The fragrance industry is changing to be more inclusive and representative of its roots, but that doesn’t discount its problematic past.
Read MoreThe Effects of Buddhism on Disability Rights
How the concept of reincarnation has reduced activism for disability rights in Buddhist countries
In comparison to the major world religions, Buddhism flies under the radar. The main three, Christianity, Islam, and Judaism, have often found themselves at the heart of wars, picking death to prove righteousness. This is a concept not found in Buddhism. Life is the highest gift. But the Buddhist belief in reincarnation means that people that are born into disadvantage often pay for it. This is easily seen in people with disabilities. If you are disabled, it is believed that you must have done something wrong in a past life and are consequently paying for it in this one. It is the concept of karma: you must accept your own suffering to be reborn into a better life.
On a global scale, disability rights didn’t enter the equation until post-WWII, gaining steam with veterans advocating for war-caused disabilities. In Buddhist countries it was even later. India didn’t start the conversation until the 1970s, where it wasn’t brought into legislation until 1995 and was only properly defined and rewritten in 2014. India today has one of the largest disabled populations in the world, yet a full definition of what a disability is wasn’t introduced until 5 years ago. This could stem from the cultural connotations associated with disabilities. Having a disability in India causes feelings of worthlessness and shame and often leads to disownment and abandonment by family members. Through modernization and standards put in place by the UN and World Health Organization, these views are changing on a governmental policy level. Unfortunately, just because the laws exist doesn’t mean that they are being implemented. For example, in Cambodia, it was found that fewer than 4% of people qualifying for disability receive the required financial support from the government. To add to it, statistics show that there is an extra expenditure of $40 a month for people with disabilities. The government aid only covers $5 (1/8 of the total cost) so even if those with disabilities get their monthly payment, it covers little of the true cost..
One of the reasons there is such an added cost to having a disability, besides added care, is because often completing education and finding employment is extremely difficult. According to Thailand’s National Statistics Office, 71.5% of people with disabilities over 15 are unemployed. For those living in a city this leads to few options: access social welfare, begging on the streets, or selling lotto tickets. Even so it can be hard to get access to the tickets and the work is unstable. And those in rural environments without access to services are completely dependent on familial support. Thai Buddhism even bans people with disabilities from becoming monks. This was initiated out of fear that people with disabilities would depend on the monastery for support and not be able to complete their duties. One, Monk Ti, was disrobed in 2016 on account of his dwarfism. Becoming a monk is the most noble profession one can have, one that is based on suffering and enlightenment, and yet disabilities completely prevent one from pursuing it.
A major obstacle to changes in disability rights in Buddhist countries is lack of representation. In Cambodia, little effort has been done to increase voting opportunities to those with disabilities and very few are registered to vote, let alone have access to voting areas. NGOs are working to try to set up systems that will start to cause change. In 2011, the General Election Network for Disability Access (AGENDA) was established in Southeast Asia. They are working both with organizations focused on disability and those working with elections to increase advocacy. Between 2014 and 2017, they had a 15% increase in the number of polling stations that had wheelchair accessible ballot boxes.
Through small organizations and increased awareness, stigma around disabilities in Buddhist countries is starting to decrease. The opportunity to participate in all aspects of society from education to voting is hopefully changing as well. Buddhism is built around the concept of suffering and reducing your suffering through your actions so that you may be reborn into a better life. It would be great if those with disabilities didn’t suffer more because of it.
Devin O’Donnell
Devin’s interest in travel was cemented by a multi-month trip to East Africa when she was 19. Since then, she has continued to have immersive experiences on multiple continents. Devin has written for a start-up news site and graduated from the University of Michigan with a degree in Neuroscience.
Iran Under Fire: Protests Break Out Over Hijab Rules
The death of Mahsa Amini in the custody of morality police after being arrested for breaking hijab rules has sparked violent demonstrations across Iran.
Read MoreBOOK REVIEW: Gay Bar: Why We Went Out
With abundant soul and piercing intellect, Jeremy Atherton Lin writes a loving elegy for the bars and clubs that continue to shape who he is today.
You step inside the bar feeling some mixture of trepidation and glee. Through the fog machine mist, a drag queen (or two, or three, or a dozen) tears through a Sylvester number that has the sweaty, dancing throng of twinks, daddies, bears, cruisers, pill-poppers, club kids and assorted deviants jumping so that the floors tremble with their weight. You order a drink, then another, and since the bartenders pour heavy, you’re already feeling some type of wonderful. Everyone at the bar is shouting over the music at their dates, or eyeing handsome strangers, if they haven’t already escaped to the dark, dank corners of the club to perform acts unmentionable in polite society. But this is no polite book. “Gay Bar: Why We Went Out” by Jeremy Atherton Lin seizes you be the hand and leads you to the dance floor. That feeling? Gay euphoria. Or someone just slipped some poppers into the fog machine.
“It’s starting to smell like penis in here. . .” the book begins, and you can imagine where it goes from there. The book veers through categories of nonfiction one would think incompatible: cultural critique within pornography, personal memoir beside centuries-old queer history, gay clubbing tales after meditations on longing and identity (namely, longing for identity, or an identity of longing). “We go out to be gay”, Atherton Lin declares. He spends the book figuring out what that entails. Between his vibrant voice, daring diction and raunchy reminiscences, Jeremy Atherton Lin simply can’t not be interesting.
Nowadays, you’re less likely to find the kinds of bars that were so formative to Atherton Lin’s queer coming-of-age. In an era of safe spaces and trigger warnings, he reflects, “ to be violated was my expectation back when I [first] ventured in”. Not that the new rules are unwelcome. “Gay Bar” bears witness to more than it judges the ebb and flow of queerness over the course of the author’s life. Historically speaking, his life passes through the end of the AIDS crisis, surges in homophobic violence and the gentrification of queer spaces. “The misogynistic old trope,” he writes, referencing the “fag hag” stereotype, “of a lonely heart attached to sexual criminals out of compatible ostracization had been replaced by one of basic bitches latching on because the gays turned out to be the winners”. What they won, however, is unclear.
“Gay is an identity of longing , and there is a wistfulness to beholding it in the form of a building,” Atherton Lin muses on gay bars. The dichotomy between the terms queer and gay acts as a schism between two generations of gay men, those two generations being Lin’s own and the kids who came after. Queer is “somehow both theoretically radical and appropriate in polite company”. Gay, however, is “like a joke or an elegy”. Indeed, “Gay Bar” reads like an elegy for the club scenes that seemed to be dying even at their pinnacles. Atherton Lin experiences gay clubs in Los Angeles, San Francisco and London, and though he often passes off personal experience as canonical gay history, his experience makes one fact undeniably clear: gay bars aren’t what they used to be.
At the same time, often in the same breath, Atherton Lin recognizes that “gay bars are actually transitioning–in that they’ve likely been something else, and will change again in the future”, but precious few are the historical records of these gay institutions. “Still now,” he writes, “when people say of East London It’s not like what it used to be. . . , I think: One could never really know what that means”. Very rarely do younger gay men seek out their own history either. As a self-proclaimed “daddy” conversing with younger twinks and twunks, Atherton Lin writes, “[t]hese boys don’t need my wisdom. Camaraderie, perhaps; it’s not guidance they’re after”. What’s left in the historical vacuum is rumor, hearsay, propaganda and a fair share of badmouthing. Certainly, the sins of gay bars are numerous–femmephobia, racist door policies and inappropriate groping. But “Gay Bar” asks the question: does rebellion against these institutions for their wrongs mortally endanger the communal memory on which the queer community is based?
Sadly, “Gay Bar” doesn’t answer this question, or many others. Nonfiction, once the venue for resolving inner turmoil and nagging questions, has become a genre for simply venting these confusions. Of course, a personal memoir needn’t answer to anybody or anything, but when Atherton Lin cites queer theorists like Judith Butler or Michael Warner, one gets the impression that he is using their erudition to suggest an argument he doesn’t want to run the risk of making. In true camp fashion, he ends most lines of argument with a witty quip, rather than a resolution to the passage’s central problem. For other writers, this would sunder the book, but since galavanting in camp fashion seems to be his primary goal, Atherton Lin still succeeds in winning the reader over, if through his electric prose and not his sound argumentation.
Still, like any gay bar, it’s hard not to love “Gay Bar”. Its endlessly interesting anecdotes, hilarious jokes and piercing reflections make for a polyphonic book that defies categorization. It is so much like the queer spaces that it describes: intersectional, cross-pollinating, intoxicating and above all fun. With countless bars–and many gay ones–closing under the stress of the COVID economy, Lin’s book provides the perfect elixir for cabin fever. When reading “Gay Bar”, you’ll often feel like you’re in one.
Michael McCarthy
Michael’s fiction, nonfiction, interviews, and book reviews have appeared in The Adroit Journal, Barzakh Magazine, Beyond Queer Words, and Prairie Schooner, among others. Currently, he is transferring from Haverford College to University of Carlos III in Madrid, Spain, where he intends to major in the Humanities. He is also seeking publication for his poetry chapbook Steve: An Unexpected Gift, written in memory of his late uncle. He can be reached at @michaelmccarthy8026.
Peace and Stability in Uruguay
The second smallest country in South America, Uruguay is one of the most stable and prosperous countries in all of Latin America.
Montevideo, Uruguay. Gustavo. CC BY-NC-SA 2.0
South America’s Uruguay has been one of the most stable countries in the world for years. It’s the second smallest country in South America, and despite not having many natural resources, they have still had a lot of economic growth and prosperity. Uruguay has in general been a symbol of peace and social inclusion, despite its small population. Their social attitudes are extremely progressive and lenient, especially towards things like legalizing marijuana and same-sex relationships and marriages. Many countries in Latin America suffer from violence, corruption and oppression, but Uruguay has grown in its economic, political and social spheres. Their policies towards immigration are also relatively open, and the people tend to welcome foreigners who want to move to the country. They have the largest sized middle class, proportionally, within Latin America and have been called the “Switzerland of Latin America” due to their economy, size, and industrial, trade, and service sectors. Uruguay has one of the highest GDP per capita in the region, and the income distribution is very equal. The World Economic Forum claims Uruguay is the most equitable country in the world.
