Africa saw the rise and fall of diverse societies, cultures, and civilizations that thrived long before colonization.
Read MoreUncovering the Diversity of African Music
If you are a music buff looking to expand your horizon, check out these 5 African music genres.
African drums. Lee Pigott. Unsplash.
People all across the African diaspora share a love for music, which connects everyone to the same frequency. Many are familiar with Afrobeats, a style of music from Nigeria, but there are many different and diverse genres to explore the sounds of, from the likes of Amapiano to Chimurenga.
Amapiano
Two people singing Amapiano together.. The Charles Gallery. Unsplash
Amapiano is a genre of music originating from South Africa characterized by a mixture of jazz, house and Gospel music. Amapiano is composed heavily of synthesizers, percussion, soulful vocals, and repetitive melodies. This genre of music is relatively new, coming into being in the early 2010’s. Amapiano is a Zulu word meaning “the pianos.” Amapiano is a form of music South Africans believe can bridge people together, and a musical escape for the younger generations.
Listen to a Youtube playlist of Amapiano music
Juju
Man playing music on the beach. Seun Adeniyi-CCO.
Juju is a genre of music that originates from Nigeria, specifically its Yoruba region. It’s a musical style that is composed of praise-singing accompanied by a guitar or banjo and a gourd shaker. This genre of music was traditionally played in taverns or during festivals as dance music, but became modernized and generally popular by the 1980’s. As it grew in popularity, it led to the birth of many other genres of music like Highlife or Afrobeats, as we know of them today.
Listen to a Youtube playlist of Juju music
Coupe decale
A group dances to Coupe Decale. Tommy. CC 2.0
Coupe Decale is a genre of music created by Cote D'ivoirians living in France in the early 2000’s. It’s a musical style composed of ‘computerized circular beats’ mixed with Ivorian rhythms . The lyrics themselves are inspired by the West African griot tradition of story-telling, and the genre’s primary message focuses on providing a space for many people to dress nice, go clubbing, and forget their problems during a time of economic and political crisis.
Listen to a Youtube playlist of Coupe Decale music
Gnawa–saharan Folk music
Man playing Moroccan bass lute. Marrakech Riad-CCO.
Gnawa is a folk genre that originates from Morocco. It’s a musical style that has its roots in ancient African tradition, as it’s the result of formerly enslaved black Africans integrating into Moroccan life. It serves as a preservation of the folkloric music of their ancestors, as well as a means to heal from collective trauma. Interestingly it is also said to have healing properties for those that are possessed by ‘genie spirits.’ Its musical style is composed of African percussion, metallic castanets, and bass lutes.’ Gnawa at its core is a combination of poetry, music and dancing. This genre shares many similarities with its American counterparts Jazz and the Blues, as all three share the same purpose. The genre’ songs consist of references to the singer’s origins and history regarding enslavement.
Listen to a Youtube playlist of Coupe Decale music
Chimurenga
Thomas Mapfumo, the creator of Chimurenga music performs. Cultrvultr-CC BY NC-SA 2.0
Chimurenga is a genre of music that was developed in Zimbabwe. It was used to protest colonial rule in the 70s, and more generally is used to discuss and inform on societal issues and movements important to the singer. Because of this, it is recognized as ‘music for the people’s struggle’. This musical genre can be accredited to the Shona musician Thomas Mapfumo. He was inspired by the rock bands he heard playing growing up and his Shona background to create a political movement through music.
Listen to a Youtube playlist of Chimurenga music
Kadija Diallo
Kadija is a student at Georgia State in Atlanta, Ga. She is a creative spirit who loves traveling and seeing new places. She also enjoys using her love for writing/storytelling to make an impact on the world. One day she hopes to make new connections and share stories as she travels to every continent.
How to Score Cheap International Flights
International travel doesn't have to break the bank - learn how to find the best deals.
Read MoreKazakhstan's Journey From Nuclear Devastation to Disarmament
The harrowing story of Soviet nuclear testing in Semipalatinsk, Kazakhstan, and the wrangling with its legacy.
The center of the Semipalatinsk nuclear test site.Alexander Liskin.CC BY-SA 3.0.
It was the summer of 1953. Valentina Nikonchik was outside playing in Semey, a village in eastern Kazakhstan, then part of the Soviet Union. The ground suddenly trembled, and the air filled with a deafening boom that shook Nikonchik to her core. Little did she know that she had witnessed the first detonation at “the Polygon” of a thermonuclear device, a monstrous weapon of mass destruction that released a force equivalent to 400 kilotons of TNT.
West of Nikonchik’s hometown of Semey lies Semipalatinsk, the testing location where the Soviet Union’s nuclear visions were accomplished. A once-thriving region, now a desolate wasteland, has a dark history. In this Central Asian Soviet Republic, the Soviets conducted nearly 400 nuclear tests, blasting a lethal storm of radioactive isotopes into the environment and soil from 1949 to 1989. Even now, the consequences of these tests are still felt, with environmental damage and public health risks ongoing in the area.
At a conference commemorating the ninth anniversary of the Nevada-Semipalatinsk movement, the first anti-nuclear protest movement in the USSR, statistics showing that between 500,000 and 8 million people were directly impacted by the test site’s operations were presented. The detonations, with their tragic and predictable repercussions, represent one of the twentieth century’s major ethical violations. Altogether, the total force of the nuclear explosions at Semipalatinsk equals more than 2,500 Hiroshima bombs. The long-term health effects for the region were harrowing, including an alarming spike in health issues such as miscarriages, birth deformities, and suicides blamed on “unsanitary conditions” in the area by Soviet military scientists in the following decades. What is so disturbing about these dismissals is that the same medical professionals had been performing creeping radiation tests on the villagers for years.
The testing site, despite being uninhabited, is encircled by villages, and the major hub of Semipalatinsk lies just 160 km away. But the testing was kept secret, known only to top Communist Party officials, while anyone who spoke out against the detonations was immediately silenced. Russian scientists confessed that they failed to follow burial and nuclear material protection protocols, as they thought that no one would be in the area. The newly independent Kazakh government officially acknowledged 1,323,000 people as negatively affected by nuclear testing in 1992. However, just 1,057,000 of them received radiation passports, leaving over a quarter of those affected without the requisite documentation. From 2003 to 2017, a $30.5 million reimbursement was intended to give relief to over 700,000 passport holders. Divided between them, a pittance of only only $40 was allocated to each individual each year.
Map of Semipalatinsk Nuclear Test Range, Area “N”. Martin Trolle Mikkelsen.CC BY 2.0.
In 1990, a year before independence, the International Physicians for the Prevention of Nuclear War (IPPNW) and Kazakh poet Olzhas Suleimenov’s Nevada-Semipalatinsk Movement banded together and pushed Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev’s to issue declaration of a nuclear testing moratorium. Kazakhstan seized the opportunity to declare independence the same year and promptly closed down the infamous Semipalatinsk plant. Then, the nation went further, renouncing its inherited position as the world's fourth-largest nuclear weapons owner, and relinquishing its stockpile.
Despite this, the inhabitants go about their regular lives, seemingly unaware of the danger that surrounds them. They swim and fish in the lakes, graze their herds and pick wild strawberries all while being exposed to the poison lurking in the ground and air. However, the danger does not end there. The area will remain a bleak wasteland for millennia, poisoned with plutonium, strontium, and cesium, unfit for human habitation. Residents continue to graze their animals and collect contaminated scrap metal on the polluted land as the 7,065 square mile region is devoid of barriers, fencing, and warnings reminding people of its radioactive status.
Semey, once a thriving city, has suffered the brunt of the devastation. While acute blasts of radiation produced immediate harm, repeated modest doses of radiation over time can accumulate to cause great damage. The wind on the Kazakh steppe has brought the radioactive fallout to nearby settlements, amplifying the impact. The repercussions of nuclear testing have been passed down to future generations as a result of radiation-induced mutations in the population’s chromosomes. As a result, the region’s life expectancy is seven years lower than the national average due to a rise in the prevalence of cancer, thyroid sickness, and birth abnormalities. Tolkyn Bulegenov, Vice President of Semey Medical University, confirms that “in the zones adjacent to the test site, one can encounter 10 to 15% more malignant thyroid and blood malignancies - hematological blastoma, leukosis, lymphoma, and chronic leukemia - than in other regions of Kazakhstan.”
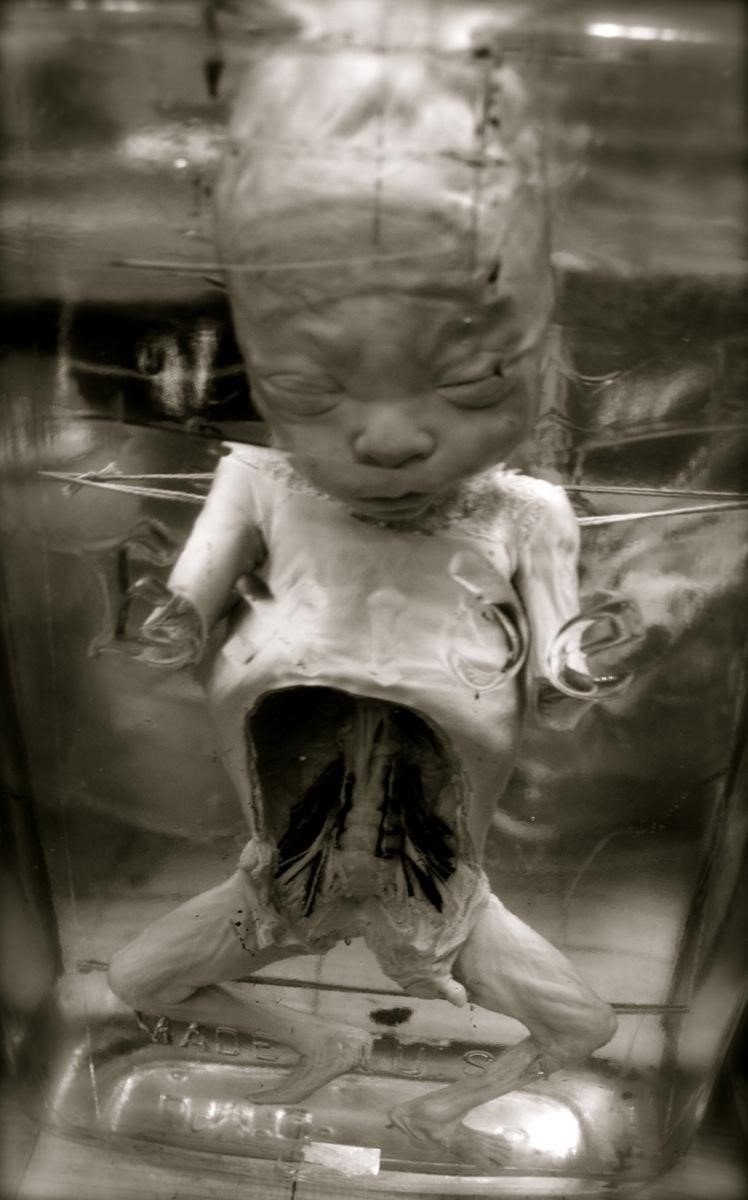
Semipalatinsk Nuclear Test, the effect of radiation on the fetus. Perrona Patrick André Perron.CC BY 3.0.
The late 1980s saw a glimmer of hope for the people of Kazakhstan. As the world was introduced to Gorbachev’s nuclear testing moratorium, the Nevada-Semey movement was born on Kazakh soil with a mission to shut down the Semipalatinsk polygon. Kazakhstan destroyed its inherited weapons testing infrastructure and disposed of the remaining vulnerable nuclear material with the cooperation of foreign partners, including the United States.
On August 29, 1991, President Nursultan Nazarbayev signed the proclamation closing the test site, popularly known as the Polygon, which marked a watershed point in Kazakhstan’s recent history. As part of the Nunn-Lugar Cooperative Threat Reduction Program, the United States collaborated with Kazakhstan between 1995 and 2001 to seal 13 boreholes and 181 tunnels at the test site. From 2012 to 2019, the National Nuclear Security Agency and the Netherlands led two major radiological security operations in Kazakhstan, securing approximately 13,000 radioactive sources from the National Nuclear Center and the Mangystau Atomic Energy Complex. Kazakhstan confirmed its commitment to a nuclear-free world in 2021, in accordance with the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.
Kazakhstan’s commitment to disarmament has allowed the nation to serve as an example of a responsible state that has relinquished its nuclear weapons, setting a global precedent for responsible statehood. Kazakhstan has created an environment conducive to the formulation of a multifaceted foreign policy by abandoning its nuclear weapons and closing the world's most extensively used nuclear test site, allowing the country to collaborate with China, Central Asia, Europe, and the United States. While each nuclear-armed state faces unique problems, Kazakhstan’s peaceful approach to disarmament has encouraged many, and its lessons serve as a guide for other countries seeking a similar path.
TO GET INVOLVED:
The Nuclear Threat Initiative (NTI) is a nonprofit global security organization focused on reducing nuclear and biological threats imperiling humanity. You can learn more about NTI and its records on nuclear disarmament in Kazakhstan here.
Togzhan Kassenova’s Atomic Steppe: How Kazakhstan Gave up the Bomb explains Kazakhstan’s denuclearization process in detail. Kassenova’s book explains how Kazakhstan’s leadership considered security interests as well as economic, political, and diplomatic priorities when making the decision to give up nuclear weapons. You can learn more about Atomic Steppe on Amazon here.
Hope Zhu
Hope is a Chinese international student at Wake Forest University in North Carolina studying sociology, statistics, and journalism. She dreams of traveling around the globe as a freelance reporter while touching on a wide range of social issues from education inequality to cultural diversity. Passionate about environmental issues and learning about other cultures, she is eager to explore the globe. In her free time, she enjoys cooking Asian cuisine, reading, and theater.
