Dive into the world of sustainable surfing and learn how to ride the waves without harming our oceans.
Read MoreGuatemala’s ‘Forest Guardians’ Save their Homeland, Providing a Conservation Model for the World
Indigenous guardians in Guatemala's Maya Biosphere Reserve combat deforestation, protecting biodiversity and cultural heritage.
Read MoreBeyond Entertainment: 10 Social Action Films to Watch Now
Social action films advocate for justice and raise global awareness — here is some powerful cinema to watch on streaming and in theaters.
Within the realm of cinema, some films have transcended beyond just entertainment and have acted as powerful catalysts for social change. Social action films have served as a medium for presenting audiences with compelling stories while additionally shedding light on contemporary issues. Behind the central issues, these films advocate for justice and humanize marginalized voices, common themes to generate broader global relevance.
Such a blend of advocacy and storytelling has served as a powerful tool to raise awareness. With a type of transformative power, these films have illuminated social injustices and empowered audiences to rewrite their scripts.
1. “Praying for Armageddon” (Tonje Hessen Schei)
In this chilling documentary, Schei follows the influence of the fundamentalist Christian lobby on U.S. politics. The political thriller explores the consequences of the fusion of Evangelical Christianity with American politics—a weakened democracy—that could ultimately destroy our civilization. Driven by faith, the movement does not just want the world to end but is working to start such a spiral. (Festival streaming this year and upcoming)
2. “Bobi Wine: The People’s President” (Moses Bwayo)
In this powerful account of Ugandan leadership, Bwayo delivers a remarkable documentary about Bobi Wine. Wine, opposition leader and musical star, used his music to fight an authoritarian regime by Yoweri Museveni. Much of the film charts Wine’s unlikely rise from pop star to politician as he seeks to restore democracy and oust Uganda’s brutal and corrupt dictatorship. (Stream it on Disney+ and Hulu)
3. “Navalny” (Daniel Roher)
In this fly-on-the-wall documentary, Roher homes in on the anti-authoritarian Russian opposition leader, Alexei Navalny. Making its debut at the virtual Sundance Film Festival, the film has introduced the Western world to a voice of the opposition in a country governed by fear with intense geopolitical stakes. Much like Roher, viewers are quite literally watching history unfold as Navalny uncovers the truth about an attempt on his life, with a finale yet to be written. (Stream it on Amazon Prime Video)
4. “Call Me Dancer” (Leslie Shampaine)
In her heart-touching and hopeful documentary, Shampaine tells the story of a disadvantaged Indian teenager who struggles against his parents’ insistence to follow a traditional path. When he meets an Israeli ballet master, he is determined to make it as a professional dancer despite the odds stacked against him. Debuting at the Santa Barbara International Film Festival, the film has won awards here and at other festivals, inspiring audiences with its joyride of mentorship, perseverance and passion. (In theaters)
5. “The Persian Version” (Maryam Keshavarz)
In her energetic semi-autobiographical feature, Kesharvarz follows Leila, a young Iranian-American woman as she navigates her family and personal life. As a vibrant portrayal of culture clashes and generation gaps, Keshavarz illustrates an affecting story about what womanhood demands versus imagines through the immigrant experience with the American dream. Just as Leila tries to strike a balance in embracing her opposing cultures, the film equally strikes a balance between heart and humor. (Stream it on Amazon Prime Video and YouTube)
6. “The Mission” (Amanda McBaine)
On North Sentinel Island, the Sentinelese encounter a foreigner who tries to bring Christianity to them, an illegal venture that results in his death. With a compassionate and nuanced approach to retelling a tragedy, McBaine explores this contextual difference between murder and self-defense. The film presents a sorrowful but introspective look at colonialism and cultural superiorities long deserving of scrutiny. (Stream it on Hulu)
7. “Oppenheimer” (Christopher Nolan)
In his unique and nuanced portrait of Robert Oppenheimer, Nolan explores themes of unchecked bureaucracy and science run amok. The film highlights the genius of its central figure while examining the detrimental effects of the atomic bomb he built at the Los Alamos National Laboratory during WWII, a creation that we were not ready for, or rather one we should not have been trusted with. (Stream it on Amazon Prime Video and Youtube)
8. “Smoke Sauna Sisterhood” (Anna Hints)
Hints’s film follows a group of women who share their secrets and intimate experiences in the darkness of a smoke sauna. As a feminist film that reveals the infinite faces of womanhood, the women wash off any shame that was trapped within them and regain their strength. The sauna and the film feel like a work of reflective art, where stories of relatable pains and joys as women are weaved together. (Available for select streaming and on Vudu)
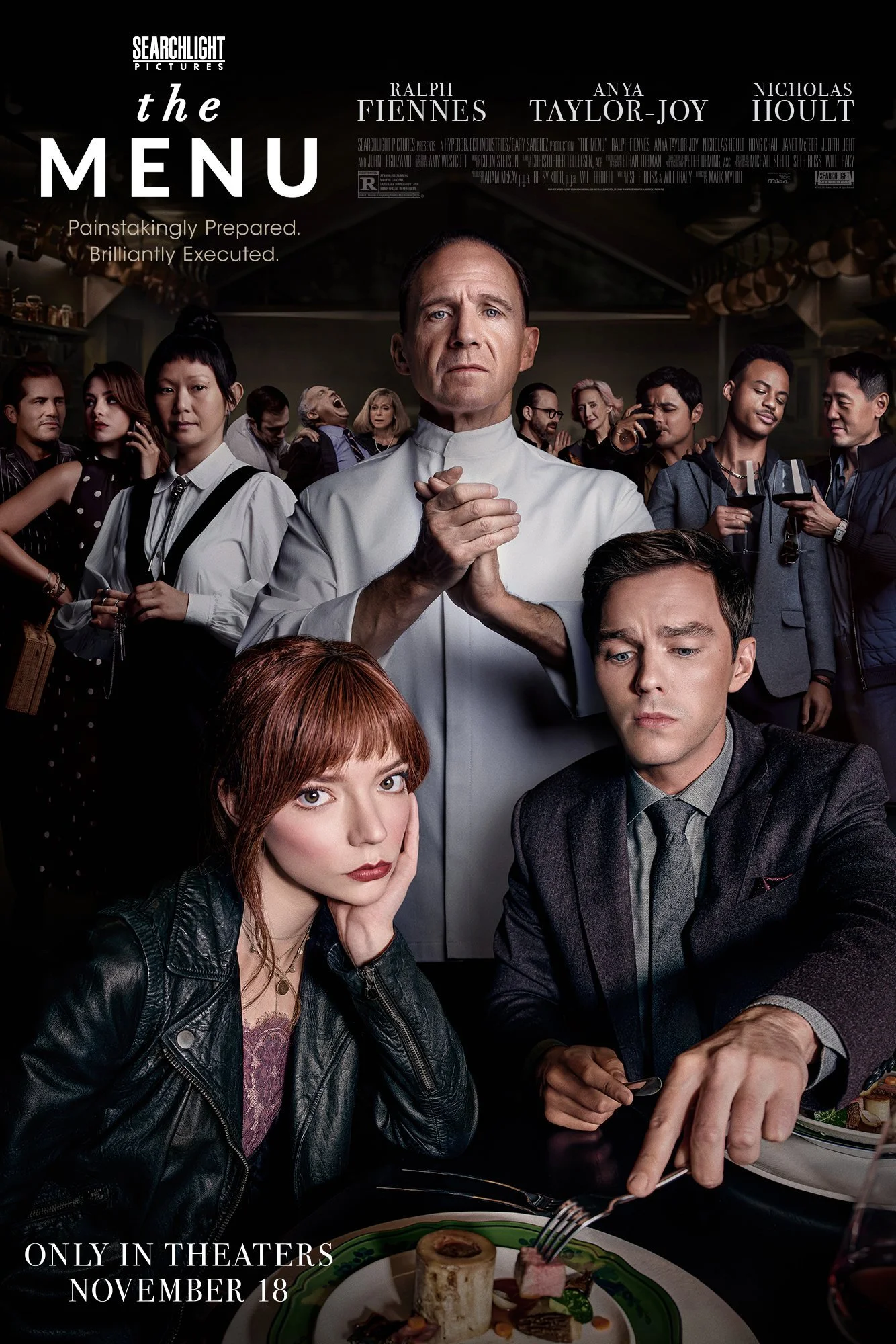
9. “The Menu” (Mark Mylod)
In this social commentary, Mylod satirizes elitism in the world of fine dining restaurants. Focusing on class anxiety and capitalistic greed, the film examines the ethics behind “eating the rich” and the hypocrisy of “ethical consumption.” Serving a tailored dish on a rigid perspective of the wealthy, the film portrays society’s tendency to pay a high price for what it wants, no matter how corrupt. (Stream it on Amazon Prime Video and Hulu)
10. “Origin” (Ava DuVernay)
Inspired by the 2020 book “Caste,” DuVernay presents an argument about the history and hierarchies of power in the United States. In order to understand these elements, people must look past race and see that caste sets the presumed supremacy of one group against the presumed inferiority of others. As an approach to simultaneously educate and entertain an audience, DuVernay examines the book’s age-old themes and gives an ambitious new way to process them. (Opening Jan. 19 in theaters)
Mira White
Mira is a student at Brown University studying international and public affairs. Passionate about travel and language learning, she is eager to visit each continent to better understand the world and the people across it. In her free time she perfects her French, hoping to someday live in France working as a freelance journalist or in international affairs.
Surfing at 2024 Olympics Destroys Coral Reefs in Tahiti
Teahupo’o locals and scientists protest the building of 2024 Olympic Games infrastructure over environmental and economic concerns.
Surfing in French Polynesia. Duncan Rawlinson. CC BY-NC 2.0 DEED
In preparation for the 2024 Olympics, Paris has placed sustainability at the heart of its environmental ambitions. In keeping with the city's aim to “assume its responsibilities” for the games' environmental and social challenges, there have been many contributions to fight carbon impact, food waste and destructive construction. However, organizers have recently faced backlash for the erection of an aluminum tower in Tahiti, built specifically for the new surfing competition, that has damaged both coral and the competition's reputation.
To take the games to new heights, Paris has decided to host a new surfing competition, set to take place in Teahupo’o, Tahiti. This setting will offer the opportunity to host a unique competition and allow France to engage with its overseas territories. Teahupo’o, described as a paradise and dream spot by surfers and travelers alike, is anticipated to bring fans and athletes together. This influx of people to the island has called for the construction of a new venue; a 14 ton aluminum tower with concrete foundations, set to host 40 people judging and televising the competition.
Coral Reefs in Tahiti. Jeremy H. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0 DEED
On 1 December, a barge intended to help build the tower got caught on a reef and damaged local coral. Save Teahupo’o Reef, a group made up of locals, surfers and NGOs, posted a video showing the broken coral and damaged boat propeller on their Instagram. After this initial damage, work was stopped to find a small barge and better route for it so as to not damage any more coral.
Plans to build the tower have been met with more resistance from locals in the form of social media campaigns or protests. Residents have fought against the construction, claiming that building it risks impacting the marine ecosystem and damaging the coral reef. Scientists based in Hawaii have advocated with locals and defended their call to stop building the tower, citing its environmental impact. Using 3D photogrammetry techniques, the researchers created maps of the reef habitat where the tower is set to be built and of the lagoon that its materials will be transported through. Their findings indicate that Teahupo’o would face devastating effects. Of the 3,500 square feet that this development would impact, there are over 1,000 corals from 20 different species. The cost of this dredging and building is estimated at $1.3 million. One of the scientists, Dr. Burns, offered no recommendation for construction that would minimize reef damage as there will be substantial damage regardless of alterations to the process. He suggested alternative solutions to broadcasting the games that included a judge in a boat, using drones or playing a live video feed, all of which are more cost-effective, environmentally friendly and presumably better aligned with the ambitions of the organizers.
Efforts to protest the tower have primarily come from groups like Association Vai Ara o Teahupo’o, who have created an online petition that has garnered over 223,000 signatures. The group is composed primarily of locals who rely on the marine environment for their livelihood and feel it is an important part of their heritage that they would like to preserve.
Coral Reefs in French Polynesia. Adam Reeder. CC BY-NC 2.0 DEED
Following the barge incident, the Olympic Committee made the decision to reduce the size of the tower by 25%. To decrease the weight placed on the foundations, the weight has been reduced from 14 tons to nine and will instead be installed at the same site as the old wooden tower. The original design required 72 four meter tall rods that would be drilled into the reef, but as a result of the now smaller design, rod length will be shortened so as to not be driven down as far. The tower is also being built in an area with fewer corals, and existing ones will be removed and taken care of to ensure regrowth.
Despite growing concern over the risk posed to marine life, there will be some benefits of the event after the games conclude. These include new infrastructure such as a pedestrian bridge, fiber internet cables and the money brought into the local economy by those renting places to stay for the games.
Paris has certainly given more thought to sustainability efforts relative to other Olympic hosts, and has certainly made concerted efforts to reduce the games' environmental impact. However, it is important to recognize the destruction that the tower has caused and the long-lasting effects that it will have even after the games end. If Paris does intend to follow through on its sustainability goals, it must ensure that the Teohupo’o reef is left undamaged not just for the short duration of the games, but even after they end. In doing this, Paris and the organizers of the games would prove themselves dedicated to both sustainability and the island's people, bringing about a new era of true environmental conservation.
Mira White
Mira is a student at Brown University studying international and public affairs. Passionate about travel and language learning, she is eager to visit each continent to better understand the world and the people across it. In her free time she perfects her French, hoping to someday live in France working as a freelance journalist or in international affairs.
Clean Cookware Used to Improve Women’s Health and Combat Climate Change
Millions of women in developing countries lack access to clean cookware. International organizations are working to change that.
