The nomadic Nenets reindeer herders of the Siberian Arctic migrate across one of the most challenging environments on Earth. Follow the story of Lena, a young Nenets mother, and her journey to birth.
Read More13 Instagram Accounts About Social Impact
Social media can be a source of toxicity. So often our feeds are saturated with ads, photoshop, unrealistic body images, and fake representations of peoples’ lives. However, many activists are using social media to promote issues that they are passionate about, in order to reach a wide audience. If you’re looking to bring more heartfelt messages to your feed, here are some accounts to follow:
Global Citizen is an organization dedicated to eradicate extreme poverty. But, their Instagram feed educates their followers on a range of social issues. Their goal is to create a global community of people who want to change the world. Their feed helps to connect that community with photos from around the world.
2. Michael Moore: @michaelfmoore
A filmmaker, author, and activist, Michael Moore raises awareness about corruption in the US government and large corporations through his work. He calls his followers to join him in the polls on his Instagram stories, and is vocal about his political viewpoints through his permanent posts. He sheds light on candidates and social issues in the US.
3. Nicholas Kristof: @nickkristof
Nicholas Kristof is a progressive journalist, and columnist for the New York Times. He uses his Instagram mostly to relevant pictures or quotes from his column that he writes. His feed will alert you of important issues or interesting points in history, and encourage you to read and learn more.
Everyday Africa is a beautiful feed that features contributions from photographers of pictures that highlight everyday life in Africa. They steer away from the extreme and violent images that often saturate the media.
5. UN Refugee Agency: @refugees
The UN Refugee Agency protects over 70 million refugees or displaced people. Their feed is educational, hopeful, and inspirational. It features photos of the people they help and the work that they do, prominent UN activists and ambassadors, as well as important quotes and statistics.
6. Christie Begnell: @meandmyed.art
Christie Begnell is an illustrator whose mission is to break down the stereotypes that people have about mental health and eating disorders. Christie is going through recovery herself, and uses illustrations to convey a more accurate, realistic depiction of eating disorders and anxiety. Her account encourages body positivity, empathy, and acceptance.
7. Leanne Lauricella: @goatsofanarchy
Leanne Lauricella runs an animal sanctuary and nonprofit that takes care of handicapped and abused animals. The account, @goatsofanarchy, features cute and funny videos of the goats they take care of. In addition to being adorable, the account raises awareness for the sanctuary, and compassion for animals in general.
8. Leighton Brown and Matthew Riemer: @lgbt_history
Leighton Brown and Matthew Riemer started @lgbt_history to educate followers about important events and figures in queer history. The account is completely objective—the goal is simply to educate users with facts. Leighton and Matthew stay relevant by coordinating their posts with current events, linking past to present.
A self-proclaimed “vegan drifter,” Shivya Nath is a nomad. She has no home base. She travels her entire life—and posts beautiful pictures wherever she goes. Shivya uses her platform to encourage a sustainable lifestyle—specifically veganism and conscious traveling.
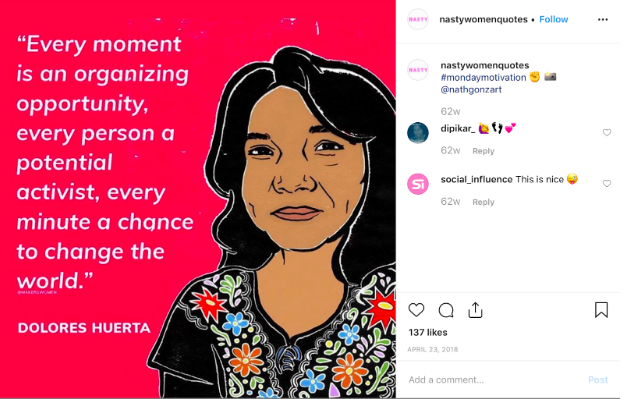
A mix of quotes from badass feminists (men and women!) and witty relevant screenshots from Television shows, a scroll through Nasty Women Quotes will have you feeling empowered.
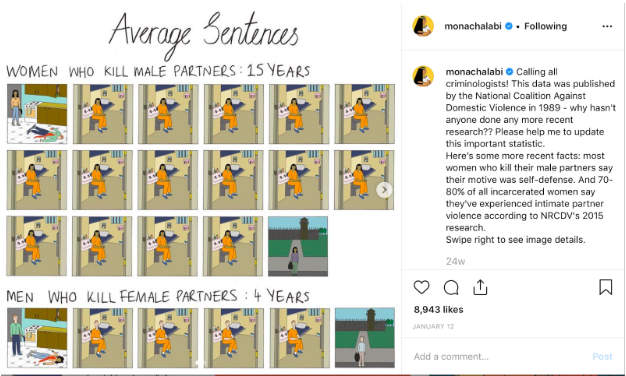
11. Mona Chalabi: @monachalabi
Mona Chalabi is a data journalist. She creates illustrations and infographics to help visualize data, and to make facts more understandable and relatable. She tackles all issues, from countering racism and ageism, to raising awareness for animal rights and wage gaps.
The accompanying Instagram account to its magazine, Indigenous Goddess Gang posts memes, quotes, art, and pictures that further their goal of “reclaiming knowledge from an indigenous femme lens.” Make sure to check out their magazine as well.
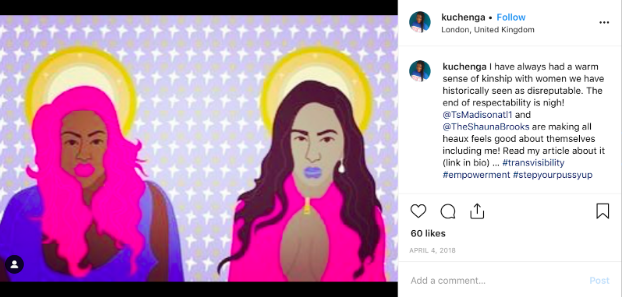
13. Kuchenga Shenje- @kuchenga
Journalist, author, and Black Lives Matter activist, Kuchenga’s page is full of empowering artwork and photography, as well as advocacy for trans representation and diversity in general.
With their stories and permanent posts, these Instagrammers give daily inspiration and empowerment to their followers.
ELIANA DOFT loves to write, travel, and volunteer. She is especially excited by opportunities to combine these three passions through writing about social action travel experiences. She is an avid reader, a licensed scuba diver, and a self-proclaimed cold brew connoisseur.
Does Humanitarian Aid Have a 'White Saviour' Problem?