Sleep Around the World
How do country and age affect how we sleep?
Read More7 Real-Life Atlantises Hidden Around the World
Exploring the hidden history of sunken sites.
Diver exploring a sunken city. Linnaea Mallette. CC0 1.0
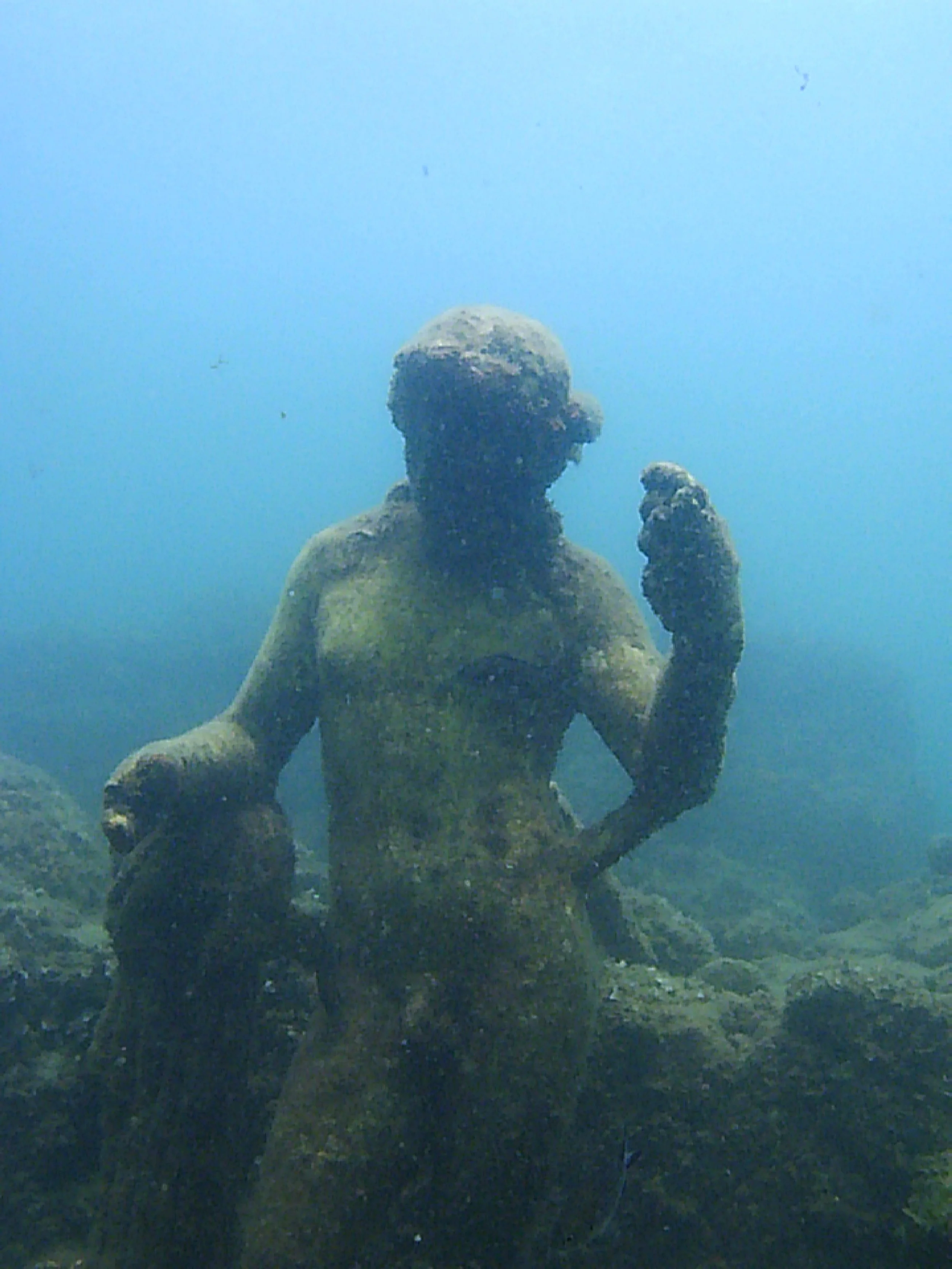
Although travel traditionally highlights cultural landmarks, distinctive experiences, and historical sites on land, much history lies where our eyes alone cannot take us – particularly under the sea. Underwater cities and towns which have been immersed in the soaking abyss of seas, lakes, and reservoirs through natural disaster or human shenanigans provide a time capsule into the defining characteristics of their era. The corpse of the city including its many artifacts can be explored through diving and even glass bottom boats. Here are seven of the most intriguing sunken cities to visit around the world.
1. Baiae, Italy
Emperor Claudius; nymphaeum submerged in Baiae, Italy. Ruthven. CC0 1.0
The ancient Roman town of Baiae overflowed with luxuries in its time: Roman elites built villas and spas fed its famous hot springs, and palace parties proliferated. That is, until an army of the Muslim Caliphate army sacked the resort city in the 8th century. By 1500, the luxuries had faded away and the town was left abandoned. The volcanic vents that had once been the joy of Roman bathers led to a steadily increasing water level and eventually, the majestic city was submerged. Now, the once-present luxuries of the city–its marble statues, mosaics, sculptures–can be viewed through glass bottomed boats and on snorkeling or scuba diving tours.
2. San Roma de Sau, Spain
The half-submerged church of San Roma de Sau. Josep Bracons. CC BY-SA 2.0
All that remains to be seen of San Roma de Sau, a thousand year old village in Catalonia, is the spire of its Medieval Romanesque church. The church, now reemerging due to drought and low water levels in Spain, reminds visitors of the artificial flood in the 1960s that sank the lightly populated town. The Catalonian government’s decision to create a reservoir forced the townspeople to leave their land, taking their valuables and their dead with them. The reservoir’s beginning led inevitably to the end of San Roma de Sau.
3. Dwarka, India
The Dwarka lighthouse on the coast of Gujarat India overlooks the submerged city of Dwarka. VasuVR. CC BY-SA 4.0
Known as “India’s Atlantis,” Dwarka is not only an intriguing travel spot, but also a religious relic. This ancient sunken city located in modern-day Gujarat appears in the Mahabharata as Krishna’s city; the city supposedly sunk in the Arabian sea after Krishna’s death according to the text. 20th century marine archaeological explorations proved its existence outside of literary myth and have uncovered stone anchors, pillars, bastions, pottery, inscriptions, stone sculptures, as well as bronze, copper, and iron objects in Dwarka. Visitors can dive off the coast of Beyt Dwarka, a neighboring island, to view the submerged city.
4. Shi Cheng, China
A sunken artifact in Shi Cheng. Nihaopaul. CC BY-SA 3.0
Shi Cheng, much like many other of the sunken cities on this list, was flooded deliberately. The ancient city was the casualty of a 1959 hydroelectric dam and consequent artificial lake, , which now envelops and obscures this “Atlantis of the East.” Located 40m under Qiandao Lake, Shi Cheng offers a snapshot of Imperial China. The city brims with stone architecture of the Ming and Qing dynasties; stonework of lions ( fitting, as the city’s name means “lion city” in Mandarin), dragons, phoenixes, and historical inscriptions lay within the five entrance gates of the sunken city.
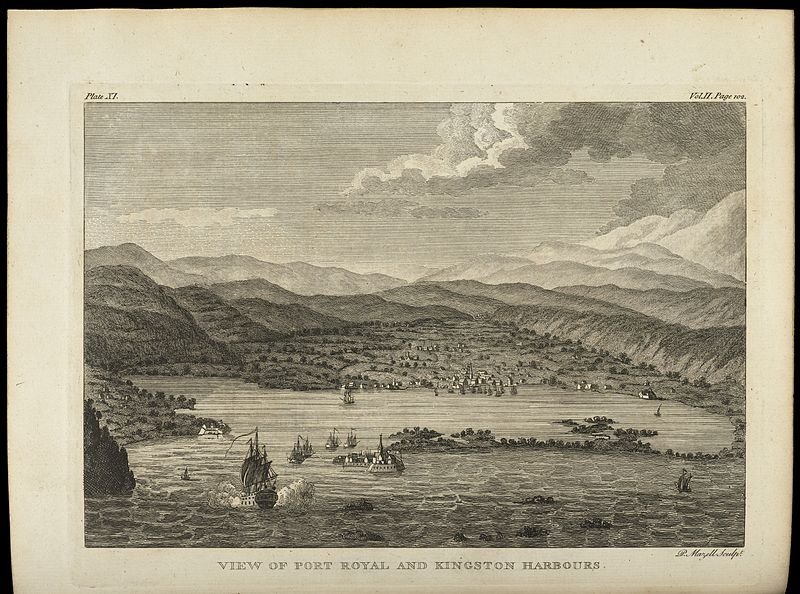
5. Port Royal, Jamaica
An image of Port Royal before the city was sunk. Wellcome Library, London. CC BY 4.0
The 1692 7.5 magnitude earthquake that submerged Port Royal did nothing to erase its rich history. The town, captured by the British from Spain in 1655, became the center of English life in Jamaica. The Englishmen brought the slave trade to the region, as well as an abundance of merchant and artisan activity. The town also possessed a strong scene for sex workers and pirates. Now, the submerged town still maintains its buildings and artifacts like skillets, pots, barrels, ceramics, and a pocket watch found by Edward Link in 1950–all underwater. Travelers can explore the 40 feet deep city through diving.
6. Thonis-Heracleion, Egypt
Thonis Heracleion. Courtesy of Virginia Museum of Fine Arts
Founded around the 8th century BC, Thonis-Heracleion was a distinguished city, one of great importance especially for merchants who frequently passed through the port to enter Egypt. The liquefaction of the city’s clay soil and ultimately the city itself resulted from various natural disasters including an earthquake, tsunami, rising sea levels, and subsidence. As a consequence of these catastrophes, the city eventually collapsed into the surrounding water. Much of the city’s culture and lifestyle remain preserved in watery depths, however. Temples, colossal statues - the most famous being the 5.4 meter tall God of Hapy - inscriptions, jewelry, coins, ritual objects, ceramics, goblets, and the sarcophagi of animals all endure, frozen in time.
7. Potosi, Venezuela
Underwater church of Potosi. Juan Tello. CC BY 2.0
Much like San Roma de Sau, only a part of a gothic church spire juts out from the underwater city of Potosi. The waters of the Uribante Reservoir flooded the town in 1985; the Venezuelan government hoped that a hydroelectric dam could replace the 1200 residents of the town. Houses and churches were abandoned in 1985 for the scheduled flooding. Yet, the gothic church of Potosi has re-emerged due to severe droughts in Venezuela, most probably a result of the natural disaster, El Niño. 30 years after the flooding of the city, its church’s structure has been uncovered.
Su Ertekin-Taner
Su Ertekin-Taner is a first year student at Columbia University majoring in creative writing. Her love for the power of words and her connection to her Turkish roots spills into her satire, flash fiction, and journalistic pieces among other genres. Su hopes to continue writing fearless journalism, untold stories, and prose inspired by her surroundings.
How Quechua Women Keep Stories Alive Through Their Hats
Having long been mistreated, Indigenous Quechua women have found ways to honor their ancestors and stories with their unique hats, which form an integral part of Peruvian culture.
Read MoreFree Airline Tickets To Hong Kong?
To bring back tourism, 3 airlines are offering 500,000 free air tickets.
Read MoreThe 10 Most Pet-Friendly Cities Around the World
From the solemn streets of Berlin to the lively waterways of the Netherlands, here are 10 places to visit with your beloved furry friend by your side.
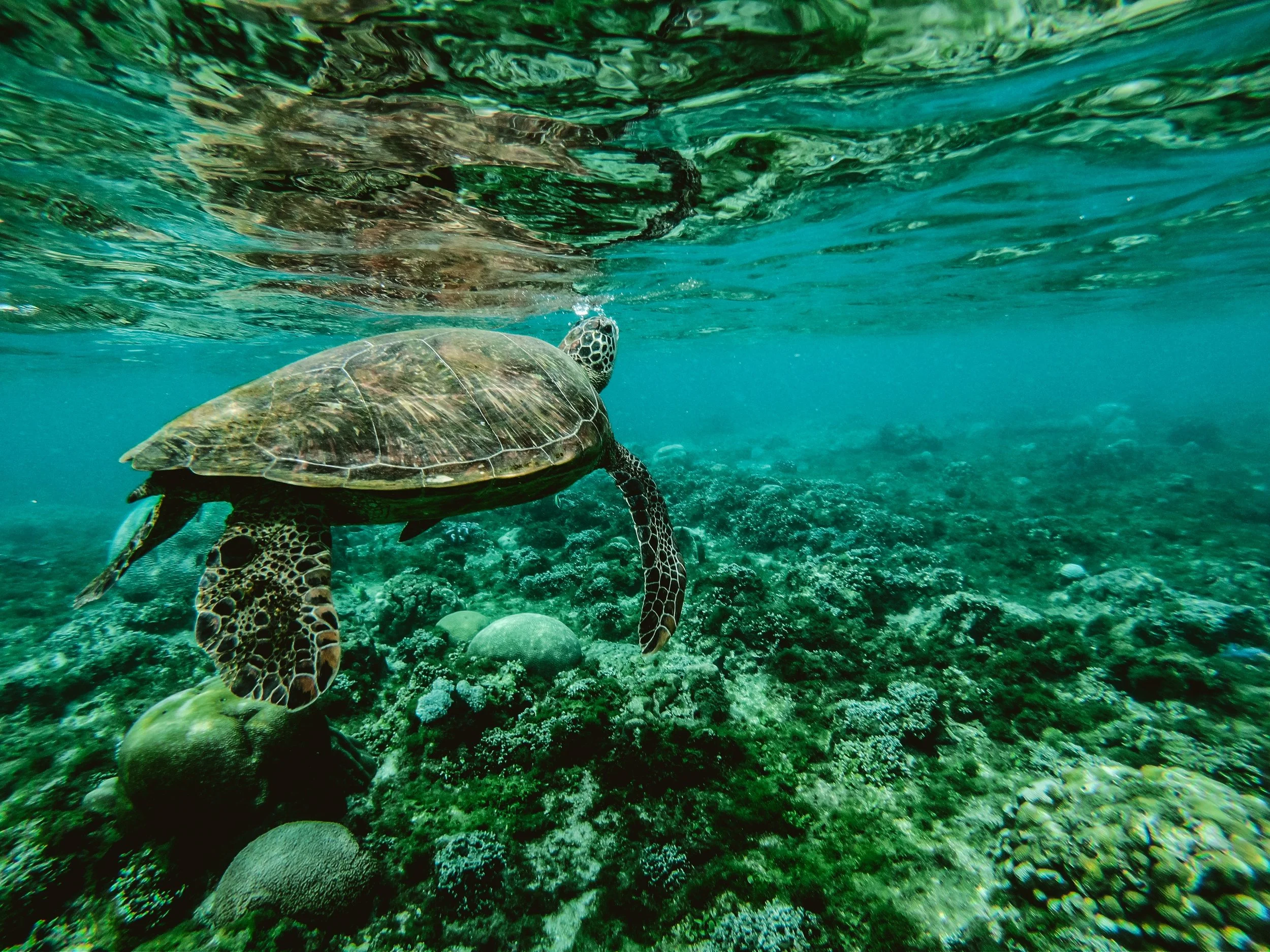
Read MoreHow Ancient Ghanaian Culture Shapes Sea Turtle Conservation
Ghana’s ancient admiration for sea turtles has inspired a modern conservation movement to protect these ecologically vital animals.
