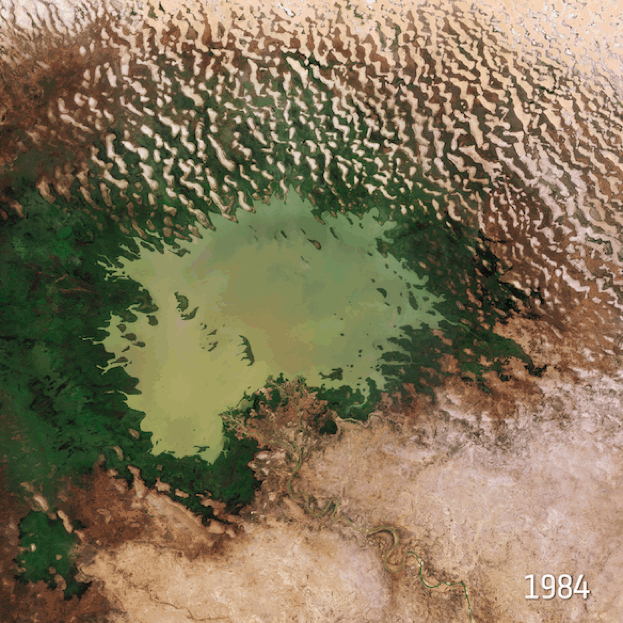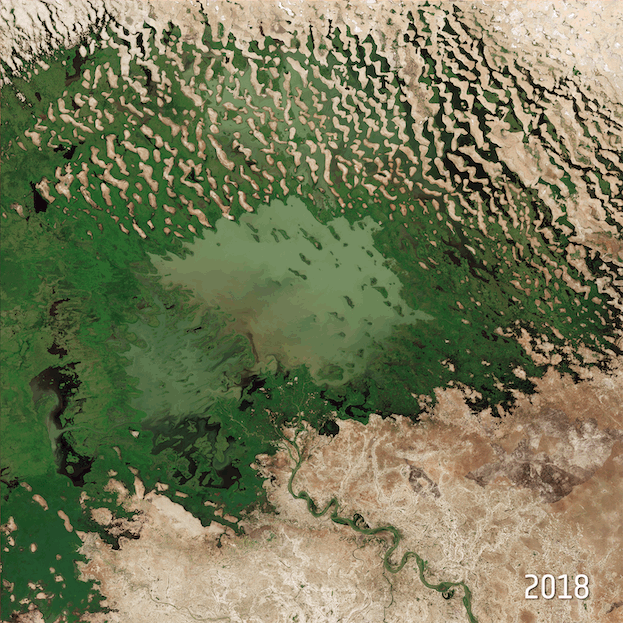
Industrialization and restricted water flow have led the Dead Sea to shrink, throwing its survival into question.
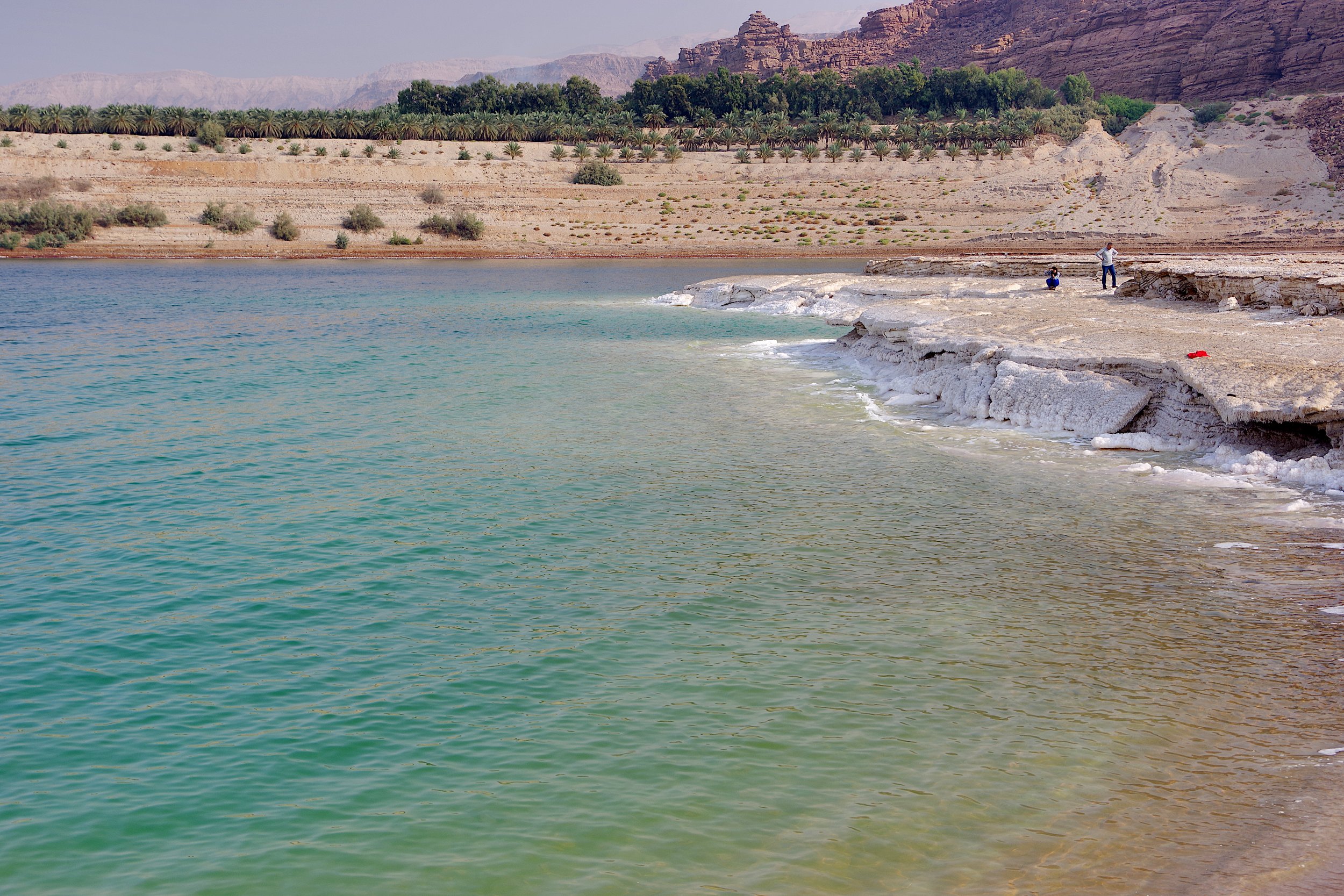
Dead Sea Shoreline. Jan Helebrant. CC0 1.0
As a landmark of the ancient world, the Dead Sea, which lies between East Jordan and the West Bank, has long been a staple for international travel. Every year, more than 800,000 people travel to the Dead Sea where they can experience the lowest point on earth and the salt lake’s extremely high salinity levels, which allow travelers to float easily on the surface while looking out on the desert’s beauty. While many travelers make the journey for the unique and thrilling experience of floating in the Dead Sea, others journey with the hope that the water will cure health ailments, including chronic skin diseases such as psoriasis and eczema.
The area surrounding the Dead Sea is a place of cultural and religious importance, and has been featured as a sacred site in Islamic, Christian, and Jewish stories. Some Muslims believe that Moses is buried at Nabi Musa, a hilltop mosque off the main road of Jerusalem overlooking the northern edge of the Dead Sea. In Christianity, Jesus’ baptism in the Jordan River was believed to have occurred after he traveled from Galilee down through the Dead Sea. And in the Judean Desert, on a peak overlooking the Dead Sea, sits fortress Masada, a spot in which a community of nearly 1,000 Jewish Israelites committed suicide in A.D. 73 in order to avoid surrender to the Romans.
The Dead Sea is not only an important cultural and historical site, but an environmental one as well. Some 500 million birds, representing about 300 different species, fly through the area during a biannual migration moving from Africa to Europe. And nearby desert mountains serve as home to ibexes and hyraxes.
In recent decades, the Dead Sea has been facing serious environmental dangers that threaten to make it, and the cultural and historic importance it carries, disappear forever. Within the past fifty years, the Dead Sea has shrunk by over a third of its original size, a rate that experts believe may lead it to completely disappear by the year 2050. The changes are already being felt on an annual level in the area, with the sea receding by more than a meter each year.
