Millions of women in developing countries lack access to clean cookware. International organizations are working to change that.
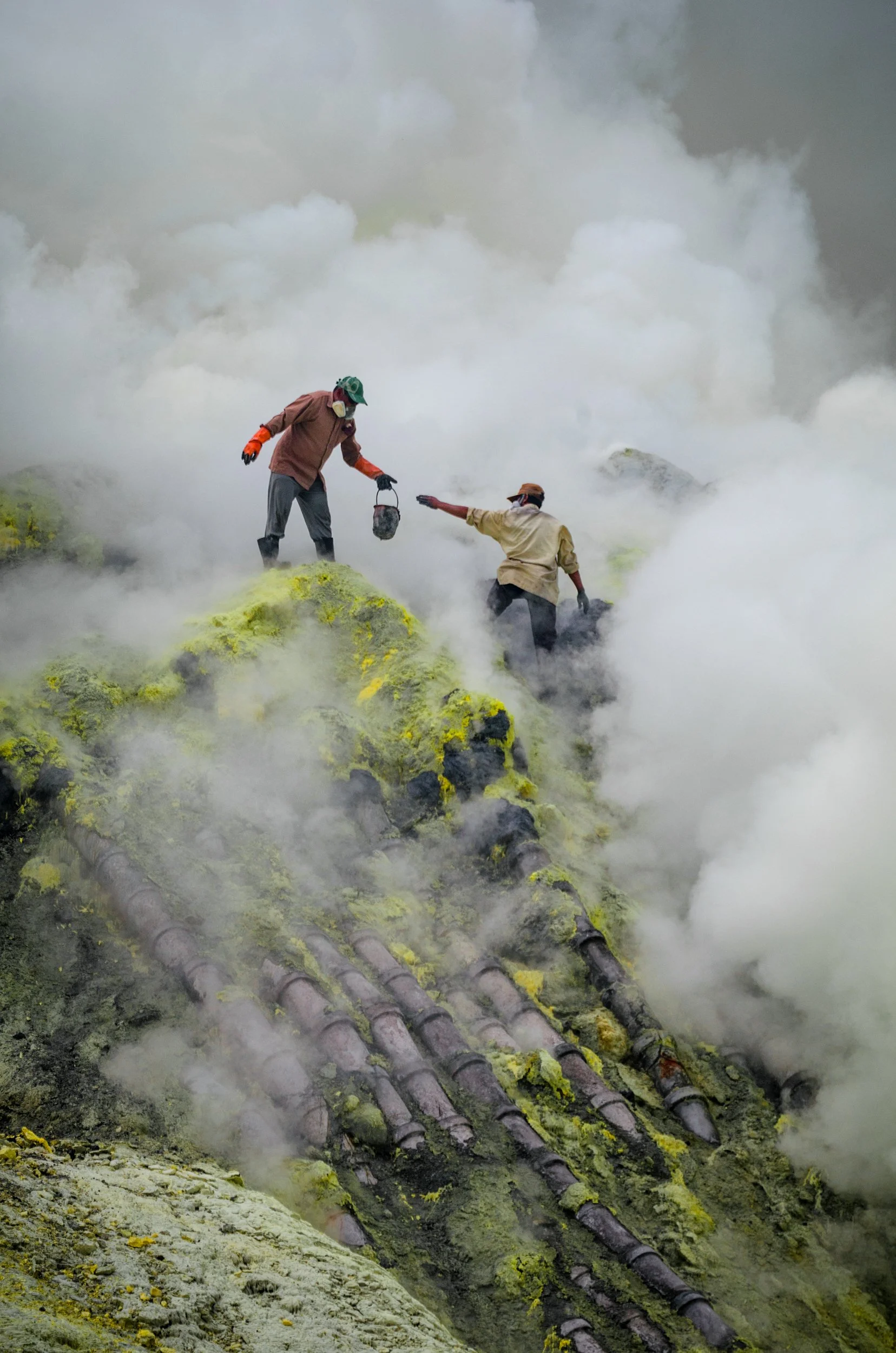
Women in India testing a solar cooker. United Nations Development Program. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
Although the Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action in 1995 made groundbreaking strides toward gender equality, one key issue was never addressed: providing households with clean cookstoves. At least 3 billion people across the developing world rely on open fires to cook their food, a task mainly entrusted to women. Cooking on open fires can hold severe environmental and health implications for women and their families.
Modern cookstoves have reduced black carbon emissions by 30-60%
According to the Clean Cooking Alliance, cooking over open fires is the second-largest contributor to global warming aside from carbon dioxide emissions. The burning process releases black carbon, or soot, which lowers the reflective quality of glaciers and sea ice, causing them to melt. Additionally, the demand for wood as fuel results in unsustainable harvesting and deforestation. Studies indicate that at least 30% of the wood used in the developing world is unsustainably harvested, negatively affecting the ecosystem’s health, biodiversity and erosion. The absence of trees prevents carbon dioxide from being absorbed from the atmosphere through photosynthesis, further compounding the effects of global warming.
Cooking on an open fire also exposes women and children to toxic levels of household air pollution, sometimes over 35 times the amount deemed safe by the World Health Organization. Exposure to air pollution can have detrimental effects on one’s health, causing increased risks of childhood pneumonia, lung cancer, strokes and atherosclerosis. In some cases, exposure to high levels of air pollution has led to complications during birth. Health conditions related to smoke inhalation kill over 4 million people each year.
Access to safe cookware in the developing world remains limited, especially in areas torn apart by humanitarian crises. Women often put themselves in dangerous and even life-threatening situations while searching for cooking fuel. Women collecting firewood near refugee camps and conflict zones face increased risks of gender-based violence. Additionally, children accompanying their mothers to find firewood cannot attend school and miss out on available educational opportunities. The time spent gathering firewood further prevents women from seeking valuable opportunities to generate income for their families and children.
Empowering Women Through the Clean Cooking Alliance
Women collecting firewood in the Democratic Republic of Congo. Oxfam International. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
Founded in 2010, the Clean Cooking Alliance is an U.N.-backed organization focused on gender equality through cooking. The alliance works with a global team to ensure that 3 billion people gain access to clean cookstoves. Its focus is on increasing consumer demand and supporting local businesses while developing a clean cooking industry in seven countries: Bangladesh, China, Ghana, India, Kenya, Nigeria and Uganda. Modern cookstoves have reduced black carbon emissions by 30-60% and help to combat climate change. Additionally, having access to cooking equipment can save women up to 300 hours and $200 per year, giving them more free time to spend with their families or economic pursuits. As the Clean Cooking Alliance expands its reach, hopes are high that women and their families will be empowered across the developing world.
To Get Involved:
Check out the Global Cooking Alliance’s initiatives on its website or head to its fundraising page.
Megan Gürer
Megan is a Turkish-American student at Wellesley College in Massachusetts studying Biological Sciences. Passionate about environmental issues and learning about other cultures, she dreams of exploring the globe. In her free time, she enjoys cooking, singing, and composing music.