Sea turtle swimming in the ocean. Belle Co. CC0.
Ghana is a vibrant country located in West Africa, bordered by Côte D’Ivoire, Burkina Faso and Togo. It is known for its rich culture, stunning beaches, and diverse wildlife. As a traveler, you would likely find Ghana to be a lively country, full of colorful markets, bustling streets, and a unique mix of traditional and modern cultures. Perhaps most importantly, Ghana is known for the warmth and hospitality of its people, where you’ll be met with a welcoming and friendly nature.
Ghanaian people are also very spiritually attuned, whether it’s native African spirituality or more newly introduced Christianity. They are very fond of their cultural and religious traditions, one of which is long-standing is their long standing connection to sea turtles.
Sea turtles have been a part of Ghana’s culture and folklore for centuries, with oral literature depicting these animals as protectors, helpers or even guides. Moreover, the reptiles are integral to Ghana’s ecology, as they help to maintain coral reefs and seagrass, which in turn ensure continued biodiversity.
It wasn’t always this way, as with Urbanization came poverty, and with poverty came poachers. These poachers saw the Sea turtles not as protectors but as a source of profit. Now, having returned to their traditions, Ghanaians are more determined than ever to protect and conserve these animals in hopes to prevent their extinction.
All over Ghana, there are different recorded myths and stories that show the ancient connection between Ghana and sea turtles.
The Ga and Akan ethnic groups of central Ghana have a story about their ancestors and how they once were caught in a storm while fishing, in which their boat had sunk. It is said that as the men were struggling in the choppy waters, the sea turtles arrived and helped them get back to shore.
The Dange people of eastern Ghana have a story in which their ancestors were trying to retreat after Ashanti armies had them cornered against the Volta River. They recount how both the crocodiles and the sea turtles helped them safely cross the river, by having the crocodiles form a bridge, while sea turtles helped heal the injured and guided the elderly across. It is said that to this day, both animals are fully protected in this region of Ghana.
Sea turtles in Ghana have been protected by law since 1971. Even then, there are still poachers, so just that isn’t enough. The Ghana Turtle Research Project (GTRP) has been around for more than 10 years. The organization encourages community members to participate in sea turtle conservation and to embrace their culture and traditions. By doing so they were able to get more than fifty community members to form a volunteer network. They also helped to tag and identify where turtle species reside most often in order to make sure that fishermen avoid those areas and to ensure they are safe-guarded.
Additionally, the Environmental Justice Foundation (EJF) is an organization that was focused on protecting nesting sites in the fishing communities of central Ghana. In 2019, during the first turtle nesting season (of that year), they were successfully able to deter poachers from the Goma Fetteh region.
As more and more Ghanaian communities return to their traditional and spiritual beliefs, more people are caring about the sea turtles. It’s due to the oral traditions in Ghanaian culture that these conservation efforts were possible, as they make people care more about these creatures of the sea. They helped form an everlasting connection between the sea turtle and man.
Kadija Diallo
Kadija is a student at Georgia State in Atlanta, Ga. She is a creative spirit who loves traveling and seeing new places. She also enjoys using her love for writing/storytelling to make an impact on the world. One day she hopes to make new connections and share stories as she travels to every continent.
9 Must-Read Works of Historical Protest Literature
The novels and essays that shaped our understanding of human rights.
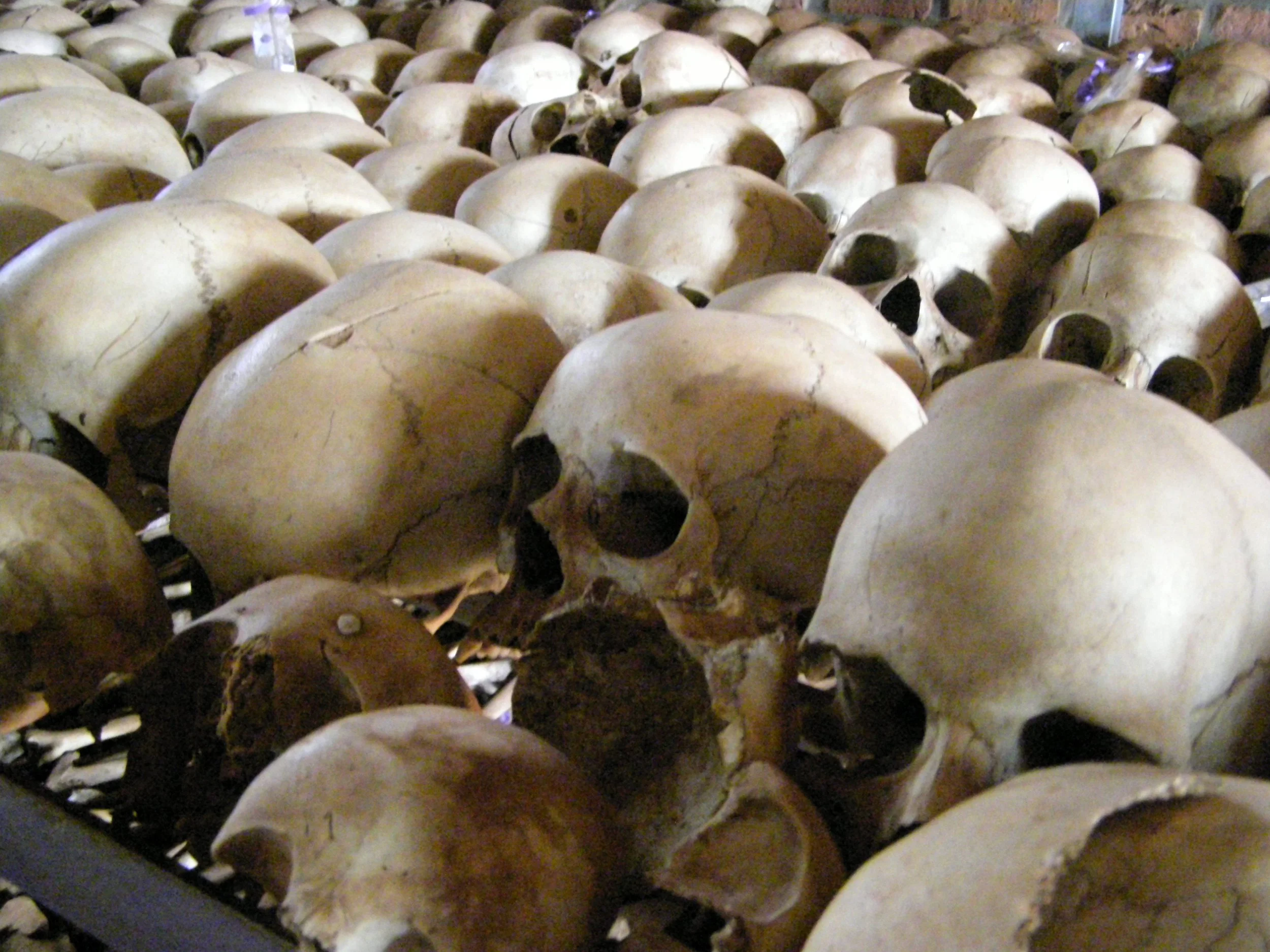
Read MoreA Brighter Future Emerges 29 Years After Rwanda's Genocide
Rwanda's unwavering determination and spirit shine as a source of optimism for the rest of the world.
Rwanda Genocide Memorial. config manager.CC BY 2.0.
This week marks the 29th anniversary of the Rwandan Genocide, a 100-day period of violence in 1994 in which more than 800,000 people were killed. The repercussions of this tragedy continue to linger, leaving survivors and their family members with deep emotional traumas. Almost 30 years have passed since the devastating genocide in Rwanda, and the country has made some commendable progress in rebuilding its economy and mending its relationships with other nations, while also acknowledging its past mistakes and the sacrifices made during the massacre. The scars of the past may still be visible, but they no longer define Rwanda. Its developments shed light on the country’s journey toward healing and growth, with infrastructure, technology, and education driving its transformation.
The genesis of the Rwanda Genocide three decades ago can be attributed to years of systemic oppression that eventually culminated in one of the most devastating conflicts in modern history. Surprisingly, the two primary ethnic groups involved in this conflict, the Hutus and Tutsis, shared no religious or linguistic differences at the outset. A deep dive into their origins reveals that the Hutus migrated to the Great Lakes region of Central Africa between 500 and 1000 BC, while the Tutsis arrived four centuries later, migrating from the highlands of Ethiopia. The Hutus primarily worked as land cultivators, while the Tutsis were cattle herders, thus creating an economic divide that eventually led to a hierarchical system. In a strange colonial mythology, Tutsi cattle herders were labeled Hamites — a separate and exceptional group — who hailed from an ancient Christian tribe supposedly linked to people of old Palestine. This system placed the Tutsis, as a minority ethnic group, in a position of disproportionate power over the majority Hutus.
Colonial powers subscribed to this concept of racial hierarchy and origin stories, believing the Tutsi to be natural leaders and granting them preferential treatment. After taking Rwanda as a colonial possession in 1897, the German Empire built a power structure that firmly established a hierarchy that favored the Tutsis. They bestowed upon the Tutsis a superior status, owing to their taller stature and lighter skin, giving them greater influence over the Hutus. However, in the aftermath of Germany’s defeat in World War I, Belgium took over the reins of Rwanda’s governance, and, rather than attempting to bridge the cultural divide, exacerbated it. The Belgian administration continued to uphold the Tutsis’ superior status while disregarding the Hutus, creating a further chasm of inequality that only grew wider with time. The introduction of identification cards during the 1930s that explicitly listed one’s ethnicity, for example, further polarized the population, and the stage was set for the tragic events that culminated in the Rwanda Genocide.
In 1973, Rwanda witnessed an event that would forever alter the course of its history. General Juvenal Habyarimana, a Hutu tribe member, rose to power and established the National Revolutionary Movement for Development (NRMD) party to secure his authority. Meanwhile, in Uganda, a group of Rwandan exiles in Uganda who had tasted victory in Yoweri Museveni’s National Resistance Army during the Ugandan Civil War formed the Rwandan Patriotic Front (RPF). This organization was largely dominated by Tutsi figures and posed a challenge to the incumbent regime. The Rwandan Civil War began, which pitted the Hutu-dominated NRMD government against the primarily Tutsi RPF, while social tensions began to simmer. It was midsummer in 1993 when Hutu extremists hatched their plan, creating a platform for propagating their racist ideology and spewing hatred against the Tutsi people. Thus, Radio Télévision Libre des Mille Collines (RTLM) came into being, which soon became a tool to incite violence and hatred against the Tutsi, using propaganda and malicious rhetoric.
Radio Télévision Libre des Mille Collines broadcasted from this office during the Rwanda Genocide. kigaliwire.CC BY-NC 2.0.
April 6, 1994, was the beginning of a nightmare for Rwanda and Burundi. The presidential plane, which was carrying the heads of state of both countries, was hit by gunfire. The news of their deaths, broadcasted by the radical Hutu RTLM radio station, served as a call to arms, sparking a wave of violence against the Tutsi population. The initial attack was planned by a group of military leaders, politicians, and business owners, who were later joined by an increasing number of supporters. This resulted in a devastating genocide, with Tutsis flocking to ostensibly safe havens like churches and administrative centers only to find them transformed into places of horror. 75% of the Tutsi population was wiped out, including many children who were labeled “little rats” and killed alongside adults. The perpetrators killed people of all ages indiscriminately, committing rape and torture on a regular basis. With nowhere to call home, over 2 million people fled the country, including many Hutu ethnic group members, while a million more were internally displaced, leaving 75,000 children orphaned.