Increased Industrialization
Dead Sea Sinkhole. Ziva & Amir. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
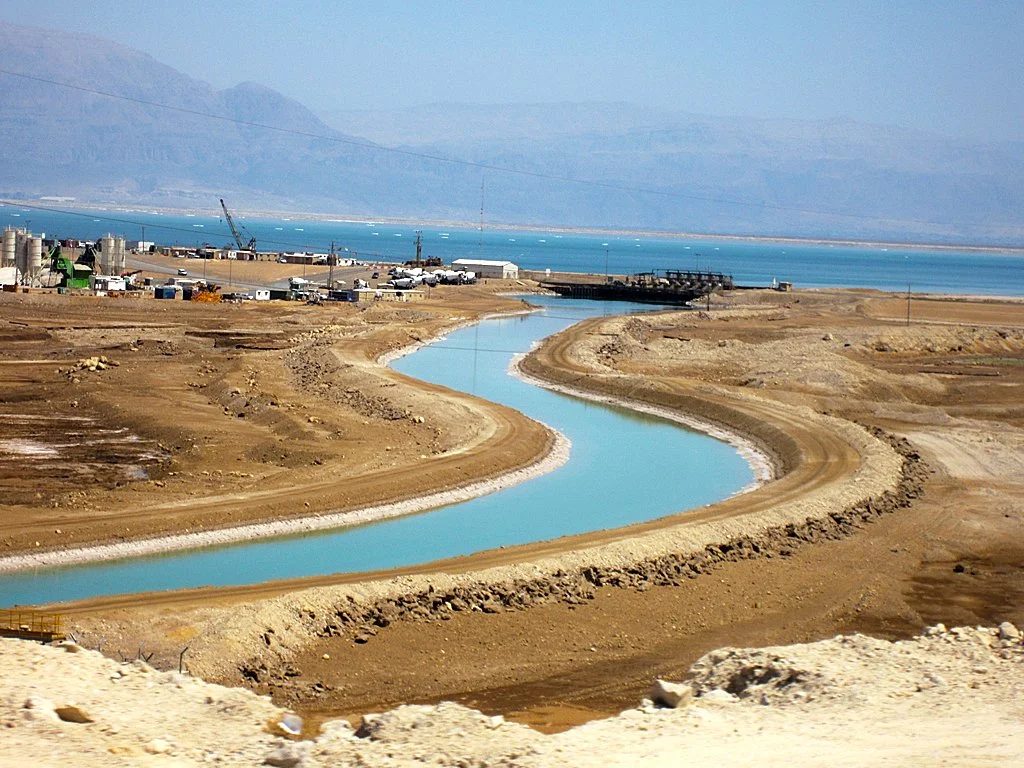
For generations, the Dead Sea was maintained by a careful equilibrium in which evaporation was offset by fresh water coming in from nearby streams and rivers. However, in the 1960s, a massive pumping station built by Israel on the banks of the Sea of Galilee re-directed the flow of water. Fresh water from the upper part of Jordan that had been feeding into the Dead Sea was moved into a pipeline to supply water across Israel. It and other industrial projects have led the Dead Sea to receive only about 5% of its original water inflow.
With these fresh water lines being redirected, the Dead Sea has been unable to make up for its high evaporation rates. Today, it receives only about 10% of the 160 billion gallons of water it would need annually to maintain its current size.
Sinkholes
A sink by the Dead Sea. CC BY-SA 2.0
Erosion of the land surrounding the Dead Sea and limited water flow has led to the creation of dangerous sinkholes in the surrounding area.
When underground salt deposits caused by receding salt water combine with fresh water from flash floods, the salt deposits dissolve, and form a kind of cavern that eventually causes the ground to collapse. Reaching depths of over 30 feet, sinkholes surrounding the Dead Sea pose a danger to surrounding communities and farmlands. Today, locals of communities must avoid the over 3000 sinkholes on the western side of the Dead Sea.
Cosmetics
Dead Sea. WebsThatSell. CC BY-NC 2.0
Another potential major source of harm to the Dead Sea lies with the cosmetic industry and beauty products that have been built around the Dead Sea’s mineral supply. The Dead Sea cosmetics market has grown to a massive industry, valued by Allied Market Research at $723.00 million in 2021, with predicted growth to $2.6 billion by 2031.
Al-Haq, a Palestinian human rights organization, is seeking to combat the exploitation of the Dead Sea’s natural resources. In their 2012 report labeled, “Pillage of the Dead Sea”, al-Haq brought attention to the exploitation of Palestinian land and natural resources by the Israeli government and the resulting environmental damage.
A major player in the Dead Sea cosmetics industry is Ahava Dead Sea Laboratories. The company, which began in 1988, has annual sales at almost $150 million.
In its report, al-Haq advocates for the restrictions from the European Union on Israeli products from Israeli settlements in Palestine as well as for the Israeli government to withdraw the mud mining permission that was granted to Ahava Dead Sea Laboratories in 2004. The group also demands that private cosmetic companies provide more information about the origins of their products and their environmental impact in order to allow consumers to make better informed decisions.
Get Involved
In the wake of an ecological crisis, environmental organizations are working to bring awareness and protection to the issues facing the Dead Sea. Founded in 1994, EcoPeace Middle East brings together Jordanian, Palestinian, and Israeli environmentalists in order to coordinate their activism. The organization is working to protect the Dead Sea with a three step plan of action: inclusion of the Dead Sea as a UNESCO World Heritage site, creating a rehabilitation plan to replace the water flow that has been diverted from the Jordan River, and ensuring that the Israeli government places a public trust obligation on companies that receive concessions to extract Dead Sea minerals.
Jessica Blatt
Jessica Blatt graduated from Barnard College with a degree in English. Along with journalism, she is passionate about creative writing and storytelling that inspires readers to engage with the world around them. She hopes to share her love for travel and learning about new cultures through her work.