Explore 32 curated gifts that resonate with purpose and panache.
Read MoreExperience Black Mexico
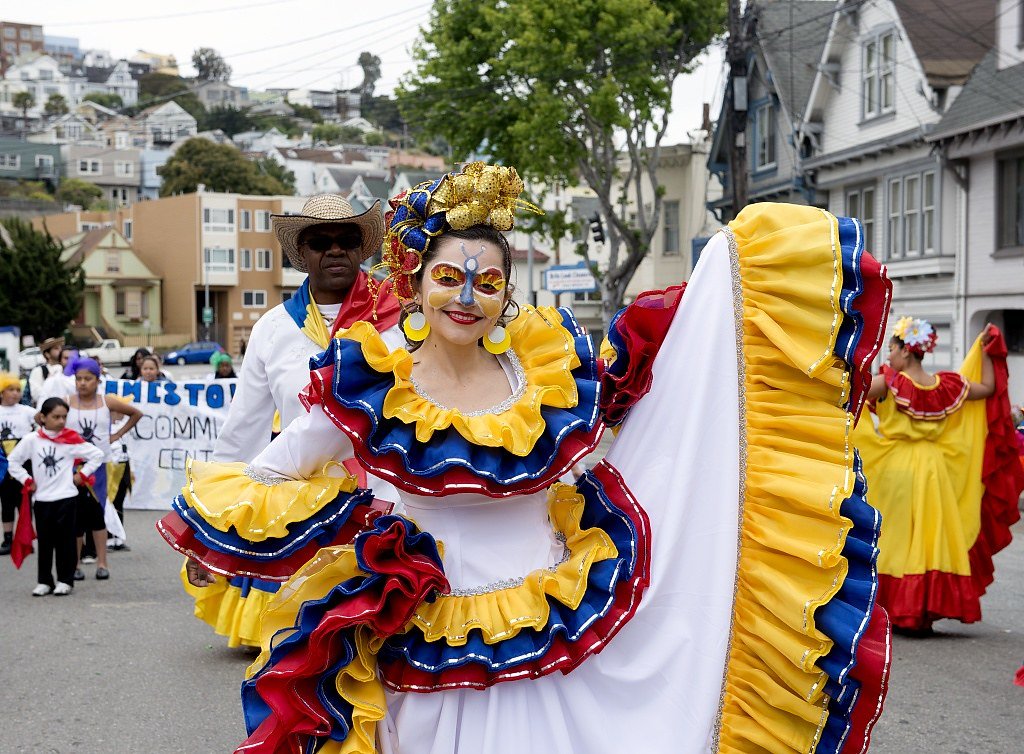
Black Mexicans celebrate their African heritage through arts and culture.
Read More7 Unique Wedding Traditions from Around the World
Beyond vows and wedding rings, these seven wedding customs exhibit international traditions of love.
A newly wedded couple. Min An. CC0.
Love is universal, but also multifaceted and varied. For couples that choose to get married, the universal yet unique nature of love translates into exciting wedding traditions around the world. Although some couples opt to create their own contemporary commemorations, many lovebirds look towards cultural customs when celebrating their big day. Whether during the ceremony, reception or pre-wedding festivities, global traditions persist and are honored in modern weddings. For centuries couples have developed and practiced these seven ways to display their affection and commitment on, around and after their wedding day.
1. Mehndi — India, Pakistan, Middle East, Africa
A bride displaying her Mehndi. Qazi Ikram Haq. CC0.
Mehndi, also referred to as Mehendi and/or Mehandi, is an intersection of celebration and art. Although its country of origin is unclear, this body art, made from dry, powdered leaves of the henna plant, is practiced in India, Pakistan, some countries in Africa and parts of the Middle East; many historians claim that Mehndi originated as a practice in India at least 5,000 years ago. It can be worn at Hindu, Sikh and Muslim weddings. The henna plant is incorporated into a paste, often dark brown or reddish brown in color, that is used to create intricate designs on the hands and feet of the bride. These beautiful designs, painted during a pre-wedding body painting ceremony, can include floral patterns, religious figures, the names of the bride and her partner, and even personal, sentimental details. Wearing Mehndi during a wedding is said to bring good luck and health to the couple’s marriage.
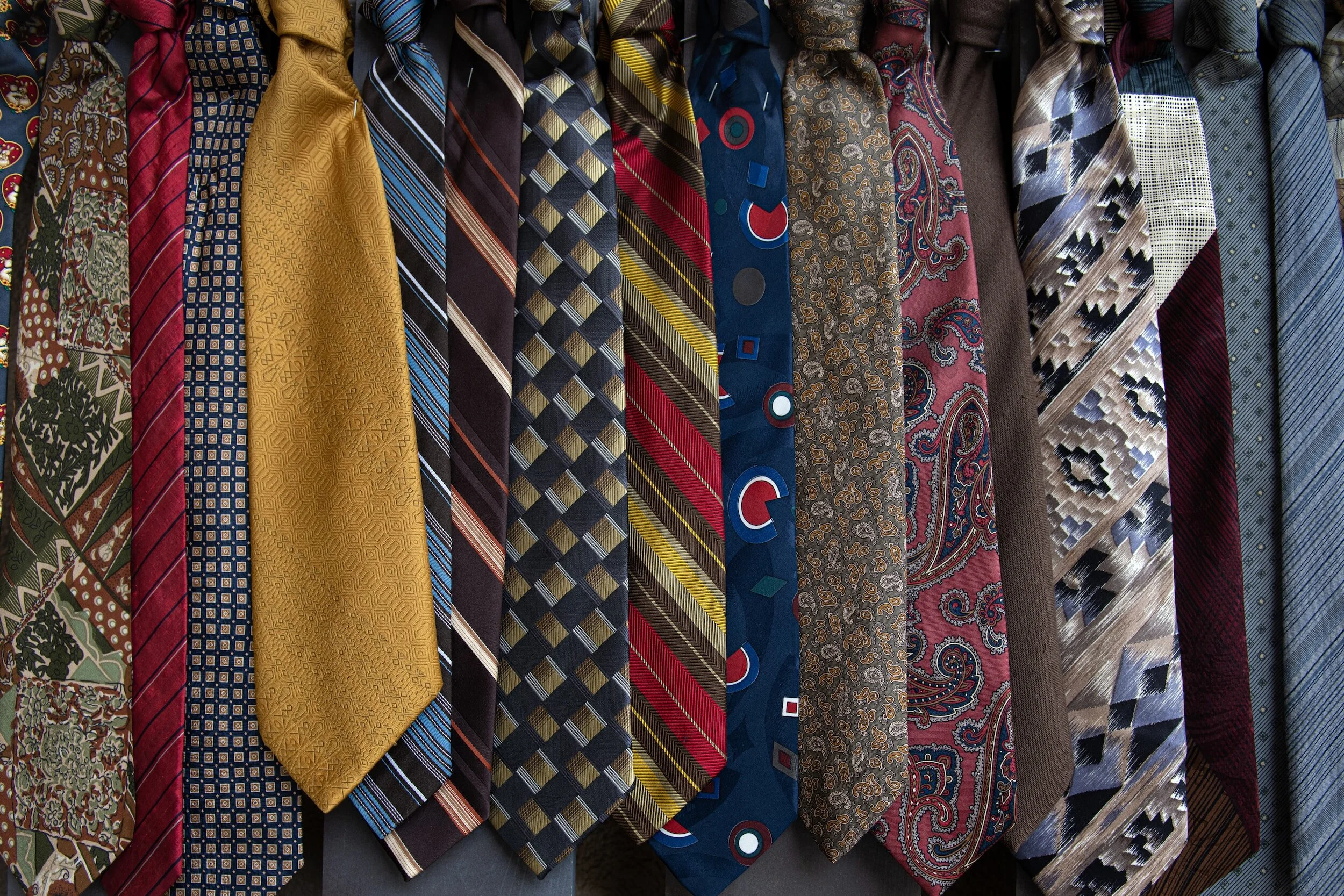
2. Cutting the Tie — Spain
A selections of ties.
Although cutting up an article of clothing on a person’s wedding day may seem alarming, this tradition, hailing from Spain, is conducted with entirely good intentions. In a post-wedding ceremony — during the reception — a groom's tie is cut up into tiny pieces by the groomsmen or close friends. The pieces of the tie are then extravagantly auctioned off to wedding guests in exchange for modest, or even large, sums of money. Despite guests only receiving a small sliver of fabric after gifting their own money, the purpose of auctioning off the tie is to give the groom and their partner one last monetary gift. Beyond representing financial abundance and luck, “cutting the tie” also represents the guests’ investment in and good intentions towards the couple.
3. The Symbolism of Red — China
Red wedding invitations. RDNE Stock Project. CC0.
Not attached to one specific element of the ceremony, the color red is often incorporated into weddings in China. The rise to popularity of the color red may have begun during the Ming Dynasty, over six hundred and fifty years ago. Red can be worn as the primary color of various garments — whether they be suits, dresses (the bridal gown is often called a qipao), jackets or veils, along with floral arrangements, candles, invitations and other decor. Perhaps the versatility and prominence of red can be attributed to its many meanings. Red can symbolize luck, joy, prosperity, happiness, honor, love, loyalty and even fertility.
4. Money Spray — West Africa
Nigerian Women wearing Iro and Buba Dance at a Wedding. Jeremy Weate. CC0.