The aftermath was massive destruction, with infrastructure reduced to ruins and hundreds of thousands of citizens dead, dealt a crippling blow to progress and development. Rwanda, however, refused to give in to despair. The RPF won the Civil War and took power after four months of horror, ending the genocide. The nation embarked on a journey of healing and reconciliation by embracing a deliberate strategy of transitional justice and transformative programs, characterized by the visionary “Rwanda Vision 2020” campaign launched in 2000. Rwanda embraced a path of renewal through initiatives such as “I am Rwandan,” which encouraged deep reflection on the nation's painful history, acknowledgment of past atrocities, and promotion of healing and reconciliation among all its people. Another example is “Umuganda,” a day of community service in which people from all walks of life work together to improve their communities. Though challenges remained, these initiatives instilled a renewed sense of vigor and solidarity, bringing new life to the difficult task of rebuilding Rwanda.
The modern capital of Kigali is safe, clean, and orderly. Dylan Walters. CC BY 2.0.
Rwanda also undergoes significant changes in its economy. The government has introduced the “Girinka” program, which provides one cow per poor family to combat poverty, with the first female calf being passed on to another family. Poverty has decreased by 23.8 percent from 2000 to 2010, and Rwanda has emerged as one of the fastest-growing economies in Central Africa, with four years of eight percent GDP growth between 2011 and 2014. These developments are positive indicators for Rwanda’s future.
Despite the indelible mark of shame left by the horrific acts, Rwanda has sought reconciliation by embracing its rich heritage of traditional pre-colonial Rwandese customs and values, while also welcoming contributions from the international community. The genocide has prompted profound reflections on critical issues such as the efficacy of peace operations, the urgency of ending international crimes, and the delicate nature of maintaining civility. These pressing issues necessitate international attention and are still relevant today.
TO GET INVOLVED:
World Help: Over the last decade, World Help has worked to bring healing and restoration to Rwandan communities through initiatives like trauma counseling, children’s homes, child sponsorship, construction projects, clean-water wells, sustainable agriculture, vocational training, and more. To learn more and get involved, click here.
IBUKA: IBUKA is an umbrella organization supporting survivors in Rwanda. Representatives from institutions like IBUKA and the National Commission for the Fight Against Genocide are invited to speak at commemorations to provide expert histories and testimonies. To learn more and get involved, click here.
Hope Zhu
Hope is a Chinese international student at Wake Forest University in North Carolina studying sociology, statistics, and journalism. She dreams of traveling around the globe as a freelance reporter while touching on a wide range of social issues from education inequality to cultural diversity. Passionate about environmental issues and learning about other cultures, she is eager to explore the globe. In her free time, she enjoys cooking Asian cuisine, reading, and theater.
How Fast Food Adapts to Local Tastes Around the World
Exploring unique regional items from KFC, McDonald’s, Pizza Hut and other fast food giants.
Fast Food Mull. Tim Reckmann. CC BY 2.0.
Fast food is a universal language that transcends borders and cultures. Whether you are craving a burger in Beijing or a pizza in Paris, you can always rely on fast food chains to provide a consistent, reliable experience. However, in the modern world, fast food chains are constantly adapting to local tastes and incorporating unique ingredients to create various flavor combinations. Here below is a flavor adventure that explores the wacky and wonderful world of region-exclusive fast food items.
1. Kentucky Fried Chicken
Kentucky Fried Chicken in Shanghai. Gwydion M. Williams.CC BY 2.0.
Kentucky Fried Chicken, or KFC for short, has come a long way since its humble beginnings in Corbin, Kentucky. Today, the iconic fast food chain can be found in almost every corner of the globe, serving up crispy fried chicken to hungry customers worldwide. But while the Colonel’s original recipe may be the same everywhere, KFC has become famous for its wildly creative region-exclusive items. For example, in the United Kingdom, KFC has introduced the “Scoff-ee Cup”, a creation that combines a biscuit cup with white chocolate to keep coffee hot and fingers crispy. Meanwhile, in Asia, KFC has rolled out some innovative treats, like the Brown Sugar Boba Tea Tart, a pastry filled with milk tea custard and boba jelly, inspired by the popular Taiwanese drink.
But KFC’s regional items are not just about sweet treats. In Korea, the chain offers Tender-Rice, a combo of crispy chicken tenders and seasoned rice. And in Malaysia, customers can try the Wasabi Rice Wrap, a fusion of Japanese and Vietnamese flavors that is designed for people on the go. According to Ling Mee Jiuan, Senior Vice President of KFC Malaysia, the Wasabi Rice Wrap was designed specifically with young, busy consumers in mind. The local team wanted to create something that was quick, convenient, and bursting with flavor for people who are always on the move.
2. McDonald’s
McArabia. Tracy Hunter.CC BY 2.0.
McDonald’s is the poster child for the rapid spread of Western fast food across the globe. The term “McDonaldization” was coined to describe what started as a Speedee Service System, which prioritized efficiency, predictability, calculability, and control by offering a limited menu of 15-cent hamburgers, fries, and shakes. However, McDonald’s has slowed its pace and started introducing region-exclusive items that cater to local taste buds. For instance, in 2001, McDonald’s added the McFalafel sandwich to its menu in Egypt. This sandwich features three pieces of falafel, a patty-shaped fritter of Arab origin that is deep-fried and served with garnishes like tomatoes, lettuce, onions, and pickles, all wrapped in a freshly baked tortilla wrap and topped with Tahini sauce.
But McDonald's is not just adding local twists to its burgers - the company also creates entirely new menu items for specific regions, you can find the Teriyaki Burger, which features a savory teriyaki sauce and is served on a rice bun instead of a traditional burger bun. In South Korea, McDonald's offers the Bulgogi Burger, which features marinated beef and a spicy sauce made from Korean chili paste.
McDonald’s has also tailored its famous bread to suit local palates. In China, for instance, McDonald’s introduced the distinctive Black and White Burgers. These “half burgers” were packaged in a small box and were possibly inspired by the yin-yang symbol. The black burger consisted of a beef patty with chopped onions, black pepper sauce, and a black bun topped with white sesame seeds. The white burger, in contrast, featured a chicken patty with sweet and spicy sauce and a white bun with black sesame seeds. While some of these attempts at innovation were mocked, they demonstrate a willingness to experiment and accommodate local tastes.
3. PizzaHut
Pizza Hut Pizza in Japan.Yoko Nekonomania.CC BY 2.0.
Founded in 1958 by two Wichita University students, Pizza Hut has grown to become the world's largest pizza company, with over 11,000 restaurants in 90 countries. But Pizza Hut's success isn't just due to its massive size - the company’s commitment to innovation and customer service has set it apart from competitors.
However, some of Pizza Hut’s more unconventional offerings have raised eyebrows, and possibly even the ire of traditionalists. Weirder items, such as the “Double Sensation” in Singapore, may seem like two pizzas squished into one. The outer crust is stuffed with a melange of melted mozzarella, Parmesan, and cheddar cheeses that ooze out of holes in the crust, while the outer pie is topped with turkey ham, bell peppers, mushrooms, and salsa sauce. And for reasons beyond comprehension, a single cherry adorns the center of the pizza.
Meanwhile, Pizza Hut in China has added Peking duck as a meat topping to its menu, alongside specialized pizzas crafted with different veggies to complement the duck’s unique flavors. For many, duck is not a meat that adapts easily to other dishes. But for the daring foodies who are willing to try new things, Pizza Hut in China offers a delicious and adventurous take on traditional pizza.
4. Burger King
Burger King Halloween Whopper Black Bun. Mike Mozart. CC BY 2.0.
In 1953, Keith Kramer and his wife’s uncle Matthew Burns were struck with inspiration after visiting the original McDonald's in California. Their brainchild, Insta-Burger King, was born from their desire to create a unique restaurant experience. Equipped with a special grill machine, the Insta-Broiler, the duo set out to make their mark in the fast-food industry.
Now, with over 19,000 locations worldwide, Burger King is a force to be reckoned with in the fast-food world. While its competitors strive to innovate their international menus, Burger King takes a different approach—stuffing as much as humanly possible between two buns. Take, for example, the Bacon Lover, available in France and Switzerland, which boasts two flame-grilled beef patties, onions, tomatoes, cheese, bacon, and smoked sauce, all served between two bacon-studded buns.
But the Garlic Meat Beast in Japan takes the cake for the most outrageous offering. This monstrosity features a quarter-pound beef patty, teriyaki chicken breast, and garlic pork patty, all slathered in scallion miso sauce and topped with lettuce, tomato, onion, and bits of fried garlic. And if that’s not enough to satisfy the consumers, Burger King‘s Windows 7 Whopper hit Japanese locations for a limited time, featuring a whopping seven beef patties, plus all the usual fixings, for the price of $5.94, a nod to the release of Microsoft's Windows 7 operating system.
5. Taco Bell
Taco Bell Beefy Fritos Burrito. Willis Lam.CC BY-SA 2.0.
Taco Bell is the new kid on the block when it comes to multinational fast food chains, but it has made its presence known around the world with its Mexican-inspired menu. The company’s catchy slogans, from “Think Outside the Bun” to “Live Mas,” have resonated with customers in Asia, Europe, and beyond. But Taco Bell’s true innovation lies in what's inside the bun (or wrap). Take, for instance, the Kimchi Quesadilla, which can be found at Taco Bell locations in Korea. This fusion dish combines the traditional Korean dish of spicy fermented cabbage with spicy chicken and a blend of melted cheeses, creating a unique flavor that is all its own. Or consider the Chicken Tikka Masala Burrito in India, where grilled chicken, Mexican rice, onion, cilantro mix, and Tandoori Mayo Sauce are wrapped in a grilled flour tortilla, showcasing Taco Bell's willingness to experiment with unorthodox flavor combinations. Other region-exclusive menu items include the Shrimp and Avocado Burrito in Japan and the Chili Cheese Burrito in the United States.
6. Domino’s
Domino’s pizza in Japan with Lazagniano and Super Deluxe. Puamelia. CC BY-SA 2.0.
Domino’s, the pizza giant with over 17,644 restaurants around the world, has managed to achieve a global presence with its menu. However, their international menu seems to be an experimental playground that has no bounds. Japan’s Boba Tapioca Pizza is a clear demonstration of the chain’s willingness to embrace bizarre combinations that cater to local tastes. The pizza’s blend of black tapioca pearls and mozzarella cheese has gotten mixed reactions from customers. While it is true that some of Domino’s experiments are not well-received, the Lotta-Chocca Pizza in the United Kingdom has won the hearts of many, thanks to its unique fusion of pizza and milk chocolate. Domino's New Zealand has also managed to make an impact with its Apricot Chicken Deluxe, a delicious combo of chicken and apricot sauce.
From rice and curry to kimchi to Beijing duck, the amalgamation of western industrialization and local cuisine gives rise to region-exclusive fast food items that are uniquely flavorful, providing a glimpse into the cultural diversity that exists across the globe. The presence of such multicultural menus in fast food chains not only reflects the dynamism of global markets but also serves as a testimony to the importance of inclusivity and open-mindedness in our increasingly interconnected world.
Hope Zhu
Hope is a Chinese international student at Wake Forest University in North Carolina studying sociology, statistics, and journalism. She dreams of traveling around the globe as a freelance reporter while touching on a wide range of social issues from education inequality to cultural diversity. Passionate about environmental issues and learning about other cultures, she is eager to explore the globe. In her free time, she enjoys cooking Asian cuisine, reading, and theater.
9 Historical Women Adventurers Who Pushed Exploration in the Last 100 Years
Despite facing prejudice and skepticism, these intrepid women adventurers conquered the world’s toughest terrain.
Read MoreThe True Culprits of Poaching
The causes and consequences of the illegal wildlife trade.
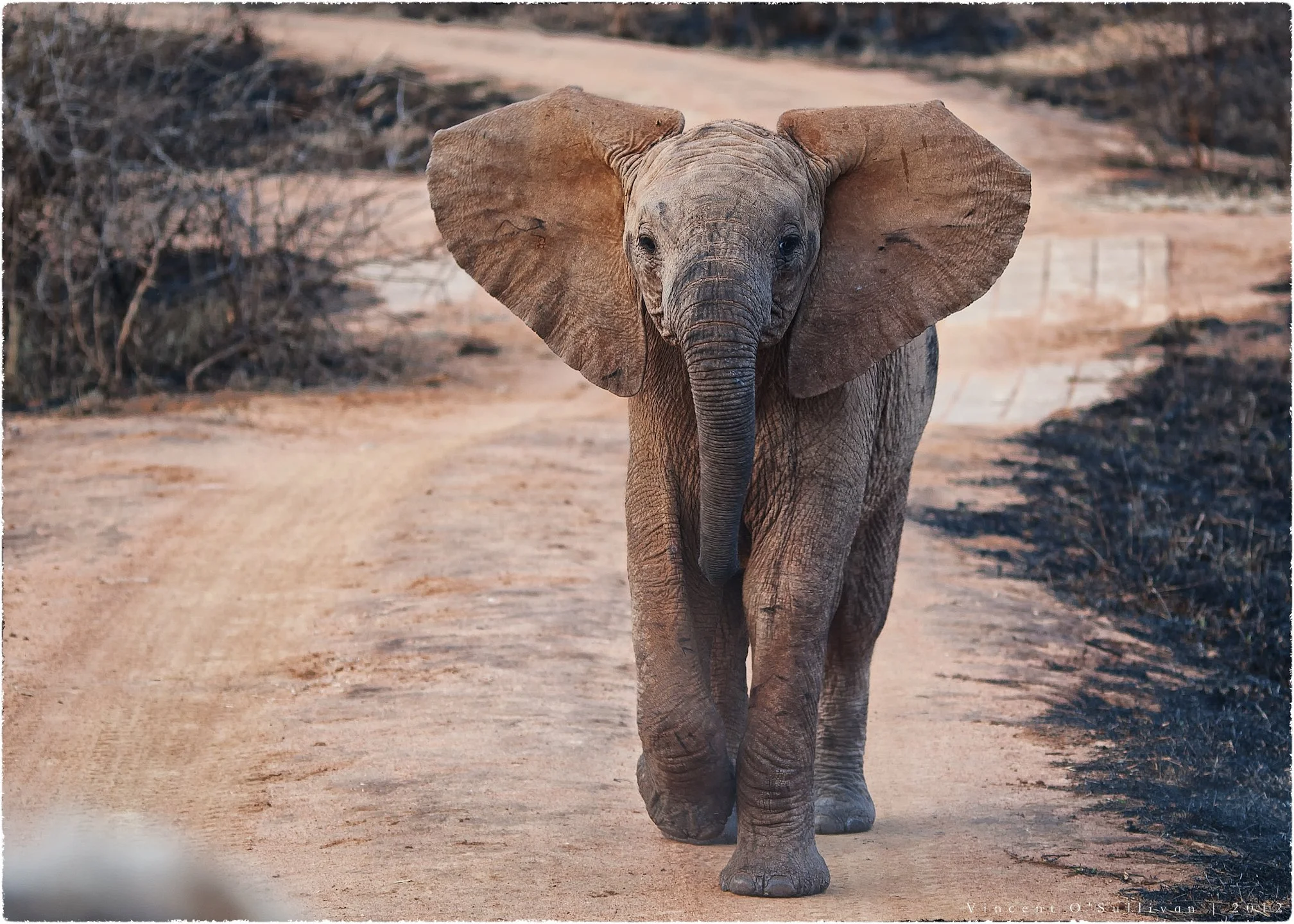
Elephant Calf - Madikwe, South Africa, Vince O'Sullivan, CC BY-NC 2.0.