Women in India testing a solar cooker. United Nations Development Program. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
Although the Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action in 1995 made groundbreaking strides toward gender equality, one key issue was never addressed: providing households with clean cookstoves. At least 3 billion people across the developing world rely on open fires to cook their food, a task mainly entrusted to women. Cooking on open fires can hold severe environmental and health implications for women and their families.
Modern cookstoves have reduced black carbon emissions by 30-60%
According to the Clean Cooking Alliance, cooking over open fires is the second-largest contributor to global warming aside from carbon dioxide emissions. The burning process releases black carbon, or soot, which lowers the reflective quality of glaciers and sea ice, causing them to melt. Additionally, the demand for wood as fuel results in unsustainable harvesting and deforestation. Studies indicate that at least 30% of the wood used in the developing world is unsustainably harvested, negatively affecting the ecosystem’s health, biodiversity and erosion. The absence of trees prevents carbon dioxide from being absorbed from the atmosphere through photosynthesis, further compounding the effects of global warming.
Cooking on an open fire also exposes women and children to toxic levels of household air pollution, sometimes over 35 times the amount deemed safe by the World Health Organization. Exposure to air pollution can have detrimental effects on one’s health, causing increased risks of childhood pneumonia, lung cancer, strokes and atherosclerosis. In some cases, exposure to high levels of air pollution has led to complications during birth. Health conditions related to smoke inhalation kill over 4 million people each year.
Access to safe cookware in the developing world remains limited, especially in areas torn apart by humanitarian crises. Women often put themselves in dangerous and even life-threatening situations while searching for cooking fuel. Women collecting firewood near refugee camps and conflict zones face increased risks of gender-based violence. Additionally, children accompanying their mothers to find firewood cannot attend school and miss out on available educational opportunities. The time spent gathering firewood further prevents women from seeking valuable opportunities to generate income for their families and children.
Empowering Women Through the Clean Cooking Alliance
Women collecting firewood in the Democratic Republic of Congo. Oxfam International. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
Founded in 2010, the Clean Cooking Alliance is an U.N.-backed organization focused on gender equality through cooking. The alliance works with a global team to ensure that 3 billion people gain access to clean cookstoves. Its focus is on increasing consumer demand and supporting local businesses while developing a clean cooking industry in seven countries: Bangladesh, China, Ghana, India, Kenya, Nigeria and Uganda. Modern cookstoves have reduced black carbon emissions by 30-60% and help to combat climate change. Additionally, having access to cooking equipment can save women up to 300 hours and $200 per year, giving them more free time to spend with their families or economic pursuits. As the Clean Cooking Alliance expands its reach, hopes are high that women and their families will be empowered across the developing world.
To Get Involved:
Check out the Global Cooking Alliance’s initiatives on its website or head to its fundraising page.
Megan Gürer
Megan is a Turkish-American student at Wellesley College in Massachusetts studying Biological Sciences. Passionate about environmental issues and learning about other cultures, she dreams of exploring the globe. In her free time, she enjoys cooking, singing, and composing music.
CATALYST PLANET's 50 BEST BOOKS OF 2023
A wealth of captivating new books flooded the shelves in 2023, enticing readers with diverse narratives and ideas—here are our top picks. These books will take you all over the world, from Malaysia to Argentina, from Palestine to Turkey, and through all of the major social issues of our time.
Fiction
1. Covenant of Water
by Abraham Verghese
Abraham Verghese's "The Covenant of Water" intricately weaves a haunting saga across three generations in Kerala, South India, exploring a family's struggle with a mysterious pattern of drownings from 1900 to 1977. Amidst the omnipresent waters of Kerala, this poignant narrative delves into love, faith and resilience, creating a vivid portrayal of human endurance, medical progress and intergenerational sacrifices in a changing India—a captivating literary masterpiece hailed by Oprah Winfrey as "unputdownable."
2. Our Share of Night
by Mariana Enriquez
In 'Our Share of Night,' a father and son confront a sinister family obsessed with immortality, spanning time and escaping the clutches of a menacing cult across different eras from 1960s London to Argentina's turbulent history. This narrative of family, the supernatural, and queer themes poses the question: Can anyone escape fate, or will love and sacrifice prevail? It's a compelling work by a visionary Latin American storyteller praised as 'mesmerizing' by Dave Eggers.
3. The House of Doors
by Tan Twan Eng
In 1921 Penang, "The House of Doors" follows Lesley Hamlyn and her husband Robert, alongside writer Somerset Maugham and his secretary Gerald. Maugham, dealing with a troubled marriage and seeking inspiration, discovers Lesley's intriguing past involving Dr. Sun Yat Sen. This captivating novel explores race, gender and power dynamics within the British Empire, weaving a tale of complex relationships and hidden truths.
4. Small Mercies
by Dennis Lehane
In Boston's 1974 heatwave, Mary Pat Fennessy's quest for her missing daughter intertwines with the mysterious death of a young Black man. As she delves into dangerous inquiries, she clashes with the Irish mob amid the city's explosive school desegregation turmoil. Dennis Lehane's "Small Mercies" is a gripping thriller exposing criminality, power dynamics and the chilling realities of American racism during this tumultuous period.
5. Straw Dogs of the Universe
by Ye Chun
Straw Dogs of the Universe follows the journey of Sixiang, a young girl sold in America, desperate to reunite with her father, a railroad worker in California, amid the challenges presented by the anti-Chinese movement. This sweeping historical saga spans generations from Chinese villages to the American West, exploring family resilience and the struggle for survival in a country that relies on and rejects its laborers.
6. The Reformatory
by Tananarive Due
In 1950, in Gracetown, Florida, twelve-year-old Robbie Stephens, Jr., is sent to The Reformatory to defend his sister, Gloria. His gift of seeing ghosts turns from solace to a window, revealing the horrors within. As the boys vanish, Robbie learns survival from friends Redbone and Blue while Gloria fights to rescue him. Tananarive Due's haunting historical fiction, "The Reformatory," unravels the hidden truths of the Jim Crow South and the notorious Dozier School for Boys, illuminating long-buried tragedies through Robbie's gripping narrative.
7. The Heaven & Earth Grocery Store
by James McBride
In 1972 Pottstown, Pennsylvania, the discovery of a skeleton in Chicken Hill, a neighborhood where Jewish immigrants and African Americans lived side by side, unravels long-held secrets. James McBride's "The Heaven & Earth Grocery Store" delves into the intertwined lives of Moshe, who integrated a theater, and Chona, who ran a grocery store, revealing their struggles and the community's resilience against adversity.
8. If I Survive You
by Jonathan Escoffery
In the 1970s, Topper and Sanya fled Kingston, Jamaica's political violence for Miami, only to face exclusion and hardship as Black immigrants. Jonathan Escoffery's "If I Survive You" follows Trelawny, navigating financial turmoil, racism, and family struggles with resilience. Through humor and vibrant storytelling, Escoffery unravels the challenges of being between cultures, offering a profound commentary on survival in a world shaped by capitalism and systemic biases. This debut marks Escoffery as a distinctive voice, chronicling the grim and hopeful aspects of American life.
9. Enter Ghost
by Isabella Hammad
Actress Sonia Nasir returns to Haifa, facing her fractured connection to Palestine. She gets involved in a West Bank Hamlet production, finding camaraderie among Palestinian actors determined to cross barriers. This poignant novel explores diaspora and resistance in present-day Palestine, highlighting the transformative power of artistry amid occupation.
10. What Napoleon Could Not Do
by DK Nnuro
This book follows siblings Jacob and Belinda Nti from Ghana and Wilder, a Texan businessman. Their varied perspectives unravel the American dream—Jacob's visa struggles, Belinda's success in education, and her marriage to Wilder, who confronts racial challenges. This poignant narrative explores their aspirations and experiences, shedding light on the promises and pitfalls of life in the U.S., capturing dashed hopes and realized dreams.
11. Loot
by Tania James
Abbas, a gifted woodcarver, enters Tipu Sultan's service, crafting a grand tiger automaton for the Sultan's sons. As war wreaks havoc across India and Europe, Abbas collaborates with renowned clockmaker Lucien du Leze. When invited to France, Abbas discovers the tiger's disappearance after British forces loot Tipu's palace. His mission changes to retrieving the automaton from an English estate, testing his skills and loyalty amid a backdrop of plundered art.
12. Chain Gang All Stars
By Nana Kwame Adjei-Brenyah
"Chain-Gang All-Stars" follows Loretta Thurwar and Hamara "Hurricane Staxxx" Stacker, stars of CAPE's death matches in a profit-driven private prison program. As fan favorites, they compete for freedom while grappling with their relationship and the brutal nature of the games. Thurwar, on the brink of freedom, wrestles with the ethical toll on her fellow Links. This searing novel examines systemic racism, capitalism, and mass incarceration in America's prison system, offering a poignant reflection on the true meaning of freedom.
13. Kantika
by Rebecca Cohen
This novel paints a vivid portrait of Rebecca Cohen, the spirited daughter of Istanbul's Sephardic elite. Displaced in Barcelona due to financial loss, Rebecca navigates life's joys and hardships, from a failed marriage to motherhood, across Spain, Cuba and New York. Her story delves into identity, exile, and the female experience in work, art and love, emphasizing resilience amid suffering and embracing life's beauty. Elizabeth Graver's lyrical novel celebrates women's strength and determination in seizing their destinies.
14. No One Prayed Over Their Graves
by Khaled Khalifa
The lives of Hanna and Zakariya are altered forever as they return to their village near Aleppo, Syria, to find it devastated by a massive flood. Hanna, once a wealthy libertine, transforms into an ascetic mystic after losing everything, delving into the meaning of life and death. The novel navigates their lives in Aleppine society at the turn of the 20th century, capturing the rich tapestry of friendships, love, and societal changes amidst the city's diverse communities.
15. Crook Manifesto
by Colson Whitehead
In this novel, set from 1971 to 1976, furniture store owner Ray Carney grapples with a chaotic city, the NYPD's clash with the Black Liberation Army, and a return to the criminal world for Jackson 5 tickets. Pepper, Carney's partner, ventures into Blaxploitation shoots, encountering Hollywood stars and criminals while displaying his prowess. Amid Harlem's upheaval in 1976, Carney and Pepper uncover corruption while facing family challenges in a crumbling city.
16. I Will Greet The Sun Again
by Khashayar J. Khabushani
"I Will Greet the Sun Again" traces K's struggle with identity as a young Iranian immigrant in the San Fernando Valley, dealing with feelings for his friend Johnny while navigating his family's expectations. After returning from Iran, K grapples with reconstructing his identity in a changed world. Khashayar J. Khabushani's novel delves into the challenges of being queer and Muslim in America, depicting a tender journey of self-discovery and belonging.
17. Birnam Wood
by Eleanor Catton
A New Zealand landslide isolates Thorndike town, prompting a guerrilla gardening group, Birnam Wood, to seize an abandoned farm for financial stability. However, an enigmatic billionaire, Robert Lemoine, claims the land for an end-times bunker, sparking a clash of ideologies and trust issues. This gripping thriller explores human survival instincts, alliances and the complexities of human nature in a tense narrative.
18. Faraway World
by Patricia Engel
This short story collection portrays Colombian expats in New York City, a Cuban woman seeking her brother's stolen bones and a couple hustling in Miami, each grappling with their pasts. These intimate and panoramic stories capture regret's liminality, the vitality of community and moments of love, offering a compassionate view of human connections.
19. Same Bed Different Dreams
by Soon Sheen
Reimagining a world where the Korean Provisional Government persists, working covertly towards a unified Korea, this novel intertwines narratives and mysterious images. Author Soon Sheen, employed by tech giant GLOAT, discovers an unfinished manuscript linking various personalities, blending reality and fiction. This imaginative tale by the acclaimed author of "Personal Days" offers an alternate reality where a unified Korea feels within reach.
20. Victory City
by Salman Rushdie
"Victory City" narrates the epic tale of Pampa Kampana, a nine-year-old girl in fourteenth-century southern India, chosen by a goddess after a divine encounter. Over 250 years, her life deeply intertwines with the rise and fall of Bisnaga, a magnificent city, sown from magical seeds and eventually ruined by human folly. Pampa strives to empower women in a patriarchal society, yet the city's complexities grow beyond her control. Crafted as an ancient epic, this saga embodies the enduring power of storytelling through love, adventure and myth.
21. A History of Burning
by Janika Oza
In 1898, an Indian teen named Pirbhai works for the British on the East African Railway, committing a fateful act. Janika Oza's multi-generational epic spans continents and time as Pirbhai's family navigates the repercussions of his deed. Born in Uganda during colonial rule's decline, his granddaughters faced upheaval and fled Idi Amin's sadistic dictatorship in 1972. The family's scattering leads to a global journey, questioning loyalties and defining their place in the world. "A History of Burning" traces an intimate saga of family, complicity, and resilience across generations.
22. The Most Secret Memory of Men
By Mohamed Mbougar Sarr and Lara Vergnaud
Winner of France's highly prestigious Prix Goncourt, "The Most Secret Memory of Men" follows Senegalese writer Diégane Latyr Faye's quest in Paris to uncover the mysterious author of a scandalous 1930s book. It delves into history's tragedies and explores themes of exile, art and cultural convergence between Africa and the West, celebrating the timeless power of literature.
23. Tremor
by Teju Cole
"Tremor" is Teju Cole's riveting exploration of life's complexities through Tunde, a West African photographer in New England. Amidst historical reflections, racial tensions and personal revelations, the novel delves into time's passage and the human capacity for survival and joy. Cole's masterful storytelling in this realistic yet inventive work resonates with literature, music and the profound experience of existence.