This tradition is straight out of a couple’s dream. In this custom, which is popular in Nigeria and other parts of West Africa, but specifically originated with the Yoruba people in Nigeria’s Southwest, the newly-wedded couple is showered with money at their reception by family and friends. People dance and laugh while spraying the money, creating a palpable upbeat energy. During the reception and money spray, the newlyweds commonly wear traditional garments of the Yoruba people. Brides wear an Iro and Buba, a combination of draped and wrapped fabric on top of a blouse that is often colorful and/or patterned, and grooms wear an Agbada, an elegant loose-fitting robe. The subsequent money spray symbolizes good fortune and happiness for the couple that guests feel.
5. Claddagh Ring — Ireland
A Claddagh Ring. Royal Claddagh. CC BY 2.0.
The Irish tradition of wearing a Claddagh ring symbolizes a person’s relationship status and, more specifically, can visually depict their shift into marriage. The Claddagh ring is made up of hands grasping a heart adorned with a crown. Depending on the hand the ring is worn on and direction of the heart, different relationship statuses are depicted: wearing a Claddagh ring on the right hand facing outwards depicts a single status, while the right hand facing inwards indicates the person is in a relationship; the left hand facing outwards represents engagement, and the left hand facing inwards shows that the person is married. Claddagh rings can serve purely as the engagement and wedding rings, or can be worn in addition to international-style Western wedding and engagement rings. Commonly worn by brides, Claddagh rings can be passed down through generations of women in families.
6. Stefana — Greece
A floral Stefana bridal crown. Faylyne. CC BY 2.0.
Ornate and delicate, Stefana are crowns commonly worn during Greek Orthodox Wedding Ceremonies. Although Stefana were traditionally made of vines, branches and flowers, modern Stefana can be made of metal with gemstones. Stefana are worn by both partners during the wedding and, during the wedding ceremony, are connected by a ribbon or thread going from one person’s head to the other. The ribbon symbolizes the strong connection between the couple, and the crowns as a whole can symbolize unity, love, faith and loyalty. During a traditional Greek Orthodox Wedding ceremony, these crowns are also blessed by a priest.
7. Hapgeunrye, or Cup Drinking — Korea
An example of a Metal Cup Set. CC0.
In Korea, Hapgeunrye is a ceremony where the couple drinks from the same cup. The tradition, however, varies depending on the region and preferences of the couple. In some cases, the couple will drink from the same metal cup while in others the couple will drink from two halves of the same gourd. In both cases, the rite occurs during the wedding ceremony itself and the liquid drunk from the cup is often a type of liquor. This custom symbolizes the couple being united as one entity, recognizing their respect for each other and the harmony they hope will be fostered in their relationship.
Carina Cole
Carina Cole is a Media Studies student with a Correlate in Creative Writing at Vassar College. She is an avid journalist and occasional flash fiction writer. Her passion for writing overlaps with environmentalism, feminism, social justice, and a desire to travel beyond the United States. When she’s not writing, you can find her meticulously curating playlists or picking up a paintbrush.
5 Cryptids for Well-Traveled Lovers of the Macabre
Cryptids are creatures that have developed cult followings despite their dubious relationship with reality.
Helmingham bestiary and mythical creatures. Rawpixel. CC0.
Cryptids are creatures or animals that cryptozoologists believe exist in the wild, but whose present existence is unsubstantiated by science. Tales of such creatures can be found all around the world and are often the subject of modern folklore. Whether you or not you are a believer, cryptids are a point of fascination for anyone who relishes in the macabre.
1. The Mothman
Point Pleasant, West Virginia
The illusive mothman creature, with red eyes, wings, and a humanoid body. Steve Baxter. CC0.
In the small town of Point Pleasant, West Virginia, it is said that the infamous Mothman creature has haunted the woods and terrorized residents since 1966. First sighted by teenagers driving on State Route 62 near an abandoned National Guard Armory building, the creature is described as being six to seven feet tall with red eyes and wings like a moth. Since its first appearance in the public’s imagination the Mothman has reached mythical status, with statues, restaurants and other tourist attractions erected in its honor.
2. Chupacabra
Mexico and Southwestern United States
The chupacabra is said to feed on human and animal blood. Michael Snipes. CC-BY-SA 2.0
Chupacabras are said to be vampire-like creatures that are often blamed for attacks on goats, sheep and other domesticated animals. According to legend, the creature stands upright and resembles a large reptilian kangaroo. First reported in 1995, many believe the appearance of the Chupacabra in the collective imagination of Mexico and the Southwestern United states was highly influenced by the horror movies of the time. That being said, the Chupacabra continues to haunt the hearts and minds of the Great Basin.
3. J’ba FoFi
Democratic Republic of the Congo
The J’ba FoFi is a giant spider said to live in the Congolese jungle. Flickr. CC0.
The J'ba Fofi, also known as the Congolese Giant Spiders, are a type of large arachnid cryptid said to inhabit the forests of the Congo, hypothesized to be a new species of spider. The J’ba FoFi is said to hunt vertebrates rather than the insects its kind normally consume. The creature creates a network of webbing that operates as trip wires for approaching prey. They are said to burrow under trees and have large, yellow eggs. The existence of this giant spider, whether it is a yet-undiscovered species or simply a myth, remains unclear.
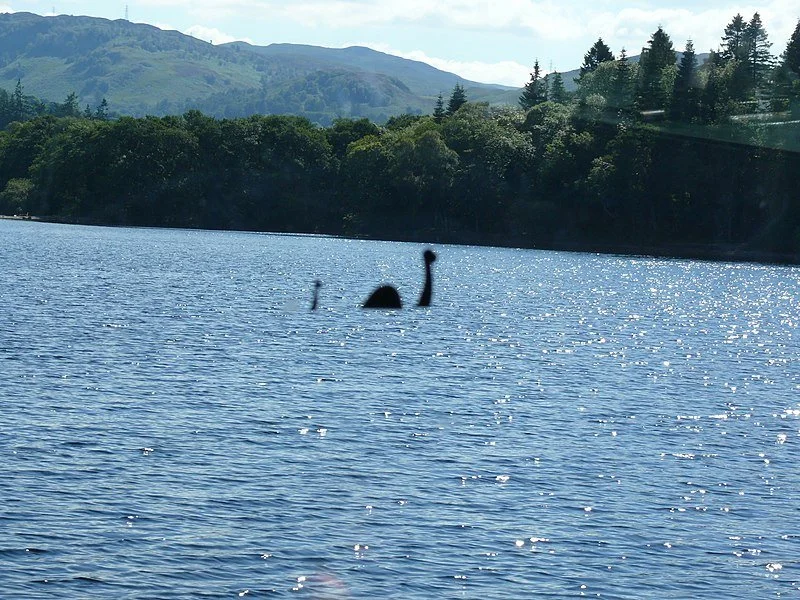
4. Loch Ness Monster
Scotland
Sighting of the Loch Ness monster. Ad Meskens. CC-BY-SA 3.0
One of the most famous cryptids in the world, the Loch Ness Monster is a creature said to inhabit Loch Ness in the Scottish Highlands. It is described as a large animal, with a long neck and often several humps protruding out of the water. Hypothesized to be the last descendant of an extinct species, potentially dating back to the time of dinosaurs, the existence of the Loch Ness Monster has never been confirmed. “Nessie,” as the behemoth is affectionately known to fans, has been the subject of sustained curiosity and numerous hoaxes, capturing the public’s attention despite the creature’s dubious link to reality.
5. Hibagon
Japan
The Hibagon is a Japanese, humanoid cryptid. John Doherty. CC0.
The Hibagon is a Japanese Bigfoot-like creature said to live on Mount Hiba, Hiroshima Prefecture. First sighted in 1970, the Hibagon is described as an ape-like being that walks upright and is approximately six feet tall. There have been many more sightings of the Hibagon since the ‘70s, causing a Hibagon craze that has become a fixture of the local tourist industry. The existence of such a creature remains unconfirmed.
Sophia Larson
Sophia Larson is a recent graduate of Barnard College at Columbia University. She previously worked as the Assistant Editor on the 2021 book Young People of the Pandemic. She has also participated as a writer and editor at several student news publications, including “The UMass Daily Collegian” and “Bwog, Columbia Student News.”
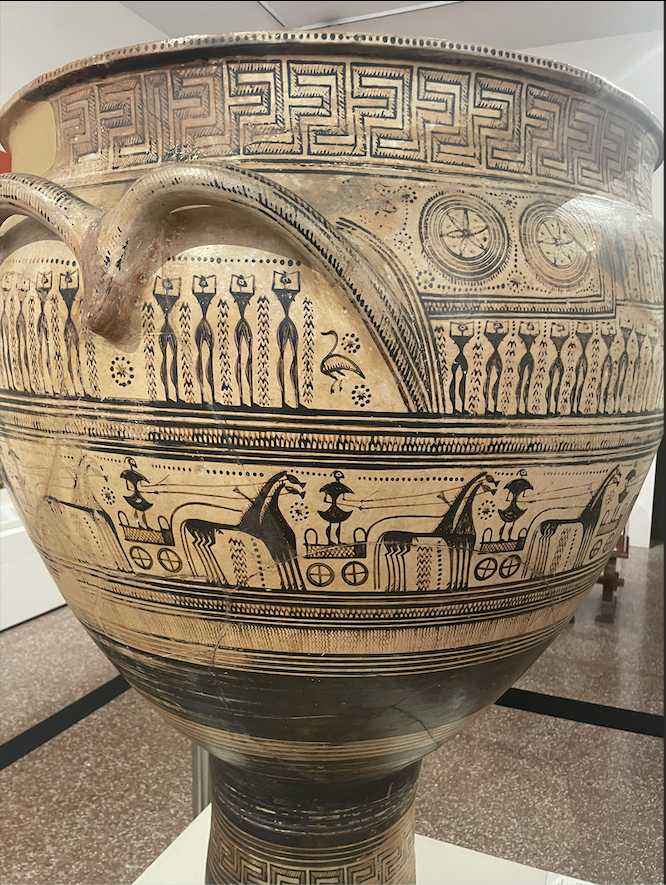
From Abstraction to Realism in Ancient Greek Art
If you ever find yourself struggling with Athens’ summer heat, cool off in its museums and discover a whirlwind of art and civilization.