American missionary Renee Bach travelled to Uganda in 2007 when she was just 18 years-old and founded Serving His Children (SHC), a nonprofit organisation she said would help Ugandan women care for ill and malnourished children. Critics, though, say Bach, who had no experience in either development work or medicine, performed complicated medical procedures on hundreds of children.
In 2015, Ugandan authorities closed SHC's facility in the town of Jinja - where a number of children were reported to have died - but the organisation still operates in other parts of the country. A lawsuit brought by two women who say their children died under SHC’s care has been adjourned until January 2020, according to the Uganda-based legal services group Women’s Probono Initiative.
Bach’s case has again highlighted the issue of medical "voluntourism", while raising questions of whether some charities in the developing world have a “white saviour problem”. In response, Uganda-based social workers Olivia Alaso and Kelsey Nielsen began the No White Saviors campaign to educate and advocate for better practices in mission and development work.
In this episode, The Stream takes a look at why some Westerners get to work in the developing world without adequate experience, and what groups like No White Saviors are doing to hold them accountable.
‘The language matters!’: Activists demonstrate in Kiev, April 2019 to demand the passage of a new language law. EPA-EFE/Sergey Dolzhenko
Ukraine: How a Controversial New Language Law Could Help Protect Minorities and Unite the Country
Ukraine is celebrating 28 years of independence – but since 1991 the country has struggled to find the right policies and practices to protect and promote Ukrainian, the state language. It has also tried to prioritise policies of inclusion for ethnic and linguistic minorities while supporting the languages and cultures of Ukraine’s indigenous peoples. A new law passed in July 2019, if successfully implemented, may finally help strike the balance.
Ukrainian is currently is the eighth most spoken language in Europe with more than 33m speakers. Along with Belarusian and Russian, with which it shares Cyrillic script, it is an East Slavic language. Despite having some similarities with Russian, it is a separate language. Russian is widely spoken in Ukraine with small concentrations of Romanian and Hungarian speakers in the west. Ukraine’s indigenous languages (Crimean Tatar, Karaim and Krimchak) are recognised by UNESCO as endangered languages.
Over the past three decades, Ukrainian politicians have too often, in my opinion, exploited the issue of language policy – especially the question of giving Russian official status in the country – as a way of mobilising their respective bases, at the expense of national solidarity and cohesion.
This is despite the fact that Ukrainians routinely rank the issue of language very low on a list of the country’s problems. In 2018, only 2.4% of Ukrainians viewed the status of the Russian language as the most important problem in the country. Despite this, the former Ukrainian president, Petro Poroshenko, made the support of the Ukrainian language a key element of his re-election campaign. But it didn’t give his campaign any discernible lift and he was ousted at the April 2019 election by comedian Volodymyr Zelensky.
Russian gets weaponised
In 2014, the Kremlin used the issue to justify its military aggression against Ukraine. Vladimir Putin repeatedly claimed that Ukraine’s post-Maidan government was targeting Russian-speakers in the country. Given that the government was led by native Russian-speakers, such as Oleksandr Turchynov and Petro Poroshenko, this was an absurd argument. But nonetheless, some western observers appeared to accept it.
The law, On the Provision of the Functioning of Ukrainian as the State Language, passed in April and took force on July 16. Unsurprisingly, it was met with a fierce reaction from the Kremlin, which called for the United Nations Security Council to debate the issue.
Russian influence: Vladimir Putin with members of the pro-Kremlin biker gang Night Wolves in Sevastopol, Crimea, August 2019. EPA-EFE/Alexei Druzhinin/Sputnik/Kremlin
But beyond the political bluster, what are the actual features of this law and does it have the potential to allow effective functioning of Ukrainian and other languages and, at the same time, bring the country together?
Securing official status
The law affirms Ukrainian as the main language of inter-ethnic communication – a role most recently played by Russian and by German and Polish in earlier historical periods. It also ensures that information and services are available in Ukrainian – something that was not previously the case in the majority of cities in eastern and southern Ukraine, where Russian dominates in all spheres of public life. But the law also allows official interactions in languages that are “acceptable to both sides”, and it doesn’t completely rule out the use of Russian.
Drafts of the law in development were criticised for forcing media (including academic publications) to publish equal numbers in Ukrainian and other languages. It was argued that this makes the existence of such newspapers like the Kyiv Post – the most famous Ukrainian newspaper in English – very problematic. As a response to this criticism, the law was changed to allow publication in English and “other official languages of the European Union”. So, while supporting multilingualism, the law clearly rules out Russian as the language of inter-ethnic communication.
But the law’s requirements to ensure that all theatrical performances and 90% of films are in Ukrainian, with an undefined exception for “artistic necessity”, seem both unproductive and excessive.
Supporting language minorities
If successful, the law will go a long way towards protecting Ukraine’s indigenous languages. Media outlets are obliged to produce a certain percentage of their content in the indigenous language, while all higher educational institutions must have the capacity to teach indigenous languages to all students who express a desire for it.
Protesters demonstrate against the disappearance of Crimean Tatar activists. Tatars are one of Ukraine’s oppressed minority groups, October 2016. EPA/Roman Pilipey
The law also stipulates that language courses must be available in the languages of Ukraine’s ethnic minorities and, for the first time in Ukraine’s history, Ukrainian sign language is given protection and support. This empowerment has been somewhat overlooked in the recent comments on the law that mostly focused on the rights of Russian-speakers.
But Ukraine’s parliament has still to pass additional legislation on the rights of the indigenous people and minorities of Ukraine, which is required under the terms of the language law. This should provide additional mechanisms to protect the rights of Russian-speakers and other minorities. The newly-created party, Servant of the People, recently won power and has declared that it will “deal with this issue”.
As we’ve heard, despite the outside world’s obsession with language as one of the critical issues in Ukraine, only a small minority of people see it as a high-priority problem. The 2018 survey referred to above also showed people are far more worried about the ongoing military conflict and the effect it is having on living standards and the economy.
What’s clear, though, is that these problems won’t be solved without national cohesion. So, whether or not Ukrainians themselves think it important, the right formula for establishing Ukrainian as the official state language, as well as supporting and protecting indigenous and minority languages, will be key to helping the embattled country pull together.
IVAB KOZACHENKO is a Postdoctoral research associate, University of Cambridge.
THIS ARTICLE WAS ORIGINALLY PUBLISHED ON THE CONVERSATION.