24. Age of Vice
by Deepti Kapoor
"Age of Vice" delves into how the Wadia family's opulence is tainted by violence, power and desire in contemporary India. Ajay, Sunny and Neda navigate ambition, corruption and forbidden romance in a gripping tale that spans from villages to the metropolis of New Delhi, revealing greed's consequences.
25. Family Lore
By Elizabeth Acevedo
Flor holds a unique power: foreseeing death dates. When she plans a living wake, her sisters wonder about her intentions and their own hidden truths. As the Marte women gather for the celebration, Elizabeth Acevedo's "Family Lore" unfolds, intertwining past and present in a vibrant tale of sisterhood, legacy, and revelations over three significant days.
26. Let Us Descend
by Jesmyn Ward
"Let Us Descend" is a vivid reimagining of American slavery, following Annis' harrowing journey from the Carolinas to a Louisiana sugar plantation. Jesmyn Ward intricately weaves family, spirituality and resilience themes in this powerful tale of sorrow and redemption set against the haunting backdrop of the American South's landscapes.
27. The Deluge
By Stephen Markley
In a turbulent 21st-century world, "The Deluge" weaves a gripping narrative involving Tony Pietrus, a threatened scientist, and a diverse array of characters. Their interconnected journeys traverse landscapes from California to Wyoming, unveiling a tale of courage, chaos and hope amid an impending ecological crisis and political upheaval. This ambitious novel confronts sacrifices made for humanity's survival, capturing a pivotal moment in time with unparalleled depth
NonFiction
28. King: A Life
by Jonathan Eig
Jonathan Eig's "King: A Life" is an extensively researched and vividly written biography, offering a fresh perspective on Martin Luther King Jr. It delves into his complex relationships, internal struggles, and his pivotal role in reshaping American race relations. This landmark biography captures MLK's brilliance as a strategist and his unwavering commitment to justice, making his message as relevant today as it was in his era.
29. Waiting to be Arrested at Night
by Tahir Hamut Izgil
In "Waiting to Be Arrested at Night," Tahir Hamut Izgil recounts the harrowing ordeal of the Uyghur people in China under the government's brutal crackdown. As a poet and intellectual, Tahir experienced the persecution firsthand, witnessing the disappearance of friends and neighbors into internment camps. His book is a plea for global awareness of the crisis and a tribute to silenced Uyghur voices.
30. The Rediscovery of America
by Ned Blackhawk
This narrative spans five centuries, highlighting how Indigenous history has shaped America. The author unveils pivotal moments where Native nations influenced colonization, the American Revolution, the Civil War and 20th-century activism. Blackhawk's retelling emphasizes Indigenous peoples’ enduring resilience and impact on the United States' history and identity.
31. Cobalt Red
by Siddharth Kara
"Cobalt Red" uncovers the grim truth of cobalt mining in the Congo through personal stories. Siddharth Kara delves into the harsh realities of child labor, militia control and global tech reliance on Congo's cobalt. With a call for global awareness, Kara highlights the urgent need to address this human rights and environmental crisis.
32. The Half-Known Life: In Search of Paradise
by Pico Iyer
One of the world’s greatest travel writers, explores this 3.64 Pico Iyer’s exploration in “Paradise,” which takes readers across diverse landscapes and beliefs, challenging our notions of utopia and peace. From Iran to North Korea and even high up in the Himalayas, he questions the essence of paradise, pondering its existence in the here and now amid life's complexities and suffering. With decades of global experiences, Iyer delivers an original, transformative perspective on finding moments of paradise within our everyday realities
33. How to Say Babylon
by Safiya Sinclair
This memoir recounts the author’s struggle against oppression within a strict Rastafari household, finding her voice through poetry and education. The book delves into her journey of breaking free from cultural constraints to reclaim her autonomy and power.
34. Some People Need Killing
by Patricia Evangelista
This gripping chronicle delves into the Philippines' drug war under Rodrigo Duterte. With meticulous reporting, Evangelista uncovers the brutal killings carried out in the name of law and order, shedding light on the nation's frightening atmosphere and the human impulses behind such violence.
35. The 272: The Families Who Were Enslaved and Sold to Build the American Catholic Church
by Rachel L. Swarns
Unveiling Georgetown University's connection to slavery by tracing the Mahoney family's multigenerational story, this groundbreaking account exposes the Catholic Church's reliance on enslaved labor, sparking a national conversation about reparations and the Church's role in American history.
36. We Were Once a Family
by Roxanna Asgarian
This gripping expose delves into a tragic murder-suicide involving six children adopted by a white couple. "We Were Once a Family" uncovers systemic faults in the foster care system, revealing racial biases and neglect. Asgarian's immersive journalism highlights the lives of the adopted children, their birth families and the failures of a flawed system that continues to endanger vulnerable youths.
37. Liliana’s Invincible Summer
by Cristina Rivera Garza
This poignant memoir, "Liliana's Invincible Summer," chronicles her quest for justice following her sister's tragic murder by an abusive ex-boyfriend. Rivera Garza honors Liliana’s vibrant spirit in luminous prose, tracing her life and final summer of 1990. Through a blend of scholarly insight and personal narrative, she confronts her the loss of her sister, crafting a moving testament to resilience and the ongoing fight against gendered violence.
38. The Great Escape :A True Story of Forced Labor and Immigrant Dreams in America
by Saket Soni
The gripping story of immigrant workers trapped in dire conditions on the Gulf Coast. Their daring escape, march to Washington, DC, and determined hunger strike unfold against the backdrop of their fight for dignity and justice. Saket Soni's narrative reveals the realities of forced labor and the challenges these workers face in their quest for fair treatment and human rights.
39. The Land of Hope and Fear
by Isabel Kershner
This expose delves into the lives of Israel’s diverse citizens, capturing the nation's divisions, aspirations and challenges through vivid narratives and on-the-ground insights.
40. Built from the Fire
by Victor Luckerson
Subtitled "The epic story of Tulsa’s Greenwood District, America’s Black Wall Street," this book unveils the story of a thriving Black community before and after the Tulsa Race Massacre. Through personal accounts and generational experiences, journalist Victor Luckerson narrates the neighborhood's legacy of strength, struggle against racism and its fight for survival in the face of adversity and urban renewal.
41. Fire Weather
by John Vaillant
"Fire Weather" recounts the 2016 Fort McMurray wildfire, highlighting its implications in our worsening climate crisis. John Vaillant examines fire's historical impact on societies, intertwining the evolution of North America's oil industry and climate science with the devastating effects of contemporary forest fires. This urgent narrative portrays our world's vulnerability to fire in an era of escalating climate change.
42. Pageboy
by Elliot Page
This poignant memoir navigates the highs and lows of fame, revealing the inner struggle of self-discovery and authenticity. From Juno's success to the suffocating pressures of Hollywood, Page shares a candid journey toward genuine self-empowerment and acceptance in a world constantly trying to define us.
43. The Secret Gate
by Homeira Qaderi
The chronicle of the gripping escape of Afghan author Homeira Qaderi and her son, aided by American diplomat Sam Aronson during the tumultuous Fall of Kabul. Amid the chaos, Sam orchestrated their daring passage through a secret entrance at the airport, navigating danger and gunfire to ensure their safety. This poignant narrative encapsulates bravery and survival against the backdrop of a collapsing Afghanistan.
44. Winnie and Nelson
by John Steinberg
Jonny Steinberg explores the intricate marriage of Nelson and Winnie Mandela, revealing their differing political paths and personal struggles amid the fight against apartheid. Steinberg unravels the complex relationship, offering a compelling narrative about love, political divergence and its impact on South African history.
45. Anansi’s Gold
by Yepoka Yeebo
The author uncovers a captivating saga of post-independence Ghana, detailing a charismatic scammer's audacious plot to exploit the nation's newfound independence. John Ackah Blay-Miezah's intricate deceptions and the chase to find Ghana's missing wealth make for a gripping narrative entwined with Cold War politics, international finance and the quest for truth in history
46. A Fever in the Heartland
by Timothy Egan
Pulitzer and National Book Award-winning author Egan delves into the rise of the Ku Klux Klan during the 1920s. The book focuses on D.C. Stephenson, the charismatic leader behind the Klan's growth, and Madge Oberholtzer, whose testimony became instrumental in its downfall. Egan delivers a gripping narrative that uncovers this dark episode in American history with compelling detail and historical depth.
47. Crossings: How Road Ecology is Shaping the Future of Our Planet
by Ben Goldfarb
Delving into the significant impact of roads on wildlife and habitats worldwide, Goldfarb explores the harm caused by roads, from animal deaths to habitat destruction, while showcasing innovative solutions like wildlife bridges. The book highlights the urgent need to minimize these environmental impacts for the well-being of all living creatures.
48. Poverty By America
by Matthew Desmond
In his eye-opening book, sociologist Matthew Desmond reveals how the affluent contribute to persistent poverty in the United States. He highlights how the wealthy drive down wages, inflate housing costs and limit financial access for the poor. Desmond calls for a reevaluation of the welfare system and collective action to achieve shared prosperity and real freedom for everyone.
49. American Gun: True Story of AR-15
by Eugene Stoner
"American Gun" explores the AR-15's journey from its creation by Eugene Stoner to its polarizing impact on American society. Authors Cameron McWhirter and Zusha Elinson investigate the rifle's rise in popularity, its adoption by the military and its controversial role in mass shootings and gun debates. They offer a balanced view of America's relationship with the AR-15, examining its allure, devastating effects and the political tensions surrounding its regulation.
50. An Inconvenient Cop
by Edwin Raymond
Edwin Raymond, the highest-ranking whistleblower in NYPD history, unveils the flaws in modern policing. His memoir reveals systemic issues, including racial profiling, moral dilemmas for officers and institutional structures that reward bias. Despite personal and professional struggles, Raymond remains committed to advocating for justice and reform within law enforcement, envisioning a future where police prioritize serving communities over statistics.
Raeann Mason
Raeann is a traveler, digital storyteller, and guide writer, with a degree in Mass Communication & Media from the Walter Cronkite School of Journalism. She is passionate about a/effective journalism and cultural exchange, and is an advocate of international solidarity and people's liberation. Her work at CATALYST focuses on reshaping the culture of travel and hospitality to be more ethically sound and sustainable.
Turkey’s Last Remaining Armenian Village Puts its Culture on Display
Discover the poignant legacy of Turkey's Armenian community at Vakifli, the country's last remaining Armenian village, now home to its inaugural museum, inviting visitors to explore this cultural heritage.
Kurdish, Armenian and Turkish women. Yeucelnabi. CC BY-ND 2.0
Most of Turkey’s Armenian population disappeared following Turkey’s leading role in the 1915 Armenian genocide. Even today, there is only one Armenian village left in the country. While Turkish-Armenians’ rich history has slowly started to wane, many community members have come forward to teach the world of their heritage. The last remaining village is Vakifli, located in Turkey’s southern Hatay province. Home to only about 100 people, it is a popular spot in the summer for those hoping to get in touch with their Armenian roots. Now the village’s first museum has opened, giving visitors more than enough reason to visit Vakifli.
History of the Armenian Genocide
Armenians being deported. Narek781. CC BY-SA 2.0
Long before the term “genocide” was coined after the Nazis’ attempt to eradicate all Jews during World War II, the Turkish-Armenians suffered a similar fate with an estimated 1.5 million deaths. In 1915, the Ottoman Empire was in decline. At the time, over 2 million Armenians lived in Turkey; by 1922 there were fewer than 400,000. Before the Ottoman Empire’s collapse, the Christian Armenians were granted religious freedom but were subjected to higher taxes, lower wages and an overall lower standard of living.
In 1908, the Young Turk movement, mostly made up of junior army officers from the Ottoman Empire, took control of the empire in an attempt to “Turkify” the region. The group was led by a powerful triumvirate who called themselves the “Three Pashas.” During World War I, the Young Turks sided with Germany but were eventually defeated. According to The New York Times, , “Armenians were blamed for siding with the Russians” against the German-led Central Powers and were subsequently massacred under the rule of the “Committee of Union and Progress,” a political party representing the Young Turks. Harsh measures were launched against the Armenians, such as making it legal to arrest Armenians on the “sense” of them being a threat. Abandoned Armenian property was confiscated, mass deportations sent men off to labor camps to be worked to death, and “death marches” led Armenian women and children across the Syrian desert to their own concentration camps. Though the German government was reportedly “disgusted and horrified” by the Turkish government’s actions, the Three Pashas fled to Germany after the Ottoman Empire’s fall in 1918 and were given protection.
To date, the Turkish government still does not acknowledge the events that occurred surrounding the genocide of Turkish-Armenians. Legal action is even used; mentioning the Turkish state’s role in the 1915 Armenian genocide is often met with arrests and prosecution.
Vakifli Village
Musa Dagh, where Turkish-Armenians successfully resisted Ottoman troops. anthiok. CC BY-NC-SA 2.0
The small village of Vakifli was established by Armenians who “successfully resisted the Ottoman army’s attacks” in 1915. 4,200 villagers were forced to retreat onto the nearby Musa Dagh (Mount Musa), “holding out for 53 days” before being rescued by Allied warships from Egypt. They were not able to return home until after the end of World War I. Vakifli sits between the Mediterranean Sea and the Syrian border and is a beautiful and unique village with a dialect no Western Armenian can understand. The iconic church that sits in the middle of the village was restored in 1994 and reopened to visitors. Now, with decreased job opportunities and lower standards of living, many of the younger generation have moved to Istanbul, a city holding far greater opportunities. This leaves the older generation to continue to hold on to what remains of the village’s culture. Recently, Vakifli has attempted to diversify its economy by promoting ecotourism and organic farming.