In 2019, a man and his four companions entered South Africa’s Kruger National Park, dead set on killing a rhino. They botched the job- the man was trampled by an elephant and killed. His four companions fled the scene. Later, the man’s body was found eaten by lions. For many, this was a story of nature’s revenge on an aggressor. Some even took to social media to celebrate his death, claiming that “It’s a shame all five didn’t die.”
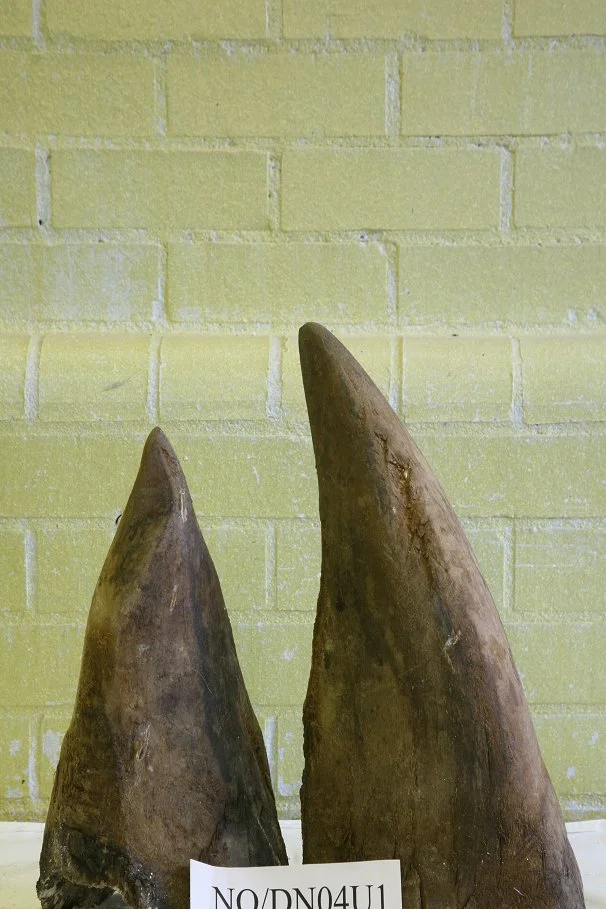
But the digital peanut gallery likely did not know that this man was from South Africa’s Eastern Cape, the country’s poorest region where the average annual income per year is less than $3,700. And, they probably didn’t know that even if he and his companions had successfully killed the rhino, taken its horn, and bolted, they would have remained in poverty, having sold the horn for a tiny fraction of its value on the international market. From there, the horn would go through multiple stages of middlemen to hide its origin and be shipped to a foreign nation, likely Vietnam or China. There, poaching kingpins such as Vietnam’s Nguyen Mau Chien would receive the horn and sell it to consumers for a huge profit.
Unwrapped Rhino Horn, cropped, ukhomeoffice, CC BY 2.0
This story is not unique. The United Nations estimates the poaching market to be worth a minimum of $7 billion per annum. The poaching kingpins who lead these operations are akin to drug lords. With few moral qualms, they are making millions, exploiting those working lower on the food chain and putting the environment in danger, all while taking very few risks themselves.
Over the past few years, dozens of species have gone extinct largely due to poaching, with hundreds more being driven to the brink of extinction. They range from smaller, lesser known species to large, iconic megafauna such as the Western Black Rhinoceros, a subspecies that went extinct in 2011.
Black Rhino, corrieb, CC BY 2.0
The impact of these extinctions goes far beyond the animals themselves. The world exists as a closely connected ecosystem. When one species becomes endangered, it affects every other species in that ecosystem. One clear example of this is the North American Gray Wolf. The wolf’s regional near-extinction caused a surge in the elk population in Yellow Stone, which nearly ate the aspen tree into extinction.
Poaching also is detrimental to countries, like South Africa, that heavily rely on animal-based tourism. When iconic animals become extinct and ecosystems are damaged, ecotourism becomes much less successful. Even worse, poaching is incredibly dangerous to those working in conservation. Each year, across Africa, 600 rangers' lives are lost in the line of duty.
Ranger and rhinos, Kruger National Park, South Africa, anoukpilon, CC BY-SA 2.0.
In addition, poaching poses a huge risk to the world at large. COVID-19, Ebola, and SARs all started in animals. In fact, 60% of all infectious diseases are thought to have begun in non-human animals. Whether through the murder of animals directly or the transfer and consumption of illegal animal products, poaching puts thousands of hands and bodies in contact with wildlife, and therefore at risk.
TO GET INVOLVED
The International Anti-Poaching Federation (IAPF), founded in 2009, aims to hire 2,000 women by 2030 to work in anti-poaching units in their local communities, as part of the all-female Akashinga Project. The IAPF has managed to reduce poaching by over 80% in the 8.5 million acres it manages, making them one of the most successful anti-poaching organizations in the world. If you want to help stop the poaching epidemic, you can donate to the IAPF here.
The David Sheldrick Wildlife Fund has been Operating in Kenya since 1977. Over the past 45 years, they have become one of the best Elephant rehabilitation organizations in the world, raising over 300 orphan elephants. Beyond this, the Fund has 23 anti-poaching teams working with the Kenya Wildlife Service, employing both Aerial and Canine Units. If you want to support them, you can donate here.
Jeremy Giles
Jeremy is a Writing Seminars and International Studies major at Johns Hopkins University. He is an avid writer and the Co-Founder of Writers’ Warehouse, Johns Hopkins’ first creative writing group. He is an advocate for Indigenous rights, and studies how Indigenous philosophies can be used to help prevent climate change. Using his writing, he hopes to bring attention to underrepresented voices in today’s world.
9 Activist Movements You Might Not Know About
From Australia to Bolivia, social movements are paradigms of collective power and triumphs of the human spirit.
Sudanese Protesters Welcome 'Positive Steps' Taken By Ruling Military Council, demonstrators rally near the military headquarters in Khartoum, Sudan, Monday, April 15, 2019. Omer. Public Domain Mark 1.0
It's easy to brush off textbook knowledge as outdated, but academic theories of social movements can provide a powerful lens to understand the changes happening in the world. The 21st-century witnesses social movements erupting all over the world, led by activists fighting to bring about change. Sociologists categorize social movements as a form of collective behavior that emerges during the political, cultural, or economic upheaval. It is precisely this decentralization that gives activists immense power to effect change, leading the masses in protest against the upper crust. With that in mind, below is a list of nine groundbreaking social movements of the 21st century that you might have missed.
1. Equality Australia, Australia
Reason Party (Australia) supporters with placards at Yes Marriage Equality rally Sydney Town Hall 10 Sept 2017.Robert.CC BY-SA 4.0.
Despite progress in other western countries, Australia still faces criticism for a dearth of LGPTQ representation in politics. For example, in 2021, the Australian government under Scott Morrison almost passed a deceptively named religious discrimination bill that in reality had the potential to legalize discrimination based on sex, disability, and age under the disguise of religious freedom. This bill not only undermines the rights of the LGBTQ community but also perpetuates stereotypes and biases. The bill was shelved after religious lobby groups withdrew support and, due to Scott Morrison’s defeat to the Australian Labor Party in 2022, seems unlikely to be reintroduced.
To compensate for the lack of legal protection for the sexual minority population, Equality Australia, an organization dedicated to improving the lives and circumstances of the LGBTQ community in Australia, has launched multiple initiatives. It tackles the pressing issues that gay, trans and queer Australians face, from being able to freely express their identity to receiving adequate healthcare and support.
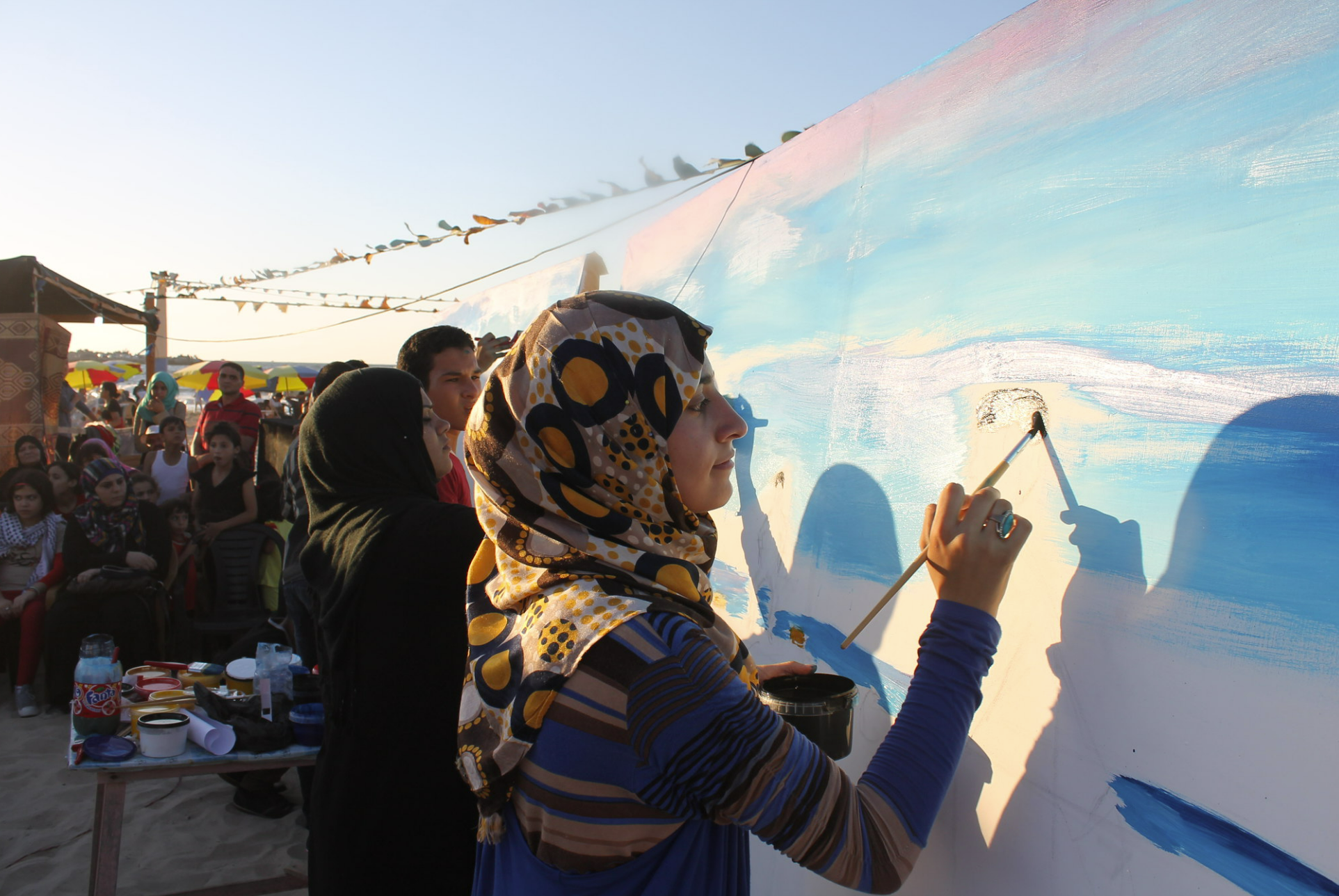
2. “Great March of Return” Protests, Palestine
Child survivors of Israeli massacres gather on the Gaza beach to finish an incomplete match.Catron.CC BY-NC 2.0.
In the Gaza Strip, a Palestinian exclave on the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea, 70% of the population are refugees suffering from the blockade by the Israeli military occupation. Essential needs like electricity, sanitation, and healthcare are a luxury for these refugees, who live constantly under the shadow of military clashes between Hamas and Israel.
The Great March of Return demonstrations (GMR), which began on March 30, 2018, brought a glimmer of hope to the Palestinian refugees in the Gaza Strip. The GMR was a call to end the Israeli blockade and the right of return for Palestinian refugees through non-violent protest at the Gaza border.