Small statues typical of the Cycladic Culture, which flourished between the fourth and second millennia BC. Taken by Dermot Curtin.
A human face represented only by an angular nose bridge and a semi-oval silhouette. A procession of curvilinear stick figures, lavished with somewhat less detail than bizarrely eight-legged horses, inanimate chariots and abstract designs. A general preference for the symbolic over the literal and the real. Much of the art you’ll find in Greece’s National Archaeological Museum (NAM)is highly abstract; parts of the collection, particularly those of the Cycladic Period, have a distinctly postmodern feel to them. Such works, however, are not the product of the 19th and 20th century revolt against Greco-Roman and Renaissance verisimilitude, long a dominant force in European art. They instead predate the Classical period and its values by hundreds or thousands of years.
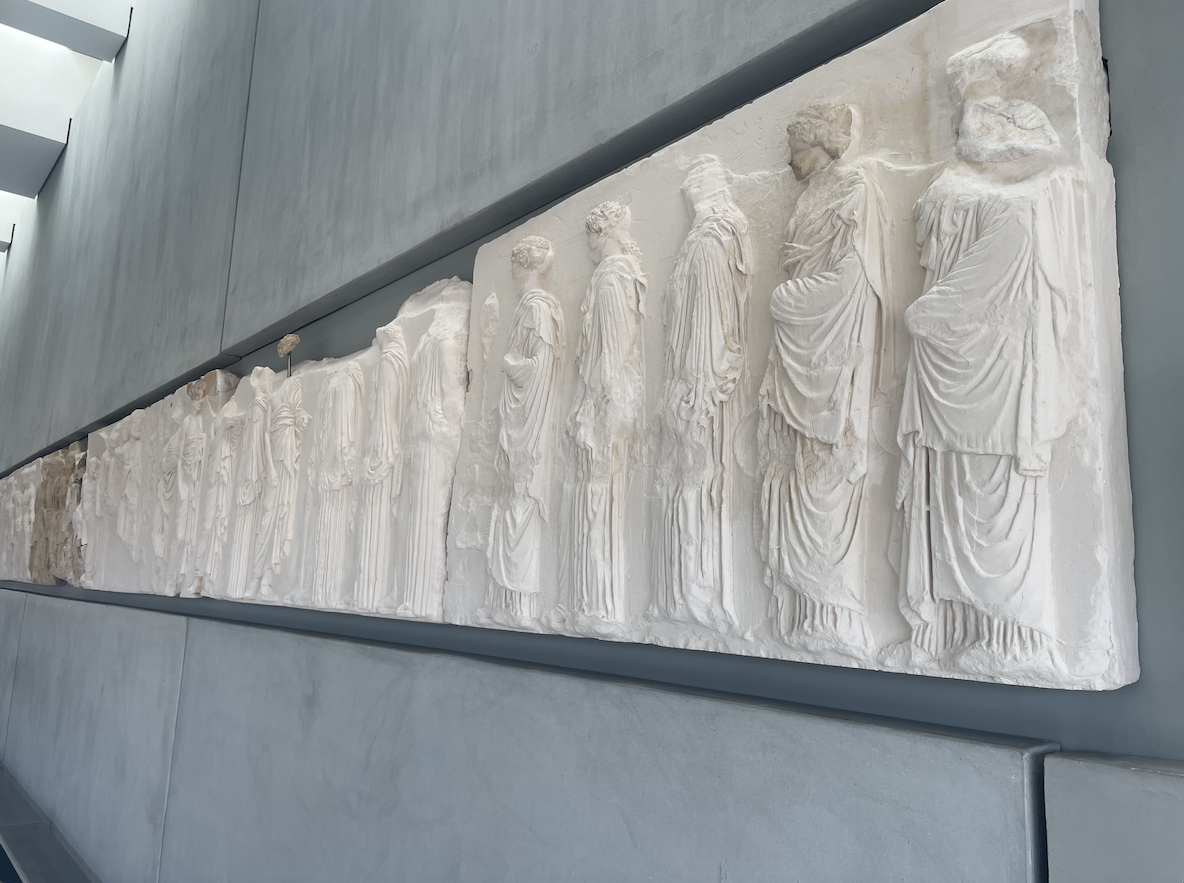
Almost all visitors to Athens who can take the heat make the long, slow trek up the Acropolis to see the Parthenon. Many of those will then visit the Acropolis Museum, a relatively new museum home to much of the pride of Greece’s classical heritage, including the portion of the Parthenon Frieze that Thomas Bruce didn’t get around to looting (plaster casts of the originals fill in gaps, labeled with an ignominious “BM” for British Museum). Still popular, but less of a universal attraction, I found the National Archaeological Museum to be the more interesting of Athens’s two great museums dedicated to antiquity. The NAM’s more varied collection allows visitors to chart the development of Greek style over several millennia, seeing works that are stunning in themselves and better understanding of one of the most radical changes in aesthetic values before the modern age.
The original segments and fragments are noticeably grayer than the majority plaster copies. Taken by Dermot Curtin.
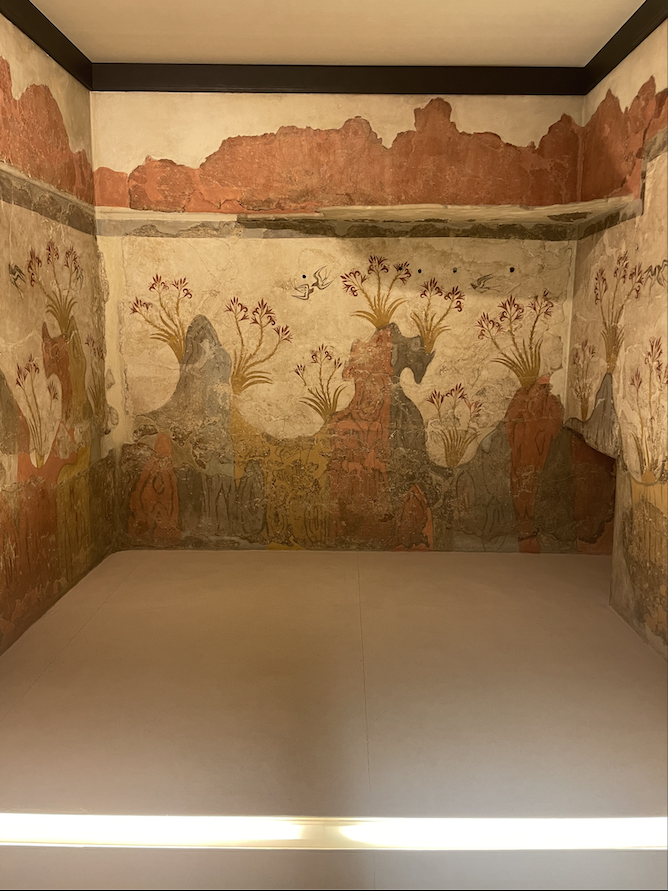
Greece’s island territories were its most precocious in terms of art and civilization. The Minoan and aforementioned Cycladic cultures left a remarkable heritage, which stand in marked contrast to later Hellenic society and each other. Cycladic art is most famous for its austere minimalism, especially as expressed in statues such as the two in this article’s introductory photograph. The Minoans took a different approach, painting vivid frescoes which have, in part thanks to a volcanic eruption sometime between 1650 and 1550 BC, survived thousands of years in good condition. Human figures in Minoan art are stylized, but are far from the degree of abstraction found in their Cycladic semi-contemporaries. Many Minoan paintings not saved by volcanic ash were unearthed at the Palace of Knossos, where King Minos of Greek myth was said to have fed young Athenians to the dreaded Minotaur every year in the Heroic Age.
Two Minoan frescoes, originally from Santorini and preserved by its great eruption. Taken by Dermot Curtin.
Although the Minoan civilization flourished on what is now Greek soil, in one respect it was not yet a Hellenic society: language. The Minoans developed their own system of writing, known to history as Linear A, around the 19th century BC. It has never been deciphered, but linguists have been sound out its symbols since its direct descendant, known as Linear B, was cracked in the early 1950’s. Linear B tablets represent the earliest recorded form of the Greek language called Mycenaean Greek, and are generally administrative documents that the elite used to keep track of their resources and labor. Mycenaean tablets from Crete are indirect evidence for the rise of Hellenic culture in insular Greece, recording a nobility that used Greek names and lower orders with older, native Minoan names. The Mycenaean culture originated in mainland Greece, and expanded south and east into what are now the Greek islands. The Minoan language has no confirmed relatives or descendants.
Linear B tablet from not long after the Mycenaean conquest/cultural shift in the 1400s BC. Taken by Dermot Curtin.