The Launch of Their First Museum
Vakifli church. Nurretingulay. CC BY-SA 3.0
While COVID-19 delayed the official opening of a museum celebrating Turkish-Armenian culture, even now the space is welcoming visitors. Filled with donated items such as audio recordings, photographs, traditional garb and one of the most popular exhibits - the wedding dress - the Vakiflikoy Museum shows visitors “how villagers speak,” along with their beliefs, holidays, food and traditions. Lora Baytar, the museum’s founder, and her husband hope that it gives Turkish-Armenian people a museum where they can preserve their history and culture for all the world to see.
Elizabeth Misnick
Elizabeth is a Professional Writing and Rhetoric major at Baylor University. She grew up in a military family and lived in Europe for almost half her life, traveling and living in different countries. She hopes to continue writing professionally throughout her career and publish her writing in the future.
Meet the Women in Pink Saris Fighting Gender Discrimination in India
Pink sari-wearing and bamboo stick-wielding feminists are fighting against a culture of rape and gender inequality in India.
Sampat Pal Devi, founder of the Gulabi Gang. Iecercle. CC BY-NC-SA 2.0
India’s rape crisis was brought to light back in December 2012 when a 23-year-old female student was raped and beaten to death by five men and a teenage boy. Protesters flooded India’s capital of New Delhi and forced authorities to seek the death penalty for the perpetrators. But the crisis lingers as cases of rape and neglect by corrupt government officials still plague India, especially in rural areas.
Approximately 70% of India’s population lives outside of major cities in the rural areas where it is even harder to seek out justice in the name of the law. Uttar Pradesh state is notorious for its high rate of sexual violence against women, even being named the “rape capital of India.” According to the National Crime Records Bureau, crimes against women in Uttar Pradesh increased by 20% from 2016 to 2019.
But there is hope for Uttar Pradesh, and it comes in the form of women wearing hot pink saris and wielding large bamboo staffs called lathis. Sampat Pal Devi is the founder and was the first leader of the Gulabi Gang, which translates to the “Pink Gang.” Their pink saris represent sisterhood and unity as they come together in droves to fight corruption and to ensure the basic rights of women and poor people in rural areas.
Devi’s story began when she was a single woman living in Uttar Pradesh’s Banda district and witnessed a man savagely beating his wife. She attempted to help, but he beat her as well. She returned a few days later with five other women and beat him with lathis. The story quickly spread throughout the town and more women came to Devi for help. In 2006, after the selection of the pink sari as their uniform, they officially established the Gulabi Gang. Their initial intention was to punish abusive men and combat domestic violence, but it has expanded into a much larger movement of feminism. The Gulabi Gang now fights for socioeconomic, cultural and political equality in order to enhance the basic skills of women to develop confidence and protect themselves from abuse through sustainable livelihoods.
Gulabi Gang resting during a protest. Iecercle. CC BY-NC-SA 2.0
Fast forward 14 years since its establishment and the Gulabi Gang has grown exponentially. Almost 100,000 women and men have banded together to join what is now a mass movement in northern India. In an interview with Vice News, Devi stated that, “The purpose of the Gulabi Gang was to unite women, because until women unite, we will never get what we believe are our rights.” She spent a great deal of her time intimidating and shaming government officials into making the correct choices and abiding by the law.
Although she made many achievements, Devi was removed from her position as leader of the Gulabi Gang for alleged self-promotion at the cost of the organization’s mission. Her removal caused quite a stir until the group’s assistant commander, Suman Singh Chauhan, was elected as its next leader. Even with the change in leadership, the Gulabi Gang stands strong as the organization continues to emphasize its mission.
The Gulabi Gang not only leads and protects but also teaches women a variety of skills necessary to be independent. Through its website, the group has raised enough money to build a school in an impoverished area. In the school, girls learn how to sew in order to earn money and delay the chance of their parents marrying them off. The group’s leaders teach new members how to defend themselves with lathis in free self-defense courses. Finally, they teach the world that through common sense and compassion one can start a revolution, even when the soldiers are wearing pink.
Yuliana Rocio
Yuliana is currently a Literature/Writing major at the University of California San Diego. Yuliana likes to think of herself as a lover of words and a student of the world. She loves to read, swim, and paint in her free time. She spent her youth as part of a travel-loving family and has grown up seeking adventure. She hopes to develop her writing skills, creating work that reflects her voice and her fierce passion for activism.
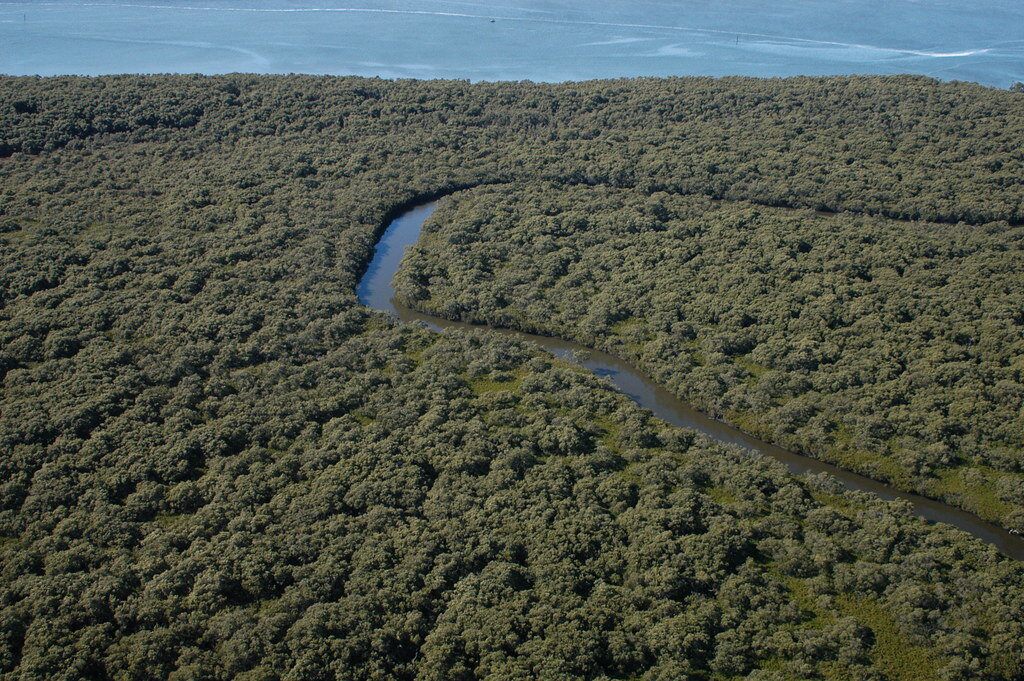
The Importance of At-Risk Mangrove Forests
Mangrove forests are an invaluable coastal ecosystem. Over the past several decades, they faced massive destruction, and now they are at risk from climate change.
An aerial view of a mangrove forest. Doug Beckers. CC BY-SA 2.0
Mangrove forests are one of the world’s most crucial ecosystems. They provide a habitat to a diverse range of creatures, help protect coastal areas from potentially harmful storm surges and are instrumental in carbon sequestration. For the past several decades, mangrove forests have been steadily destroyed by industrial development and aquaculture, as well as wood harvesting.
Naturally occurring in tropical and warm temperate areas, mangrove forests—sometimes called mangrove swamps—are groups of trees and shrubs that grow along coastlines. There are around 80 species of mangrove trees, all of which are some of the few coastal plants in the world that can prosper in salt water.
Mangrove forests are recognizable by their complex root systems which rise above the water, as though the trees are on stilts. Their raised roots allow mangrove trees to thrive despite the movement of the ocean, as the coastal areas where they grow are flooded at least twice a day with the coming of high tide. The protection provided by tangles of mangrove roots goes both ways, preventing storm surges from damaging inland areas and preventing pollutants from rivers and streams from entering the ocean environment. The above-ground section of the roots helps to slow tidal surges, allowing sediments to settle and build up on the ocean floor, reducing erosion. The entire root system filters out pollutants, like nitrates and phosphates, flowing from streams and rivers into the ocean.
The roots of a mangrove forest. Ravi Sarma. CC BY 2.0
A 2010 study found that mangroves were disappearing globally at a rate of one to two percent a year, and that between 1980 and 2005, 35 percent of all mangroves were lost. About half of the mangrove forests that do remain are reportedly in poor condition. In the past few decades, mangrove destruction was largely due to human activities. Most mangrove forests grow on public lands, very few of which receive any sort of protection. Coastal development such as the construction of hotels, power plants and marinas as well as aquaculture, agriculture, tourism and logging have been the main culprits behind global mangrove loss.
Today, satellite data suggests that human-caused mangrove loss has greatly declined. Thanks to conservation efforts from activists and governments across the globe, mangrove loss rates have decreased by 73 percent since 2000. This is good news, as the loss of mangroves has numerous negative effects on the environment, such as less protection for coastal areas and the loss of biodiversity. Mangroves are home to a variety of species of fish, especially juveniles, which use the mangroves’ root systems as a safe nursery habitat until they mature and migrate to coral reefs and other ecosystems. Mangroves are also the primary habitat for many seabirds and waterfowl, and even some terrestrial animals.
Yet, mangrove forests are still not safe. They face a new pressing threat, which is still rooted in human activities: climate change.
Scientists predict that, as a result of global warming, global sea levels will rise to unprecedented levels by as early as 2050. By the end of the century, sea levels will have risen at least a foot. Mangrove trees will be unable to withstand such rising sea levels; they are unlikely to be able to adapt to new sea levels within the time frame. As sea levels are rising, the chemistry of the ocean is changing as well, becoming more acidic than creatures in mangrove habitats are accustomed to. The creatures are also unlikely to adapt to a new environment quickly enough to survive, meaning that mass biodiversity loss could occur.
The harm to mangrove forests also has broader effects , as mangrove forests are one of the most important ecosystems in the fight against climate change. Mangrove trees are powerhouses of carbon sequestration, capturing carbon and other greenhouse emissions from the atmosphere and storing them in their root systems and soil for thousands of years. As global warming causes sea levels to rise and mangrove forests are lost, this stored carbon will be released back into the atmosphere, creating a positive feedback loop that further worsens the effects of climate change.
Experts agree that saving mangrove forests is key to combating climate change. In 2017, the World Wildlife Fund, Conservation International, The International Union for Conservation of Nature, The Nature Conservancy and Wetlands International partnered to form the Global Mangrove Alliance, which aims to fund monitoring and researching mangrove forests, as well as conservation and restoration initiatives.
To Get Involved:
For more about the Global Mangrove Alliance and how to support its mission, click here.
For information on how to preserve mangrove forests, visit conservation.org.
Rachel Lynch
Rachel is a student at Sarah Lawrence College in Bronxville, NY currently taking a semester off. She plans to study Writing and Child Development. Rachel loves to travel and is inspired by the places she’s been and everywhere she wants to go. She hopes to educate people on social justice issues and the history and culture of travel destinations through her writing.
The Sexism Woven into Language
Subtle sexism in language emerges when the male gender is prescribed as default, contributing to gender inequalities and linguistic biases.
Language Across the World. Emma Howard. CC BY 2.0
Language shapes and reflects the cultural norms and values of its speakers. Unfortunately, many languages around the world include subtle forms of sexism which have historically prescribed the male gender as their default. From grammatical structures to the usage of words that perpetuate unequal dynamics, language can unintentionally serve as a vehicle for sexism.
Most languages around the world fall into three categories: gendered languages—nouns and pronouns have a gender (Spanish—el es pequeno/ella es pequena—he/she is little, French—il est petit/elle est petite—he/she is little), genderless languages—nouns and pronouns do not have a gender (Mandarin—他很小 / 她很小—he/she is little) and natural gender languages—gendered pronouns and genderless nouns (English, he is little/she is little). Of the gendered languages listed, the two share patterns of a masculine grammatical default, mixed-gender groups taking masculine endings and feminine nouns derived from masculine ones. In Spanish and French there is a male default that applies when the gender of a subject is unclear or if a group is mixed-gender. A male friend in French is ami while a female friend is amie. In French, there is no gender neutral pronoun for ‘they’ and the masculine is considered the dominant plural form. Therefore, if there is a group of French girls who are amies; add one male and they become amis. Aside from grammar, some words in French did not have a feminine form until official guardians of the French language approved the feminisation of certain titles to eliminate male linguistic dominance. Insistence on calling female presidents Madame le president was subsequently dropped in an attempt to end the bias putting women at a disadvantage.
Mandarin, unlike some European languages, does not assign gender to its nouns, but some of its written characters ascribe negative stereotypes to women. Chinese characters are made up of phonetic and semantic radicals that are listed together in dictionaries. The Chinese radical for “woman” (女) can be found in characters such as “mother,” (妈) “sister” (姐) and “safety” (安) but is also found in more negative characters including “jealousy,” (妒) “slave” (奴隶) and “rape” (强奸). The contrast between these positive and negative connotations are stark but even those that are positive are representative of gender stereotypes themselves; “safety” (安) is thought to represent a woman under a roof. Conversely, the word for “man” (男) is made by the radicals for “field” (田) and “power” (力). Aside from the makeup of the characters themselves, grammatical word order has been said to favor men, for example, in instances where the word “parents” means literally “father and mother.” Ironically, even the phrase for “gender equality” places the male character before the female one (男女平等).
Globally, some languages are representative of a time where the patriarchy was more powerful. They serve as a reminder that words and grammar can sustain sexism covertly and can also impose particular worldviews on their speakers. Some words have different meanings depending on whether they are used in a masculine or feminine form. Others have no male equivalent for a derogatory female word. For instance in Italian, un passeggiatore is a man who loves to walk. Make this word feminine and the definition drastically changes to have a sexual connotation. Alternatively, in English, there is no male equivalent of a “spinster,” the closest being “bachelor” which tends not to carry the same negative, undesirable connotations.