I am Congo
Get to know the Congo before you walk through the streets yourself. In this immersive experience, you'll see the vast forest of the congo, the countries colorful style, and break taking shots of life in the city. As part of the "I am" series, videographers spent time in the Congo meeting local artisans, traders and musicians. Their experience, laid out for you here.
Firefighters and volunteers have been working around the clock to tackle the flames. Ipa Ibañez, Author provided
It’s Not Just Brazil’s Amazon Rainforest That’s Ablaze – Bolivian Fires are Threatening People and Wildlife
Up to 800,000 hectares of the unique Chiquitano forest were burned to the ground in Bolivia between August 18 and August 23. That’s more forest than is usually destroyed across the country in two years. Experts say that it will take at least two centuries to repair the ecological damage done by the fires, while at least 500 species are said to be at risk from the flames.
The Chiquitano dry forest in Bolivia was the largest healthy tropical dry forest in the world. It’s now unclear whether it will retain that status. The forest is home to Indigenous peoples as well as iconic wildlife such as jaguars, giant armadillos, and tapirs. Some species in the Chiquitano are found nowhere else on Earth. Distressing photographs and videos from the area show many animals have burned to death in the recent fires.
The burnt region also encompasses farmland and towns, with thousands of people evacuated and many more affected by the smoke. Food and water are being sent to the region, while children are being kept home from school in many districts where the air pollution is double what is considered extreme. Many families are still without drinking water. While the media has focused on Brazil, Bolivians are asking the world to notice their unfolding tragedy – and to send help in combating the flames.
Dry forests of the Chiquitanos before the fires. Alfredo Romero-Muñoz, Author provided
It’s thought that the fires were started deliberately to clear the land for farming, but quickly got out of control. The perpetrators aren’t known, but Bolivian President Evo Morales has justified people starting fires, saying: “If small families don’t set fires, what are they going to live on?”
The disaster comes just a month after Morales announced a new “supreme decree” aimed at increasing beef production for export. Twenty-one civil society organisations are calling for the repeal of this decree, arguing that it has helped cause the fires and violates Bolivia’s environmental laws. Government officials say that fire setting is a normal activity at this time of year and isn’t linked to the decree.
Fires burn across Santa Cruz state. Ipa Ibañez, Author provided
Morales has repeatedly said that international help isn’t needed, despite having sent just three helicopters to tackle the raging fires. He argued that the fires are dying out in some areas – although they continue to burn in others and have now reached Bolivia’s largest city, Santa Cruz de la Sierra. Many say that the fires could have been contained far sooner with international help, as videos show volunteers trying to beat back the fires with branches.
As the fires worsened, people gathered to protest in Santa Cruz state. Chanting “we want your help”, they complained that the smoke was so bad they were struggling to breathe. They want Morales to request international aid to fight the fires. While firefighters and volunteers struggle to tackle the blaze in 55℃ heat, Bolivians have set up a fundraiser to tackle the fires themselves.
The extreme heat has made fighting the fires intolerable for those involved. Ipa Ibañez, Author provided
A fortnight after the fires began, a supertanker aeroplane of water arrived, hired from the US. But if the reactions to the president’s announcement on Twitter are anything to go by, many Bolivians think this is too little, too late. Morales is fighting a general election and has faced criticism for staying on the campaign trail while the fires spread.
Some Indigenous leaders are asking for a trial to determine responsibility for the fires, and the response to them. Alex Villca, an Indigenous leader and spokesperson, said:
It is President Evo Morales who should be held accountable. What are these accountabilities going to be? A trial of responsibilities for this number of events that are occurring in the country, this number of violations of Indigenous peoples and also the rights of Mother Nature.
The dry forest understorey ignites while firefighters deploy fire breaks. Ipa Ibañez, Author provided
President Morales came to power in Bolivia in 2006, on a platform of socialism, Indigenous rights, and environmental protection. He passed the famous “Law of the Rights of Mother Earth” in 2010, which placed the intrinsic value of nature alongside that of humans. His environmental rhetoric has been strong but his policies have been contradictory. Morales has approved widespread deforestation, as well as roads and gas exploration in national parks.
While the fires in the Chiquitano have dominated the media within the country, hundreds more rage across Bolivia, assisted by the recent drought. It’s unclear whether the response to these fires will affect the October election outcome, but sentiments are running high in the country, where more than 70% of people prioritise environmental protection over economic growth.
Bolsonaro and Brazil might grab the headlines, but Bolivia too is now host to a desperately serious humanitarian and environmental situation.
CLAIRE F.R. WORDLEY is a Research Associate, Conservation Evidence, Department of Zoology, University of Cambridge.
THIS ARTICLE WAS ORIGINALLY PUBLISHED ON THE CONVERSATION.
NEPAL: Kung Fu Nuns
This nunnery has an empowering claim to fame—it’s the only one in Nepal where the nuns practice martial arts. The nuns of the Buddhist Drukpa Order train three hours a day, and they break bricks with their bare hands. Heroes in the Himalayas, these strong women delivered supplies to hard-to-reach villages after an earthquake struck Kathmandu in 2015. The kung fu nuns have also taught self-defense classes for women and biked 14,000 miles to protest the human trafficking of women and girls.
The Netherland’s New Burqa Ban is a Sign of Hostility Towards the Dutch Muslim Community
The discriminatory law violates both religious freedom and freedom of movement.
Photo of Library Hall in the Rijksmuseum by Will van Wingerden on Unsplash. This is one of many buildings now off limits to people wearing burqas or niqabs.
Last June, the Upper House of Parliament passed a ban on face-covering garmates such as burqas and niqabs by 35 to 40 votes. The law came into effect early this month, banning those wearing such garmates from entering public places including government buildings, public transport, hospitals, and schools.
Amnesty International has released a statement calling the ban an infringement on women's rights to dress as they choose. The ban follows similar laws throughout Europe and will make the Netherlands the 6th country in the EU to ban burqas and niqabs in public buildings. The law does not apply to streets and other outdoor public spaces.
While the exact number of women impacted by the law is unclear, the Guardian writes that according to a 2009 study by University of Amsterdam professor Annelies Moors, an estimated 100 women routinely wear a face veil and less than 400 sometimes wear a veil. Moors, a critic of the bill, states that it has the power to interfere with women's daily lives. It restricts their access to hospitals, police stations, and schools, preventing them from accessing education, reporting crimes, and other necessary abilities.