But while most refugees marched peacefully, Israeli forces have taken a brutal toll, killing at least 210 Palestinians and injuring over 18,000 since 2018, according to Gaza health officials. The aftermath of these marches has left many with life-long physical and psychological scars from generation to generation. A staggering 80% of all children treated by the United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near East were injured by gunshot wounds. In contrast to the aggressive response from Israel, the largely nonviolent Great March of Return “restored credence to the concept of peaceful struggle”, according to Palestinian journalist and peace activist Ahmed Abu Artema.
3. EndSARS, Nigeria
Protesters at the endSARS protest in Lagos, Nigeria 92. CC BY-SA 4.0.
Nigeria's history of police brutality and unjust criminal investigations reached a boiling point in 2020 when the world was shocked by a viral video of two men being dragged out of a hotel and shot by members of the Special Anti-Robbery Squad (SARS). Despite being established in 1992 to arrest and prosecute those involved in violent crimes, SARS quickly became known for its human rights violations, including arbitrary detention, torture, extortion, and murder.
As the hashtag “EndSARS” quickly spread across social media, fueled by the support of high-profile celebrities like footballer Marcus Rashford and actor John Boyega, the movement transitioned from an online trend to a physical reality. Peaceful protests erupted in cities across Nigeria, from capital Abuja to metropolis Lagos, and in major centers like Ibadan and Osun, as the people took to the streets to demand an end to the police brutality and human rights violations. Though the Nigerian authorities made empty promises to disband SARS, the movement continues to fight for justice and accountability to this day.
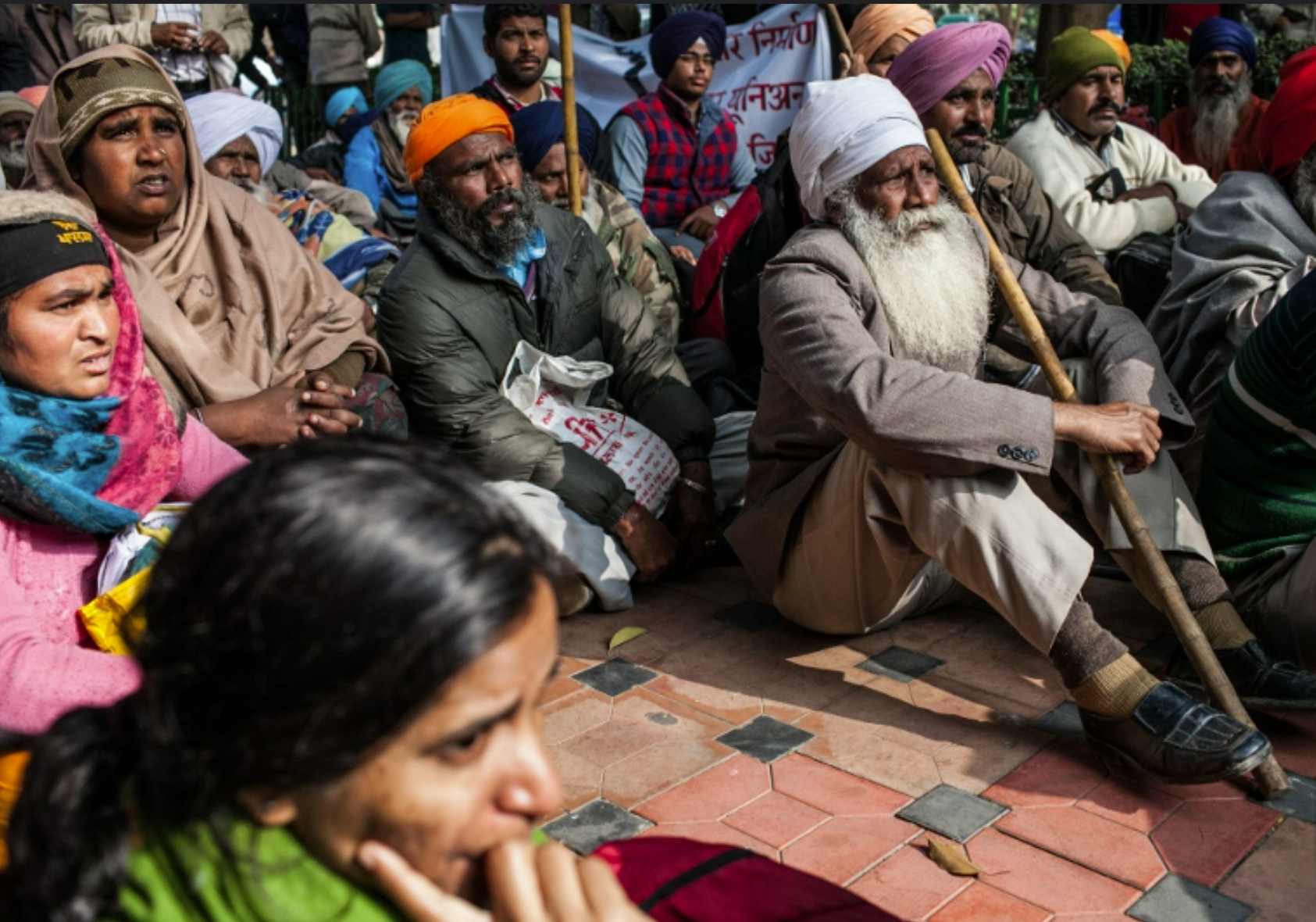
4. India's Farmer Protest, India
Protests outside Odisha Bhawan New Delhi. Brick. CC BY-NC-SA 2.0.
In September 2020, as the pandemic and economic woes plagued the country, the Indian government passed three farm acts that many farmers regard as a breakdown of the existing, stable relationship with agricultural small businessmen.
The farmers were furious and took to the streets, shutting down railways, taking over highways, and protesting en masse in Delhi, Punjab, Haryana, and Western Uttar Pradesh to demand change. On Nov 26, 2020, millions struck in Delhi, calling for a change in labor laws, but were met with violence and teargas. The protests coincided with the Covid outbreak, leading some to view the government's social distancing requirement as a conspiracy to shut down its critics.
After ten rounds of talks, the government agreed to grant farmers’ unions a rare concession in January 2021, with the Prime Minister allowing the repeal of the controversial reform due to public pressure. The Indian farmer protest highlighted the deep frustration with the government's handling of the agriculture sector, which 60% of rural households depend on for their livelihoods.
5. Subway Fare Protests, Chile
Students take part in violent Protests in Santiago de Chile. C64-92. CC BY 2.0.
In Chile, a tiny $0.0 was all it took to ignite social upheaval in 2019. What started as a protest over a 30 peso, equivalent to $0.04, exposed the massive wealth inequality in the country, where the per capita income of the bottom quintile is $140 a month.
During the height of the protests, high school students started to overrun the turnstiles, using the hashtag “Mass Evasion” on social media to encourage others to join the cause. The young protesters soon joined in mass demonstrations by many other Chileans who are frustrated with rising living costs, low wages, and an inadequate education system.
The protests and counterforce led to the death of at least 18 civilians, the burndown of 21 metro stations, and the destruction of several trains, buses, and buildings, including 200 supermarkets. Eventually Chile’s militarized national police managed to suppress the October riots, but the protests and their aftermath shed light on the ongoing fight against wealth inequality in Chile.
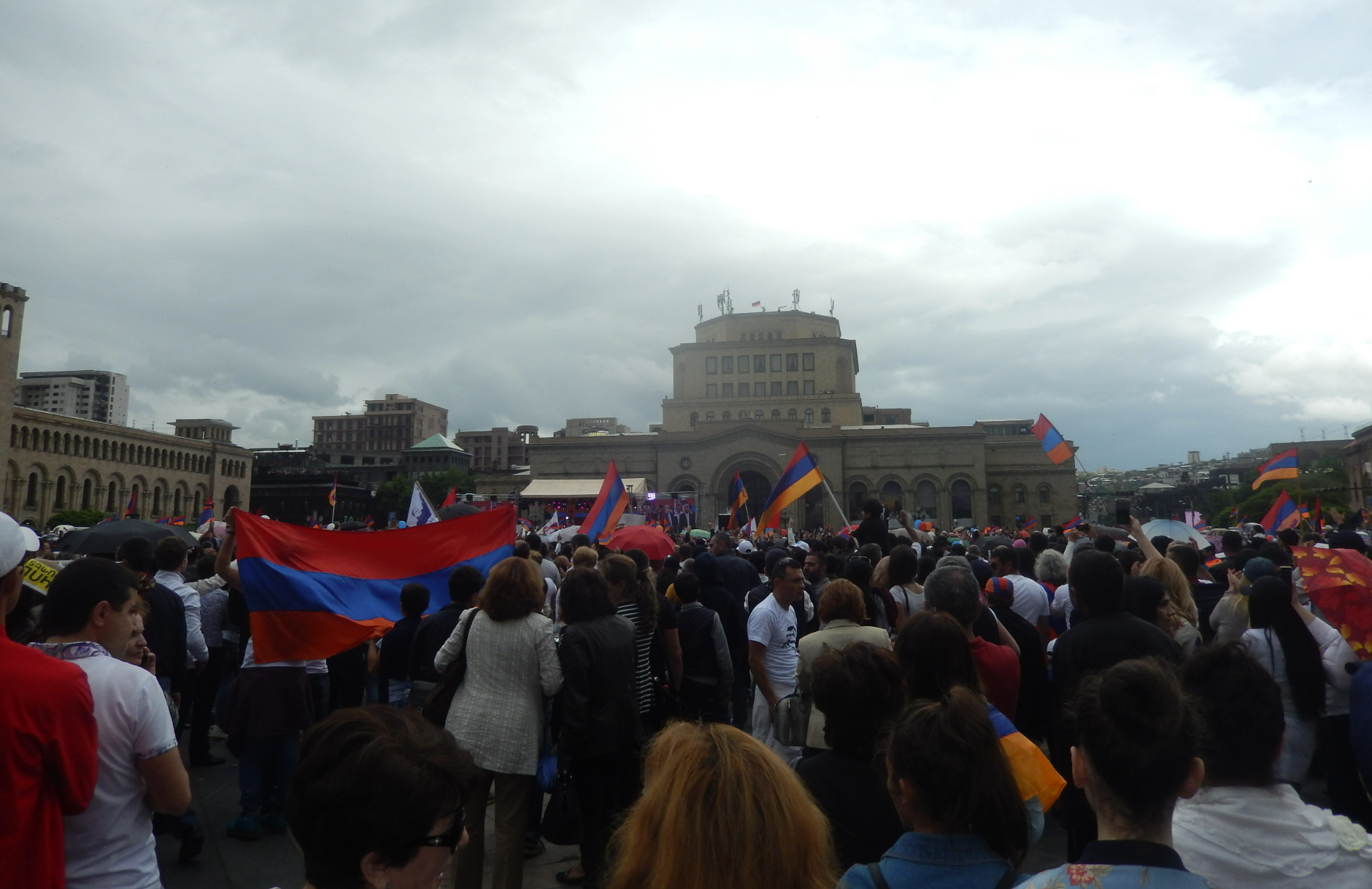
6. Velvet Revolution, Armenia
Velvet Revolution in Armenia. Armineaghayan.CC BY-SA 4.0.
The Velvet Revolution, otherwise known as the “Reject Serzh” civic initiative, is the archetype of a social movement that succeeded in overthrowing an entire regime without a single bullet fired. In 2018, the protest called for the removal of former President Serzh Sargsyan from his third consecutive term. Sargsyan took office as president in 2008, following a violent suppression of anti-government protests in which at least 10 people were killed. A youth movement was established soon after, contributing to the formation of current Prime Minister Nikol Pashinyan’s Civil Contract party.
This peaceful protest was politically motivated, with support from human rights advocates, journalists, and information organizations. The demonstration started on March 18, 2018 when Pashinyan began his protest walk in Gyumri. It reached the peak when over 250,000 protesters gathered in Republic Square for the largest demonstration in Armenia's post-Soviet independence period. The movement was able to unite all Armenians regardless of political views and sparked hope for a lasting democratic government.
7. “Slipper uprising”, Belarus
Protests in Minsk, Belarus. Shnipelson. CC0 1.0.
The “Slipper Uprising” broke out in Belarus in 2021, as protesters used the simple yet powerful symbol of a slipper to push for change. The series of protests followed a controversial presidential election that declared Alexander Lukashenko, the incumbent Belarusian President, as the winner.
The call, “stop the cockroach” came from popular blogger Sergei Tikhanovsky's video, in which an elderly woman compared Lukashenko to the main character of the children’s poem “The Mighty Cockroach.” This nickname, combined with opposition supporters’ demand for Lukashenko's resignation, fueled mass protests in the streets.
Demonstrators showed their defiance against Lukashenko’s rule by waving slippers high in the air. Over 360 people were taken into custody for protesting in just one weekend, but the fire of dissent continued to burn. The “Slipper uprising” proved that even the simplest of symbols can be a catalyst for change.
8. Wildfire protest, Bolivia
March in favor of Evo Morales. Santiago Sito.CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
The heat is on in Bolivia as hundreds of thousands of protesters took to the streets to voice their outrage over President Evo Morales’ government's response to the wildfires that ravaged the country’s forests in October 2019.
Many of the protesters were residents of Santa Cruz, Bolivia's largest city and home to vast areas of the biodiverse Chiquitano dry forests. Protesters called for a “punishment vote” against Morales in the upcoming presidential election. The rallies have drawn massive crowds, with an estimated 350,000 people marching through Santa Cruz in late October, according to reporting from Reuters. The growing public anger and frustration highlight the urgent need for action to address environmental justice and protect the country's precious forests.
