story, several other female journalists began to speak out about their own experiences with sexual harassment in the workplace. For example, Sahla Ilham spoke out about being sexually abused by an editor who pressured her family to remain silent. Another who shared their experience was Jordana Narin, who was harassed by a senior colleague until he was forced to resign by the chief editor.
The Sri Lankan government appears to be taking these allegations seriously, as the Minister of Mass Media, Keheliya Rambukwella, asked the Government Information Department to further investigate the claims to help ensure that female journalists feel safe at work.
Currently, the only type of law that Sri Lanka has to address sexual harassment is a criminal law, which would result in imprisonment of up to five years, or a mere fine, for those found guilty. However, according to human rights lawyer Ermiza Tegal, the problem is that the criminal law is rarely used and victims are often undermined and invalidated.
This recent movement shares its roots with the global #MeToo campaign which started back in 2017 following numerous sexual assault allegations against Harvey Weinstein. The movement fostered awareness of sexual abuse, as well as a safe space for victims to speak about their experiences. Similarly, the journalists who have come forward in Sri Lanka have shared their own experiences, many of them from different news publications, in hopes of fostering change and reform within newsrooms.
Zara Irshad
Zara is a third year Communication student at the University of California, San Diego. Her passion for journalism comes from her love of storytelling and desire to learn about others. In addition to writing at CATALYST, she is an Opinion Writer for the UCSD Guardian, which allows her to incorporate various perspectives into her work.
Pachuco: A Short History of a Timeless Style
Mexican and Mexican American “Pachuco” culture formed in the late 19th century along the the US-Mexico border. Zoot suits and lowriding cars are popular symbols, but the unique look singled out Pachucos as targets of racial discrimination, such as the Zoot Suit Riots in Los Angeles in 1943.
Read More