While the Dutch government has stated that the law is a non-discriminatory effort to ensure public safety, the far-right has been quick to cite the ban as a party victory. "Finally, 13 years after a majority in the Dutch Parliament voted in favor of my motion to ban the burqa, it became law yesterday!" Geert Wilders of the far-right Freedom Party tweeted last June including the telling hashtags #stopislam #deislamize.
Al Jazeera writes that Wilders hopes to go even further with the ban."I believe we should now try to take it to the next step," he told the Associated Press. "The next step to make it sure that the headscarf could be banned in the Netherlands as well."
Under the new law, someone wearing a banned clothing item must either remove it, or face a fine from 150 to 415 euro. Police and transport officials, however, have expressed a reluctance to comply with the ban.
After a statement from the police saying that enforcing the law is not a priority for them, transportation authorities announced that they would not be enforcing the law as police assistance would not be readily available.
“The police have told us the ban is not a priority and that therefore they will not be able to respond inside the usual 30 minutes, if at all,” Pedro Peters, a spokesman for the Netherlands transport network told the Guardian. “This means that if a person wearing a burqa or a niqab is challenged trying to use a service, our staff will have no police backup to adjudicate on what they should do. It is not up to transport workers to impose the law and hand out fines.”
Hospitals also stated that they would continue to treat patients regardless of clothing.
The Muslim community has rallied to support those affected by the law. The Nida (Rotterdam’s islamic party) has stated that it will pay all fines imposed on those wearing niqabs. The party even created a community account where people can donate money to be used for fines. Algerian activist Rachid Nekkaz also offered to cover fines.
Despite the lack of enforcement surrounding the ban, its existence alone is a sign of hostility towards the Dutch Muslim community. According to Al Jazeera, Nourdin el-Ouali, who leads the Nida Party, called the ban a “serious violation” of religious freedom and freedom of movement, and warned that it will have far-reaching consequences.
EMMA BRUCE is an undergraduate student studying English and marketing at Emerson College in Boston. While not writing she explores the nearest museums, reads poetry, and takes classes at her local dance studio. She is passionate about sustainable travel and can't wait to see where life will take her.
As 2020 Race Heats Up, Sunrise Movement Activists Push for Climate Legislation
For a coalition built in the era of the climate crisis, the question is not just how to save the planet but how to salvage the fate of humanity as we know it.
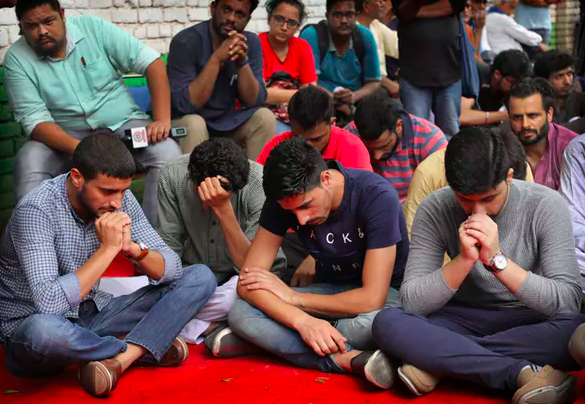
Read MoreKashmiri Muslims shout slogans during a protest after Eid prayers in Srinagar. AP Photo/ Dar Yasin
What’s Behind the Protests in Kashmir?
India recently enacted a law which will end a special autonomous status given to the state of Jammu and Kashmir, known in the West as simply “Kashmir.”
Amit Shah, India’s minister for home affairs, announced in Parliamentthat the Bharatiya Janata Party government was revoking Article 370 of the Indian Constitution in the name of bringing prosperity to the region.
Since 1954, this article has governed federal relations between India and Kashmir, India’s only Muslim majority state.
I’m a scholar of South Asian politics and have written extensively on the evolution of the India-Pakistan conflict in Kashmir.
Article 370 is woven into that history.
History of Kashmir’s autonomy
Article 370 originated in the particular circumstances under which the former prince and last ruler of Kashmir acceded to India shortly after the partition of the British Indian Empire into the independent states of India and Pakistan in 1947.
The prince, or maharaja, agreed to have Kashmir become part of India under duress. His rule was threatened by an insurrection supported by Pakistan.
Article 370 was designed to guarantee the autonomy of the Muslim majority state, the only one in predominantly Hindu India. The clause effectively limited the powers of the Indian government to the realms of defense, foreign affairs and communications. It also permitted the Kashmiri state to have its own flag and constitution.
More controversially, Article 370 prohibited non-Kashmiris from purchasing property in the state and stated that women who married non-Kashmiris would lose their inheritance rights.
Changes over time
But the independence of the Kashmiri state has been declining for decades. Beginning in the early 1950s, a series of presidential ordinances, which had swift effect much like American executive orders, diluted the terms of the article.
For example, in 1954, a presidential order extended Indian citizenship to the “permanent residents” of the state. Prior to this decision the native inhabitants of the state had been considered to be “state subjects.”
Other constitutional changes followed. The jurisdiction of the Indian Supreme Court was expanded to the state in 1954. In addition, the Indian government was granted the authority to declare a national emergency if Kashmir were attacked.
Many other administrative actions reduced the state’s autonomy over time. These have ranged from enabling Kashmiris to participate in national administrative positions to expanding the jurisdiction of anti-corruption bodies, such as the Central Vigilance Commission and the Central Goods and Services Act of 2017, into the state.
What it means for India and the world
What has happened as a result of the move to revoke Article 370?
Kashmiris living in New Delhi gather for a function to observe Eid al-Adha away from their homes in New Delhi. AP Photo/Manish Swarup
Kashmiris living in New Delhi gather for a function to observe Eid al-Adha away from their homes in New Delhi. AP Photo/Manish Swarup
The decision has been met with considerable unhappiness and resentment in the Kashmir Valley, which has a Muslim population close to 97% – versus 68% of the population of the state as a whole. The government of Jammu and Kashmir, meanwhile, does not have the legal power to challenge the move.
China and Pakistan have expressed displeasure.
Pakistan has long maintained that it should have inherited the state based upon its geographic contiguity and its demography.
India and Pakistan have fought three wars over Kashmir. While I don’t believe Pakistan will initiate another war with India over this issue at this time, I doubt it will quietly resign itself to the changed circumstances. At the very least, it will seek to draw in members of the international community to oppose India’s action, as it has sought to do in the past.
China, which considers Pakistan to be its “all-weather ally,” has stated that the decision was “not acceptable and won’t be binding.”