Uruguay’s main exports are agricultural products, such as corn, rice soybeans and wheat, as well as meat products, especially dairy. They love meat, especially beef, and their national dish is asado, which is literally just barbecued meat. Interestingly enough, pasta is another widely consumed food due to the arrival of Italian immigrants that came during the late 1800s and early 1900s. Though Uruguay’s pasta has Italian inspiration, Urguay has its own spin on a widely-loved cuisine. In terms of beverages, yerba mate is one of their favorites, a tea-like drink that has become a respected cultural aspect for the people. There was a military regime in the 1970s that strongly discouraged public gatherings, and so people would get together to drink yerba mate and socialize. This tradition has carried on even today and people now love to gather, drink it, and talk.
Their tourism industry is another factor that has increased their economic growth. People love Montevideo, the capital, and say that it is has the highest quality of life out of all the cities in South America. Punta del Este is an extremely popular beach resort that doubles as a college town that also adds to their tourism industry. It helps that the country is relatively safe, ranking 32nd on the 2020 Peace Index, compared to the United States’ 121st. Because of this, the country has had a solid 15 years of positive economic growth, and their poverty rate decreased by 22% from 1999-2019. In addition, their literacy rate is extremely high, the highest in all of Latin America, and both education and healthcare are free and accessible to everyone.The government is very transparent, considered the least corrupt government in Latin America and the 23rd least corrupt government in the world. Their political stability in the Global Economy was rated as 1.05 in 2020 (the scale is from -2.5 – 2.5) and they have had an overall upward trend since 1996. The United States, in comparison, was rated -0.02 in 2020, with a major downward trend since 1996.
Shot of Montevideo. Gustavo. CC BY-NC-SA 2.0
Despite all this, Uruguay’s rise in prosperity hasn’t always been the most stable. The rate at which their poverty levels is decreasing also slowed down and stagnated a bit in the past few years, and, like most countries, Uruguay suffered from the pandemic. The poverty rate increased by 2.8% the first year of the pandemic, even through Uruguay’s preexisting social protection systems and the new measure they introduced in response to the virus. In 2021, however, the economy recovered a little and the poverty fell from 11.6% to 10.6%.
The country as a whole, though, did not have to make many changes in order to adjust to virtual life. Since they place such a high value on education and technology, they were able to easily use online platforms, and their universal health care allowed them to take preventative measures at a lower cost than other countries. All this combined allowed Uruguay to slowly reopen their schools earlier and faster than other countries in the region. Like many countries in the world, their poverty rates, though low, are disproportionate in areas such as race, sex and religion , but they do have a strong commitment and desire to strengthen the country and create policies to overcome these factors.
Katherine Lim
Katherine is an undergraduate student at Vassar College studying English literature and Italian. She loves both reading and writing, and she hopes to pursue both in the future. With a passion for travel and nature, she wants to experience more of the world and everything it has to offer.
Devastation in Pakistan: Information and How to Help
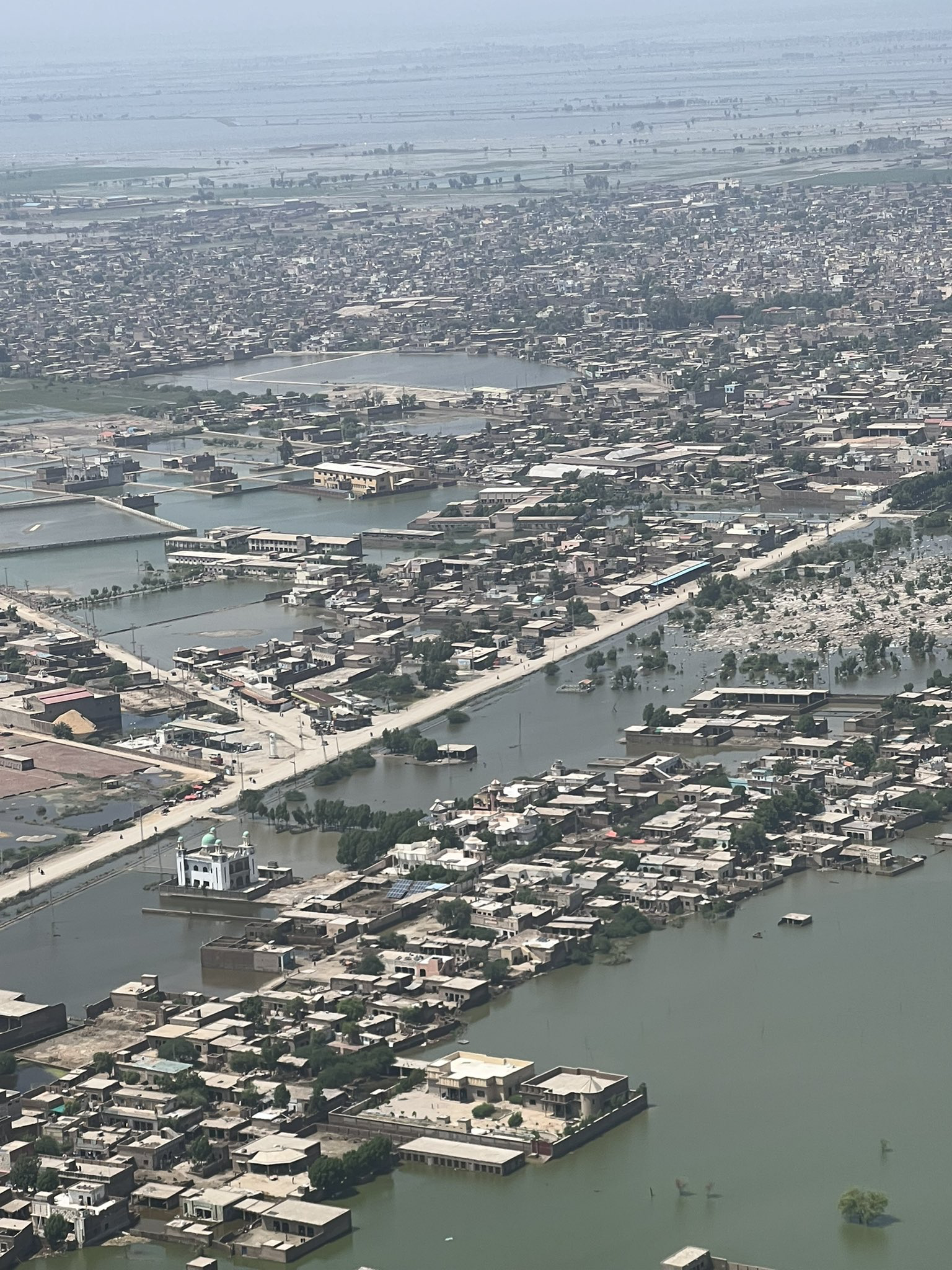
One third of Pakistan is underwater due to flooding, killing more than a thousand and destroying the homes of millions.
Sindh province in Pakistan underwater 2022. Ali Hyder Junejo. CC BY 2.0.
Since June of 2022, Pakistan has been hit with floods, monsoons and tsunamis. These floods have tragically ended the lives of thousands, including many children, and forced millions of families to abandon their homes, as an astonishing one third of the country is underwater as of September, causing the death of approximately 1,500 people. Many people are wondering how an environmental disaster of this scale is possible: how have the floods not ceased for months, and how can people around the globe help the people of Pakistan? Scientists say it all comes back to climate change. For about two months prior to the floods, Pakistan experienced severe heat waves, with temperatures ranging from 40 degrees celsius to a high of 51 degrees celsius (a range of 104 to 123 degrees fahrenheit). These heat waves alone qualify as an environmental crisis, but what they led to was much worse.
There are two primary reasons that this heat wave led to flooding. The first is that hot air tends to contain more moisture than cold air, leading to higher rates of rainfall following the heatwave. The second is a devastating effect of climate change that has been seen all over the world: higher temperatures cause glaciers to melt, flooding into bodies of water which then overflow. In the case of Pakistan, this overflow of water has caused dams to break, leading to extremely dangerous floods, with water unexpectedly rushing onto the land.
Previous flood in Pakistan, 2010. Oxfam International. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
These disastrous climate events have resulted in destroying agricultural products, displacing roughly 30 million Pakistanians and killing over 1,000 people, with around 500 being children. The destruction of crops has led to further economic crises as well as increased hunger and disease. The chief of the World Health Organization noted an increased risk of several diseases in Pakistan, such as gastrointestinal diseases, skin infections and respiratory illness. Additionally, many hospitals have been destroyed, leaving the country even less prepared to address the millions of people in need.
Get Involved
There are several organizations which are sending aid to Pakistan right now, such as UN Women, which is sending food, medical supplies and sanitary products to Pakistan. There are also several Pakistan-based organizations to support, such as HANDS Pakistan and the Indus Hospital & Health Network, which provides free healthcare to people in need in Pakistan, at a more-important-than-ever moment like this.
Calliana Leff
Calliana is currently an undergraduate student at Boston University majoring in English and minoring in psychology. She is passionate about sustainability and traveling in an ethical and respectful way. She hopes to continue her writing career and see more of the world after she graduates.
