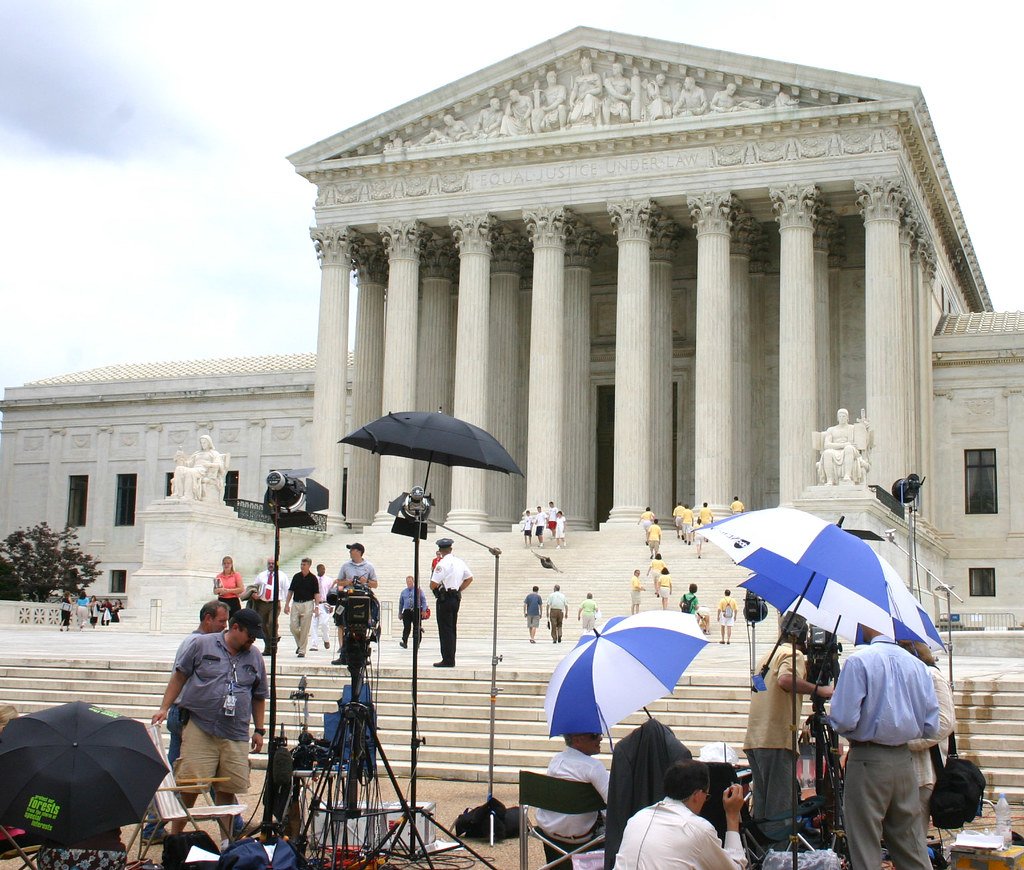
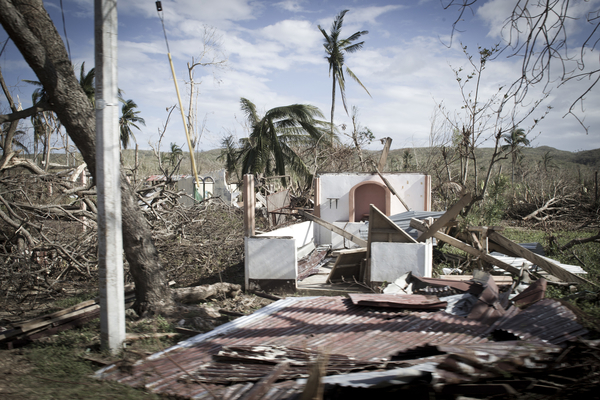
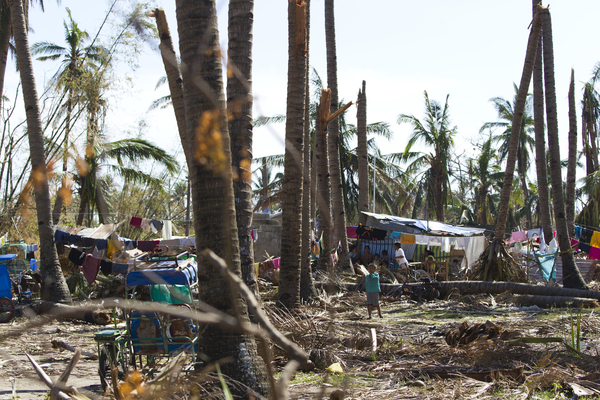
This past Earth Day, climate activist Wynn Bruce lit himself on fire on the steps of the Supreme Court, dying the following day. Set on demonstrating the importance of global warming, Bruce chose the world’s most radical form of protest to emphasize his commitment to martyrdom.
Steps of the Supreme Court. Dbking. CC BY 2.0.
On April 22, 2022, Wynn Bruce, a climate activist from Colorado, made a fateful and radical decision: he would go to the front of the Supreme Court and, using self-immolation, become a martyr for the fight for global-warming-related policy change. Fed up with the lack of commitment to the issue of climate change, Bruce seemed to feel this was the only way he could get United States policy makers to listen—by lighting himself on fire and dying for his cause.