SUMIT GANGULY is a Distinguished Professor of Political and the Tagore Chair in Indian Cultures and Civilizations at Indiana University.
THIS ARTICLE WAS ORIGINALLY PUBLISHED ON THE CONVERSATION.
Death in detention: the aftermath of an airstrike on the Tajoura camp in Tripoli in July 2019. EPA
Libya: Ongoing Atrocities Reveal the Trouble with International Military Intervention
It’s been eight years since the NATO-led military intervention in Libya. Many analysts consider the action a crucial step forward in protecting civilians from looming atrocity. But today, Libya stands further from peace than ever.
Since April 2019, battles between the UN-sponsored Government of National Accord (GNA) and General Khalifa Haftar’s Libyan National Army have raged in Tripoli. By the end of July, an estimated 1,100 people had been killed and a further 104,000 displaced.
In early July, an airstrike on Tajoura migrant detention centre near the Libyan capital Tripoli reportedly killed more than 50 civilians and injured 130. When a strike landed close to the centre just six weeks before, Amnesty International warned of the dangers faced by detainees. Their warnings were ignored and 610 migrants were trapped in Tajoura when a bomb struck. According to one doctor working for Médecins Sans Frontières, there were “bodies everywhere, and body parts sticking out from under the rubble”.
As our new book chronicles, today’s battle for Tripoli is the latest in a long line of horrors. Post-intervention Libya has faced political and economic collapse, with 7,578 violent deaths recorded between 2012 and 2018. Hundreds of thousands of people have been displaced and weapons have spread across the region.
Read more: Libya conflict boils down to the man driving the war -- Khalifa Haftar
While spectacular acts of violence dominate headlines, the horrors facing civilians in Libya are routine and every day. Migrants are left to die from treatable illness in awful detention centres. One migrant in Libya, writing anonymously for The Independent, said: “We panic every day, we are dying slowly, because of too much depression and starvation.”
Back in late November 2017, the European Union’s migration commissioner, Dimitris Avramopoulos, said he was, “conscious of the appalling and degrading conditions in which some migrants are held in Libya”. And yet, extreme human rights abuses are still being actively enabled by European policies.
Targeting Gadaffi: NATO bombs hit the Libyan leader’s compound in June 2011. EPA
Humanitarian rescue missions have been criminalised, leaving people to drown in the Mediterranean. Migrants captured at sea are sent back to detention centres, including 90 who were forced to return to Tajoura mere days after the airstrike.
Read more: EU sued at International Criminal Court over Mediterranean migration policy – as more die at sea
Fuelling more violence
Ghassam Salame, special representative of the UN Secretary-General and head of the UN Support Mission in Libya, reports that “external support has been instrumental in the intensification of airstrikes”.
The UN is currently investigating allegations that the United Arab Emirates has supplied Haftar with weapons in violation of a UN arms embargo, and French weapons have been found at a Haftar base. Meanwhile, Turkey is providing weapons to fighters from the GNA.
The G7 and the UN have condemned the violence in Libya. In practice, however, the actions of some of their members fuel the killing and prevent co-ordinated diplomatic action.
It’s often argued that Libya shows the need for more robust post-intervention planning of humanitarian military interventions. This is misleading. Instead, the situation highlights the need for new thinking on civilian protection.
The question of intervention usually emerges at that dramatic moment when civilians are at risk of extreme violence. Often brushed aside is the every day atrocity of the kind seen in Libya today: civilians at risk of starvation, death through treatable illness and killing at the hands of callous policies. This is not only an atrocity in its own right. As our research shows, it also creates an ideal habitat for mass atrocity crimes including genocide and ethnic cleansing. Instead of calling for military action when atrocity crimes occur, our focus should shift towards addressing the injustices that help create them.
Also forgotten is the role the international community plays in fuelling conflict through stoking division and selling arms. France provided Rwanda with weapons used to commit genocide in 1994. Claims that France also provided military training for perpetrators are under investigation by a French commission of experts. US and UK arms are being used against Yemeni civilians. Moreover, members of the international community have supported different sides in the Syrian civil war.
Read more: Why British arms sales to Saudi Arabia ruled unlawful – what this means for the future
Other options
Events in Libya show what can happen when international players claim to do good things through military action. To prevent future atrocities, the international community must recognise the absurdity of dropping bombs to protect people while also detaining migrants in the centre of war zones, dealing arms, and preventing rescue missions.
Military intervention does not protect civilians. We should call on the international community to change their callous policies that kill every day. We should demand that they stop fuelling atrocity crimes. And we should support non-violent forms of protection such as unarmed civilian peacekeeping, which have proven effective in Colombia, South Sudan, Kosovo and Sri Lanka.
To support military intervention gives further licence to the militarism of those already fanning the flames of atrocity. This will only result in more of the violence seen in Libya today.
MICHAEL NEU is a Senior Lectuer in Politics, Philosophy and Ethics at the University of Brighton.
ROBIN DUNFORD is a Principal Lecturer in Globalisation and War at the University of Brighton.
THIS ARTICLE WAS ORIGINALLY PUBLISHED ON THE CONVERSATION.
Small change can make a difference. Photo by Kat Yukawa.
7 websites and apps that make giving easy!
New technology has allowed giving to be easier, and more accessible for those who don’t have the time or funds to give hundreds to charities or conduct due-diligence. Organizations have created websites and apps that allow anyone to give directly from their cell.
Good Today members give a small amount to charity every day. You can sign up for a payment plan of as little as $.25 a day. Each day, members receive an email with the cause of the day, and then an option of two different charities that have the cause as their mission. You can then select which charity you would like your money to go to, or have your money roll over to the next day.
2. Amazon Smile
With Amazon Smile, you can shop for the same exact products as Amazon.com. However, .5% of the price of each item that you purchase will go to the registered charity of your choice. Just do your shopping on smile.amazon.com.
3. Budge
On Budge, you can play games and play charity at the same time! You can create an account, and then challenge a friend to any game of your choice. If you win, your opponent will make a small donation to charity. But if you lose, you give.
For those who need an extra incentive to work out, Charity Miles can help you and others. The best part? All of the money donated is from outside corporations, so you don’t need to give anything yourself. Download the app, and for every mile you move, you earn money for an organization from Charity Miles’ corporate sponsorship pool.
This app is sponsored by Johnson and Johnson. Donate a Photo curated a list of charities that Johnson and Johnson will donate to every time you share any photo to their app.