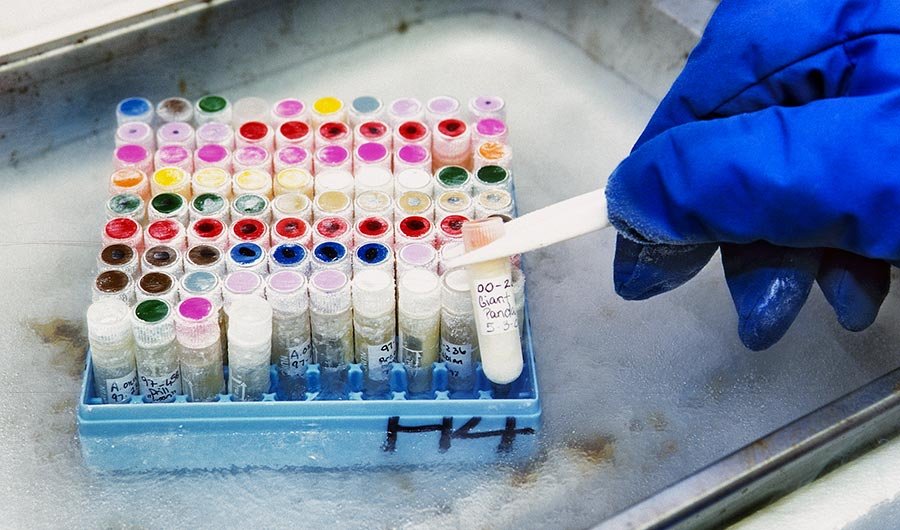
Frozen Zoos Might Be The Key to Saving Dying Species
The San Diego Frozen Zoo is the largest collection of animal gene samples in the world, and might be the answer to saving endangered animals from extinction.
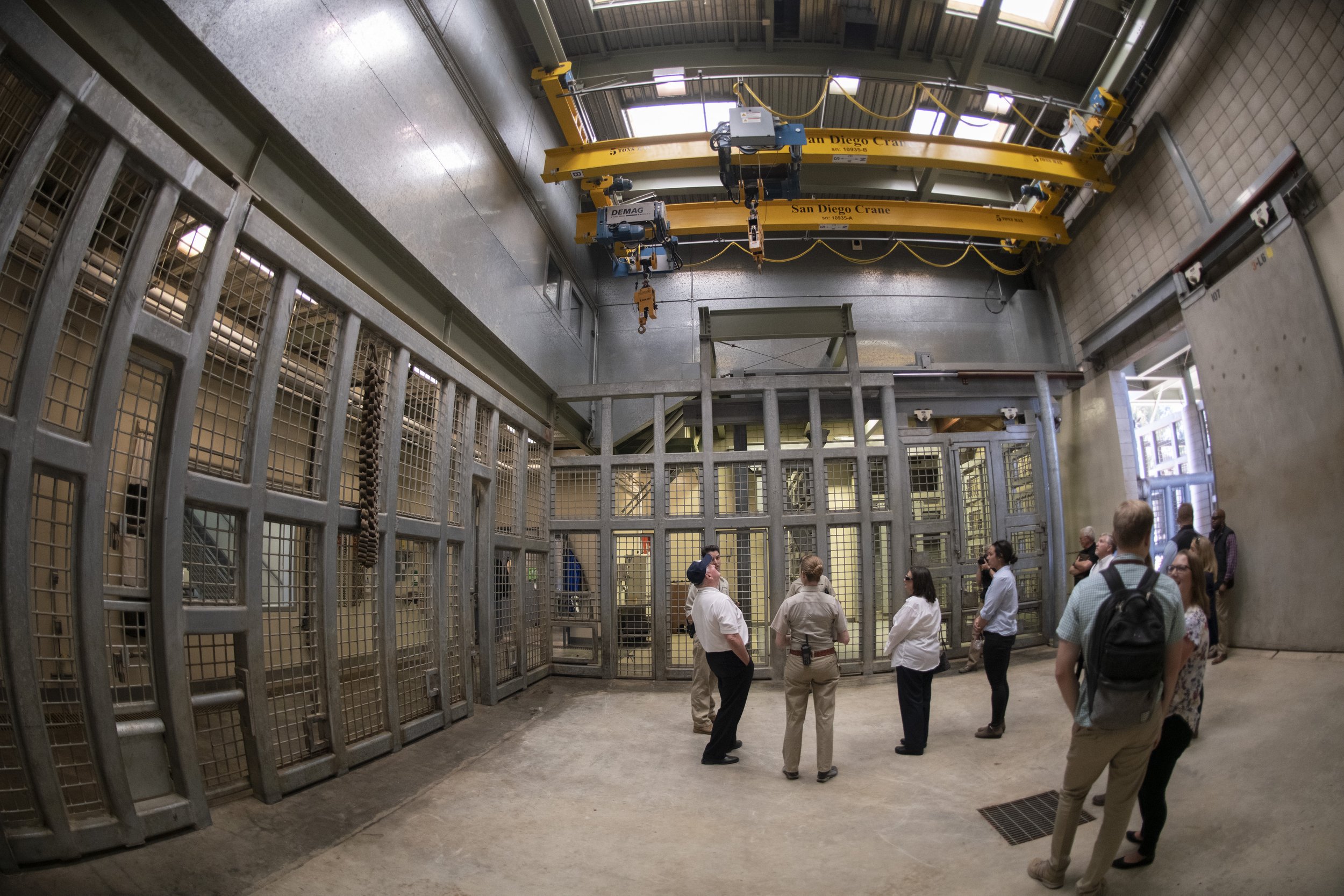
A collection of vials containing gene samples from different species of animals. San Diego Zoo. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Although the San Diego Zoo regularly receives a few million visitors every year, very few, if any at all, are aware of a collection much larger than the one on public display. Diligently maintained by a team of dedicated scientists and researchers, the San Diego Frozen Zoo houses gene samples from over 10,000 individual animals, all being preserved in the hopes that they will be able to help resurrect the rapidly dwindling populations of many at-risk species. It is the largest and most diverse collection of its kind in the world, and even includes a sample from the extinct po’ouli bird that vanished in 1988.
This ingenious strategy of species conservation can be traced back to the work of the German-American pathologist and geneticist Kurt Benirschke. He began his collection of skin samples from rare and endangered animals back in 1972 while working as a researcher with the University of California San Diego, and he quickly grew it into the very first cryobank of its kind at the San Diego Zoo. While Benirschke unfortunately passed away in 2018, his legacy is still very much alive in the continuing efforts of the growing team of scientists at the Frozen Zoo, who contribute their expertise on everything from recovery ecology and biodiversity banking to population sustainability and disease investigations.
Kurt Benirschke, the late scientist and founder of the San Diego Frozen Zoo. San Diego Zoo. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Using cutting edge in vitro fertilization technologies, the Frozen Zoo has made huge strides towards developing a sustainable procedure, using artificially inseminating sperm that has been frozen for extended periods of time to produce viable offspring. Early attempts saw the successful development of cheetah and white rhino embryos in the lab, as well as the birth of chicks from a number of pheasant species, all from cryopreserved sperm. Perfecting this method would allow scientists to increase populations of rare and endangered species by introducing animals delivered in vitro back into the wild.
Another strategy the Frozen Zoo is looking into involves the genetic cloning of endangered species using the frozen genetic material in their collection. Since 2001, the zoo has cloned the Black-Footed Ferret, the Indian Gaur (an Asian humpbacked ox), the Banteng (a Southeast Asian species of cattle) and Przewalski’s Horse (a species from Mongolia that was extinct in the wild until not long ago). While their cloning process is still very much in the works, any advances in this type of cloning and genome sequencing can also be used to better understand the biology of endangered species in the wild and help with current conservation efforts.
Scientists from the Frozen Zoo successfully cloned a wild horse (center) believed to be extinct in the wild using cryopreserved sperm. Tanya Durrant. CC BY-ND 2.0.
One of the zoo’s most recent projects has a slightly different focus: they are putting together a database of unique barcodes to help identify species of primates and deer being transported as part of the illegal bushmeat trade. Another recent collaboration with The Scripps Research Institute involves members of the zoo’s Reproductive Sciences and Conservation Genetics teams looking for new state of the art stem cell technologies that could help to revive the critically endangered Northern White Rhino. This collaboration is also just the first step in the zoo’s goal to create a worldwide network of similar cryobanks, which will share knowledge and resources to continue developing an even more diverse bank of genetic material in support of species conservation.
The Frozen Zoo stores thousands of samples of genetic materials in their cryobank. US Department of Agriculture. CC0.
For those interested in getting involved, the zoo runs a number of educational opportunities for high school and college students in the form of fellowships, internships and externships, as well as a master’s degree program in conjunction with Miami University, Ohio. They also have a regular schedule of seminars run by various experts in the field which are open to the public.
Tanaya Vohra
Tanaya is an undergraduate student pursuing a major in Public Health at the University of Chicago. She's lived in Asia, Europe and North America and wants to share her love of travel and exploring new cultures through her writing.