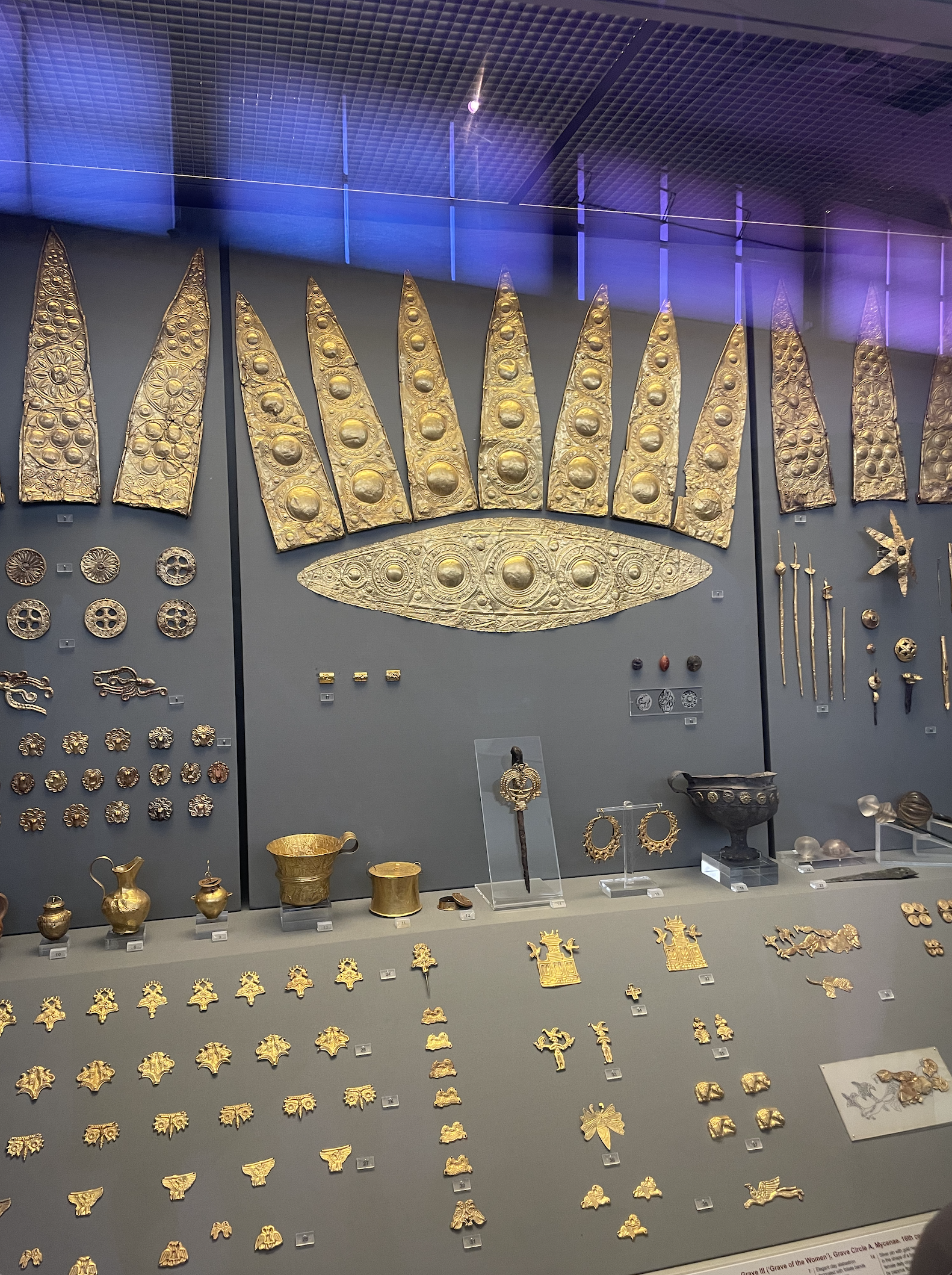
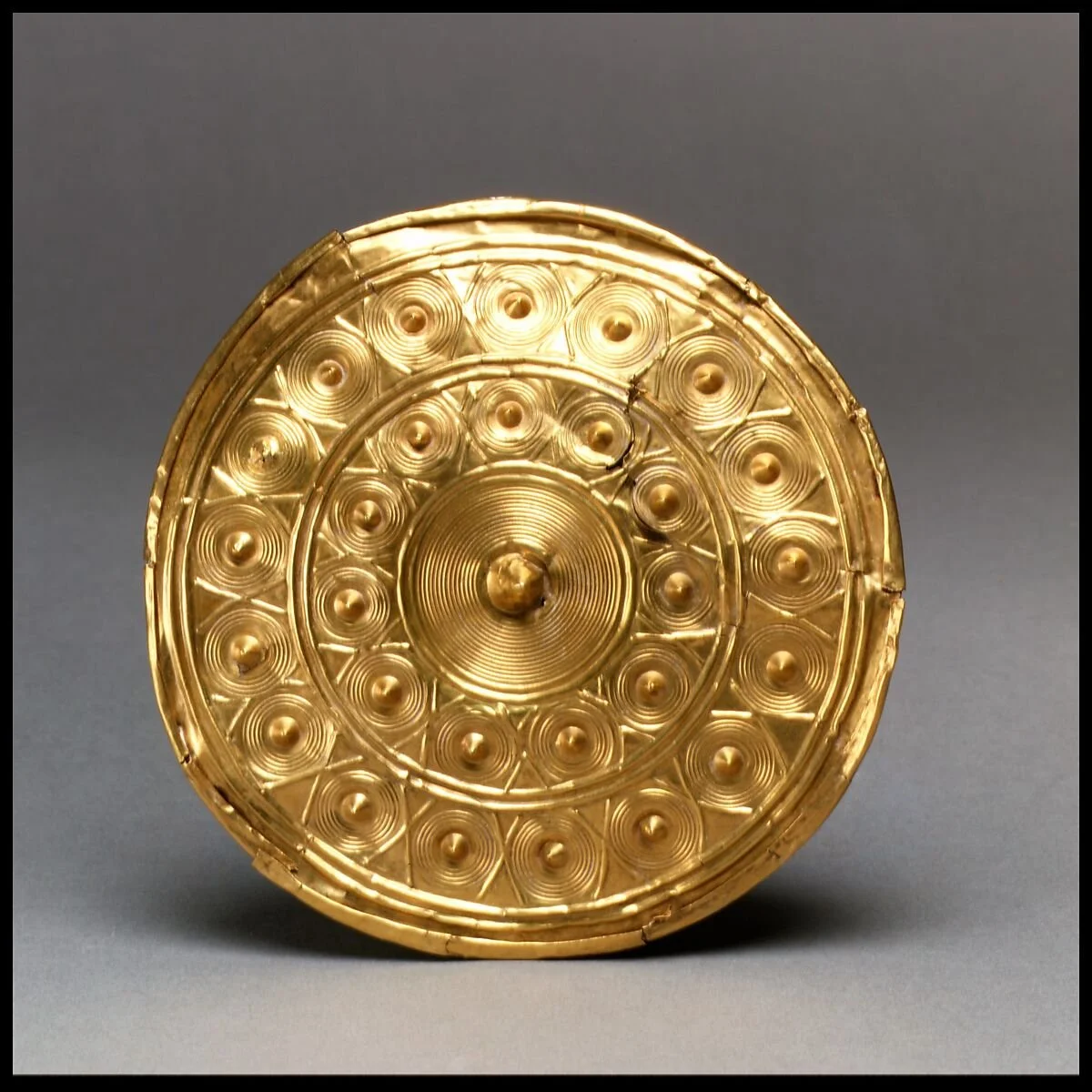
Mycenaean Civilization was famous long before its archaeological rediscovery in the late 19th century as the setting of Homer’s Iliad and Odyssey. Although Homer composed centuries after the Bronze Age Collapse of circa 1200 BC, he knew many details about the earlier period; the blind poet placed Agamemnon, the the most important leader of the Greeks in the Trojan War, on the throne of Mycenae, which modern archaeology has revealed to be the largest city of the age. Many of the most significant finds from the Hellenic Bronze Age are ornately decorated thin gold sheets, which are part of a broader European artistic trend of the same period. I was immediately reminded of similar (albeit less intricate) artifacts from Bronze Age Ireland. Other works, such as the beautiful inlaid dagger below, have no obvious parallel.
Many gold Mycenaean artifacts from the National Archaeological Museum. Taken by Dermot Curtin.
Disk from a Reel, Irish, c. 800 BC. The Metropolitan Museum of Art. CC0.
Gold Dagger from the National Archaeological Museum. Taken by Dermot Curtin.
The Bronze Age Collapse hit many areas hard, and Greece harder than most. Linear B fell out of use around 1200 BC, leaving the Hellenic world without a script until about 200 years later when the Phoenician abjad was modified for the purpose, with vowels added to make it a viable option for the Greek language. Greece had entered its Dark Age, a radical departure from the centralization, trade and literacy of the Mycenaean and Minoan eras. Despite this, literature flourished; Homer and Hesiod composed their epics, laying the foundation for millennia of inspiration and adaptation.
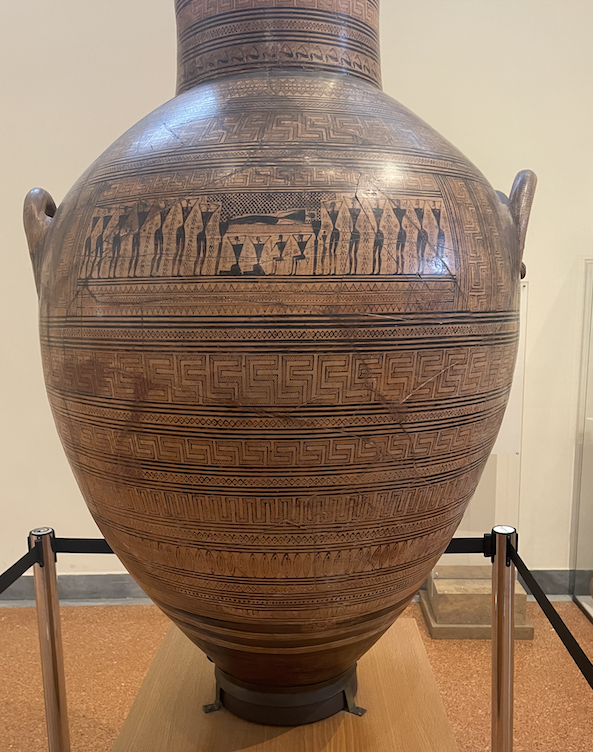
Two Geometric amphorae from the National Archaeological Museum, from an age (900-700 BC) defined by abstract art. Taken by Dermot Curtin.