6.JustGive
JustGive is an online platform that makes fundraising and donating easy and seamless. You can provide direct support to a charity or family in need. Or, you can create a fundraising campaign yourself!
If you want to give time instead of money, VolunteerMatch is the website for you. Just type in your area and VolunteerMatch will provide you with a multitude of volunteer opportunities for organizations.
With these apps and websites, giving has never been easier. There is no need to write large checks in order to be a philanthropist.
ELIANA DOFT loves to write, travel, and volunteer. She is especially excited by opportunities to combine these three passions through writing about social action travel experiences. She is an avid reader, a licensed scuba diver, and a self-proclaimed cold brew connoisseur.
Syria’s Struggle: How 10-Day Span Air Raid Wiped Out Over 100 Civilians
On July 26, 2019, an air raid over Syria caused many casualties and sparked concern about why the violence was not being addressed by media outlets.
Protestor sign in London. chrisjohnbeckett. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Many people have lost their lives in an air-bombing raid in Syria in the past few weeks. The raid killed 103 people in only 10 days. Michelle Bachelet, human rights advocate, blames the government for the mass bombings, condemning the “failure of leadership by the world’s most powerful nations”. Syria, as well as Syria's ally – Russia, have denied the attack on civilians, claiming they are not responsible for the violence.
UN specialist Michelle Bachelet, brought the UN’s attention to what was going on, stating that “These are civilian objects, and it seems highly unlikely, given the persistent pattern of such attacks, that they are all being hit by accident,” she added. “Intentional attacks against civilians are war crimes, and those who have ordered them or carried them out are criminally responsible for their actions.”
The air raids occurred over the Idlib regioni and in rural Aleppo region. Bachelet states, the areas “have experienced civilian casualties as a result of airstrikes in the past ten days alone, causing a minimum of 103 civilian deaths, including at least 26 children”. The reason Bachelet was so passionate about bringing the UN attention to the violence was because no one else was. The events happened over a 10 day span and in those ten days, little to no coverage was happening to address and possibly stop the violence. Bachelet states that she is “concerned that the continued carnage in Syria ‘is no longer on the international radar.’”
The air raids targeted a rebel-populated base, attacking “medical facilities, schools and other civilian infrastructure such as markets and bakeries”. These frequent and malicious attacks are too premeditated to be labeled as an “accident”, claims Bachelet.
According to a statement made in the Daily Star, “The region under attack is home to some three million people, nearly half of them already displaced from other parts of the country. It covers nearly all of Idlib and parts of Aleppo, Hama, and Latakia provinces. The Idlib region is controlled by jihadist alliance Hayat Tahrir al-Sham, led by Al-Qaeda’s former Syria affiliate.” Still, because there was such a lack of response to the air raids, no one is taking responsibility.
The office for the coordination of humanitarian affairs (OCHA) issued a statement claiming the air raids were seen as the “deadliest days” in the Idlib and Aleppo regions.
Bachelet states, “This is a failure of leadership by the world’s most powerful nations, resulting in tragedy on such a vast scale that we no longer seem to be able to relate to it at all.”
OLIVIA HAMMOND is an undergraduate at Emerson College in Boston, Massachusetts. She studies Creative Writing, with minors in Sociology/Anthropology and Marketing. She has travelled to seven different countries, most recently studying abroad this past summer in the Netherlands. She has a passion for words, traveling, and learning in any form.
Senior Welfare Benefits Universal Across Uganda
Uganda recently raised the age for welfare benefits to 80. At the same time, the government expanded the program to be universal across the country, thus both increasing and cutting the number of people who will receive benefits used for necessities.
Uganda’s Senior Citizens grant gives 25,500 Ugandan shillings each month to those who are part of the program, which launched in 2010. Vjkombajn. CC0.
It is estimated that 8 million Ugandans (out of 37.7 million people) live below the poverty line. With a faltering tradition of family support, people are forced to continue working past the point when they should. Generally, they continue with trade or small-scale farming. Those who are ill or otherwise unable to work doubly suffer.
In 2010, Uganda, together with the UK Department for International Development, Irish Aid and the United Nations Children’s Fund, began to create social pensions that assist those who have such precarious incomes.
As of July, Uganda’s welfare Senior Citizens grant, part of their Social Assistance Grants for Empowerment (SAGE) program, has raised their age of entry to 80, which cuts people out between the ages of 65 and 79 who had previously been eligible. These people will have no access to monthly benefits as of the upcoming year. However, at the same time, they expanded the grant so it is universal in Uganda. For the first 100,000 people who joined, the age for eligibility was 65, which was lowered to 60 in Karamoja due to the lower life expectancy there. After that number was reached, the government rolled out the pension to another 40 districts. However, with those districts, it was available only to the 100 oldest in a village. Now, the pension is universal, though the entry age is 80. As of June, according to HelpAge, more than 160,000 people have been enrolled in the program. Due to making everyone eligible, roughly 365,000 Ugandans now have the opportunity to receive a pension. The exact number is unclear.
There is also the problem of earlier deaths, possibly increased by the enlarged population of those living below the poverty line. Julius Mukunda, co-ordinator of the Civil Society Budget Advocacy Group, believes that the government’s failure to care for the elderly is because of their prioritization of political projects, according to The East African. Inflation pressures have also lowered power levels for SAGE benefits.
The non-contributory pension gives each person 25,000 Ugandan shillings, which converts to $7 US, each month. People use it for food, school supplies, and other necessities. "[The pension] has been instrumental in my life. When I get the money, I become happy. I have used it to buy a goat for my family to rear. I use it to pay school fees and buy books for my children," said Longora, an older man in Napak, Uganda, according to HelpAge.
Households that receive the grants have had their poverty reduced by 19 percent while spending has gone up 33 percent. Households also use the pension to further increase their income, for example by buying livestock. Children who are part of these households have been found to have better education and are less likely to be involved in child labor.
Several other countries in Africa, such as Mauritius, Kenya and Zanzibar, have implemented a social welfare pension, while Mozambique is planning to create a social protection program. However, issues persist, such as mobility issues in getting to the pay point, missing records, and financial abuse.
If the people receiving these pensions continue to speak out about how they have helped themselves and their families, they can hold their governments to account for how services are used. This assertion helps to reduce long-term problems such as financial abuse and other errors. It is each government’s responsibility to make sure citizens are aware of social protection programs and that those services are accessible, inclusive, and efficient.