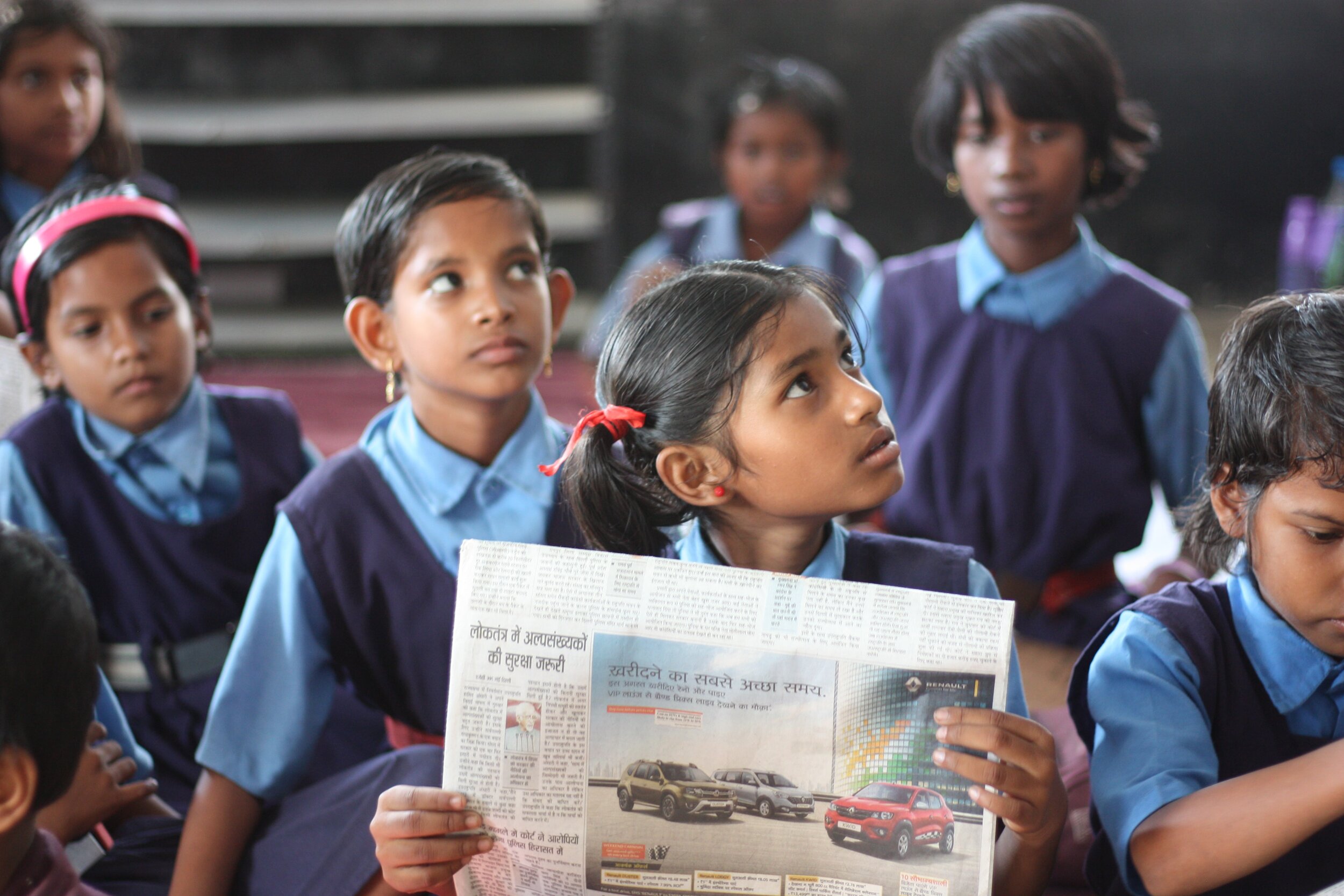
As education increases, more women in rural areas are able to access schooling. Here, young girls in India’s Chhattisgarh state attend government school in their uniforms. Jaikishan Patel. Unsplash.
The Gender Education Gap is Narrowing. Here’s How You Can Help Close It
More girls are enrolling in education than ever before, and the gap between educated women in men is narrowing. Based on a report given by UNESCO, 180 million more girls have enrolled in primary and secondary education since the Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action, a commitment signed in 1995 by 189 countries in which they pledged to advance the rights of girls and women. The report shows that the global enrollment rate for girls in school increased from 73% to 89%, and the biggest improvements are seen in sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia, especially in India. The reasons behind this inequality are historical, social and economic, as barriers like poverty and rigid gender roles place large burdens on accessing schooling.
Young men and women studying in the classroom in Klaten, Indonesia. Husniati Salma. Unsplash.
This push for women’s education did not stop at the primary level, with three times more women enrolling in universities than 25 years ago, and the most significant progress is seen in North Africa and Western Asia. Morocco has particularly excelled, reaching enrollment parity in 2017 after more than 20 years of the rate of enrollment being just 30 women for every 100 men. The report found that although women are present in the classroom more frequently, there is still a culture of dismissal revolving around women’s education, so the efforts toward educating women are now focusing on representation and validation.
Ways You Can Get Involved:
In relation to the report, a personal way to involve yourself is to participate in the #Iamthe1stGirl campaign, started by the Global Education Monitoring (GEM) sector of UNESCO. This campaign asks women and girls who were the first of their family to graduate from high school and/or university to share their own stories of education and success. By sharing your own story, you can inspire women and girls to continue fighting for their right to be educated. The stories have been shared on Instagram and Twitter by the GEM account, and while the campaign did not go viral, the social media interactions show girls being inspired to continue their education in real time.
There are several ways to get involved financially, and most involve the direct sponsoring of a woman in the process of getting her education. World Vision has a simple and effective sponsoring process, and your money goes toward not only providing school supplies, but also ensuring that proper sanitation and transportation is offered to women at school.
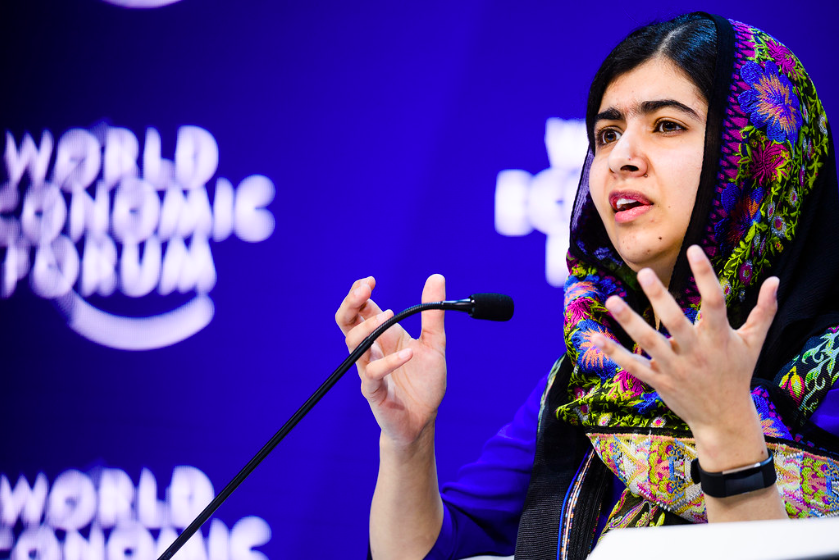
Malala Yousafzai speaking on the creation of a shared future through education and empowerment. World Economic Forum. CC BY-NC-SA 2.0.
A fund with a story you may be familiar with is the Malala Fund, started by Pakistani girls’ education activist Malala Yousafzai in 2013 “to champion every girl’s right to 12 years of free, safe, quality education.” The money in the fund goes toward their board along with the leadership council and staff, championing “the creation of a more equal world by making sure all girls can go to school.”
On a smaller scale, you can ensure the girls and women in your community do not face barriers to their education by creating or participating in school supply and sanitary product drives and by sharing your own story about education.
Donations collected during a 2015 school supply drive in Tallahassee, Florida. flguardian2. CC BY-NC-SA 2.0.
There are several ways to get involved in closing the gap. To donate towards causes that sponsor women’s education through providing instructors and supplies, you can visit World Vision or Malala.org.
In order to make sure that menstruation does not interfere with learning, you can donate money and time to several organizations that supply period products like, DoSomething.org. Two other organizations that also supply products are, DayForGirls.org and BintiPeriod.org. Days for girls is a women’s equality organization so it provides other avenues of involvement as well.
To donate school supplies you can visit, Kinf.org to help students in the United States. Another school supply organization, Classroom Central, finds local schools in need of donations. For international involvement, you can directly donate to UNICEF USA.
For those who want to learn more information and sign petitions, Plan International provides both on their website, Plan International. Another petition to sign can be found on One.org where you can pledge to support the closing of the gender education gap. Lastly, you can even start your own fundraiser for school supplies and education funding at Room to Read.
Renee Richardson
Renee is currently an English student at The University of Georgia. She lives in Ellijay, Georgia, a small mountain town in the middle of Appalachia. A passionate writer, she is inspired often by her hikes along the Appalachian trail and her efforts to fight for equality across all spectrums. She hopes to further her passion as a writer into a flourishing career that positively impacts others.
The Great Pacific Garbage Patch
In the middle of the Pacific Ocean, plastic debris gets caught in ocean currents that drag it all together, creating a massive island of trash double the size of Texas
Plastic from the Ocean. Kevin Krejci. CC BY 2.0
In the Pacific Ocean lie two massive islands of garbage, known as the Great Pacific Garbage Patch. The Western Garbage Patch is located near Japan, and the Eastern one is in the waters between Hawaii and California. Combined, both patches are estimated to span 1.6 million square kilometers (over 620,000 square miles). This is equivalent to twice the size of Texas, the second largest state in the United States in terms of land, and it is not even an exact measurement. Due to the fact that a lot of marine debris sinks to the ocean floor, the exact size of the patches is unknown. Trillions of pieces of plastic have all found their way into the ocean and were carried to these island patches by various ocean currents.
Washed up plastic. Fabi Fliervoet. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Part of that problem is because much of the debris consists of microplastics, small pieces of plastic 5 millimeters or less that have flaked off from larger items. These microplastics are also easily ingested by fish and other marine life, which is absolutely damaging to them. The chemicals in the plastic will affect the animals, which can start affecting the food chain as the smaller ones get eaten, and it could eventually make its way up to humans. It is hard to determine the full extent of the effects of them in human bodies due to the fact that we don’t know how long microplastics stay in our bodies, but studies show microplastics harm cells. Microplastics are the most dangerous and harmful part of all the litter in the ocean due to these effects.
Besides humans, the litter in the ocean is harmful to marine life. There are turtles that ingest plastic bags, thinking they are jellyfish, birds that mistake some bits for fish eggs and feed it to their chicks, causing their organs to rupture and other sea animals that die of starvation because their stomach is full of plastic that has no nutrients. Beyond that, some plastics will release methane and ethylene when exposed to sunlight, both of which are greenhouse gasses that contribute to global warming. In addition, the microplastics affect the efficiency of photosynthesis in plankton, which in turn affects the ocean’s ability to absorb carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Microplastic negatively impacts so many parts of life and the environment.
Cleaner beaches. Paul van de Velde. CC BY 2.0
To Get Involved
There are many organizations that fight plastic pollution in the ocean. As most plastic ends up in the ocean, a lot of them are focused on helping reduce the amount there, but there are organizations that aim to reduce the use of plastic in the world overall. For example, the Oceanic Society lowers plastic use by raising awareness of its effects, reducing usage in tourism practices and by supporting coastal communities. The Plastic Soup Foundation based in the Netherlands aims to prevent plastic from entering the environment in the first place. By sharing knowledge and monitoring research related to plastic pollution, the Plastic Soup Foundation educates people and formulates projects to aid in their goal. It also advocates for diminishing individual plastic usage and creating regulations and legislations for decreasing plastic.