As civilization began to recover from the Collapse in the tenth century BC, the Geometric style emerged to fill the void left by Mycenaean art. This style was deliberately abstract, characterized by repeating linear patterns on large amphorae. People, when present at all, appear as small stick figures. Mourners dramatically and uniformly put their hands on their heads, their arms bent at sharp angles that would look unnatural on a more realistic human design; such a pose is necessary to convey distress, as the faces are not given enough detail to show any kind of emotion. The meandros, a repeating pattern that would later be a common fringe for other designs, here takes center stage, while the funerary procession is confined to a narrow box in the upper-center of the amphora. There is little to differentiate one person from another, the exceptions being a child, who is clearly smaller than the adults, and the deceased, who lies on his or her back. Geometric style seems to be the product of a culture that did not value the individual human being as a subject for artistic expression.
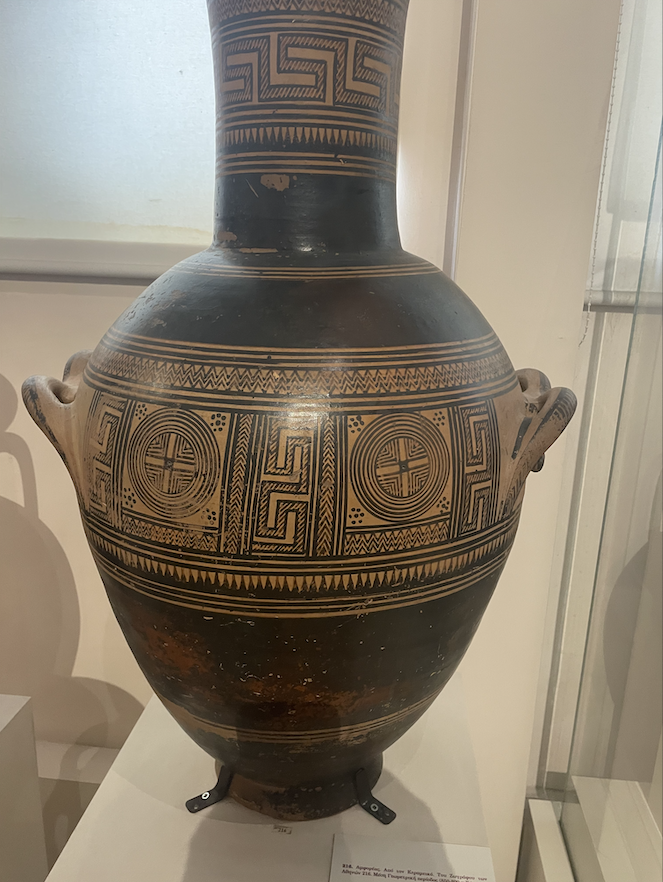
Marble statue of a youth, from Archaic Greece c. 590-580 BC; you can see the abstract art of the Geometric give way to stylized human forms. Metropolitan Museum of Art. CC0.
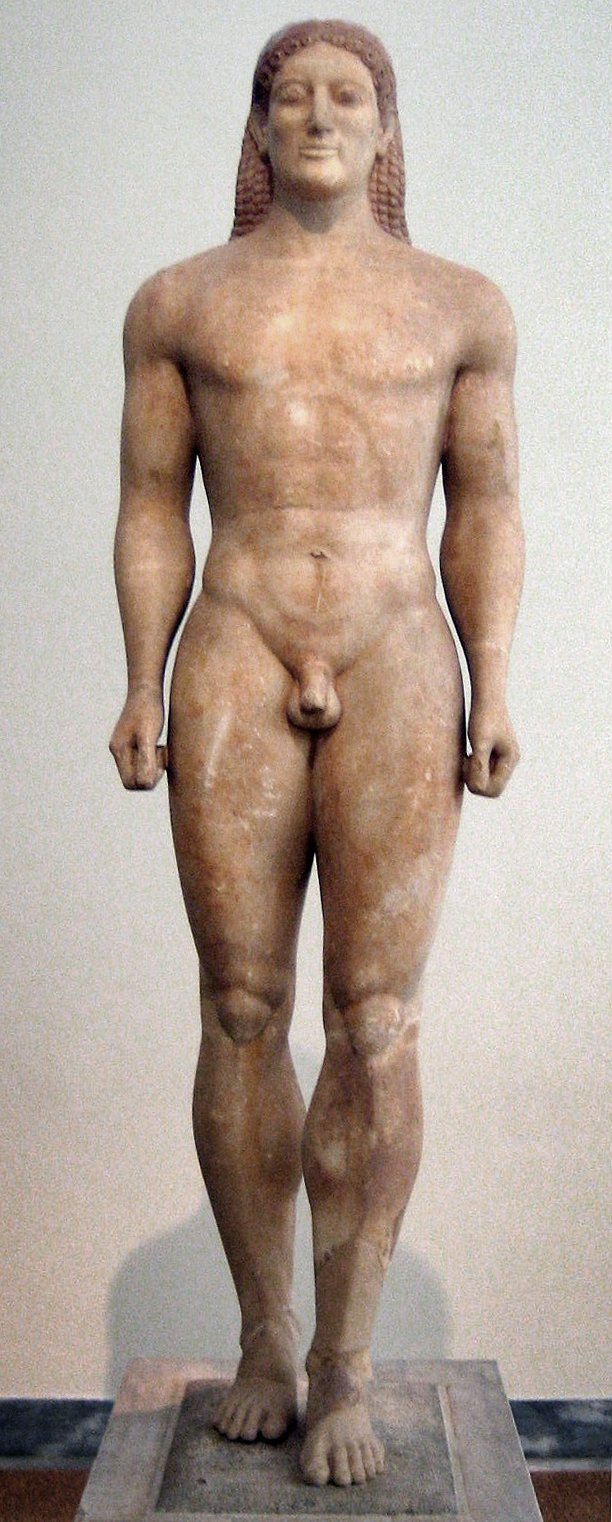
The Kroisos Kouros, c. 530 BC. User:Mountain. CC0.
Greece only fully recovered from the Bronze Age Collapse as it transitioned into its Archaic period around the eighth century BC. In this period, as Greek culture built up to its fifth century zenith, the seeds were planted for many of the institutions and conventions that would flourish in the Classical era (beginning 480 BC with the end of the Persian Wars). The Olympic games were founded, dramas began to be staged in Athens and lawgivers like Solon imposed constitutional reforms that would eventually lead to democracy. The visual arts made a dramatic turn, as abstract designs retreated to the background in favor of a strong emphasis on the human form. The most typical art form of the time is the kouros, a strongly stylized nude statue of a male youth. Although sometimes differing in size and detail, all kouroi adhere to the same basic plan, standing up straight with the left foot out front, braided hair and a serene affect. The figure on the right was made about 50 years later than its counterpart to the left, and although clearly the product of more skilled craftsmanship does not deviate from the essence of the older model.
Statue from the Egyptian Old Kingdom that resembles the Greek Kouros; note the forward left foot. The Metropolitan Museum of Art. CC0.
Although impressive in their own right, such statues are not dissimilar to art produced by Middle Eastern cultures in the Bronze and Iron ages. Initial kouroi designs seem to have been borrowed in part from Egypt during the early part of the Archaic period. In the jubilant aftermath of the Greek victory in the Persian Wars, however, Hellenic artists made an unprecedented turn toward realism that would cement Greece’s place in art history for all time.
Roman copy of Polykleitos’s famous Diadumenos, original circa 420 BC. Taken by Dermot Curtin.
A Greek sailor looks out wistfully on the sea battle where he died, funerary stele. Taken by Dermot Curtin. (melancholy)
Ancient art reached its apogee in the Classical period of the fifth and century BC. This is the era which would come to define Greek civilization, and marks one of high water marks of cultural production the world over. In the visual arts this meant a form of idealized realism, meant to portray natural forms in their best possible state. This involved more than technical skill, as sculptors like Polykleitos incorporated specific mathematical proportions into their work in their drive for perfection. The incredible detail allowed for greater subtlety of design; compare the melancholy of the fallen soldier on the left to the sharp and uniform gestures on the Geometric mourners above. The sculptures look like people you could actually know, except fitter and far better looking.
Geometric amphora. Taken by Dermot Curtin.
Terracotta volute-krater with red figure design, circa 450 BC. Metropolitan Museum of Art. CC0.
The period between 750 and 450 BC saw a revolution in aesthetic values, matched only by the modern rise of modern art in the 19th and 20th centuries. In the Ancient Greek world, however, the shift was in the opposite direction, from the abstract to the concrete. The change in taste was coincided with a dramatic rise in skill, leading to works that still keep many of the world’s art historians and critics occupied. If you ever find yourself in Athens, make sure to visit the National Archaeological Museum to experience the whirlwind for yourself.
Dermot Curtin
Dermot is copy editor and a contributing writer at CATALYST PLANET. He is a recent graduate of William & Mary, majoring in History and Government, and enjoys learning about the world and conveying his experiences through writing.