NOEMI ARELLANO-SUMMER is a journalist and writer living in Boston, MA. She is a voracious reader and has a fondness for history and art. She is currently at work on her first novel and wants to eventually take a trip across Europe.
A Crisis of Violence Pushes Honduran Women to the U.S. Border
For women facing rampant femicide and rape in Honduras, the risks of a treacherous trip across the border are minor compared to the dangers of remaining at home.
High rates of violence against women in Honduras has been attributed to a culture of machismo. Paul Lowry via Wikimedia Commons. CC BY-SA 2.0
Yo no quiero ser violada.
I do not want to be raped.
So read the signs plastered across walls and doors in the cities of Honduras. Simple black lettering is inscribed beneath a pair of thickly lashed eyes, with the eyebrows above turned downwards in an expression of anger—or, more accurately, indignation—at the dangerous injustices Honduran women face every day.
Honduras has been called the most dangerous place on Earth to be a woman, and with good reason: As of 2015, the Central American nation ranked alongside war-torn countries like Syria and Afghanistan for the highest rates of violent deaths among women. Although the overall murder rate of Honduras, which has long been wracked by drug- and gang-related violence, has declined in recent years, murder remains the second-leading cause of death for women of childbearing age.
In 2014, a high-profile “femicide”—the murder of a woman because she is a woman—rocked the nation and brought its murder rates into the international spotlight. Nineteen-year-old Miss Honduras winner Maria Jose Alvarado, just days from departing for London to compete for the title of Miss World, was brutally murdered and buried in a shallow grave in a riverbank. Authorities surmised that her sister’s boyfriend, 32-year-old Plutarco Ruiz, shot his girlfriend, Sofia Trinidad, before opening fire on Maria Jose as she attempted to flee. The ensuing investigation yielded the sisters’ bodies within a week, but their mother, Teresa Muñoz, believed it would not have happened at all if Maria Jose had not been famous: “Here in Honduras, women aren’t worth anything,” she told ABC News.
In 2013, the year before Maria Jose’s violent death, statistics showed that 636 women were murdered during the year, one every 13.8 hours. Most victims lived in urban areas, particularly San Pedro Sula and the Central District—in fact, 40 percent of all murders of women could be traced to those two areas. Nearly half of all women targeted annually were young, with the 20–24 age range being the most at risk. And murder is far from the only danger facing Honduran women. Rape, assault, and domestic violence are also rampant, and perpetrators enjoy near-total impunity: In 2014, the UN found that 95 percent of sexual violence and femicide cases were never investigated.
San Pedro Sula, a city with high rates of femicide. Gervaldez. CC BY-SA 4.0, CC BY-SA 3.0, CC BY-SA 2.5, CC BY-SA 2.0, CC BY-SA 1.0
Honduras’ shocking levels of violence against women can be traced in part to harmful attitudes bubbling below the surface. Suyapa Martínez, a local feminist and co-director of the Center for Women’s Studies—Honduras, points to “machismo,” a Spanish term describing a society built by men “who consider themselves to be the owners of women’s bodies.” In such a society, women have historically lacked political power: Only about half of Honduran women work outside the home, and when they do, they earn just half of what their male colleagues bring in.
Meanwhile, those ostensibly tasked with protecting all Honduran citizens—women included—have done little to mitigate the crisis. A 2015 report from the UN special rapporteur on violence against women concluded that the administration has paid “minimal attention” to gender empowerment and implemented only “ineffective measures” to address social reform. And in many cases, the government inflames the problem by limiting women’s options after sexual violence: Emergency contraception is completely banned, as is abortion, even in the case of rape, incest, or threat to the mother’s life. Women who seek abortion can receive a prison sentence of up to six years. These strict rules stem from the stranglehold of the Catholic and Evangelical churches, who have resisted even minor liberalizations to legislation—even after the UN joined with other human rights groups in 2017 to call for the allowance of abortion in cases of rape, incest, or possibility fatality. To make matters worse, the government is expected to decrease the penalty for violence against women later this year to between one and four years in prison.
Trapped in a repressive society and seeing little hope for a safer future, huge influxes of women and children have embarked on the treacherous journey to America’s southern border. In what the UN has called an “invisible refugee crisis,” women from the Northern Triangle—which includes Honduras, El Salvador, and Guatemala—have been fleeing in droves, with more than half listing violence as their reason for requesting entry to the United States. Lori Adams, director of the U.S.-based Immigration Intervention Project at Sanctuary for Families, told Politico, “Women are leaving with no other option but to flee north, even knowing that the journey itself might be life-threatening, but knowing it’s a near certainty that they will be killed if they remain.”
Migration office in Honduras. KriKri01. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
Yet even if women survive the trek north, their hopes are often dashed when they reach the border. According to researchers at Syracuse University, the percentage of asylum applicants denied by U.S. immigration courts has been increasing since 2012, reaching 65 percent in 2018. That year, prospects for Hondurans were particularly grim, with judges granting just 21 percent of asylum cases. And as of mid-August, new policies from the Trump administration will privilege green-card applicants—immigrants aiming to become naturalized citizens—who are educated and monied while denying those who are considered likely to rely on government welfare programs. Given the financial dynamics of Latin America, the new rule will almost certainly affect Honduran women seeking safety in the United States. Dario Aguirre, a Denver-based immigration lawyer, told the New York Times that Trump’s policy gives officers carte blanche to deny green cards to many working-class immigrants from less developed countries, such as El Salvador, Guatemala and Honduras. Thus, another option is ripped from the hands of already desperate Honduran women—and until the U.S. government or Honduran officials enact substantive change, their eyes will stay wide open like the posters on the walls, watching keenly for danger.
TALYA PHELPS hails from the wilds of upstate New York, but dreams of exploring the globe. As former editor-in-chief at the student newspaper of her alma mater, Vassar College, and the daughter of a journalist, she hopes to follow her passion for writing and editing for many years to come. Contact her if you're looking for a spirited debate on the merits of the em dash vs. the hyphen.
President Duterte Calls to Revive the Death Penalty
The president of the Philippines, Rodrigo Duterte, requested to revive the death penalty a few days ago, solely for drug-related crimes.
HIgh level drug offenders could go from prison to the death penalty, if Filipino President Rodrigo Duterte’s call to revive it is sucessful. Jody Davis. CC0.
Filipino President Rodrigo Duterte asked Congress to revive the death penalty for drug-related crimes on July 22, during his State of the Nation Address (SONA).