To learn more about the Oceanic Society, click here.
To learn more about the Plastic Soup Foundation, click here.
To learn more about the Plastic Pollution Coalition, click here.
Katherine Lim
Katherine Lim is an undergraduate student at Vassar College studying English literature and Italian. She loves both reading and writing, and she hopes to pursue both in the future. With a passion for travel and nature, she wants to experience more of the world and everything it has to offer.
Dust Storms: Syria and Iraq’s Orange Skies
Syria and Iraq are experiencing dark orange skies due to an uptake in dust storms these past few months.
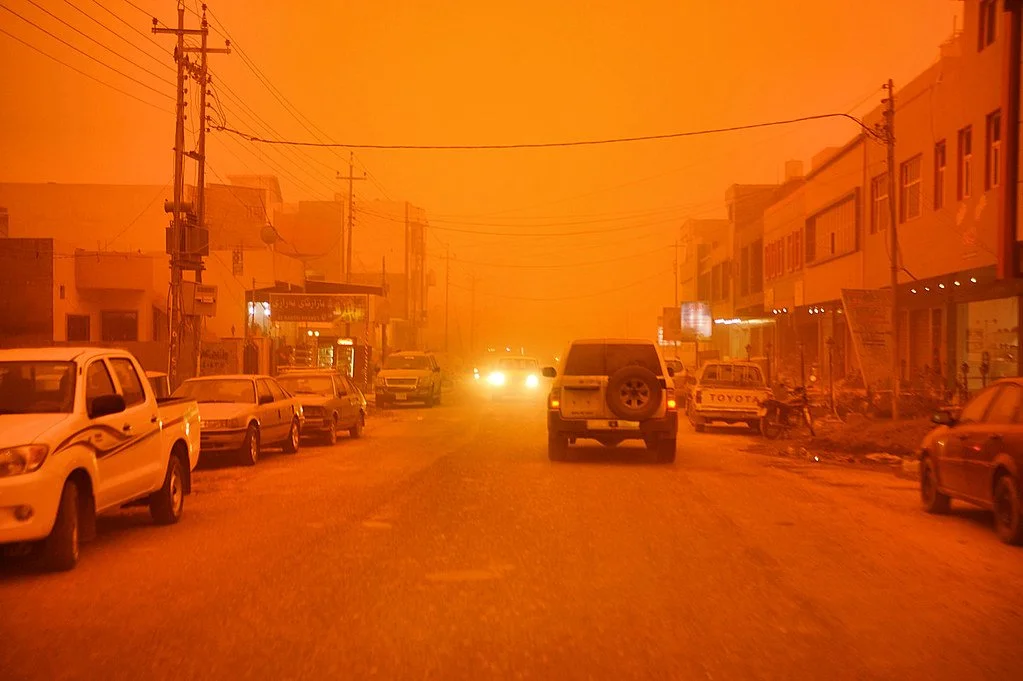
Orange dust air in Kurdistan. Lachica Photo. CC BY NC-ND 2.0.
Since March, the Middle East has been plagued with dust storms that have continued into early June. Accredited to climate change, these severe dust storms have been causing mass destruction around the Middle East, forcing the closing of schools and places of work, reducing the air quality over extended periods of time and even sending people to the hospital. With citizens unable to breathe outside their homes and damage being done to property and people, the Middle East is in a state of emergency.
The Middle East is a region familiar with dust storms. Dubbed “Shamal Winds”, the northern wind current that often rips through Middle Eastern areas like Iraq has sent storms to the area for decades. However, the instances taking place this year are said to be far too frequent compared to previous national averages, and climate change is to blame. Typically, the Middle East will face on average around 270 dust storms a year. The Ministry of Environment of Iraq believes that number is predicted to rise to around 300 storms by 2050.
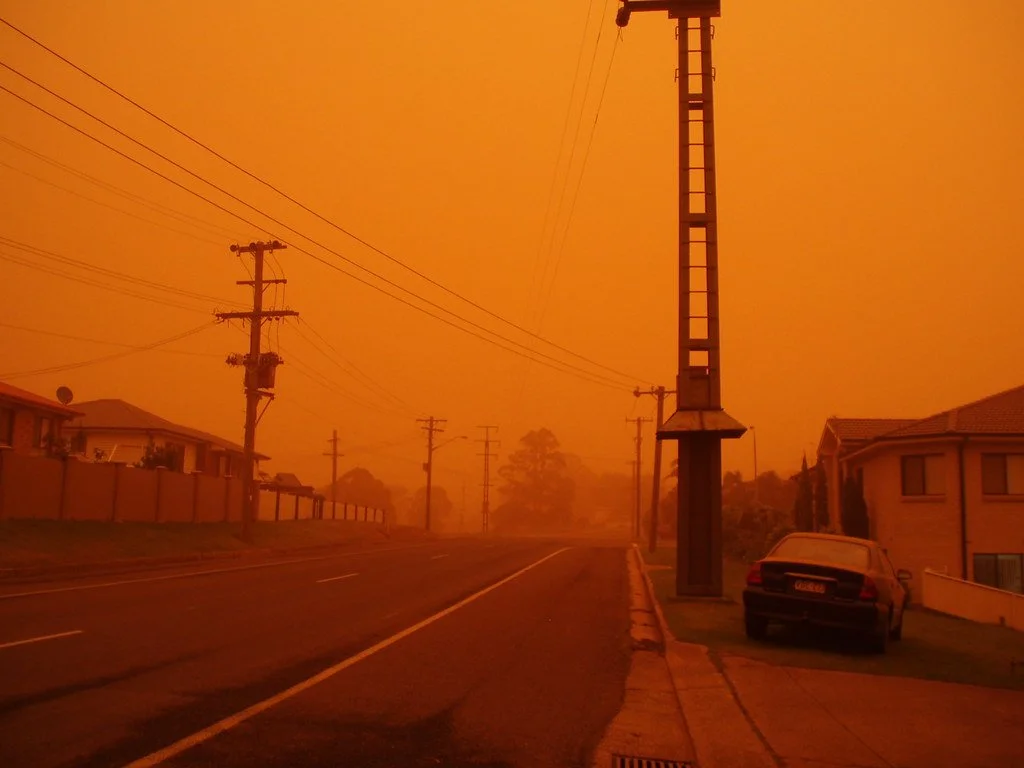
Orange sky after dust storms. Kaptain Kobold. CC BY-NC-SA 2.0.
The main effects of climate change on both the frequency and severity of dust storms have been linked to drought and the “desertification” of large land masses. Dust storms frequently affect arid or semi-arid lands; arid lands describe lands that lack water and become exceptionally dry. The Middle East is experiencing a time of excessive drought and declining rainfall rates. Brookings Institute states that the Middle East is a region listed 12th out of 17 for the most water scarcity, and the rate of rainfalls in the region have declined over the last few decades.
These findings are heavily affecting the ability for northern currents like the Shamal Winds to pick up sand and dust particles from dry hot land, sending them sweeping across the skies of the Middle East. Because such large areas of the Middle East are drying out, strong currents are now able to pick up the dry sand and dust particles into the air, increasing not only the frequency of these dust storms because they are easier to create with progressively dry lands, but also increasing the severity due to particle-heavy air. These particles are also what create the dark orange tint to the air and sky.
Dust storm over the Middle East. Nasa Earth Observatory. CC BY 2.0.
With the air so packed with dust and sand, and with the temperatures rising as summer closes in, the Middle East is suffering. The air quality has now sent thousands to the hospital looking for reprieve from the unbreathable air, suffering from illnesses like asthma, breathing trouble and even lung congestion. Additionally, four deaths in Iraq and Syria have been attributed to the orange air.
As of June, The Weather Channel reported there had been more than 10 dust storms in both April and May, and The Guardian stated that Saudi Arabia had already experienced 35 dust storms in only the first four months of 2022. Scientists and climate activists alike are concerned with the way these dust storms have been ravaging the Middle East, and fear the far-reaching impacts of the severe natural weather.
The Dean of the School of Public Health at the University of Nevada spoke with The Guardian and stated that, “The impact of dust storms exceeds regional and continental boundaries,” making this problem something every country should be concerned about. Greatly linked to climate change and unconcerned with borders, dust storms may be an indication of what is to come for the rest of the globe with rising temperatures drying out massive areas of land.
Ava Mamary
Ava is an undergraduate student at the University of Illinois, double majoring in English and Communications. At school, she Web Writes about music for a student-run radio station. She is also an avid backpacker, which is where her passion for travel and the outdoors comes from. She is very passionate about social justice issues, specifically those involving women’s rights, and is excited to write content about social action across the globe.
The Most Endangered Species of Penguin
The yellow-eyed penguins of New Zealand are the rarest species of penguins in the world.
Group of Yellow-Eyed Penguins. Chris Gin. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
Known as hoiho penguins in the Māori language of New Zealand, yellow-eyed penguins are the most endangered penguin species. There are estimates of fewer than 3000 of them left in the wild. In the past 30 years alone, the population has decreased by 50-75%.
Yellow-eyed penguins are easily identifiable, as they have yellow feathers around their eyes. It is a unique trait they have, along with the band of yellow that extends around their heads. Like other penguins, yellow-eyed penguins are predators, eating mostly fish and crustaceans. Adult birds generally have no land predators, but the chicks and eggs are in danger from animals like cats, dogs, ferrets and stoats. This is also common in Antarctica, where penguin chicks and eggs are vulnerable to other Antarctic birds, but the adults have almost nothing to fear from the other animals. In the water, however, yellow-eyed penguins are in danger from large marine predators, such as sharks and seals. Penguins have no defense mechanisms, so they mostly rely on their speed and maneuverability in the water to survive. Yellow-eyed penguins can swim up to 12.4 miles per hour. In comparison, the average human can swim around 2 miles per hour. If necessary, penguins also avoid ocean predators by jumping up on land. Like every other species, yellow-eyed penguins have a black back and white stomach to camouflage underwater. Their backs blend in with the dark depths for creatures above looking down on them, and their stomachs blend in with the surface for creatures looking up at them.