Self-immolation is the most radical and rarest form of nonviolent protest. It is said by ABC to have “the ability to harness both the morality of nonviolent action with the visceral nature of violent action.” By Merriam-Webster's definition, it is the “deliberate and willing sacrifice of oneself often by fire.” Typically, protestors who choose this form of action will use flammable substances such as petrol and lighter fluid to make sure flames catch and spread across the body. The goal of this form of protest is not to live to see its impact, it's to sacrifice oneself as a martyr for a cause in order to stress the dire importance of certain issues.
Used now for decades to protest a variety of social issues, self-immolation has continued its way into the practices of the modern day protest. Wynn Bruce is just one example; a civil rights lawyer named David Buckle burned himself to death in 2018, also protesting climate change. Wynn Bruce, alongside being a son, climate activist and citizen of the world, was a Buddhist, which is the religion credited by many to have started the practice of self-immolation.
Self-immolation has been used across the globe and did not necessarily start as a form of active protest. Buddhists are commonly credited not only with self-immolation’s creation but also with the practice’s infamy. ABC explains that many Buddhists believed that the ability to renounce the body and “transcend[ing] it’s limitations” was when “perfection is reached.” In Buddhism, to transcend is to reach enlightenment—a state of compassion and one that also ends the cycle of rebirth—so often, self-immolation was done as a religious act and not as a form of protest.
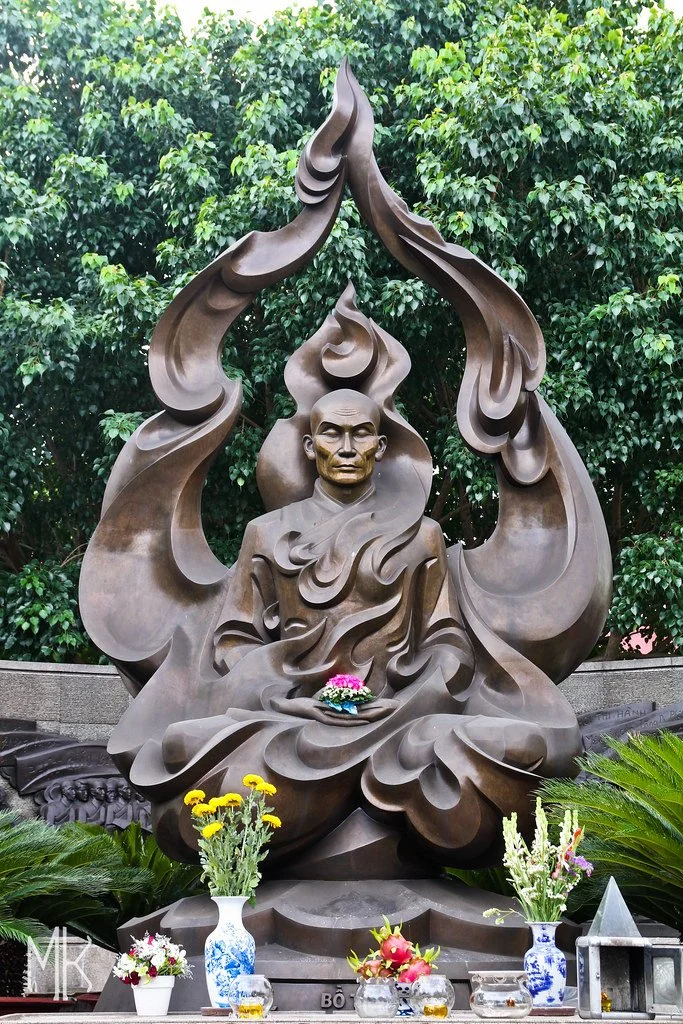
Buddhists used self-immolation first as a form of religious ceremony, but then turned to its more aggressive usages during the Vietnam War. Thich Quang Duc, known as The Burning Monk, used self immolation to protest a massacre that was allowed by the Vietnamese government. The president of Vietnam at the time had laws in place that restricted religious practices of faiths other than Catholicism, which eventually led to the. In response to this outrage, Thich Quang Duc made an ultimate sacrifice; gathering nearly 350 monks and nuns, Thich Quang Duc sat cross legged in the lotus position as a peer poured petrol over his body and lit a flame. Thich Quang Duc remained perfectly still as his body caught fire. This was an act of protest heard around the world, and the imagery from the day was quickly iconized in canonical protest media.
Thich Quang Duc being covered in petrol. Manhhai. CC BY 2.0.
Because self-immolation has the power to so strongly influence those who hear of it, it is not surprising how fast the news of Thich Quang Duc’s sacrifice reached all areas of the globe. Published in magazines such as TIME and the Associated Press, the image circulated the globe and continues to be brought up in tribute articles and memorial pieces by publications.
The act of self-immolation hurts no one except the martyr involved. It attracts all the right media attention, and it emphasizes the threat of pressing social issues in such an extreme way that the world is forced to listen. Wynn Bruce seemed to know this, and his peers claimed to understand his motivations. Dr. Kritee Kanko, a Buddhist priest took to Twitter to write, “This act is not suicide. This is a deeply fearless act of compassion to bring attention to climate crisis.”
A statue of The Burning Monk. MK Photography. CC BY-NC-ND-2.0.
To Get Involved
MCE Cares is an organization designed to help people learn about how to become a climate activist. To learn more about the ways in which you can support the fight for policy change and climate activism, click here.
Ava Mamary
Ava is an undergraduate student at the University of Illinois, double majoring in English and Communications. At school, she Web Writes about music for a student-run radio station. She is also an avid backpacker, which is where her passion for travel and the outdoors comes from. She is very passionate about social justice issues, specifically those involving women’s rights, and is excited to write content about social action across the globe.