Speaking before a joint session of Congress, he first brought up the revival as the first priority legislative measure in his fourth Address, according to Rappler. His party, PDP-Laban, currently has a supermajority in the House of Representatives. He mentioned the 5-month siege that evolved between the state and extremists after terrorists held onto drugs in Marawi in May 2017, citing it as a prime example as to why further action and harsher actions were and are necessary.
Duterte’s war on drugs has been ongoing since his candidacy in 2016. He has been calling for the reinstatement of the death penalty for the same length of time. He also requested capital punishment in his 2017 SONA.
Senator Ronald dela Rosa, a trusted aide to the president, won his senatorial election in 2019 on a single promise: to bring back the death penalty for drug-related crimes.
Duterte also effectively began a war on corruption in Filipino society. On July 19, three dozen of Duterte’s critics were charged with sedition and cyber libel after a series of anonymous videos that accuse the president and his family of having monetary links to the illegal drug trade, according to Newsweek.
Amnesty International believes the call will only increase the country’s environment of exemption from punishment during the continuous war on drugs.
However, Senate President Vicente Sotto III believes that restricting the reinstatemnt of capital punishment to high-level offenders would be more likely to pass in the Senate. He also mentioned this bill would be among the first to be discussed. Two years ago, the House of Representatives passed a measure for the death penalty for crimes related to drugs.
“The state of our nation is a state of mourning. We should not be burying our children amid deadly and ill-conceived police raids,” said Butch Olano, Section Director for Amnesty International Philippines, according to Amnesty International.
There has been one conviction of police officers, for the killing of a 17-year-old boy. During a police operation in late June 2019, a three-year-old girl and a police officer were killed. The girl’s mother and the government both have different stories about the operation. Overall, so far the Philippine government has noted at least 6,000 killings at the hands of police officers. Amnesty International has found that there are many more unlawful killings, likely done by armed people with ties to the police.
Olano says that, despite being told to file cases before the courts if they feel there has been an unlawful death or that the police have acted illegally, many families are too afraid to speak up. There are also the problems of costs or being unable to secure evidence or the police reports.
The Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights is meant to deliver a report in June 2020 on the state of human rights in the Philippines. President Duterte’s remarks didn’t commit to assisting with this report, which was requested last month in a resolution by the UN Human Rights Council, particularly since Duterte has been accused of human rights abuses.
Duterte has been battling against drugs since before he was elected in 2016. Requesting the revival of the death penalty for drug-related crimes may be extreme, but it isn’t terribly unexpected from this president. If this request passes, Duterte’s war on society’s corruption will most likely increase, as he will have already have gained one victory. Amnesty International’s prediction also seems likely of coming true. However, if this request isn’t passed, it’ll be a blow to Duterte’s war on drugs. The war itself will continue, but this particular battle won’t. The human rights report will be written throughout this year and next, regardless of what happens with the death penalty. President Duterte is already under investigation, though the Philippines will become an even more dangerous place if the death penalty is passed in any form.
NOEMI ARELLANO-SUMMER is a journalist and writer living in Boston, MA. She is a voracious reader and has a fondness for history and art. She is currently at work on her first novel and wants to eventually take a trip across Europe.
This Is the Only Shelter for Refugees in NYC
Edafe Okporo is the director of the only shelter in New York City that provides housing for asylum seekers, refugees and migrants. He knows what it’s like to arrive in the U.S. with nowhere to go. Okporo left Nigeria seeking asylum after he was attacked by a mob because of his sexual orientation. With the hope of a better life, he came to the U.S., but soon realized he faced another battle. Refugees can undergo harsh treatment, having to navigate complex asylum law and face time in detention centers. Still, he persevered, and built a life for himself. Now, Okporo is helping others do the same.
Swimming in Toxic Water
There’s a reason no one has gone for a dip in New York City’s Newtown Creek in recent history. In Christopher Swain’s words, it’s like “swimming through a dirty diaper garnished with oil, gasoline and trash.” He’s a clean water activist who has swum over 3,000 miles in 25 different contaminated waterways across North America as a means of advocating for their cleanup. Taking a dip in these waterways does not come without its risks. Despite the precautions Christopher takes—wearing a puncture-resistant drysuit, goggles, ear plugs, etc.—he still gets sick from the various contaminants. It’s the hazards that come along with the cause, but Christopher continues to swim, all out of love for the water.
Dalia Yashar, one of the first Saudi female students in training to become commercial pilot, pictured on July 15, 2018. Her future passengers will include solo women travelers, too. Reuters/Hamad I Mohammed
Saudi Women are Fighting for Their Freedom – and Their Hard-Won Victories are Growing
Saudi women will soon be allowed to obtain passports and travel without permission of a male relative, a big change from Saudi Arabia’s “guardianship system” which puts men in charge of their female relatives.
Read MoreMisfits Market: A Cheaper, More Sustainable Way to Buy Groceries
Quirky produce doesn’t have to be thrown out
Markets typically like to display “perfect” produce. Photo by Ja Ma.
Have you ever felt excited when you found a cute mini potato in your groceries? Or marveled at a cool way that carrots grew intertwined together? Produce with quirks can be fascinating, and not dangerous to eat. However, many supermarkets have become obsessed with finding the “perfect” produce—the picture-perfect produce that customers would want to buy. Therefore, the produce that don’t fit the bill will end up as waste.
Misfits Market is a service that simultaneously helps the world and your wallet. They collect food from farmers that would normally go to waste, and package it to sell to their customers. The customers get their produce at a markdown of up to 50% compared to regular grocery stores, while the farmers are able to make extra money. So, customers save money, farmers make money, and both Misfits Market and their patrons are working to reduce the 3.3 billion tons of carbon dioxide that are generated annually because of food waste.
Misfits Market makes life easier by delivering your groceries straight to your door. You can subscribe to the Mischief Box or a larger Madness Box, that can be delivered either once a week or every other week. Misfits Market delivers to a large number of states in the US, but it is growing quickly. The produce varies by season, and is always organic.
Additionally, their packaging is entirely eco-friendly. The boxes are recyclable and compostable, and the insulation to protect the produce from the elements during delivery is also home-compostable. Misfits Market’s website gives directions for how to compost the insulation at home.
Check out Misfits Market’s blog to see recipes to make with their produce.
ELIANA DOFT loves to write, travel, and volunteer. She is especially excited by opportunities to combine these three passions through writing about social action travel experiences. She is an avid reader, a licensed scuba diver, and a self-proclaimed cold brew connoisseur.