Yellow-Eyed Penguin. Bernard Spragg. CC0 1.0.
Yellow-eyed penguins mate for life and breed two eggs a year. Their average lifespan is 23 years, and these penguins start breeding at different times. They reach sexual maturity around two years of age, and most females begin breeding then. With males, however, it is more common to start breeding at three. The parents will incubate the eggs until they hatch, and then raise the chicks for around twelve months. Their nesting sites are in the bushes and shrubs along New Zealand’s coast, though deforestation has become a major threat to them. Humans have been clearing out land to make room for new houses or grazing fields for their animals, so the penguins have been forced to find new homes. The loss of their natural nesting habitat and the introduction of predators such as dogs and cats have contributed a lot towards why yellow-eyed penguins are endangered. There is also a high chick mortality rate, and some penguins get caught in gillnets, which lead to their deaths. The other major contribution to their decline is the food shortage due to global warming.
There are two main yellow-eyed penguin populations: the northern and southern ones. The size of each population is determined by how many breeding pairs there are, and in 1991, the northern population had 741 pairs. By 2020, it has decreased into a population of 233 breeding pairs. This decline has been mostly due to lack of food, diseases and predators. The northern population is spread out over South Island, Stewart Island and various other ones near to them.
The southern population, on the other hand, has been doing much better. In 1992, the estimated number of breeding pairs was 400, and in 2017, the number increased to 570. The southern population is divided into two colonies, one on Auckland Island and the other on Campbell Island. Though the penguins on these islands are doing much better than their northern counterparts, the overall population of yellow-eyed penguins is still decreasing.
Solitary Yellow-Eyed Penguin. Ben. CC BY-ND 2.0
To Get Involved:
There are multiple conservation organizations that exist in order to protect these penguins. One such organization is The Yellow-Eyed Penguin Trust, specifically focused on protecting the habitats and livelihoods of these birds. The easiest way to help them is by donating to them through their website, but it is possible to volunteer for them, if you live in New Zealand. Their office is based in Dunedin, but there are penguin preserves in other parts of the country. To learn more about the Yellow-Eyed Penguin Trust, click here.
Penguin Place is another organization dedicated to helping yellow-eyed penguins. They are the first conservation program funded entirely by tourism. They do take donations on their website, but most of their funds come from tours. Their funding comes from guided tours on penguin reserves and the money goes to preserving their habitats, helping sick or wounded penguins and controlling predators. To learn more about Penguin Place, click here.
Katherine Lim
Katherine Lim is an undergraduate student at Vassar College studying English literature and Italian. She loves both reading and writing, and she hopes to pursue both in the future. With a passion for travel and nature, she wants to experience more of the world and everything it has to offer.
VIDEO: Gaza Farmers Fighting for Their Lives
The Israel-Palestine conflict has been a dire diplomatic issue for the past half century, and unfortunately the situation is not getting any better, at least for those caught in the line of fire.
The Gaza Strip has been one of the most dangerous places for Palestinians ever since Israel set up a blockade in 2005, preventing Palestinians from accessing imports and exports out of the area, or even access the outside world. Violence in the area has increased in the last few years, with incidents such as Palestinian protesters being killed by Israeli snipers, drawing the eyes of the world to the conflict.
Still, the civilians must find a way to survive each day. This video tells the story of farmers in Gaza, who have to deal with both cripplingly low wages and Israeli gunfire to make ends meet. Matthew Cassel’s filming is gripping, thought-provoking, and painfully honest, showing that even those who have no desire for conflict cannot escape its deadly consequences.
Food Deserts, Food Swamps and Food Apartheid
Around 2.2 percent of all U.S. households live in areas without access to inexpensive healthy foods, leading to higher rates of obesity. These “food deserts” stem from a history of racism and inequality.
Food deserts are areas where residents don’t have easy access to healthy, affordable food. Instead, they may be overrun with fast food options. Mike Mozart. CC BY 2.0
Approximately 23.5 million Americans live in areas with limited or no access to affordable, healthy foods—especially fresh fruit and vegetables. These areas are commonly known as “food deserts” and are disproportionately found in low-income, minority communities.
Food deserts occur when there are few or no grocery stores within convenient distance; for example, a survey by the U.S. Department of Agriculture found that 2.3 million people live more than one mile away from a grocery store and do not have a car. In urban areas, the nearest grocery store might be a long trip away via public transportation, and not everyone is able to take time out of their day to make the trek, especially those in low-income neighborhoods who may be working more than one job.
Despite common misconceptions, living in a food desert does not necessarily mean that a person is food insecure. In fact, food deserts are often flooded with food choices—just not ones that are both healthy and affordable. A food desert may have plenty of smaller stores to buy food from, but these stores typically have limited options compared to grocery stores, specifically in the availability of fresh produce. Without easy access to grocery stores, people living in food deserts must turn to more convenient and affordable options, namely fast food.
Experts have coined the term “food swamp” to describe areas that are oversaturated with unhealthy food options. A study by the University of Connecticut’s Rudd Center for Food Policy and Obesity found that an average food swamp has four unhealthy eating options for every one healthy option.
Because people living in food deserts and food swamps have easier access to unhealthy food than healthy options, these areas also suffer from higher obesity rates. Studies have shown that food swamps may be a more accurate predictor of obesity rates than food deserts. However,food swamps and deserts tend to occur in the same areas, and more often than not these areas are low-income, minority communities.
The USDA has identified over 6,500 of what they refer to as “food desert tracts” based on census data and data about the locations of large grocery stores. In a 2012 study about the characteristics and causes of food deserts, the USDA found that areas with greater levels of poverty were more likely to be—or to become—food deserts. The study also concluded that “food desert tracts have a greater concentration of all minorities” than tracts that are not considered food deserts.
Because of the way that food deserts disproportionately impact minority communities, some food justice activists, like Karen Washington, prefer the term “food apartheid,” as it better captures the racial and economic nuances of the situation. Washington points out that “food desert” brings to mind “an empty, absolutely desolate place” with no food to be found, but this is not what a community with poor access to healthy food looks like. Nina Sevilla, another food justice activist, notes that “desert” implies that these areas are naturally occurring, which is not the case.
“Food deserts” are the result of decades of systemic racism that led to housing segregation; under the Federal Housing Administration starting in the 1930s, middle and lower-class white families migrated to the suburbs while minority families remained in urban housing projects. Redlining policies prevented minority groups from moving into what were seen as white neighborhoods. As white middle-class residents shifted to the suburbs, so did new supermarkets, leaving minority neighborhoods without easy access to a wide variety of food.
The term “food apartheid” highlights how these racist policies shaped low-income minority communities’ access to healthy food.
Since food inequality and so-called food deserts and food swamps are so rooted in racism, they are not an easy problem to address. However, there are many organizations working on different solutions to food apartheid, from championing policy reform to building alternative food systems, such as urban and small-scale farming and affordable organic grocery stores.
To Get Involved:
To learn more about where “food deserts” in the U.S. are located, look at the USDA’s Food Access Research Atlas here.
For a comprehensive policy platform on food, visit the HEAL Food Alliance here.
Rachel Lynch
Rachel is a student at Sarah Lawrence College in Bronxville, NY currently taking a semester off. She plans to study Writing and Child Development. Rachel loves to travel and is inspired by the places she’s been and everywhere she wants to go. She hopes to educate people on social justice issues and the history and culture of travel destinations through her writing.
A Country Divided: Marking the 75th Anniversary of the Indian Partition
Decades after India and Pakistan gained their independence in 1947, the cultural and political ramifications of partition continue to shape the lives of the new generation.
India celebrated their 75th Independence Day on August 15, 2022. Sanstuthi Nath. CC BY-NC 2.0.
2022 marks 75 years since British colonizers divided up the Indian subcontinent, officially declaring India and the Islamic Republic of Pakistan as sovereign states and leaving a trail of violence in their wake. Unlike the 50th anniversary of the event celebrated back in 1997, many, if not most, of the generation who lived through the horrors of partition have aged or gone, leaving fewer and fewer with first-hand memories of the difficult time. Despite this, discussions of South Asian affairs continue to be inextricably linked to the birth of Pakistan, the idea of an unified Indian nation, and the difficulties of birthing a new democracy in the wake of such upheaval.
Refugees desperate to escape massacre cram themselves onto trains during partition. Derek Barry. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
The pro-independence movement in India had long preceded partition, gaining most of its following in the years just after World War II. By this time, the country had been under British colonial rule for just under a century, and the country, while still heavily divided by caste, religion and ethnicity, largely agreed upon their desire to be self-governed. The newly elected British government at the time also appeared to be on the same page, but their exercises in subjugating the Indian population, in order to maintain control over them, had the unexpected consequence of inter-group violence, specifically when it came to deciding who would inherit the British Raj’s political power. This was especially true among religious groups: influential Hindu, Sikh and Muslim groups in politics were unable to agree on their vision for the new India with one such failed conference in 1946, resulting in Muhammed Ali Jinnah, head of the Muslim League, demanding the creation of a Muslim state. This call to action incited violence all over the country which the British decided would only end by partitioning the country into a Hindu-majority India and a Muslim-majority Pakistan. Their minimal logistical support, however, resulted in even more violence and ethnic cleansing, causing millions of people to flee their homes after discovering they were on the wrong side of the border. A million people perished in the refugee crisis and fifteen million were forced from their homes.
The Beating the Retreat ceremony is performed by Indian Border Security Forces and Pakistani Rangers at a border post. AFP Photo. CC BY-NC 2.0.
The ramifications of partition, 75 years after its occurrence, are still prevalent in many aspects of life for the younger Indian and Pakistani generations that may not even realize it. Their experiences of partition, unlike those of their grandparents, are largely based on knowledge learned in school and second-hand accounts from elder relatives. To those interested in the rapidly diminishing value of independence in an increasingly globalized society, the younger generation’s lack of connection to the event, which single-handedly birthed the modern nation of India as we know it, is placing a much larger burden on other institutions -- the media in particular -- to ensure an accurate historical memory of partition. In light of the waves of recent cultural, political, religious, gender and border conflict that have reignited across the subcontinent, remembering the sacrifices and hardships endured by those who fought for a unified India could provide a useful point of mediation.