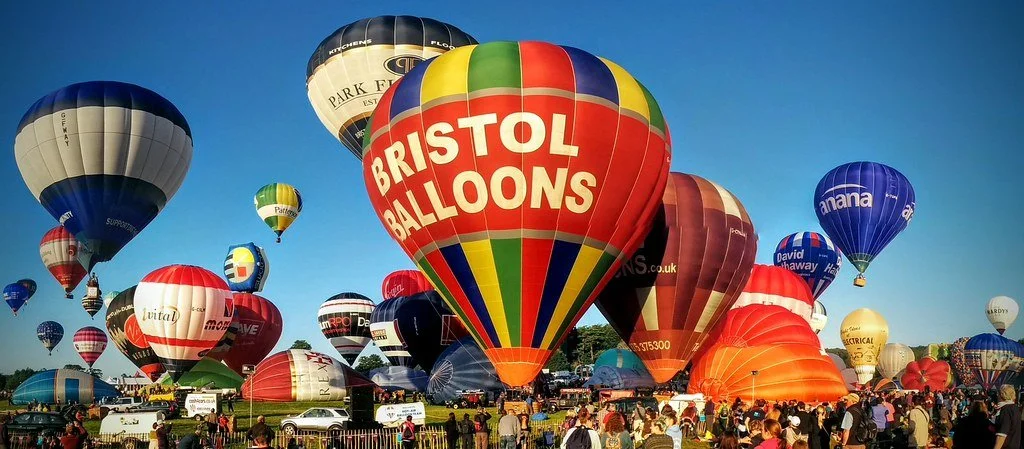
Hot Air Ballooning in Bristol
Known as the hot air balloon capital of the United Kingdom, Bristol prides itself on lighter-than-air travel.
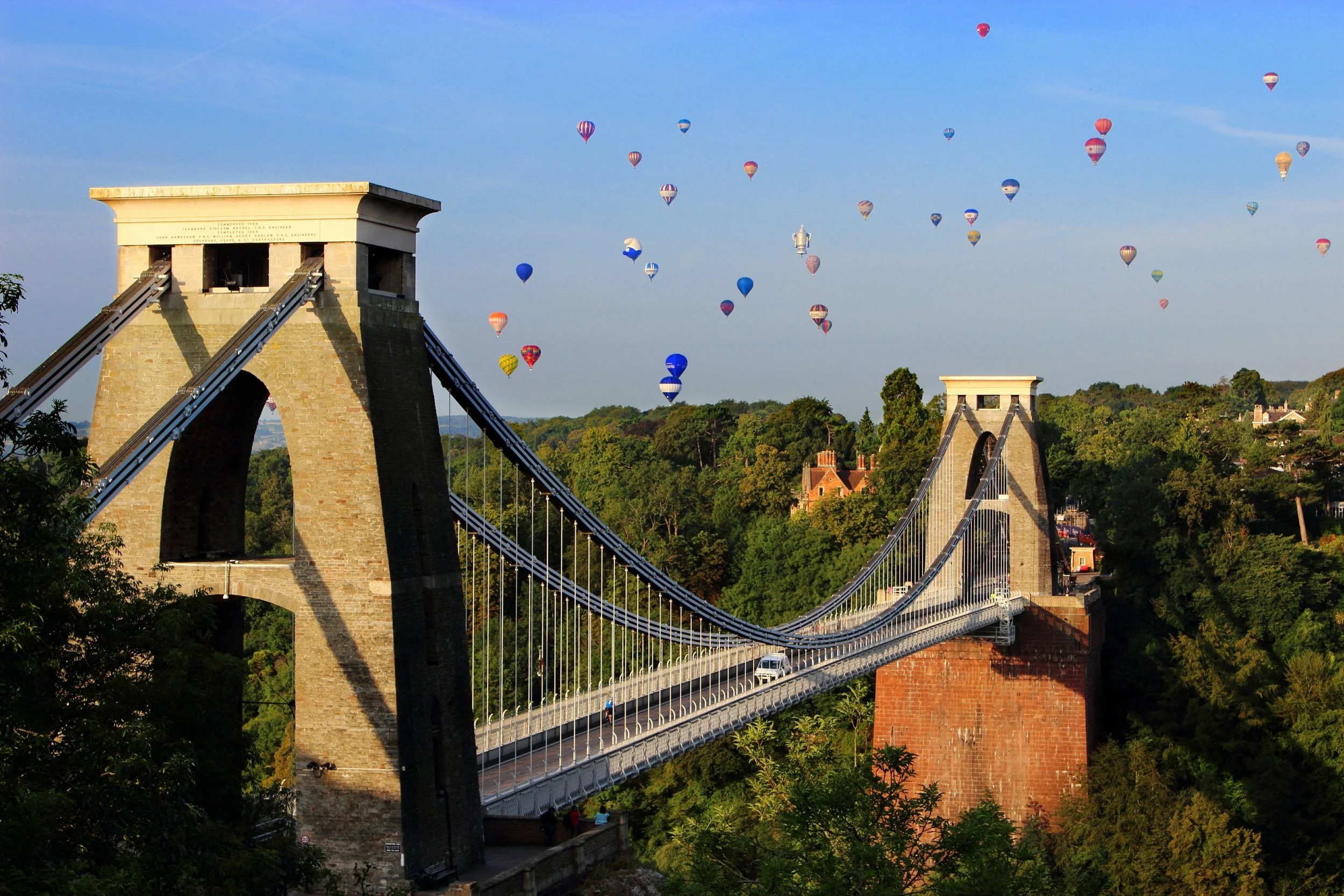
Bristol International Balloon Fiesta. PughPugh. CC BY 2.0.
The sun is shining and the air is still. Laying on the soft grass, I watch the fluffy clouds float along. I wonder what could possibly make this day better. Then, just as my eyelids begin to close, I am jolted awake by a loud sound overhead. It is the iconic roar of a hot air balloon igniting. Passing over me, the cushiony balloon glides effortlessly, allowing the gentle breeze to direct it through the sky. I sit up to get a better view and realize two more hot air balloons are following behind the first. Pops of red, yellow and purple embellish the blue skies.
On these perfect summer days in my hometown of Bristol, just two hours west of London, that familiar roaring sound is bound to be heard. And once you see one hot air balloon in the sky, keep an eye out, as there are probably more coming. Although the weather conditions don’t always favor ballooning, Bristol takes great pride in its culture in the clouds.
Hot Air Balloons over Bristol Suspension Bridge. Matt Prosser. CC BY-SA 3.0.
Hot air balloons were the first form of air travel and date back to 1783, all thanks to the French Montgolfier brothers. Having created a balloon contraption, the brothers successfully transported living animals — a sheep, a rooster and a duck — two miles in their invention. A year later, Michael Baggini brought the invention to Bristol. In 1784, he launched a balloon in Cooper's Hall, now known as the Bristol Old Vic Theatre. Demonstrating the potential of this exhilarating form of air travel, he sparked great excitement in the public as they watched the balloon float around the room.
Nearly 200 years later, Britain’s first modern hot air balloon was created by Don Cameron, a member of the Bristol Gliding Club. He named the craft the Bristol Belle, a red and yellow striped balloon which took flight in 1967. This event put Bristol on the map as a pioneer of the ballooning industry.
Nowadays, Bristol celebrates its hot air balloon culture with the International Balloon Fiesta, the largest hot air balloon festival in Europe. Taking place in mid-August every year since 1979, thousands of people, from Bristol and beyond, gather over its four days to experience the graceful balloons brightening up the sky. When the weather permits, up to 100 hot air balloons launch at the same time, turning the sky into a playing field of different colors, shapes and sizes. Every year, quirky balloon designs can be spotted, such as 2023’s screwdriver, various animal shapes and even a shopping trolley. This eye-catching event sparks excitement all around the city as the balloons float over Bristol.
Bristol International Balloon Fiesta. Karen Roe. CC BY-2.0.
The magic continues into dark for the night glow. Dozens of balloons ignite while stationary on the ground. The roaring flames warm the whole fiesta in an otherworldly illumination.
Bristol International Balloon Fiesta. Mike Peel (www.mikepeel.net). CC BY-SA 4.0.
While the Balloon Fiesta showcases the best of Bristol’s balloons, it is not the only time they appear in our skies. Serendipitous balloon sightings are arguably more impressive, as their unexpected presence is so calming. A balloon in the sky signifies the winds are resting and the air is undisturbed. In harmony with the clouds, their graceful, humble nature allows them to be unobtrusive as they soar through the sky.
Another way to experience the serenity of the balloon is to step inside the basket and go on the journey of a lifetime. What better way to see Bristol than an unforgettable one-hour flight over this home of the hot air balloon? A variety of operators fly in the area, including First Flight Hot Air Balloons and Bailey's Balloons. Flights cost from $250 per person and can accommodate families, private parties and even romantic proposals.
However you experience it, the hot air balloon epitomizes Bristol, representing innovation and creativity and creating peace and calm. No matter how many times I see the colorful contraptions overhead, I will always be in awe of them. They will continue to light up the skies for centuries to come as Bristol will always be known as the ballooning capital of the UK.
Eva Adorisio
Eva is an avid traveler and writer from Bristol, England. In her writing, she aims to show the true nature of what a place is really like. Her Italian roots have led to a love of food, culture and language. She also spends her time staying active out in nature and is always searching for the next adventure.
24 Hours in Berlin
Getting to know the Grey City in a jiffy.