Negative connotations have made their way into technology as well, with one study finding that Google Translate often assumes that, when translating from other languages into English, the subject is male. Male default has also shown up in translator applications where gender bias shows up most in “fill in gender” translations. One tweet focused on Turkish and its gender-biases when translating to English. Sentences like o bir ascı translated to “she is a cook” while others like o bir muhendis translated to “he is an engineer.” Because Turkish is a gender neutral language it becomes clear that Google Translate filled in genders based on stereotypes and bias. Modern neural network-powered machines derive meaning from the statistical patterns of large texts during training, meaning that if our data is biased, machines will be as well.
Women already face barriers to their participation in society, but now with gendered languages playing a role. One research project examined the grammatical structure of over 4,000 languages spoken by 99% spoken by the world’s population, finding that nearly 40% of people speak a gendered language. From this it was found that grammatical gendered language is associated with roughly a 15% gap in female labor force participation. Consequently, gendered languages have become associated with worse labor market participation for women and regressive gender norms. Recognizing how linguistic sexism is causing quantifiable effects is a crucial step in creating more inclusivity in language and society. Efforts to challenge sexist vernacular have gained momentum in the form of gender-neutral language or inventing female-gendered nouns, as opposed to the old practice of adding suffixes onto male ones. In Spanish, the masculine “o” and feminine “a” endings are being replaced by a gender-neutral “e” to create more inclusion for women and those who identify as non-binary. Similarly, in Russia women are advocating for female-gendered nouns which are not mere add-ons to male nouns. In Russian, “doctor” is vrach but becomes vrachinia in its feminine forms, roughly translated as “doctoress,” housing some sexist undertones.
As to be expected, there has been some backlash over leaving behind current gender structures and deviating from the original languages, but speech is not a stagnant entity. Language, to be inclusive, must evolve and change over time in order to progress and mitigate pervasive forms of gender inequality. Recognizing and challenging these linguistic biases is crucial for dismantling the systematic disadvantages and stereotypes that women face.
Mira White
Mira is a student at Brown University studying international and public affairs. Passionate about travel and language learning, she is eager to visit each continent to better understand the world and the people across it. In her free time she perfects her French, hoping to someday live in France working as a freelance journalist or in international affairs.
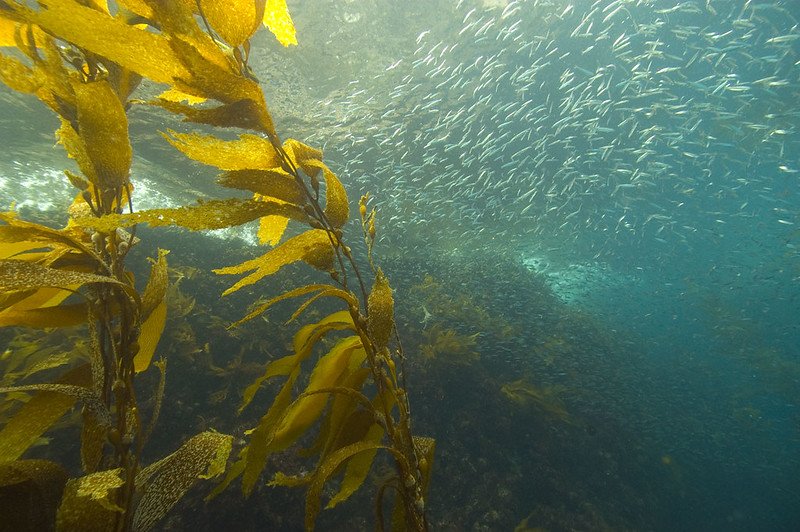
The Ethics of Kelp Farming in Alaska
From food, medicine, climate mitigation and preserving Indigenous traditions, kelp is the shape shifting superhero a polluted world needs.
Kelp with sardines. National Ocean Service. CC By 2.0.
Ethereal and elusive, an unconventional forest grows in the ocean—not full of trees, but of kelp. These captivating, yet occasionally uninviting, greenish tendrils are classified as a type of brown algae that grow as coastal seaweeds; they are typically found in colder waters. In a way, the ethereal kelp borders on the mystical and magical. Kelp is a shapeshifter; a veritable phenomenon that can morph into a variety of forms. Kelp can be used as biofuel, an eco-friendly alternative to fossil fuels derived from renewable biological materials. This multi-talented algae can also be used to make utensils, soap and clothing as well as food—all manner of products people use in their daily lives.
Beyond biofuel, food and everyday household items, the production and usage of kelp is a key debate amongst climate scientists and environmentalists alike. Farming kelp could be a solution in mitigating negative effects of climate change; it could also bolster coastal locations’ economies and positively affect the livelihoods of communities living in and around these shores. But, on the other hand, farming kelp is also fraught with bureaucratic convolutions and, in the long run, could potentially backfire and end up re-polluting oceans. In short, the implications of kelp farming are complex; they are enigmatic and double-edged, much like the kelp itself.
Alaskan Company Barnacle Foods’ Kelp Products. Josephine S. CC By 2.0.
The Eyak People of Alaska—and particularly one Dune Lankard—understand kelp farming. Lankard is the co-founder of The Eyak Preservation Council as well as the President and Founder of Native Conservancy, both of which are groups that support Alaska Native peoples’ efforts in preserving and conserving land and biodiversity on the Alaskan Coastline. People in Alaska and beyond have begun to farm kelp because of commercial, food security and climate change mitigation possibilities. And, because of its optimal climatic conditions, Alaska has become a hotspot for kelp farming.
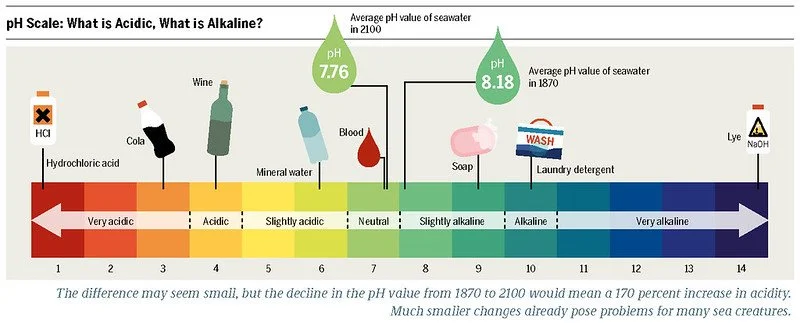
But why is kelp—this mysterious, gangly sept of seaweed—so valuable and beneficial for the environment? For humans consuming kelp, the benefits lie within its nutritional content: kelp contains calcium, magnesium, iron, vitamin C and potassium. But, perhaps more importantly, people like Dune Lankard and fellow Alaskan kelp farmers are more concerned with kelp’s ability to mitigate climate change. Kelp’s primary ability to mitigate climate change comes from its ability to sequester carbon dioxide. You may have heard of carbon dioxide because it is a greenhouse gas. But, what you might not know, is that carbon dioxide from the atmosphere can also enter the ocean, resulting in a mechanism called ocean acidification.
pH reference scale — Ocean Acidification lowers pH. Heinrich-Böll-Stiftung. CC by 2.0.
As more carbon dioxide enters the ocean and gets absorbed, the pH of the ocean itself decreases, meaning the ocean becomes more acidic. But, this is where Kelp the superhero rushes in and saves the marine phyla. Kelp require carbon to grow because of photosynthesis—they absorb sunlight as well as carbon dioxide to produce the sugar and oxygen they need to live—and, through their uptake of carbon, they leave oceans less acidic and marine organisms more happy. Additionally, when kelp float out to sea and die, sinking deep beneath the surface of the water, their carbon sinks into the depths along with them.
Perhaps it makes sense that kelp, with its bewitching appearance, could be responsible for such intricate—almost magical—climate processes. While there are over 500 species of seaweed in Alaska, the three most-commonly grown species are bull kelp, sugar kelp and ribbon kelp. Bull kelp is strong, almost proud-looking—its thick stalk beholds a sense of authority in the water. Sugar kelp, on the other hand, is more delicately enchanting—its slightly-curled, yellow blades are like rays of sunlight spattering the sea. Ribbon kelp, with its thick spine and greenish appearance, are more reminiscent of a looming forest, or the shifting of willows in the wind.
Bull kelp bulb. James St. John. CC By 2.0.
These kelp, however, represent more than just their life cycle, climate mitigation abilities and appearance. Historically, the Eyak people—located on the Copper River Delta near Cordova, Alaska—have long used kelp for food, medicine and even tools. But, through colonialism and imperialism, some of these traditions were disrupted over decades. Today, however, the Eyak and other Indigenous peoples’ kelp farming has allowed them to reclaim these traditions. Additionally, there are immense economic benefits for any employees involved in kelp farming. The fall-to-spring growth cycle of kelp, as well as the need for regular visitation and observation of kelp farms, offer both seasonal and year-round employment opportunities. The increasing amount of kelp farms subsequently increases the number of job opportunities in Alaska, bolstering the state’s economy. Although mariculture in Alaska is currently a $1.5 million dollar industry, newly awarded $45 million in grants could potentially grow it to more than $1.85 billion in 10 years.
Kelp farming and consumption, however, is not all sunshine and rainbows. One of the most difficult aspects of kelp farming is getting started in the first place—a kelp farm requires a permit. Most states require multi-step permit application through boards of aquaculture as well as departments of fish, wildlife and game. Luckily, on average Alaska has a lower permit processing time than most states. Beyond the bureaucratic complexities of even getting started, there are also questions being raised by environmental and climate scientists about the future of kelp farming. Although—as is outlined above—kelp farming is believed to help ocean acidification through carbon sequestration, some scientists are questioning the ability for kelp to continue to sequester carbon as ocean temperatures warm as a result of climate change.
While people should be mindful of the ambiguous future of kelp farming, for now it is safe to say that the more immediate outcomes of farming are helping kelp maintain a positive reputation. Kelp—delicate and mysteriously distant—is, in actuality, an aid toward a variety of more tangible, positive outcomes. Kelp is food. Kelp is medicine. Kelp can even represent community and prosperity. Of course, kelp can also be a huge factor in sequestering carbon in a post-industrial society. But, for many people, these scientific processes can feel overwhelming or unimportant simply because they seem intangible. This is why the effects of kelp that people can really see and feel—the sense of community, the positive economic impacts and the reclamation of tradition—are something to celebrate. Despite its unconventionality and elusivity, kelp can be a superhero.
Carina Cole
Carina Cole is a Media Studies student with a Correlate in Creative Writing at Vassar College. She is an avid journalist and occasional flash fiction writer. Her passion for writing overlaps with environmentalism, feminism, social justice, and a desire to travel beyond the United States. When she’s not writing, you can find her meticulously curating playlists or picking up a paintbrush.
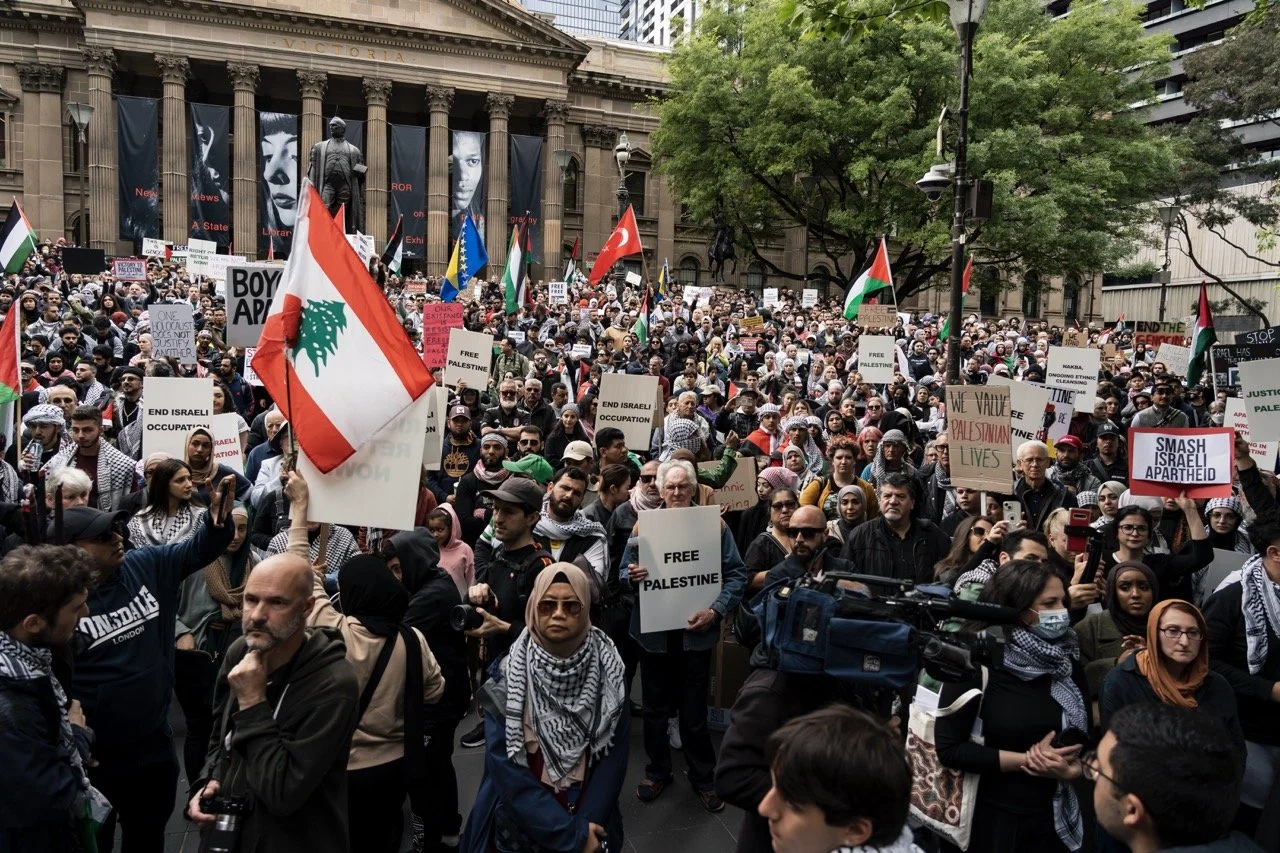
Protests for Palestine and Israel Take Off Around the World
Countries across the world have taken to protest in response to the Israel-Hamas War.