Millions of displaced peoples set up refugee camps after being forced to flee their homes due to religious violence. The Guardian. CC-BY-SA 2.0.
If nothing else, celebrating 75 years of Indian independence has caused a lot of stories to resurface. Younger generations are making more of an effort to retrace their family histories across time and borders, digging into family archives and questioning their relatives before they are lost to time. The decades have done nothing to erase the history and emotions of what happened, and it is becoming increasingly common among those who have inherited the burden from their parents and grandparents to rediscover these narratives, both sweeping and personal, in the name of developing a personal identity. By posting these stories and sharing them online, young Indians and Pakistanis are building a community of their own and collectively defining what partition means to them. Hopefully, it will also be these communities that can overcome the legacy of pain and trauma that has followed the event through the years, and turn it into a new foundation of strength of unity for future generations of Indian and Pakistanis to come.
Tanaya Vohra
Tanaya is an undergraduate student pursuing a major in Public Health at the University of Chicago. She's lived in Asia, Europe and North America and wants to share her love of travel and exploring new cultures through her writing.
Freedom at Risk: Religious Persecution Around the World
Religious persecution still exists throughout the world, affecting people of all religions.
A protest at a Chinese embassy advocating for freedom of religion for Tibetan Buddhists and Uyghur Muslims. futureatlas.com. CC BY 2.0.
In April 2021, the United States announced that it would withdraw all troops from Afghanistan. In his reasoning to withdraw, President Joe Biden said that it is “the right and responsibility of the Afghan people alone to decide their future”. That future, however, is compromised as the Taliban quickly took over the country and imposed laws that undermine the rights of women and religious minorities.
Religious minorities in Afghanistan have “faced harassment, detention and even death due to their beliefs”, according to the U.S. Commission on International Religious Freedom. The commission has recommended Afghanistan be included in the State Department’s list of “countries of particular concern” in terms of religious liberty. Many Jewish, Hindu and Sikh Afghans have been forced to flee the country and Ahmadiyya Muslims, Baha’i’s and Christians have been worshiping in secret in fear of persecution.
While many people think that the world is now much more enlightened than before, religious persecution is not a practice of the past. Conflicts are still being fought over religion. Religion is the key of freedom of conscience, which makes up a key part of the human being. Totalitarian regimes, that attempt to claim the whole person, are intent on suppressing religion, with controlling the individual as the end goal. However, religious persecution is not just limited to authoritarian states, as a 2018 report claims that harassment of religious groups occurs in 90% of all countries.
With authoritarian regimes on the rise in countries like China, religion is being suppressed there. In China, Xi Jinping is embarking on a campaign against religion in general and sending countless Uyghur, Kazakh and Kyrgyz Muslims to concentration camps. In addition, the Chinese government is trying to impose forced assimilation of Tibetan Buddhists and closed many Protestant churches.
Though officially a secular democracy, Prime Minister of India, Narendra Modi, and his Hindu nationalist party the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) has led a fierce anti-Muslim campaign in India. The Indian government has recently moved to limit the rights of Muslims, including a new law that allows for fast-tracked citizenship of non-Muslim immigrants from nearby countries. There has also been an increase in violence against Muslims in India during Modi’s time in office.
Religious persecution in India is not just limited to Muslims, however. Christians are also facing animosity in India. Hindus are committing violence against Christians under the pretext of the country’s anti-conversion law, which prohibits missionary activity. To Hindu nationalists, the notion that some Hindus are willing to convert to Christianity throws a dent in their plans for a purely Hindu nation. The only problem is, that the Christians under the threat of vigilante violence are not engaging in conversions. Instead, the anti-conversion law is used as an excuse to justify violence against Christian communities in India.
There are countless other examples of religious persecution around the world that are not getting much attention. According to Open Doors, an organization that advocates for persecuted Christians, more than 360 million Christians across 76 countries suffer high levels of discrimination, with Christians in the Middle East and Africa under particular threat. In Kenya, six Christians were killed in early 2022 by Al-Shabaab, an Al-Qaeda aligned terrorist group. Even in Uganda, where 82% of the population is Christian, a Muslim hanged his wife and children in January 2022 because they converted to Christianity.
Even Western countries, which are generally considered more tolerant, are not bereft of instances of religious persecution. France in recent years instituted a “burqa ban”, prohibiting some people from wearing their religious garments. While some justified the ban as an embrace of secularism and public safety, France also instituted a compulsory mask mandate during the Coronavirus pandemic without reversing the “burqa ban”, showing that Islamophobia was the driving force behind the ban.
These instances of religious persecution are a direct affront to human rights. Article 18 of the United Nation Universal Declaration of Human Rights establishes the freedom of religion to be a fundamental human right. While the world may not be the most tolerant place currently, there are numerous organizations and individuals working to change that.
To Get Involved
There are plenty of organizations that fight for religious freedom around the world. The Religious Freedom Institute is working to convince stakeholders around the world that religious freedom can help them achieve their goals. The International Association for Religious Freedom promotes the work of individuals fighting for religious freedom. Other organizations advocating for religious tolerance can be found here.
Bryan Fok
Bryan is currently a History and Global Affairs major at the University of Notre Dame. He aims to apply the notion of Integral Human Development as a framework for analyzing global issues. He enjoys hiking and visiting national parks.
A Cycle of Dependency: How Donations Worsen Income Inequality
Regardless of the good intentions behind donations, the short-term gain experienced by poor communities often leads to the persistence of income inequality and an endless cycle of dependency.
Secondhand clothing in Haiti. Vanberto. CC BY-NC-SA 2.0
Donations are often associated with a positive image of helping destitute populations get the resources they lack. Yet, this short-term aid often results in far-reaching consequences detrimental to a country’s economy, which leads to the persistence of income inequality.
The donation of money that goes toward buying resources for impoverished communities often creates an endless cycle of dependency, especially if such service is repeatedly conducted through organizations or companies. First, the repeated nature of such service creates a false assumption among receivers that there will always be a supply of that resource without work, making them reliant on such aid. Moreover, the organizations themselves are indirectly relying on marginalized areas to promote their businesses’ charitable work. For instance, back in 2006, when TOMS started its “one for one” program, it would donate a pair of shoes for every pair that was purchased. Although the company’s motive seemed to be pure, it relied on underprivileged populations’ need for shoes to increase its business revenue.
84% of unwanted clothing is thrown into landfills
When donations are consistently provided, those living in poverty often learn to become dependent on the donors as they see less reason to get out of their current situation. Local businesses also shut down, as the need to produce items goes away when high-quality donations are provided at a minimal price from external sources. Although that may come as great news for citizens of developing countries, most of the profit in this exchange goes to the exporters. A 2006 report found that, “textile and clothing employment in Ghana declined by 80% from 1975 to 2000; in Zambia it fell from 25,000 workers in the 1980s to below 10,000 in 2002; and in Nigeria the number of workers fell from 200,000 to being insignificant.” Such statistics imply that despite the good nature of external aid, it often comes at the expense of the receiving countries.
Haiti is a common dumping ground for secondhand clothing primarily from the United States, and due to its regular occurrence, locals have given this process the name “Pepe.” The Netflix documentary “The True Cost” elaborates on how Haiti’s textile industry is suffering due to the widespread popularity of Pepe, leading the country’s local clothing industry to disappear. For this reason, some countries have started to refuse the import of secondhand clothing, and more of it ends up in recycling facilities. Yet according to Newsweek, 84% of unwanted clothing is thrown into landfills.
To combat waste, then, the fast-fashion industry needs to start recycling its own goods, minimize seasonal sales, make more durable products and normalize wearing recycled apparel. Additionally, governments need to start promoting the creation of more jobs for impoverished communities, so that all the necessary resources are available in the market at reasonable prices. Finally, donors should remember that regardless of good intentions, deprived communities may suffer long-term consequences due to misunderstood charity work.
Swati Agarwal
Swati Agarwal is a sophomore at University of California, San Diego, where she is studying Environmental Sciences and Theatre. Although born in India, she was raised in Tokyo, which gave her the opportunity to interact with diverse people from distinct cultures. She is passionate about writing, and hopes to inspire others by spreading awareness about social justice issues and highlighting the uniqueness of the world.
The Great Green Wall: Preventing Desertification in the Sahel
Desertification has negatively affected the area south of the Sahara Desert, but one initiative is fighting back.
Read More10 Must Read Novels About the Immigrant Experience
Here are 10 fictional narratives detailing aspects of the immigrant experience from the hilarious to the heart-wrenching and everything in between.
Bookshelves. Hannah Gersen. CC BY-SA 2.0.
Travel has been a popular topic among authors for almost as long as writing has existed. From the heroic tales of Odysseus’ journey first published in Homer’s 7th century BC epic, to the many articles highlighting hidden wonders on this very website, the idea of reading about far away places and getting lost in descriptions of exotic foreignness has always drawn a huge following. The subsection of this genre that focuses on migrant experiences, however, adds a completely unique flavor to these stories of new discovery. Here are 10 books that highlight, among others, themes of cultural assimilation, hardships encountered in completely foreign settings and the balance between wanting a better life and loyalty to one's country.
1. Transcendent Kingdom by Yaa Gyasi (2020)
After her critically acclaimed debut novel Homegoing, Ghanian-American novelist Yaa Gyasi has finally gifted her readers another emotional rollercoaster in “Transcendent Kingdom”. Her protagonist, Gifty, a whip smart first generation neuroscience candidate at Stanford, finds herself struggling to accommodate her Ghanian mother’s pervasive religious beliefs alongside her scientific research. Maybe more importantly, Gifty is also struggling to find herself, her place in society, her true calling in life and love. “Transcendent Kingdom” is raw, honest and unsparing in its examination of one woman’s journey to self-acceptance.