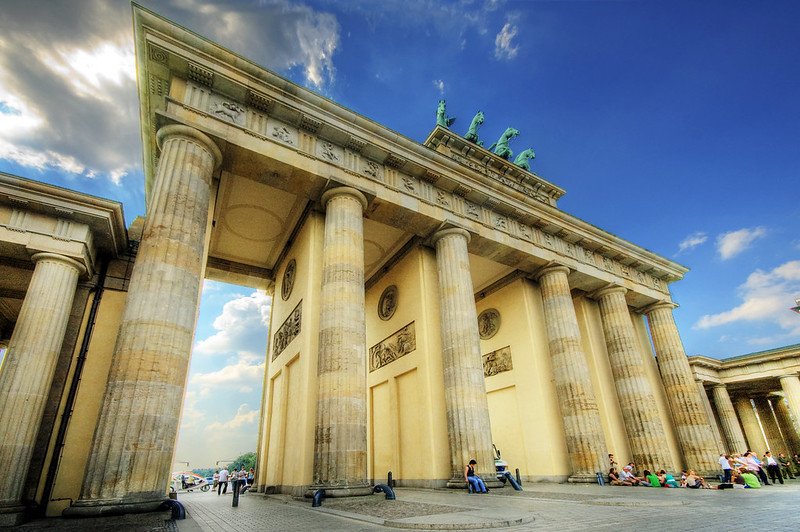
Brandenburg Gate. Wolfgang Staudt. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
Berlin is a gritty city, and one whose food, architecture, monuments and culture can only be explained through its grave past. The German capital is a historic center of Europe as the nerve center of Nazi Germany in World War II, the greatest symbol of the Cold War’s infamous Iron Curtain and the prime city to see grand Prussian architecture. While many German institutions like monuments, transportation and active government buildings paint a picture of this historical influence, the picture of Berlin would be left incomplete without mentioning its spirited present.
In between landmarks like the Reichstag, Germany’s Parliament building, the famous Brandenburg Gate, the remains of the Berlin wall and Prussian palaces lies an amalgamation of diverse restaurants with owners from every corner of the world, a bustling nightlife of clubs and bars, a thriving local music scene and a fashion-forward community.
Berlin is an urban city through and through; its streets and unassuming apartment buildings (sprinkled between colorful modern architecture) comparable to those of Istanbul with an artistic, stylish flair reminiscent of New York. Live through a bit of history and a bit of present with me as I spend a day in Berlin:
We’re out and about today, but refuse to approach our day on an empty stomach, so we head to a local breakfast place, Erchy’s. Other days we have feasted on the cinnamony pastries of a staple German breakfast cafe, Zeit fur Brot, and even some German-made cheeses bought from German grocery store REWE when we really wanted to masquerade as Berliners. But today is Erchy’s. Their food will fuel the traveling to be done.
Swans in the palace gardens of Charlottenburg. Su Ertekin-Taner.
Graffiti near the S-bahn. Su Ertekin-Taner.
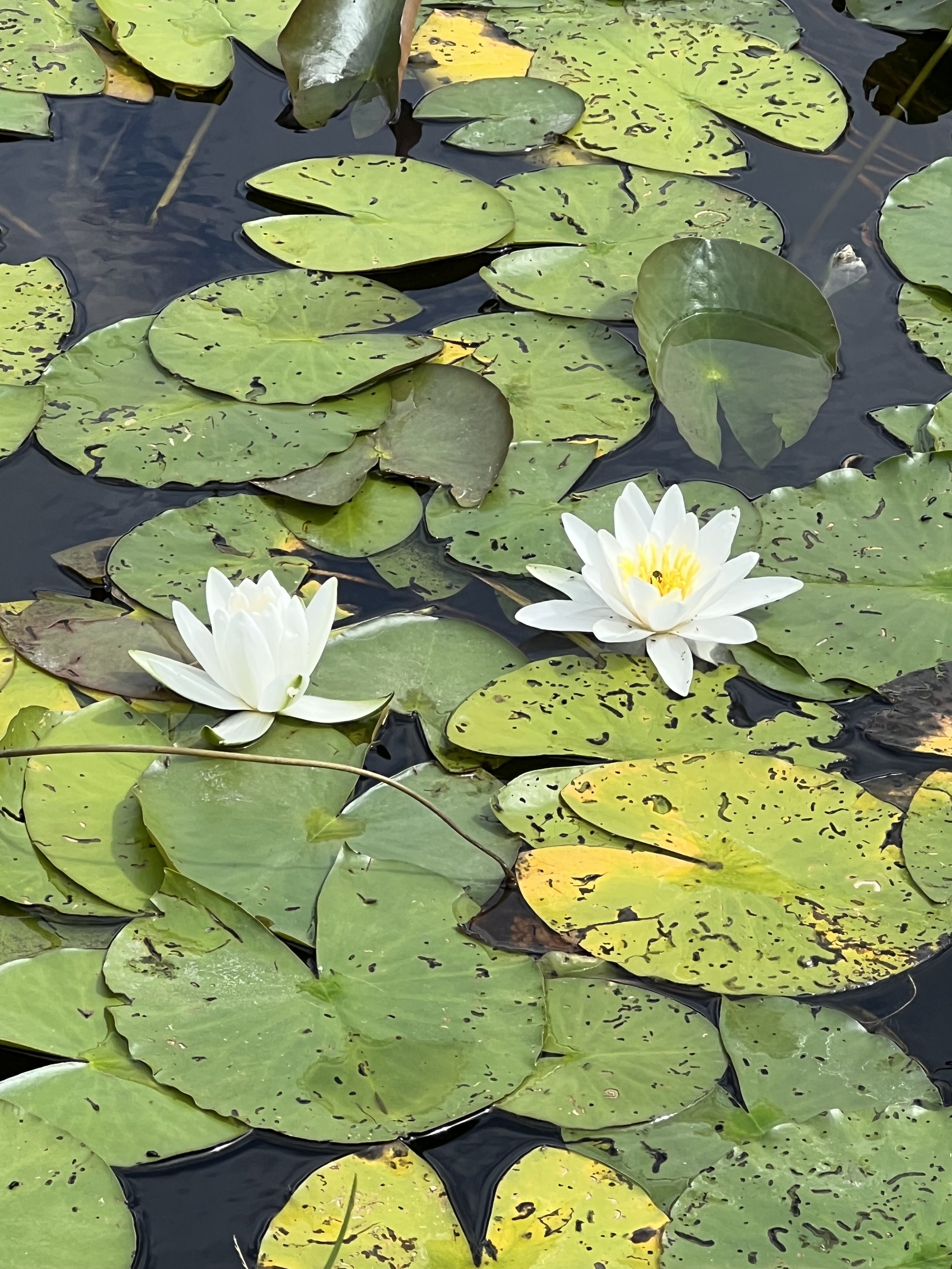
Lily pads in the palace gardens of Charlottenburg. Su Ertekin-Taner.
Charlottenberg. Rfunnell. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
Graffiti in Berlin. Mitch Altman. CC BY-SA 2.0
We immerse ourselves in Berlin’s public transportation system after food. We use the U-bahn, the German metro, and then the S-bahn, Berlin’s fastest form of transportation to get to today’s location. At times using Berlin’s transportation reveals more about the divide of Berlin via the Berlin wall than any museum could, I think.
Altogether, the journey takes about 45 minutes from the center of East Germany. As we travel, the underground tunnels melt into cloudy skies that overlook old beige buildings decorated completely with graffiti. Berlin’s graffiti scene is one of the most vibrant in the world due to the rise of a countercultural voice during the Cold War and the Berlin Wall days. Graffiti galleries, exhibits, and alleys like the East Side Gallery, Cafe Cinema and Raw Gelande are staples of the Berlin community. As I wander through my thoughts, I sense the train stop. The trek has been made and so, we expect to be met with a reward.
The Charlottenburg Palace more than qualifies as a reward. This Baroque palace was originally constructed on behalf of Friedrich III’s (later King Friedrich I) wife Sophie Charlotte, hence the name. The interior of the palace is richly decorated, representing the height of Prussian high culture: porcelain from the royal porcelain providers KPM lines the walls, mantels are decorated with an East Asian-inspired blue and a ballroom fit with large windows divides the palace in two and overlooks the gate. The signs that guide us through the palace also note, however, the racist portrayal of Middle Eastern and East Asian figures throughout the palace’s art; the Prussian monarchy hoped to assert its dominance in every corner.
Behind the palace, we escape into nature, or a manufactured sort of nature: the Charlottenburg Palace Gardens, inspired by those of Versailles. We walk near rivers of lily pads, greet some sheep tended by palace attendants, swans and even some bike riders; the access to this park is free.
Chicken gemuse kebab at Ruyam. Su Ertekin-Taner.
Doner kebab. Addison Berry. CC BY-NC-SA 2.0
By the late afternoon, we have ambled back near the center of East Berlin. We decided on chicken gemuse doner at Ruyam Doner, which offers the best doner kebab in Berlin, though we did consider a meal at one of the many Vietnamese restaurants — established by the large Vietnamese community —in the area. The line spills out of the restaurant and into the street; everyone is craving some of this chicken gemuse. But the line quickly shortens until we are ordering our kebab of moist chicken, a spicy blend of sauces, and slightly heated bread.
Turks are the largest ethnic minority group in Germany and often occupy entire neighborhoods like Keuzberg. Many Turks immigrate to Germany for work and stay, or accompany family members who have already migrated. As a Turk, I feel lucky to taste a part of my culture on the streets of Berlin.
A biergarten in Elisabethmarkt. digital cat. CC BY 2.0
We end our day with a biergarten, or beer garden experience. A biergarten usually consists of an open air bar filled with long tables of merry drinkers and well, their drinks; the biergarten is integral to the German citizen and open-air lover.
We encounter fewer merry drinkers than we plan to, but still sit alongside friends talking and a couple laughing. I have a feeling we’ve arrived in the belly of Berlin, especially as more Berliners gather round, huddle up, and grab some warming alcohol during this chilly summer.
For travelers hoping to find a warm community with a common motivation–tasting the richness of German beer–a biergarten might fulfill your needs.