Protest for Palestine in Melbourne. Matt Hrkac. CC BY 2.0
On October 7, Hamas launched an unprecedented attack on Israel from the Gaza Strip that killed more than 1,200 people. Since the assault Israel has responded with a ground invasion that has resulted in the death of more than 11,000 people in the exclave. In light of the growing humanitarian crises in Israel and Palestine, protests supporting either side in the conflict erupted globally.
In the Middle East, and particularly Egypt, pro-Palestinian rallies have broken out, expressing solidarity with the population of Gaza over the hostilities. A mass protest on October 20 resulted in the prosecution and detainment of at least 100 people at al-Azhar Mosque in Central Cairo. On October 29, thousands gathered in Islamabad, which became the largest pro-Palestine rally in Pakistan since the beginning of the war in October. Protests denouncing Israel’s aerial bombardment in Gaza have ramped up around the Middle East, particularly in Jordan. On October 13, riot police dispersed hundreds of protestors attempting to reach a border zone within the West Bank. Jordanian anti-riot police clashed with protesters again on October 18 after demonstrators planned to march to the Israeli embassy and were torching property along the way. In Africa, Israel has substantial support from the Ivory Coast and Kenya, but public sympathies have predominantly tilted toward the Palestinians.
Reactions to the war have varied across Europe. In Paris, hundreds gathered on October 12 to express solidarity with Palestinians and call for a ceasefire from Israeli strikes in Gaza. This demonstration resulted in police using tear gas and water cannons to control crowds. Across France there were around 40 other demonstrations, including one in Lyon with an estimated turnout of 5,000 people, according to French police who, again, used force to control the protest. Conversely, thousands marched in support of Israel. On October 9, a crowd gathered at Place du Trocadero for a march that rallied 20,000 people at an Eiffel Tower lit to resemble the flag of Israel.
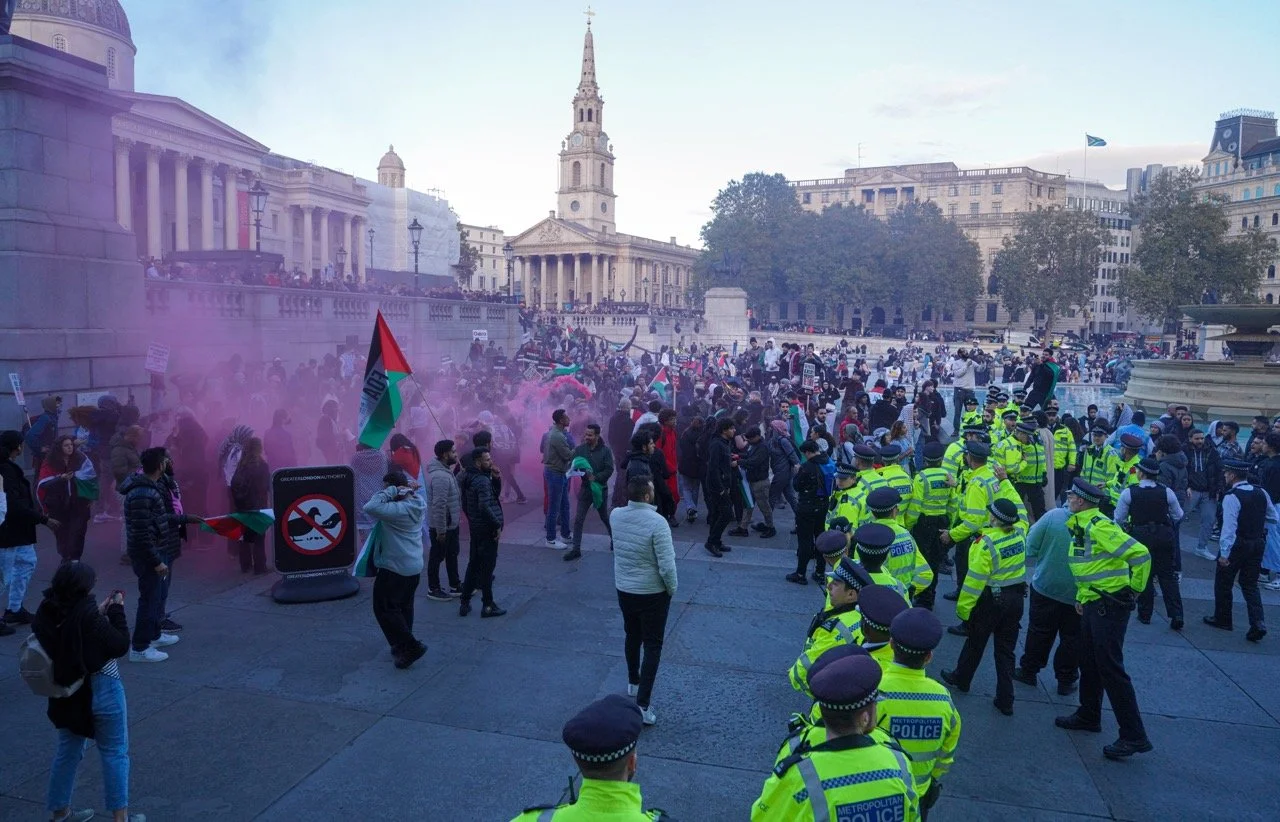
London has also experienced thousands of pro-Palestine protests. On October 21, nearly 100,000 protestors took to the streets of Central London to call for an end to Israel’s bombing of Gaza. Hundreds more gathered in Trafalgar Square on November 5 for a sit-in that brought Oxford Circus to a standstill. On November 11, hundreds of thousands of people gathered for what became the largest pro-Palestine protest in British history. Demonstrators also expressed support for Israel in Trafalgar Square in response to the pro-Palestine demonstration a day before. The rally filled Central London Square and included posters of those who are missing, calling for the release of hostages taken by Hamas in the initial attack.
Palestine Solidarity Protestors in Trafalgar Square, London. Alisdare Hickson. CC BY 2.0
Similar to Europe, in the United States there has been widespread support for the Palestinian cause. A November 4 protest in Washington D.C. drew supporters from around the country with 300,000 people in attendance, making this the largest pro-Palestine mobilization in U.S. history. Other cities across the country have also demonstrated support for Palestine: hundreds marched in Boston on October 16, over 1,000 people attended a demonstration in Chicago on October 18 and a peaceful march on November 7 in New York City. Tens of thousands of demonstrators have crowded city streets to demand a ceasefire in Gaza, including Jewish advocacy groups. On October 27, thousands of Jews gathered in Grand Central Station to denounce the violence against Palestinians. The gathering was organized by the Jewish Voice for Peace organization, which held a second protest on November 6 at the Statue of Liberty, attended by hundreds. The group has been involved with cities across the country and has mobilized demand for a ceasefire in many other places: JVP-Philly, JVP-Seattle, JVP-BayArea and JVP-Triangle (Durham NC). In concentrated efforts, universities across the country have held protests. At Harvard University, more than 1,000 students rallied in Harvard Yard in support of Gaza on October 15. In Providence, around 500 Brown University students walked out of class on October 25 to support Palestine and a second walkout was held on November 8. On the evening of the 8th, a peaceful sit-in of about 20 Jewish students took place in Brown’s University Hall.
Jewish Allies for Palestine in NYC. Pamela Drew. CC BY 2.0
Comparable to other global responses to the conflict, Asia has also experienced an influx of pro-Palestine support. In Indonesia and Malaysia, protests against Israel’s offensive in the Gaza Strip have erupted. In Jakarta, thousands gathered at the National Monument on November 5 to express solidarity and support with Gaza. In Kuala Lumpur, 15,000 people gathered on October 15 to condemn Israel’s attacks, including prominent politicians such as former prime ministers Muhyidden Yassin and Mahathir Mohamad. Much of Southeast Asia has been swept by solidarity for Palestinians, including Singapore, and in response to the ban on public rallies, activists have mobilized online to demonstrate their support. In New Delhi, two Muslim scholars used a WhatsApp display photo reading ‘I stand with Palestine’ to extend their support. Online mobilization has perhaps created a way to reach a broader audience. In India, pro-Israel rallies have been permitted; however, there has been a crackdown on Palestinian solidarity demonstrations.
In Latin and South America, protests have spread across most countries in support of the Palestinian cause, including Belize, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile and Venezuela. On November 4, pro-Palestine supporters gathered on Avenida Paulista in Sao Paulo for a demonstration. They held rolled clothes stained with red paint to represent children who have been lost to the violence. Outraged by the conflict, thousands gathered on October 25 at the outskirts of Santiago de Chile for a concert expressing solidarity with Palestinians. Support for Israel in South America in the form of protests or demonstrations appears to be minor; however, it may just be overwhelmed by the abundance of support for Palestine.
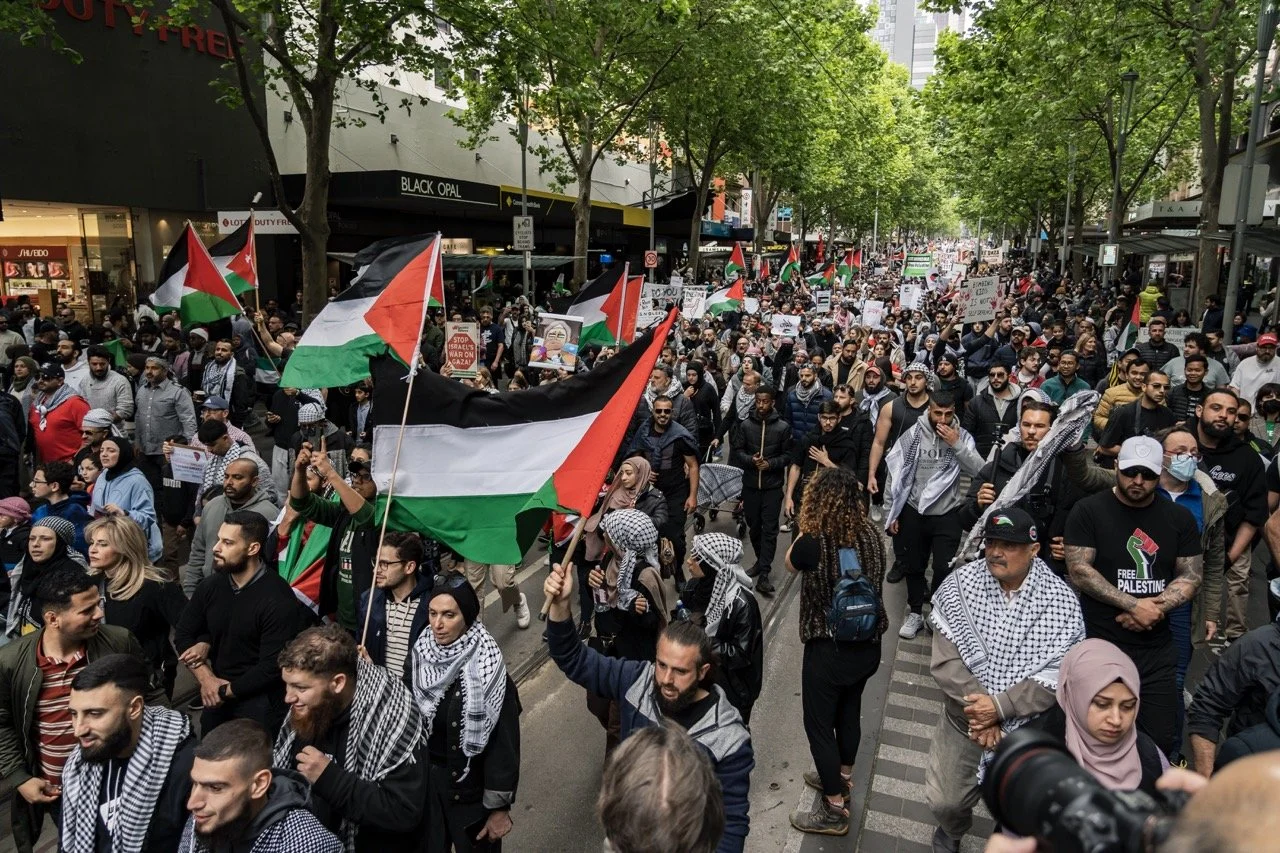
In Australia, pro-Palestine rallies in Sydney have called for the government to drop its support for Israel. On October 5, 20,000 people participated in a pro-Palestine rally that came after the one in Washington D.C., calling for a ceasefire of the hostilities. Protests in Australia have continued to be primarily pro-Palestine, with 15,000 marching through Sydney on October 21 and other rallies held in Perth, Hobart and Brisbane. On November 7, a pro-Palestine protest of about 100 people blocked a busy intersection in Melbourne. The police subsequently used pepper spray on the activists and dragged them from the intersection in an attempt to get traffic moving again. Hundreds of people showed up to a protest the following day, preventing trucks from entering the operating area of an Israeli shipping line.