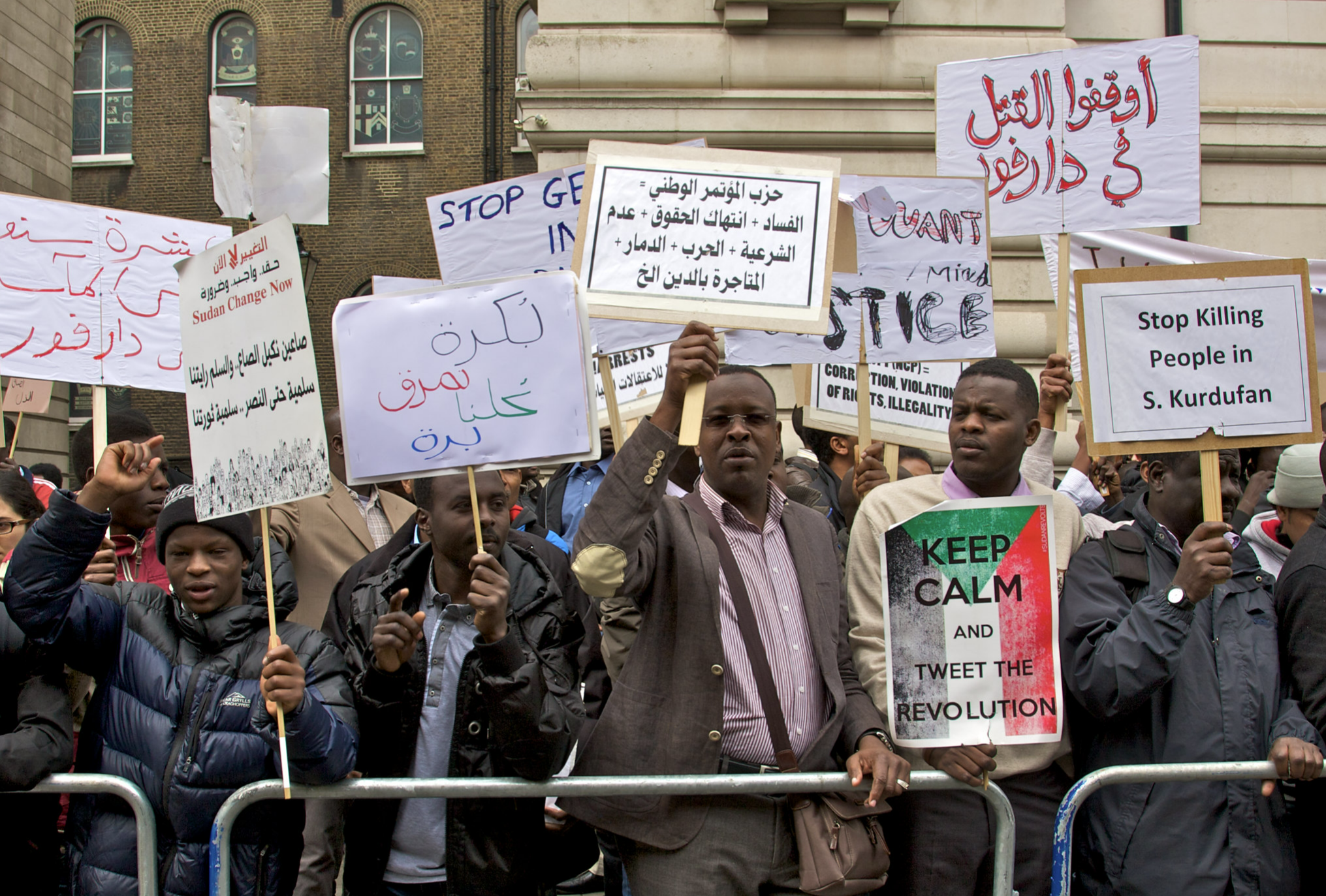
9. “Million-man March”, Sudan
Demonstrators hold placards against the Khartoum regime, April 28, 2013. Sari Omer. Public Domain Mark 1.0.
Sudan’s "Marches of the Millions" was a massive demonstration held in the capital city of Khartoum on June 30, 2019. The nationwide protests were orchestrated by the Sudanese Professional Association (SPA), an influential activist coalition. The protesters had six demands, including a swift transfer of power to a civilian government and aid to the victims of government-initiated attacks.
The nationwide protest also exposed the danger of police crackdown, as national security agencies used violent tactics, such as teargas, to confront the marching citizens. Despite the violence, the protest movement continued, leading to the agreement between the military and its opposition in August 2019. The agreement marked the first step towards a democratic transition for Sudan.
From trending hashtags and posts that amplify the voice of activism on social media, to throngs of individuals marching in the streets and rallying for a shared goal, social movements embody the spirit of resistance against oppression and tyranny. It is through the eruptive energy of collective action that humans can truly exhibit their strength and determination in the face of injustice.
Hope Zhu
Hope is a Chinese international student at Wake Forest University in North Carolina studying sociology, statistics, and journalism. She dreams of traveling around the globe as a freelance reporter while touching on a wide range of social issues from education inequality to cultural diversity. Passionate about environmental issues and learning about other cultures, she is eager to explore the globe. In her free time, she enjoys cooking Asian cuisine, reading, and theater.
The Concept of Time in Different Cultures
How where you live and the language you speak affects your view of time.
Self portrait - Ticking away, MattysFlicks, CC BY 2.0.
Over the summer I would get up at about 7:00 am every morning. By 8:30, I’d have eaten breakfast, showered, gotten dressed, and left for work. When work ended, I’d make sure to always have a plan for what to do after, whether that was hang out with friends, work out, or write something. I’d usually be done with that by around 8, at which time I’d heat something up for dinner, usually a meal I prepared in bulk on the weekend. Afterwards, I’d watch shows until I fell asleep. The next day, I would get up, and repeat.
Like most other English speaking Americans, I view time as linear, heading from a defined beginning to a final end. Every moment is something that I can spend, save, or waste. And, I believe that if I waste too many of these moments, it could have a disastrous impact on my future.
However, this is just one of many ways to view time. Depending on where you live, what you believe, and what language you speak, you may view time in a completely different way.
Monochronic Time and Polychronic Time
Business Calendar & Schedule, photosteve101, CC BY 2.0.
Monochronic Time is divided into small segments, allowing it to be managed and scheduled easily. It is treated as a resource, just like any other. Being used by countries such as the United States, Japan, and Germany, monochronic time is essentially the time model of industrialization. People in monochronic societies tend to be on time to meetings; similar to the schedule I described above, every moment has a distinct purpose. Wasted time can cause great stress, and going off-schedule can mean that all necessary tasks may not get completed. This causes countries with monochronic time to typically have a faster pace of living. Even times of rest are often scheduled, regulating them to certain days or hours.
Four seasons in Japan, vitroid, CC BY 2.0
Polychronic time is much more fluid, where many things can be done at once. Rather than emphasizing the efficient use of each and every moment, people in polychronic societies tend to focus more on their relationships and traditions. Instead of organizing time through rigid schedules, for people in these cultures the seasons, religious calendars, and community life serve as the main signs of the passage of time. India, Mexico, and many other countries in Latin America are Polychronic.
I am currently studying abroad in Ecuador, a largely polychronic country, where I have had to adapt to the different view of times. Unlike the United States, deadlines are rarely strict. I’ve frequently been told lunch is at 1, and then ended up not eating until 2:30. In addition, planning is often more last second. I have lived with two host families, and we often have weekend plans. In each case, I have rarely known said plans until I’m on the way to my destination. While this was stressful for me at first, I have come to appreciate it, as my host families have seemed to have a much easier time living in the present because of it.
Past, Future and Present Oriented Societies
Go Fisherman go - Gokarna India 2011, rundenreisen.org, CC BY 2.0
Past Oriented Countries, like the UK or India, have incredibly long and storied histories. Instead of living for the present alone, past oriented societies see themselves as only the newest iteration of an incredibly old tradition. This causes them to view time in a more casual manner, as the waste of an hour or a day is inconsequential when compared with thousands of years of history.
In addition, many eastern past oriented countries adhere to what is called cyclic time. This is the idea, that like the seasons, time repeats itself, and events are bound to happen again. This means that, whenever considering a major decision, it is critical to evaluate the events of the past.
Getting cab times square, new york, andre stoeriko, CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
Future oriented countries, like the United States, are young and hungry. Without thousands of years of culture to fall back on, citizens of the United States tend to look forward. In future oriented countries, every moment matters, as only by maximizing these moments can a person truly succeed.
Juma River, Amazonas, Brazil, Alexey Yakovlev, CC BY-SA 2.0
Present Oriented Societies are rare, but they do exist. The Indigenous Piraha tribe of the Amazon Rainforest has no past tense in their language. They have no origin story or particular religious beliefs, no reverence for their ancestors, and tell no stories. For them, things just are. What has happened in the past is not relevant.
Language and Time
Washing line, Kate#2112, CC BY 2.0.
Anglophones usually think about time as something that has length. Phrases such as “a long day” or “a never-ending year” are common. In Swedish, time is viewed in this same way.
In Spanish, days are described as “full,” instead of long. Rather than as a line, time is visualized as a container waiting to be filled.
This is most interesting when it comes to bilingual speakers, as it has been proven that they have the ability to, in switching languages, change how they view time. If someone bilingual is spoken to in English, they will view time as a line, and if they are spoken to in Spanish, they will visualize it as a container, giving them a foot in both worlds.
Jeremy Giles
Jeremy is a Writing Seminars and International Studies major at Johns Hopkins University. He is an avid writer and the Co-Founder of Writers’ Warehouse, Johns Hopkins’ first creative writing group. He is an advocate for Indigenous rights, and studies how Indigenous philosophies can be used to help prevent climate change. Using his writing, he hopes to bring attention to underrepresented voices in today’s world.
The Disappearing Snows of Mt. Kilimanjaro
As the mountain's snow melts, its ecosystem faces escalating pressures from tourism, climate change, and deforestation.
Read MoreUS Lags Behind Other Nations in Recycling
Germany, Austria and South Korea recycle 20% more trash than the US. Can they lead the US to a new era of recycling?
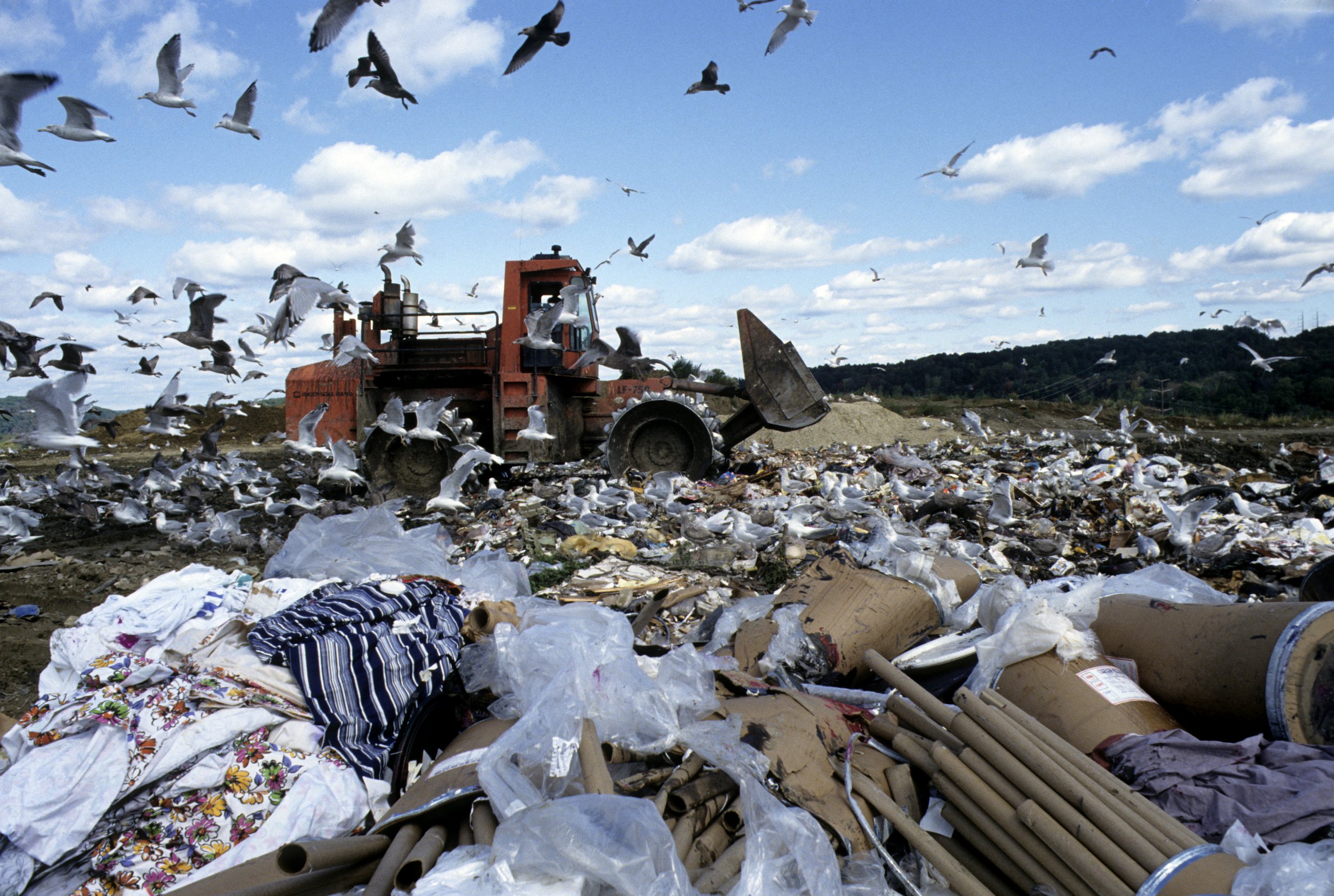
Landfill in Danbury, Connecticut, United Nations Photo, CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
The United States recycles 32.1% of its trash, meaning the other 67.9% of U.S. waste ends up in landfills, is incinerated, or gets lost somewhere else in the environment. Moreover, only 5 to 6 % of plastic ends up being recycled, while 85% of plastic American plastic goes to the landfills, and another 10% is incinerated. These numbers are especially concerning given that plastic is the one of the most difficult types of waste to biodegrade.
