Iceland has a reputation for being one of the safest and most accepting countries for the LGBTQ+ community, travelers as well as Icelandic residents.
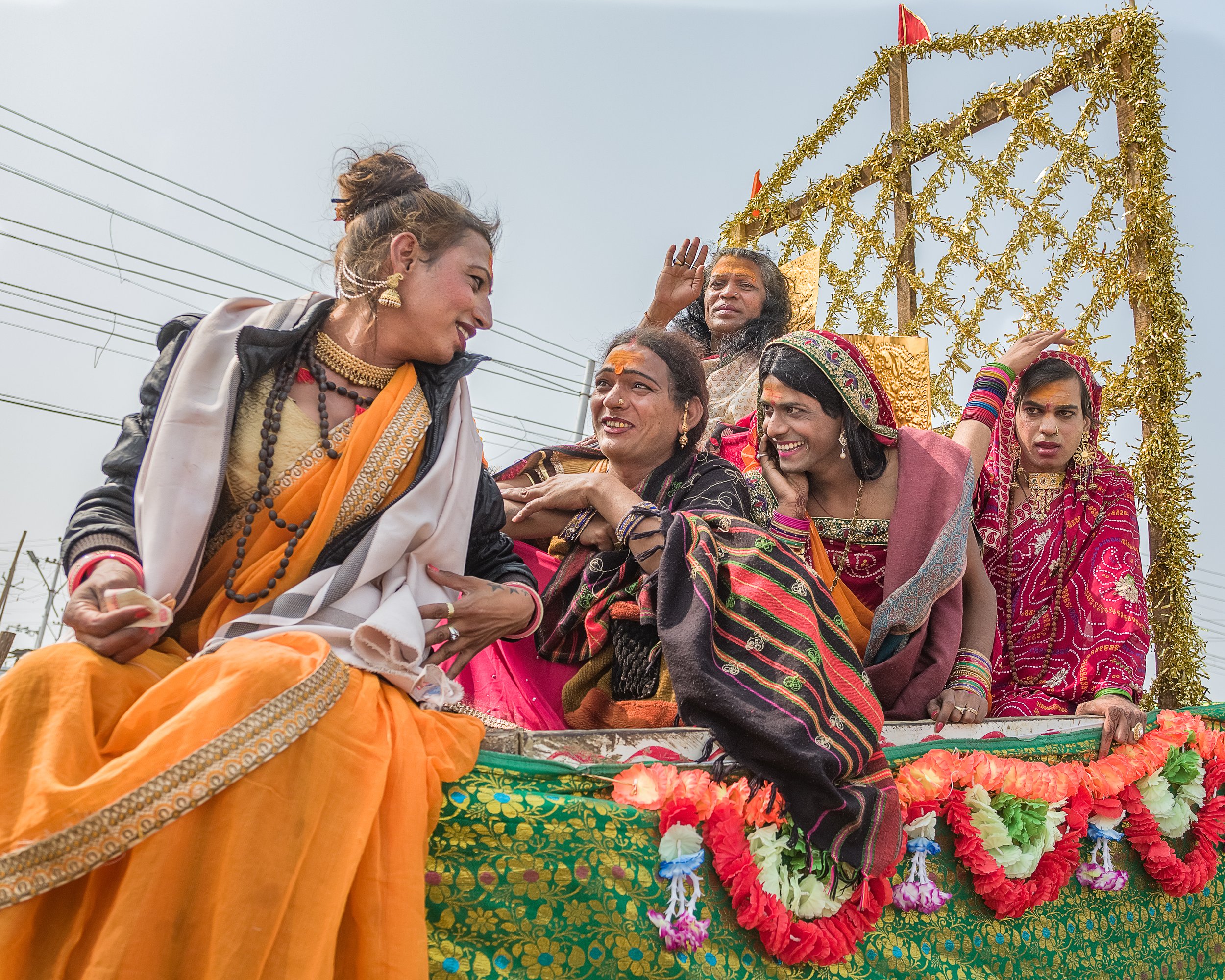
Pride flags in Reykjavík. Symbioticadesign. CC BY-NC 2.0.
While Iceland is an unusually safe and accepting place today, it has had a rocky history with LGBTQ+ rights just like everywhere else. Because Iceland is so geologically isolated from the rest of the world, Icelandic people rarely even married people from other countries prior to World War II. During World War II, Icelandic women began coupling up with and marrying non-Icelandic soldiers who were stationed in the country, and even these heterosexual relationships were met with disdain. This attachment to “traditional marriage” bled over into the public perception of LGBT+ relationships, meaning that homophobia was also rampant at that time. Even thirty years later, the first famous Icelander to come out as gay in the 1970s, Hörður Torfason, was driven out of Iceland by the extreme homophobia he faced.
However, the tide turned relatively quickly in Iceland between the 1970s and the 1990s, but not without great struggle. In 1978, the Icelandic National Queer Organization was formed, which played a major role in promoting gay rights in Iceland. In 1996, Iceland became the fourth European country to officially recognize same-sex unions. By 2004, 87% of Icelanders supported gay marriage (which was officially legalized in 2010) while in 2004, only 42% of Americans did.
Today, Iceland is a popular travel destination for LGBTQ+ travelers wishing to go somewhere that they can feel comfortable and safe. In fact, Iceland has several popular travel guides and agencies that specifically serve LGBTQ+ travelers: Gay Ice and Pink Iceland. While these websites acknowledge that like anywhere, queer people can still be targetted in Iceland, it is apparently rare, and most hotels, nightlife, gyms and other public places are known to be accommodating of same-sex relationships as well as transgender and nonbinary identities, providing gender-neutral facilities and acknolwedging and respecting preferred pronouns.
Reykjavík Pride 2009. Filip J. Cauz. CC BY-NC-SA 2.0.
A large number of businesses and homes in Iceland have pride flags outside their windows, and Iceland hosts several LGBTQ+ events throughout the year that attract hundreds of thousands of tourists. In fact, travelers for the Reykjavík Pride Festival, which occurs in August, account for nearly a quarter of the people in Iceland that month. Reykjavík Pride is regarded as one of the major events of the year in Iceland for everyone, not only people who identify under the queer umbrella. How widespread and anticipated Reykjavík Pride is each year reflects how far Iceland has come in terms of acceptance and safety for LGBTQ+ people. Reykjavík also has a festival in February, called the Reykjavík Rainbow Festival. This is another highly anticipated and attended LGBTQ+ festival in Iceland. Additionally, there are smaller celebrations throughout the year all over the country.
Iceland is known for being very open about same-sex relationships, with queer couples openly showing affection in public generally without fear. There are also LGBTQ+ historical landmarks in Iceland: Gay Ice recommends the LGBT History Walk, which is a walking tour through Reykjavík’s most important LGBTQ+ destinations, along with information about historical events in Iceland throughout the LGBTQ+ rights movement.
Iceland is an excellent destination at any time of year for anyone, but especially travelers in the LGBTQ+ community. However, August and February are two of the most interesting and inspiring times to visit, so that one can catch the famous pride festivals.
Calliana Leff
Calliana is currently an undergraduate student at Boston University majoring in English and minoring in psychology. She is passionate about sustainability and traveling in an ethical and respectful way. She hopes to continue her writing career and see more of the world after she graduates.