Melbourne Rally for Palestine. Matt Hrkac. CC BY 2.0
Even in the midst of polarized opinions, Jewish peace activists in the United States called for a ceasefire in Gaza and justice for Palestinians. 10,000 people, including Jews, marched on Capitol Hill on October 18, calling on the U.S. government to stop providing aid to Israel and acknowledging the conflict as a “sobering reminder” of Jewish history. Stark reminders of Jewish people lost to or missing in the conflict have taken shape in the form of “kidnapped” posters or empty Shabbat tables, representing the plight of the Israeli psyche and spreading awareness of those being held hostage. These kidnapped posters have subsequently been torn down by anti-Israel activists, quickly become its own form of protest, often characterized as antisemitic. An empty Shabbat table installation was created in Times Square to raise awareness for the 224 hostages being held by Hamas. An estimated 290,000 people gathered on November 14 in D.C. to demonstrate the solidarity of the Jewish community and in response to critics of the Israeli military.
Globally, people are demanding peace and justice through action. In spite of challenges towards a sustainable solution, global protests embody the collective hope for Israelis and Palestinians to coexist in peace and security.
TO FIND OUT WHERE TO JOIN PROTESTS
Jewish Voice for Peace - As the largest anti-Zionist organization in the world, this group identifies themselves as a political home for Jews on the left and a Jewish community with solidarity for the Palestinian cause.
Palestine Solidarity Campaign - PSC is the biggest organization in the UK, dedicated to securing Palestinian rights and freedom for everyone in the region.
National Students for Justice in Palestine - The group supports over two hundred Palestine solidarity organizations on college campuses in the U.S. and Canada, promoting an agenda for Palestinian liberation.
ANSWER Coalition - As an acronym that stands for Act Now To Stop War and End Racism, the coalition has mobilized anti-war and peace movements for the people of Palestine.
Palestinian Feminist Collective - PFC is a group of Palestinian and Arab feminists committed to Palestinian liberation by addressing gendered and sexual violence.
Rabbis for Ceasefire - A group of Rabbis who have called for ceasefire to genocidal violence, calling on American representatives to demand immediate action.
Israeli-American Council - The IAC’s mission is to build a united community of Israeli-Americans to strengthen the Jewish identity. It is the United States’s largest Israeli-American organization.
The Jewish Federations of North America - Made up of 146 federations across North America, the group's mission is to protect and enhance the well-being of Jewish people through contributions to Jewish communities and Israel.
Mira White
Mira is a student at Brown University studying international and public affairs. Passionate about travel and language learning, she is eager to visit each continent to better understand the world and the people across it. In her free time she perfects her French, hoping to someday live in France working as a freelance journalist or in international affairs.
The Essential Palestine Reading List
Dive into this collection that illuminates the rich tapestry of Palestinian history and culture.
An aerial view of Palestine. CC0
Curated with a respect for the multifaceted narratives of the region, this collection encapsulates an array of perspectives, histories and lived experiences. Each title delves deep into the heart of Palestinian identity, the intricacies of the conflict and the resilient spirit of a people striving for justice and peace.
NON-FICTION
1. They Called Me a Lioness
by Ahed Tamimi and Dena Takruri
Ahed Tamimi, an iconic Palestinian activist, garnered global attention for her fearless activism against the Israeli occupation. Her imprisonment as a teenager after confronting an Israeli soldier in her village of Nabi Saleh turned her into a symbol of Palestinian resistance. This compelling memoir offers a firsthand account of Tamini’s experiences and the ongoing struggle for justice in Palestine, providing profound insight into the realities Palestinians face under occupation.
2. The Ethnic Cleansing of Palestine
by Ilan Pappé
In this seminal work, Ilan Pappé meticulously traces the events of the 1948 Palestinian exodus, revealing the hidden reality of forced displacement and the establishment of Israel. With unflinching detail, Pappé unearths harrowing stories of dispossession and illuminates the profound impact of this historical upheaval on the Palestinian people.
3. Love Is an Ex-Country
by Randa Jarrar
In her memoir, Randa Jarrar fearlessly challenges stereotypes about Muslims and Palestinians. Embarking on a cross-country journey, Jarrar proudly embraces her queer, Muslim, Palestinian and unapologetically confident identity, offering a raw, authentic exploration of the intricacies of life.
4. The Iron Cage: The Story of the Palestinian Struggle for Statehood
by Rashid Khalidi
Historian Rashid Khalidi masterfully dissects the intricate history of Palestinian nationalism and aspirations for statehood. With scholarly precision, Khalidi navigates through decades of political intrigue, chronicling the challenges, setbacks and enduring resilience of a people bent on self-determination and recognition on the world stage.
5. The Hundred Years' War on Palestine
by Rashid Khalidi
Rashid Khalidi's meticulously researched book paints a vivid historical tapestry from the 1800s to the present in this unshrinking account of the assault on Palestinian society.
6. We Are Not Here to Be Bystanders
by Linda Sarsour
Linda Sarsour's memoir portrays her journey from Brooklyn to becoming a powerhouse in activism, stirring profound reflections on solidarity and advocacy.
7. Except for Palestine
by Marc Lamont Hill and Mitchell Plitnick
Marc Lamont Hill and Mitchell Plitnick's critique navigates the inconsistencies within progressive circles, urging universal consistency in advocating for all oppressed communities.
FICTION
1. Mornings in Jenin
by Susan Abulhawa
Susan Abulhawa crafts a poignant, multigenerational narrative that traverses the emotional terrain of a Palestinian family's journey through displacement and loss. Through exquisite storytelling, Abulhawa offers a deeply moving portrayal of resilience amid a tumultuous landscape of conflict and highlights the enduring spirit of the Palestinian people.
2. The Tiny Journalist: Poems
by Naomi Shihab Nye
Naomi Shihab Nye, the esteemed Palestinian-American poet, weaves poetic wonders inspired by Janna Jihad Ayyad, Palestine's youngest journalist. Ayyad, capturing anti-occupation protests at the age of seven using her mom's smartphone, becomes Nye's muse in this must-read collection.
3. You Exist Too Much
by Zaina Arafat
Zaina Arafat's debut novel is a transcontinental tale which oscillates between the United States and the Middle East. A fresh voice in Palestinian-American literature, Arafat artfully dismantles Israel’s pinkwashing while unraveling the complexities of Palestinian society for diverse readers.
4. Enter Ghost
by Isabella Hammad
Isabella Hammad's evocative narrative navigates modern-day Palestine, delving into the artist's struggles amid diaspora, displacement, and the shadow of occupation.
5. Evil Eye
by Etaf Rum
Etaf Rum's exploration of womanhood as a Palestinian American is a profound journey through intergenerational trauma, clashes of culture and labyrinthian family dynamics.
6. Salt House
by Hala Alyan
Set in the aftermath of Israel’s conquest of the West Bank and Gaza in the 1967 Six-Day War, "Salt Houses" chronicles a Palestinian family's odyssey from their homeland to Kuwait, painting a poignant legacy of longing and displacement passed through generations.
7. Mother of Strangers
by Suad Amiry
"Mother of Strangers" presents a cinematic love story against the backdrop of the Nakba in Jaffa, weaving themes of love, loss, and a nation's upheaval.
Raeann Mason
Raeann is a traveler, digital storyteller, and guide writer, with a degree in Mass Communication & Media from the Walter Cronkite School of Journalism. She is passionate about a/effective journalism and cultural exchange, and is an advocate of international solidarity and people's liberation. Her work at CATALYST PLANET focuses on reshaping the culture of travel and hospitality to be more ethically sound and sustainable
Amsterdam's Quest for a Safer Red-Light District
Propositions for legislative shifts strive for balance between tourism, public safety and the well-being of sex workers.
Red Light District Canal Street View. Alejandro Forero Cuervo. CC BY 2.0
For decades Amsterdam has been inundated by rowdy crowds of eager sightseeing tourists and a hotspot for visitors craving a subversive experience. The Netherlands’ progressive capital has long had a uniquely tolerant approach to often prohibited substances such as marijuana and psilocybin as well as toward the legalization of sex work. While the city openly celebrates this unique facet of its culture, the Dutch government has been forced to grapple with an influx of unruly visitors and an increasingly polluted, noisy, and at times unsafe Red Light district.
Amsterdam Smoke Shops. Travelmag.com. CC BY 2.0
In response to the district’s increasingly obstreperous environment, the city sought to address local residents’ noise and substance abuse concerns by proposing new regulations this past spring. The city has insisted on earlier closing times for bars (2 a.m., with no entry after 1 a.m.), stopped sex workers from working after 3 a.m., and banned the use of marijuana, alcohol, and other drugs in the streets. In response to the city’s regulatory shifts entrepreneurs, business owners and bartenders have been outspoken in frustration against the new policies, claiming little has changed in regards to the safety and cleanliness of the area. Sex workers have also voiced complaints over the restriction placed on the time they are allowed to work, expressing concern that the reduced hours have put them under financial pressure. This destitution can force them to accept clients they would normally reject.
Canal View Red Light District. Pixabay.com. CC BY 1.0
To further alleviate the pressure on the Red Light district, Amsterdam's authorities are considering a more drastic approach: creating a new location for legal sex work in a different neighborhood. This new location would be in a suburban area, and many are referring to the proposed locale as a “suburban erotic center” The goal of the move is to spread out the demand and ease the burden on the current district.
Since the legalization of sex work in the Netherlands in 2000 the country has been vigilant about enforcing a safe environment for individuals in the field, with regulations in place to combat human trafficking and other criminal behavior. For instance, sex work is illegal to practice in any space outside of a registered business (e.g. at home, in hotels, or in public spaces). In an attempt to protect and respect workers the city has banned tours of the Red Light district, required visitors to identify themselves with a valid form of ID, and set 21 as the minimum age for sex workers.
An Amsterdam Sex Shop. Rob Kievit. CC BY-SA 2.0
The city’s proposition of a new epicenter for sex work is still in its early phases, but it would dramatically change the scope of Amsterdam’s tourism. With fewer than a million residents, the city hosts roughly 20 million visitors annually, and tourism is one of the leading markets for local businesses. Any major change to laws regarding sex work and the overall functioning of the district will inevitably lead to shifts in the travel industry. The question remains as to whether the new area created to host erotic work will fix the industry’s systemic problems and help protect workers, and if it will solve the issues of over-tourism and noise pollution.
Avery Patterson
A rising junior at Vassar College in New York State, Avery is a Media Studies and French double major. She is an avid reader, writer, and traveler. She loves to immerse herself in new cultures and is an avid explorer who loves being in nature. She is passionate about climate and social justice and hopes to use her love of writing as a catalyst for positive change.
Stolen Childhoods: Unveiling Orphanage Tourism Across the Globe
Traffickers exploit the vulnerability of children for financial incentives from donors in orphanages and child residential homes.
Two young Haitian children. CC0
Across the globe, there are an estimated eight million children living in orphanages. Of this, 80% are not actually orphans and have at least one living parent. These children have been taken from their families and placed into children’s residential homes so that the caretakers can make a profit.
Orphanages, which are often viewed as a place of refuge for children, have begun using foreign generosity to profit off of their vulnerability. “Orphanage trafficking” involves children being recruited into residential care institutions for profit or exploitation and is not confined to any one country. This has sparked a new industry — orphanage volunteering — that has created a demand for institutions that will present children as ‘in need’ to make a profit from foreign donors. In Cambodia, for example, residential care institutions have increased by 75% in the last decade despite a decrease in the number of “real orphans.” Similarly, in Uganda, residential homes have increased the number of children under their care from 1,000 to 55,000 even with the subsequent decline in the prevalence of orphans themselves. This rise in residential institutions has taken place primarily in tourist hotspots so that orphanages can capitalize on financial incentives.
As a system that takes advantage of the international market and tourism business, this has become a global problem. A significant rise has been observed in post-conflict Nepal, beginning in 2006. During the Nepalese Civil War, traffickers posed as boarding school representatives and promised children and their families better living conditions in Nepal’s capital, Kathmandu. Rather than being taken to educational institutions, children were taken to under-resourced orphanages and declared “paper orphans.” This sales pitch has evolved accordingly, shifting from inter-country adoption alone to running orphanages in tourist areas to attract donations — 90% of homes being in the top 5 tourist districts. In 2015, Next Generation Nepal (NGN) and UNICEF released statements warning about the increase in child institutionalization. The government of Nepal subsequently passed a directive prohibiting children to cross district borders unless they were with their parents or had government approval. There are still hundreds of children living in orphanages in Nepal today, although the COVID-19 pandemic restricted operational space and allowed local governments to better implement their child protection mandates, contributing to the strengthening of the overall system.
In China, there is also an opaque relationship between trafficking and adoption. It was discovered in 2012 that Americans alone adopted almost 3,000 Chinese children who were taken from their parents and sold into orphanages. As a country that is aware of the existing issue, parents often have to take matters into their own hands to conduct searches because local law enforcement will silence anyone who is publicly discontent. Aside from the financial incentive of orphanage volunteering alone, scammers have even gone as far as to request large sums of money from parents for information on their child’s whereabouts, information that is ultimately fake.
Aside from the vulnerabilities of the children, traffickers also prey on those of their parents. In Haiti particularly, parents placed their children into orphanages after the 2010 earthquake. They were pressured to believe that their children would be better off; they would have a roof over their heads, food and access to education. One woman, struggling to provide for her sons, was approached by Jonathas Vernet who offered to help her. Vernert, previously running the Four Winds Spirit orphanage, was found to have subjected children to cooking, cleaning and abusively harsh discipline. The children did not attend school and lived in distressed conditions, but Vernet justified this by blaming American donors for neglecting to offer sufficient financial support. An estimated $100 million a year is donated to all orphanages in Haiti by churches and nonprofits in the United States for the purpose of providing food, water, medical care and education. However, most of this money is used to drive the continuation of profit from orphanage volunteering and further expand the business. To end the institutionalization of children, Lumos, an to replace orphanages with foster care systems and advocates for local adoption practices. The organization also advises donors to ensure that the projects they are supporting have a sustainable care vision.