This debut novel from Queens local Daphne Palasi Andreades is a beautifully lyrical homage to young women of color making their way through the complexities of teenage life in the New York borough. The book follows “girls like Nadira, Gabby, Naz, Trish, Angelique” among others as they face the realities of reconciling their American dreams with histories and cultures rooted in the faraway homelands of their parents. Andreades masterfully balances the day to day of life in Queens while tackling the issues of race, class, identity and cultural marginalization dealt with by brown girls everywhere.
Charles Yu is back with another satirically analogous novel, this time tastefully playing back and forth between Asian-American stereotypes and Hollywood clichés to narrate, literally, the far reaching aspirations of “Generic Asian Man” Willis Wu. Willis feels so much an unremarkable member of Chinatown’s exotic foreign aesthetic, that he can’t even see himself as the main character in his own life. His dreams, on the other hand, have him playing “Kung Fu Guy”, a role achieved only by those lucky enough to claw their way out of Chinatown’s grasp, but one that will force Willis to confront his family’s heritage in the context of a hostile America.
Romance novel fans look no further -- Kasim Ali’s debut novel “Good Intentions” follows the love story between Yasmina and Nur from reckless college parties to the uncertainties of post-graduation adulthood. Both first generation immigrants from Sudan and Pakistan respectively, Yasmina and Nur are navigating the balance between traditional Muslim values and their feelings for each other. While Yasmina, passionate and headstrong, seems to have everything figured out, Nur can’t bring himself to tell his parents about his relationship, even four years in. Comforting and heartbreaking all at the same time, the romance novel is the ultimate homage to young love in vibrant color.
This award-winning novel is Indian-British author Sunjeev Sahota’s second publication, telling the sweeping narrative of four young Indians facing the punishing realities of building a new life in foreign surroundings. Avtar, Randeep, Tochi and Narinder want nothing more than to leave their pasts in the rural Indian villages which they fought so hard to escape, but they have no idea how much hardship still awaits them. Stretching from the most remote corners of Eastern India to the crumbling housing complexes in Sheffield, Sahota shares a story of dreams and ambition, of the ever-pervasive sufferings of generational poverty and inequality and of the sheer strength of the immigrant spirit in the face of seemingly insurmountable difficulty.
A love letter to Khmer teenagers, monks, donut shop owners, badminton players and everyone else in the Cambodian enclave of Stockton, California, Anthony Veasna So’s collection of short stories paint a darkly humorous picture of his community. Each vignette holds up a microscope to a crucial turning point in a young Khmer life, some of which lead their protagonists to long-awaited clarity and relief while others are simply plagued by more questions and emotional instability. So is unrelenting in his study of the good, the bad and the ugly of what it means to be “Cambo” -- what it means to carry the searingly fresh wounds of recent history while chasing success in 21st century America.
Toronto-based author Zalika Reid-Benta’s debut short story collection follows the conflicted Kara Davis who constantly feels as though she is falling between the cracks of her Jamaican ancestry and her Canadian nationality. A coming of age story set against the rich backdrop of Toronto’s Little Jamaica neighborhood, “Frying Plantain” perfectly captures the power of a single moment to completely alter a relationship, an intention and even an entire life. Familial relationships are tested and generations clash over what it means to be a “true Jamaican” while embracing new opportunities, all while being wrapped up in ever-present tensions of being black in a predominantly white country.
Marked by its huge cast of unforgettable characters, “Mama Tandoori” is the heart-warming story of author Ernest van der Kwast’s childhood under the watchful eyes of his austere Dutch father and big-hearted Indian mother. With hilarity around every corner, van der Kwast introduces his heptathlete aunt and Bollywood star uncle amongst a colorful lineup of relatives, each adding spices of their own to the recipe of his youth. It is his mother, however, the talented bargainer and ever tenacious Veena van der Kwast, who lies at the center of this novel and breathes life into this moving portrait of familial love.
Siri Ranva Hjelm Jacobsen’s critically acclaimed debut novel approaches the immigrant story from an exhilaratingly new perspective. Island follows a young woman completely removed from her ancestral heritage in the Faroe Islands despite having called it home her whole life. When she is called back by family, she journeys to the rocky shores of the northern archipelago to discover stories about her ancestors that will change the way she sees herself forever. An incredible tale of perseverance and cultural discovery, “Island” explores the complex definition of “home” to those who have more than one.
This final one is an oldie but a goodie -- Chinese American author Amy Tan is most well-known for her novel “The Joy Luck Club”, and this novel follows proudly in its footsteps, touching on similar aspects of the Chinese-American immigrant experience, while introducing a refreshing dose of Chinese mysticism and ghostly folklore for good measure. The Hundred Secret Senses follows half-sisters Olivia and Kwan, the former desperately trying to find her place at the intersection of her mixed heritage, and the latter perfectly content in her ability to communicate with the departed souls of those she knew in past lives. Tan weaves a heart-wrenching narrative of love and loss that carries readers from the sunny shores of San Francisco to the bloody terrors of Manchu China, honoring the bonds of familial loyalty and the ties of tradition the whole way through.
Tanaya Vohra
Tanaya is an undergraduate student pursuing a major in Public Health at the University of Chicago. She's lived in Asia, Europe and North America and wants to share her love of travel and exploring new cultures through her writing.
From the U.S. to Bangladesh: Declines in Clean Drinking Water
From the southeast coast of the United States to Bangladesh, rising sea levels due to climate change are causing a troubling phenomenon called “saltwater intrusion”.
Read MoreThe Story of Willie Kimani: Police Brutality in Kenya
The story of human rights lawyer Willie Kimani’s murder by police officers has sparked a larger conversation about police brutality in Kenya.
Rally against police brutality. Wa-J. CC BY-NC-SA 2.0.
Willie Kimani, a 32-year-old human rights lawyer, was brutally murdered by police alongside his client Josephat Mwenda and their taxi driver in 2016. All three men had their bodies disposed in the Ol-Donyo Sabuk River outside the capital of Kenya by police officers who found themselves in the crosshairs of Mwenda’s litigation. Police officers Fredrick Leliman, Stephen Cheburet, Sylvia Wanjiku and police informant Peter Ngugi were all found guilty this year of the murders, a whopping six years after the crime.
Mwenda accused officer Fredrick Leliman of shooting him at a traffic stop in 2015, BBC reports. Kimani had been working for the International Justice Mission (IJM) when he picked up Mwenda’s case, IJM being an organization dedicated to punishing human rights violations through litigation.
Police officers in front of Kenyan station. JRandomF. CC BY-NC 2.0.
Officer Leliman started threatening Kimani and Mwenda during the proceedings of the case in 2016 and had even detained Kimani and Mwenda, after court appearances for fabricated reasons. The detainments were an abuse of power, and though Kimani and Mwenda were released, they were not protected against the wrath of the Kenyan police force for much longer. The murders of Mwenda and Kimani occured shortly after in June.
Peter Ngugi, the police informant, stated in court that after they committed the crime, Leliman hosted Ngugi and the police officers for “beer and 5kg of fried beef”, at a bar in Mlolongo to celebrate.
The case of Willie Kimani sparked outrage in Kenya. Protests formed over the murders, even leading a mob of angry citizens to burn the police station that employed the officers responsible.
Police medal ceremony. AMISOM Public Information. CC0 1.0.
But this is not the first big tragedy at the hands of Kenyan police. During the pandemic, police officers in Kenya had been said to beat and kill civilians just for breaking curfew. In 2017, a boy no older than 16 was shot and killed after surrendering to police officers. NPR reports that although the young boy pleaded for his life, a police officer shot him twice.
Stories like Willie Kimani’s murder have ignited demands for police reform, but due to the overtly oppressive nature of the Kenyan police, many who protest fear for their lives. In a country where you need to plead to be arrested rather than killed, it takes bravery to stand up and fight for what is just. Extrajudicial killings occur often in Kenya; in 2020, Missing Voices Kenya reported that “police killed or disappeared 167 people”.
Many countries struggle with police brutality and the systems in place that perpetuate such abuses of power. In Kenya, many think the violence is a result of colonial influence on structures of policing policy. After Kenya gained independence, influences on the police force were already hardened into place.
During the colonization of Kenya, British imperialists created a bifurcated policing force in Kenya based on settlement segregation. Because white colonizers lived separately from Kenya’s native people, certain Kenyans were given policing power over other natives in their area. In martial-law structures such as the Home Guard, these officers were given authority over their own people.
These police forces, however, lacked basic structure, and officers had few limitations to their power. After Kenya’s independence, the lack of structure and rules created systemic issues for future police forces. Foundationally, policing was enacted on the grounds of violence, of oppressive force and of hierarchical power disparities that related to inherent class structures between colonizers and the colonized. A structure without limitations on violent policing led to modern-day overt shows of power and cops who, as Sapiens puts it, “operate outside formal avenues of accountability”.
The history of Kenyan policing, the colonial influence on the structure and the systemic issues that weaken the foundation of policing are all problems being debated globally today. Kenya still sees the effects of colonialism in the practices of its police officers. However, protests in Kenya still occur in the face of likely consequences, and the Kenyan people fight to ensure a greater future for those like Kimani and Mwenda.
To Get Involved
Organizations like Article19 help protect the rights of Kenyans to protest, even against the oppressive forces of the police. In their #FreetoProtest campaign, Article19 fights hard to ensure that protesters in Kenya are free to practice their human right to protest in the face of violent police retaliation. To learn more about their mission and campaign, click here.
Willie Kimani worked for the International Justice Mission (IJM), a legal organization that works to fight human rights violations across the globe. They actively fight against police brutality and killings at the hands of law enforcement. To learn more about the work IJM does to fight police brutality, or to donate to their organization, click here.
Ava Mamary
Ava is an undergraduate student at the University of Illinois, double majoring in English and Communications. At school, she Web Writes about music for a student-run radio station. She is also an avid backpacker, which is where her passion for travel and the outdoors comes from. She is very passionate about social justice issues, specifically those involving women’s rights, and is excited to write content about social action across the globe.