Nationally, there are few to no laws in the U.S. that mandate recycling. There have been efforts to change that. On March 5, 2021, Democratic Senator Jeff Merkley and Representative Alan Lowenthal reintroduced the Break Free from Plastic Pollution Act, a bill that would ban single use plastic bags and discourage the use of plastic utensils and straws. In addition, it would increase post consumer recycling minimums to 25% by 2025 and 80% by 2040. However, like many similar bills in the United States, it has not been passed.
While the federal government lags behind, certain states have been considerably more active in promoting recycling. Since 2022, New York has passed two important laws; one demanding that the carpet industry becomes more responsible for its waste and the other allowing consumers to fix their own electronics. California has banned certain types of produce bags, and Michigan has committed to overhauling its recycling system, striving for a 45% recycling rate, albeit without a clear deadline as to when this needs to be achieved.
With that said, even with state efforts, the US still remains far behind the world’s leaders in recycling; Germany, Austria, and South Korea. They recycle 56.1%, 53.8%, and 53.7% of their waste, respectively, each of which is over 20% more than the current US figure and around 10% more than Michigan's new recycling goal. This largely is due to enhanced recycling laws, as well as cultures and practices in those countries that incentivize and engage their populations to be environmentally conscious.
Germany
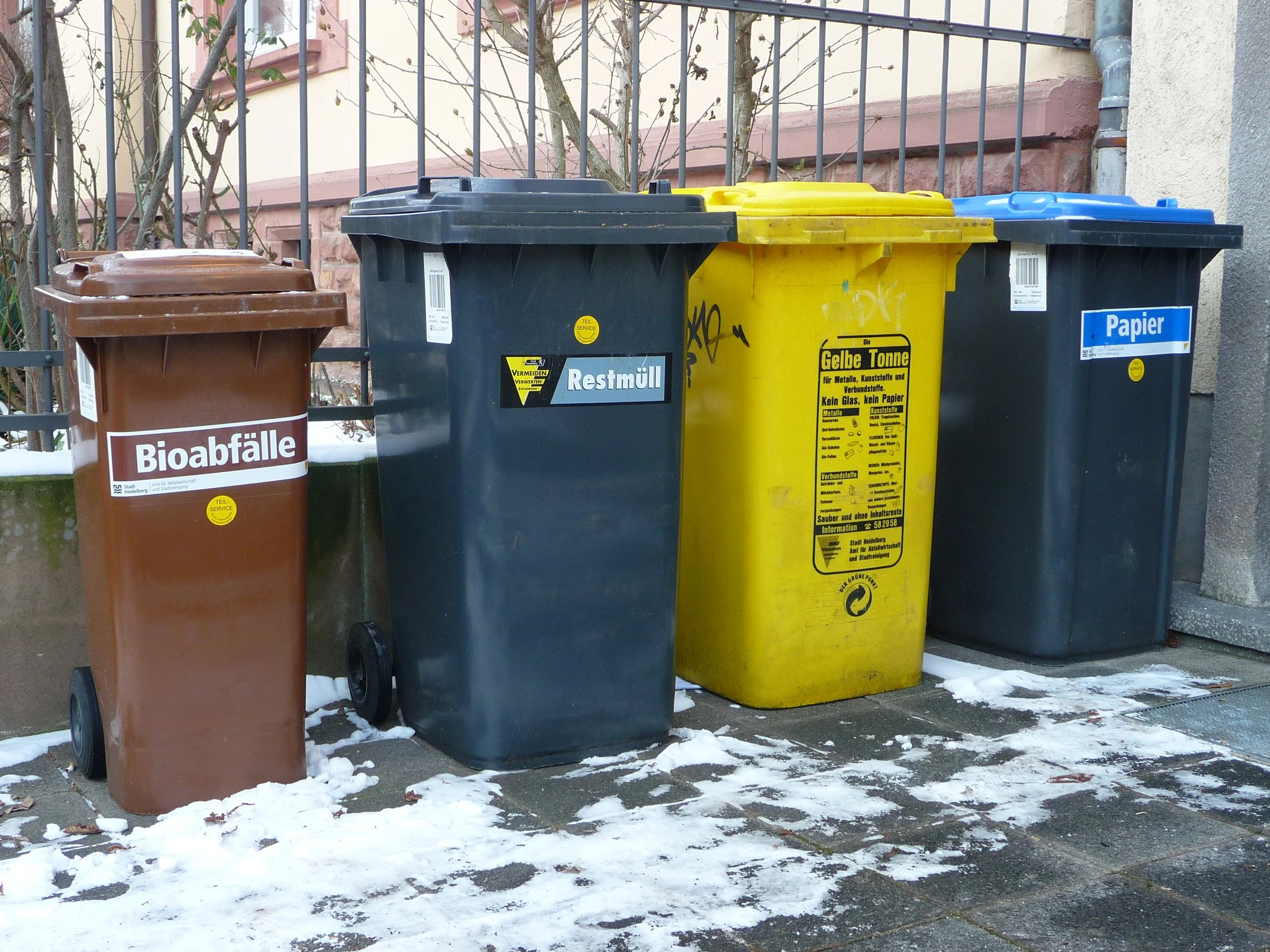
German Recycling Bins, 3268zauber, CC BY-SA 3.0
The first pillar of Germany’s recycling success is its Deposit Refund System (DRS). In Germany, when consumers purchase a bottle that can be recycled, they must pay a deposit between 0.08 and 0.25 euros. Single use plastic bottles and more environmentally harmful products tend to have a higher deposit. Once the items are returned to a retail store, the consumer will be reimbursed for their deposit. This system has proven to be incredibly successful, reaching a 98.4% return rate. In 2024, Germany plans to expand their DRS to include all milk and dairy product containers.
Germany also has a mandatory recycling system. Each household has four different recycling bins: yellow bins for lightweight packaging, green or blue bins for waste and cardboard, black or gray bins for residual and household waste, and brown bins for compostable kitchen and garden waste. If the waste is not sorted correctly, workers at the recycling plant will go through the waste and sort it manually, and the household that failed to sort the waste will be fined.
Austria
Plastic Bags Package, zeevveez, CC BY 2.0.
Three major policies contribute to Austria’s high recycling rate. First, like Germany, Austria has a rigorous recycling sorting system. Second is the country’s blanket landfill ban. This policy instructs that any item with a total organic carbon emission rate of more than 5% is banned from going into landfills, meaning that the most harmful products have to be recycled. Finally, in 2020, Austria prohibited the use of plastic bags, completely removing one of the longest lasting products in landfills, with a decomposition time of 200-500 years.
South Korea
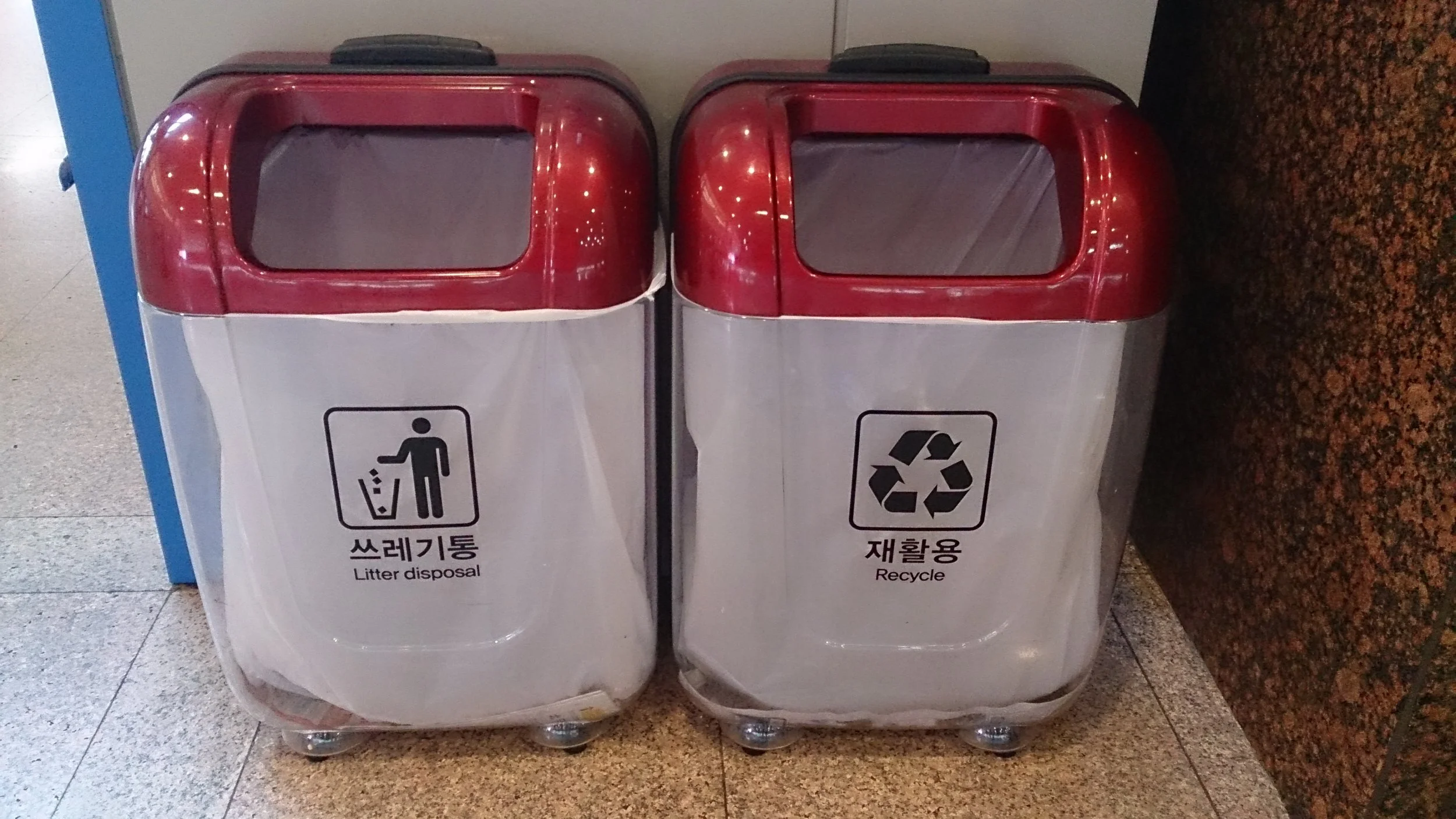
Recycling bin in South Korea, ProjectManhattan, CC BY-SA 3.0
South Korea’s “pay-as-you-throw” recycling system requires consumers to buy specialized food waste bags, costing about 20 cents. The profits from the food waste bags goes straight back into the recycling market, greatly minimizing the cost of recycling to the government. When these bags are full, consumers leave the bag in a special bin. These bags are then picked up and composted, leading South Koreans to recycle almost 100% of their food waste.
In 2022 Keppel, a Singapore-based company, spent about 600 million dollars to buy EMK Co, South Korea’s biggest waste management and recycling company. Keppel expects the value of their investment in EMK to almost double in five years. South Korea has created a system in which private companies are able to make a profit buying and selling waste, greatly increasing the percentage of their waste being recycled.
It's important to recognize that while all these systems are successful in their own countries, the cultural, political, and economic environment in the US is very different from that of Germany, Austria or South Korea. Additionally, the US has a population about four times the size of Germany, the biggest of the three countries, meaning any recycling measures are much more difficult to implement. Yet, with the US lagging so far behind the world leaders in recycling, it would be foolish to not at least consider the solutions that have worked so well for these other countries.
GET INVOLVED
Keep America Beautiful was founded in 1953. Since then, they have created many different recycling programs, including recently a Cigarette Litter Prevention Program. Within a ten year period, they earned their communities over a billion dollars in economic value, have planted millions of plants, flowers, and bulbs, cleaned over 500 kilometers of roads, and collected over 750 million pounds of litter. You can donate to Keep America here.
Ample Harvest Inc. was founded in 2009 by Gary Oppenheimer as a way to reduce food waste by having gardeners donate their surplus food. Beyond this, they have created an Emergency Food Assistance Program to help food insecure families. Currently, they are working with over 62 million gardeners, spread over all 50 states, allowing them to generate billions of pounds of food they donate to over 8,000 different charities. This has given 4,200 different communities a sustainable food supply free of charge and, in 2020 alone, saved 1.6 million pounds of produce from being discarded. You can donate money to Ample Harvest Inc. here and give your excess food produce to your local food pantry here.
The Container Recycling Institute functions much like a Think Tank, researching recycling so they can provide recycling options and insights to local communities and governments. With a perfect 100% score for Finance and Accountability on Charity Navigator, The Container Recycling Institute, since its founding in 1991, has grown into an incredibly trustworthy Institution. As a leading recycling resource, they helped expand the Connecticut recycling Bottle Bill, the largest expansion of this kind in 10 years. In California, they helped raise the annual consumer recycling budget to over 100 million dollars. You can donate to The Container Recycling Institute here and become a member here.
Jeremy Giles
Jeremy is a Writing Seminars and International Studies major at Johns Hopkins University. He is an avid writer and the Co-Founder of Writers’ Warehouse, Johns Hopkins’ first creative writing group. He is an advocate for Indigenous rights, and studies how Indigenous philosophies can be used to help prevent climate change. Using his writing, he hopes to bring attention to underrepresented voices in today’s world.
Travel to NYC, Not for Times Square, but for the Parks
Check out the many green areas in NYC where culture and nature abound.
Read More