Today, orphanage trafficking in Haiti has not changed much. As of 2021, it was estimated that there were 30,000 children in 750 orphanages, with only 35–50 of those being licensed. Despite efforts to develop and regulate the foster care system in Haiti, attempts to combat orphanage tourism have been static as a result of continued high poverty and unemployment rates.
Globally, orphanages have become hubs where child exploitation for profit can thrive, so long as there are still unmonitored donations and vulnerable children. To better curb the proliferation of child trafficking into orphanages, it is recommended that governments prioritize community-based care and better inform philanthropists how their donations to orphanages may be misused. By combating this issue with strengthened child protection systems, increased awareness and the promotion of family-based care over institutionalization, the root causes of this problem can be mitigated and children better protected.
Mira White
Mira is a student at Brown University studying international and public affairs. Passionate about travel and language learning, she is eager to visit each continent to better understand the world and the people across it. In her free time she perfects her French, hoping to someday live in France working as a freelance journalist or in international affairs.
The Atacama Desert’s Fashion Graveyard
Once a vast, uninterrupted plateau, Chile’s Atacama Desert is now a technicolor testament to overconsumption.
The Atacama Fashion Graveyard. Antonio Cosio. CC BY-NC.
A cursor hovering over the checkout of an Amazon cart; an unassuming paper bag carrying the new, trendiest cut of jeans from Forever 21; a Gmail notification that indicates a menagerie of Shein clothing has been shipped. These testaments to overconsumption in daily life may produce a quick, subtle pang of guilt. But, ultimately, this engagement with the world of fast fashion tends to be “out of sight, out of mind.” After all, once the clothing is donated or discarded most people assume it will end up in a landfill, neatly tucked away, never to be seen again. With no visual proof of the waste guilt subsides, and the cycle of overconsumption repeats.
The cyclical and rampant nature of overconsumption, however, has real, tangible implications — implications that can be seen and felt by citizens of Iquique, a Northern Chilean city in the Atacama Desert. An average of 39,000 tons of fast fashion waste are dumped in Iquique per year, in addition to the approximately 60,000 tons of clothing imported into Chile annually. Roughly 40,000 square miles, the Atacama desert was once a pristine yet arid plateau; a prime sight for stargazing under a clear, open sky. The desert landscape, covered in salt flats, valleys and rocky topography, averages about 40,000 visitors per year but has since been contaminated.
The clothing pile has grown to such an extent that it can be seen from space using satellite technology. But, before the magnitude of clothing became noticeable from an extraterrestrial viewpoint, people residing in Alto Hospicio, a municipality next to Iquique, watched as the unbridled clothing dumping grew out of hand. Clothes manufactured in China and Bangladesh that fail to sell in U.S. stores are brought in through the port of Iquique and subsequently dumped into the Atacama. The dumping site raised concerns among citizens of Alto Hospicio as early as 2012, but their unease was ignored.
The Atacama Desert. NASA. CC0.
Disheartened, the people of Alto Hospicio claimed to have experienced negligence by local and national government officials firsthand. For years, the waste grew despite continual pleas for action. Although in 2021 the former Minister for the Environment of Chile, Javier Naranjo Solano, expressed his worries about the vast quantities of textiles being imported into Chile and proposed remediation, some Chilean environmental engineers and scientists feared that the the laws he proposed, entangled with bureaucratic processes, would be far too slow-moving considering the urgent, rapid growth of the clothing pile. Other citizens, however, have faith that Chile’s newly appointed Minister for the Environment, Maisa Rojas, will be able to translate eco-anxiety into concrete action.
Even under new leadership, however, the already massive pile of clothing is a nearly indestructible hazard. Much of the poor-quality fast fashion clothing dumped in Atacama is polyester, a material made out of the non-renewable resource petroleum. The open-air clothing pile secretes pollutants into the air; they seep into the ground. Thus, petroleum and other harmful materials can contaminate any remaining groundwater in aquifers under the desert. As potent as plastic and as enduring as steel, the clothing dumped in Atacama will take 200 years to biograde.
The Atacama Desert is often considered the driest climate on the planet, with annual rainfall averaging at only .03 inches. Atacama’s arid climate dangerously aids the spread of intentionally ignited fires. In order to curtail the amount of clothing discarded, fires are illegally and mysteriously started. These fires only serve as a further pollutant on top of the fabric already decomposing in the hot, arid environment.
Although many merchants reside in Iquique, one of South America’s largest duty free ports, many in the municipality of Alto Hospicio live in poverty — 25% of residents in Alto Hospicio specifically live in extreme poverty and, with many having poor access to quality housing. Although many residents travel to the Atacama fashion graveyard to salvage and sell discarded clothing, their proximity to the dump site has sinister implications: the negligence of the Atacama fashion desert and subsequent pollution acutely harms low-income communities in Northern Chile. Fast fashion waste, both burnt and decomposing, creates fumes that are linked to respiratory diseases, chronic illnesses, reproductive issues and even types of cancer.
The Port of Iquique. Diego Delso. CC-BY-SA 4.0.
Although there are efforts to repurpose the dumped clothing, with companies such as Ecofibra Chile taking the fabric and transforming it into thermal insulation panels, only one method of curtailing fast-fashion waste can truly have an impact: curbing our own overconsumption. Instead of purchasing that cost-effective Amazon fashion find, or the trendy new jeans from Forever 21, look into your own closet. Rediscover a dress that has been tucked away in the depths of your dresser. Organize a clothes swap with friends. Borrow your Aunt’s blouse or your Grandfather’s wool sweater. Rather than falling victim to trend cycles, explore what has been cherished, saved and passed down.
Carina Cole
Carina Cole is a Media Studies student with a Correlate in Creative Writing at Vassar College. She is an avid journalist and occasional flash fiction writer. Her passion for writing overlaps with environmentalism, feminism, social justice, and a desire to travel beyond the United States. When she’s not writing, you can find her meticulously curating playlists or picking up a paintbrush.
Flooding in Libya: A Harbinger of Climate Change’s Deadly Effects
Sustainable infrastructure is the world’s best defense against increase in precipitation due to climate change.
Aid workers struggle to reach city in Libya where catastrophic flooding killed thousands. PBS.
Catastrophic flooding in Libya in September has taken as many as 5,300 human lives, according to the Interior Ministry of Libya’s eastern government. Amid such massive human casualties, many around the world are left wondering how such losses may be prevented as climate related natural disasters become increasingly common.
Extreme flooding events like the one in Libya are on the rise as Earth’s average temperature increases, causing more evaporation and thus greater precipitation. According to the EPA, global precipitation has increased by an average of 0.04 inches per decade since 1901. In more than half of recorded locations, flooding is now at least 5 times more common than it was in the 1950s. This month alone, the effects of extreme precipitation and flooding have been felt in Hong Kong, Greece, Turkey, Brazil, Libya and the United States.
In Libya and around the world, urban planning must adapt quickly to the rising threat of flooding. However, this poses a challenge for many developing nations where resources are often either limited or diverted elsewhere. For example, in Derna, the city in northeast Libya that was the most affected by the flooding, neglected infrastructure was in part to blame for the catastrophic loss of human life. Heavy rains caused two dams to burst, dams that experts have been warning are prone to collapse for years. Unfortunately, resources in Libya are generally diverted towards the ongoing civil war. More busy with conflict than governing, public officials failed to provide the necessary repairs on the dams.
Moreover, climate change not only increases precipitation but also hinders the environment’s ability to withstand heavy rainfall. In Derna, the inundation of the area has washed away much of the soil, which would have helped absorb some of the precipitation. The ground in and around Derna has been left hard, cracked, and stripped of vegetation. Due to these conditions, very little water was retained in the ground, worsening the flooding. Globally, similar conditions must be prevented if flooding events like the one in Libya are to be curbed.
Libya is far from the only place where the infrastructure is inadequate in the face of increasingly heavy rains. Most urban areas around the world, even those in rich countries with the resources to adapt like the United States, have not created infrastructure nor correctly supported the local environment to prevent extreme flooding. Globally, urban planning must now be rapidly modified to account for increasing precipitation.
Making the ground more permeable is the most impactful way urban planning can help reduce extreme flooding. One way this can be achieved is through the incorporation of permeable pavement. Using this type technique allows water to pass through porous paved surfaces into groundwater stores instead of overwhelming the local drainage systems. Further, creating more green spaces, including green roofs, trees, parks, and rain gardens, all increase the permeability of the ground. When the ground can absorb more water, flooding events like the one in Libya may be prevented.
Get Involved:
To help Libyan flood victims you can donate to UNICEF, International Rescue Community, or Doctors Without Borders.
Sophia Larson
Sophia Larson is a recent graduate of Barnard College at Columbia University. She previously worked as the Assistant Editor on the 2021 book Young People of the Pandemic. She has also participated as a writer and editor at several student news publications, including “The UMass Daily Collegian” and “Bwog, Columbia Student News.”
Free The Nipple: Unpacking Inequality in the Feminist Movement
Evaluating the absence of inclusive representation in a movement that claims to empower all women.
Read MoreWhat India’s Successful Moon Landing Means for Space Exploration
India is now the fourth country to land on the moon, and its lunar rover is making some big waves in space exploration.
The Chandrayaan-3 lunar exploration craft was launched from the south of India on July 14. Sky News. CC BY-SA-NC 2.0
On August 23, the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) landed its Chandrayaan-3 craft near the moon’s south pole, marking both the country’s first ever moon landing and the world’s first on that specific lunar region. Not only has this achievement finally placed India among the ranks of other space exploring nations, but has also made it one of only four countries to land a craft on the moon. The location of the craft’s landing near the unexplored south pole is significant given the multiple failed attempts by other nations to do just that in the past and stake a claim to lead future research in the area. Chandrayaan-3’s successful landing will hopefully cement the credibility of the ISRO on the international playing field and allow for continued collaboration with other foreign space agencies. During its two-week lifespan, the rover investigated the existence of frozen water deposits beneath the surface of the moon, and has made a number of surprising discoveries that orbiting crafts were unable to.
A digital rendering of the Chandrayaan-3 craft and its lunar rover. NDTV. CC BY-NC 2.0
While India’s space program was first established in 1962, it took another decade or two for the ISRO to really pick up steam. Many of the first projects involved sending satellites up into Earth’s orbit in order to map and survey the country from above, bringing telemedical and communication services to communities in remote regions. Chandrayaan, a Sanskrit term meaning “mooncraft,” is the name of India’s lunar exploration program, which made its debut between 2008 and 2009 with the Chandrayaan-1 lunar space probe, which found water deposits on the moon using various mapping techniques and reflection radiation. The next craft, launched in 2019, was comprised of an orbiter, moon lander and rover, and was actually intended to be the first to land on the south pole of the moon, but after successfully entering lunar orbit, the ISRO lost communication with the landing craft and rover before touchdown.
Chandrayaan-3 is therefore the culmination of more than a decade of scientific research and technological development and is undoubtedly the crown jewel in India’s space program. The probe was launched on July 14 from Sriharikota Range, the country’s largest launch site located in the southern state of Andhra Pradesh, and successfully touched down on the moon on August 23. Unlike its recent predecessor, the Chandrayaan-3 traveled without an orbiter module, further cementing its intention to land on the moon and conduct experiments in situ. Additionally, while this craft was unambiguously an Indian project and creation, some of the technology on board resulted from various collaborations between the ISRO, NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA), proving once again the importance and benefits of scientific collaboration.
Students in India watch a video explaining the lunar mission. Al Jazeera. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
Aside from proving that landing on the south pole of the moon is indeed possible, the information sent back by the Chandrayaan-3 rover has already resulted in some groundbreaking discoveries about the moon. One such finding has to do with understanding the temperature of lunar soil, an important factor when considering building long-lasting structures or even settlements on the moon. The Indian rover is equipped with a temperature probe that can reach nearly four inches (10 cm) beneath the surface, and found that the temperature drops 140ºF (60ºC) at a depth of just roughly 3.14 inches (8 cm). This has provided an updated and more accurate reading as compared to the data currently in use from NASA’s 2009 Lunar Reconnaissance mission, which lacked precision because it was an orbiter and therefore not actually on the lunar surface. Another interesting discovery took place in the form of a series of strange vibrations detected by the rover’s seismograph: scientists have suspected it as being a minor moonquake, although further exploration and longer-term observations would need to confirm this.
While these scientific discoveries are of course extremely significant and promising for the future of lunar exploration and research, the Chandrayaan-3 project also set a historic precedent in terms of the budget they used to complete this mission. The ISRO has a long held reputation amongst international space research circles for their ability to work on limited funds, at least compared to other major space exploration agencies. NASA, for example, has a $25.4 billion budget for the current fiscal year, while the ISRO received a measly $1.5 billion from the Indian government for the fiscal year ending this March by comparison. If that wasn’t enough, the ISRO actually spent 25% less than what it had been allocated. The Chandrayaan-3 mission cost a total of $74.3 million USD, ironically less than half of the budget that director Christopher Nolan had to make Interstellar, his award winning film about space travel.
The actual Chandrayaan-3 craft before it was launched into space. The Week. CC BY-SA 2.0
In addition to finally taking its place amongst the other lunar landing nations, Chandrayaan-3 has opened countless doors for both the ISRO and the space exploration community as a whole. Going forward, the example that this mission has set with regards to the resources it used as well as through the international collaboration it benefitted from. The moon’s south pole has now been unequivocally proven accessible and investigable, new information about lunar composition has been brought to light, and like all other missions into space, has helped to deepen our understanding of both the universe and ourselves.
Tanaya Vohra
Tanaya is an undergraduate student pursuing a major in Public Health at the University of Chicago. She's lived in Asia, Europe and North America and wants to share her love of travel and exploring new cultures through her writing.
The Global Social Ladder: The Best and Worst Countries for Social Mobility
The World Economic Forum's Global Social Mobility Report 2020 unfolds a gripping narrative.
Read More