While my day quickly ended after my biergarten experience, no two 24 hours in Berlin can be alike, so here are some more options for day adventures to quench your traveling thirst.
Reichstag building. Jurgen Matern. CC BY-SA 3.0
Monuments
Reichstag: The Reichstag, the Parliament building of Germany, actively houses Parliament meetings throughout the year, and somewhat unusually, also allows visitors year round. Attending a tour of the Reichstag means sitting in the German Parliament’s main chamber, observing interior corridors with Russian graffiti completed after the Russian capture of the building in the Battle of Berlin and receiving an oral history from World War II on.
Memorial to the Murdered Jews of Europe: This Holocaust Memorial, designed by New York architect Peter Eisenman, consists of 2711 concrete blocks of varying heights laid out in a rectangular city block. Visitors might note that the blocks increase in height as they approach the middle of the monument; many speculate that this effect reflects the rising fear and agony of the Jewish community throughout World War II.
Brandenburg Gate: While this neoclassical gate was originally constructed in the 18th century, much of its history lies in the coming centuries. The Quadriga statue of horses perched on the top of the gate, for example, tells a history of Napoleon’s acquisition of Berlin. Napoleon transported the statue out of Berlin to reflect his victory over the Germans. The Brandenburg Gate also symbolizes the division between East and West Berlin during the Cold War, as the Wall was constructed within a couple meters of the gate.
World Clock at Alexanderplatz. Berthold Werner. CC BY-SA 3.0
Berlin TV Tower. A_Peach. CC BY 2.0
Public Squares
Alexanderplatz: This public square named after Russia’s Tsar Alexander I is a commercial and transportation center that houses malls, public art and even live events like concerts. Visit the world-famous World Clock that tells the time of countries around the world, watch a stark yellow tram pass by through crowded streets, or even spot the Berlin TV Tower from afar.
Potsdamer Platz: Potsdamer Platz, located about a mile from the Brandenburg Gate, contains much of the city’s culture. Find the Sony Center dome housing an international cinema, restaurants, offices, museums and the center of underground transportation here —all constructed after the destruction of the public square during World War II.
Museums
Ishtar Gate in the Pergamon Museum. Rictor Norton and David Allen. CC BY 2.0
Pergamon Museum: The Pergamon is one of the museums located on Berlin’s “Museum Island.” The building boasts its collection of classical antiquities from Middle Eastern civilizations and Islamic cultures. The most famous exhibits include the Market Gate of Miletus, the Ishtar Gate that opened up to the processional way to the eponymous capital of the Babylonian Empire and the Aleppo room featuring paneling with images of both the Islamic and Christian faith.
Topography of Terror: Such a historical city requires a history-based museum. The museum itself is located on a plot that once housed administrative buildings of the Nazi Party, like the headquarters of the SS and the Gestapo. The one-floor museum uses exhibition panels (supported by historical documents and quotes) to guide visitors through the rise and eventual fall of the Nazi Party.
Other
Brandenburg Gate. Dennis Jarvis. CC BY-SA 2.0
Historical Walking Tour: A city with such plentiful history necessitates a historical walking tour. Sightseeing walking tours take visitors through World War II and Cold War monuments like the Memorial to the Murdered Jews of Europe and the demarcation of the Berlin Wall, respectively, as well as some of Berlin’s must-see sights like the Brandenburg Gate and even the Reichstag.
Cuisine
A dish from Madami. George M. Groutas. CC BY 2.0
German cuisine: While much of German food pays its cultural respect to other international cuisines, some German dishes are uniquely synonymous with German culture. Sausages accompanied by sauerkraut or potato salad, rouladen, beef-wrapped bacon, onions, mustard, and pickles and sauerbraten — a German pot roast — all grace the menus of German restaurants. Try restaurants Schwarzwaldstuben in Mitte, Max and Moritz in Kreuzberg, and Clarchens Ballhaus also in Mitte for a taste of Germany.
Vietnamese cuisine: Due to the influx of Vietnamese immigrants —many of whom were temporary contract workers — into East Berlin during the Cold War, the city offers much authentic Vietnamese food. Some high-rated restaurants include Madami located on Rosa Luxemburg Street, Monsieur Vuong on Alte Schonhauser Street, and Maison Umami on Schlesische Street.
Turkish cuisine: Much like the Vietnamese, a Turkish community slowly immigrated to Germany for work and stayed to build institutions that reflect their culture, like the Turkish restaurant. Doner, lahmacun (the Turkish Pizza) and borek (a salty Turkish pastry) proliferate in Berlin. Some high-rated restaurants include Hasir in Kreuzberg, Adana Grillhaus on Manteuffel Street, and Osmans Tochter near Helmholtz Platz.
Nightlife
Clubs: The Berlin party scene is second-to-none. Berlin’s clubs are perfect for those craving a new eccentric song to add to their playlist or a place to wow their friends for a night. Room 4 Resistance’s playlists of tunes with genres ranging from contemporary pop to industrial techno attract a diverse group of music lovers. For those music lovers who prefer to stick to a genre or two, Weeeirdos’ techno sets and Hoe_Mies’s R&B and trap music might be a perfect fit.
Biergarten: Outdoor lovers might prefer the biergarten, or beer garden, night experience. Under a dusk sky, between clumsily strung up lights, lies a comforting community of German beer lovers gathering around wooden benches and tables and self-serving the ale. Try the Prater Beer Garden, Schleusenkrug, and Golgatha Beer Garden for some biergarten action.
Bars: Whether you desire a cocktail or a dance floor for the night, a Berlin bar or two will satisfy your appetite. When in the party capital of Europe, you must do as partiers do, and partiers love to gather on these alcohol-washed oases. Gay bar Model Olfe, aesthetic Victorian-inspired bar Geist im Glas and the traditional Bar 3 are all excellent alternatives for a night of drinking and dancing.
Su Ertekin-Taner
Su Ertekin-Taner is a first year student at Columbia University majoring in creative writing. Her love for the power of words and her connection to her Turkish roots spills into her satire, flash fiction, and journalistic pieces among other genres. Su hopes to continue writing fearless journalism, untold stories, and prose inspired by her surroundings.
Independence and Adventure in Nordic Parenting Culture
Nordic countries’ healthcare and parenting culture allows for an unusual amount of balance and independence — for both children and parents.
Winter stroller walks are the norm. William Fortunato. CC0.
When walking through the streets of Orestad — a developing neighborhood just seven minutes by metro from central Copenhagen, Denmark — it's not uncommon to see dozens of strollers being pushed by young parents clad in thick jackets and scarves. In fact, it seems that this relatively new and modern neighborhood is populated primarily by young parents with babies and toddlers.
Meanwhile, in Oslo, Norway, streets outside of coffee shops and grocery stores are also crowded by parked strollers. Despite the same cold temperatures, the parents are nowhere to be seen. Bundled tightly, the children are left alone to enjoy the cold weather.
Although these two Scandinavian countries take slightly different approaches to monitoring young children, there is much overlap in the parenting cultures of many Scandinavian (and, more broadly, Nordic) countries. In general, many of the parenting techniques new mothers and fathers practice are rooted in a desire to teach their children independence, empathy, respect, and responsibility all while keeping them safe and healthy — even though some tips and tricks may seem shocking to outsiders.
Orestad in Copenhagen, Denmark. Jonas Smith. CC by 2.0.
Perhaps the time and care it takes to foster this unique parenting culture stems from the unusual, yet tremendously beneficial, length of parental (both maternal and paternal) leave in many Nordic countries. In Norway, for example, parents of all genders have the option to take fifteen weeks of paid leave and are paid 100% of their pay, or can take nineteen weeks at 80%. The only difference is that mothers must take the first six weeks after their child’s birth off while their partner begins their quota from week seven after birth. Similarly, in Sweden parents together are entitled to 480 days or paid parental leave (240 per parent). Days off not taken by one parent can be transferred to another if needed.
The result of these lengthy leaves has not only fostered a deeper sense of shared responsibility by both parents, but also a greater amount of care and attention focused on personalized early childhood development. The level of shared cultural focus on and respect towards young children is just one of the many factors that contribute to the level of safety and health among infants and toddlers in Nordic countries.
Because of their time at home, a huge staple of Nordic parenting culture is “play” time. Whether children bond with parents at home, or are encouraged to go outside the home and make friends independently, children in Nordic countries are encouraged to explore, play and discover their adventurous side from a young age. There is even a word for this: “friluftsliv.” The word can be roughly translated to “open-air living” and serves as a mantra for parents (and non-parents, too!)
“Friluftsliv” has been a norm for decades. Anders Beer Wilse. CC0.
While play in any capacity is important, play outside is considered especially beneficial to young children. Rather than being scolded for being too rambunctious or messy, children in Nordic countries are encouraged to run and climb to their hearts’ content. Even in the cold weather that pervades Nordic countries for more than half of the year, children bundle up and get outside in the fresh air.
Rain or shine, it is completely normal to see little ones either running around outside or sleeping! Although there is a deep emphasis on energetic outdoor activities, one of the most prevalent cultural and parenting norms is to leave children outside to sleep. Even in freezing cold temperatures, children are put down to nap outside. Of course, they are accompanied by warm blankets and outerwear. Few in Scandinavia fear the cold, where doctors in Nordic countries recommend outside napping to decrease the risk of illness and infection.
And, when children aren’t enjoying playtime with parents, bundled-up naps, or outdoor adventure, they have the opportunity to start day care as mere one-year olds. In Denmark, childcare charges are capped at 30% of the actual cost for nurseries and after school centers. In Norway, child centers are open 10 hours per day and charge a maximum fee of US $250 a month.
While having a child is a tremendous responsibility, both the healthcare benefits and parenting culture in Nordic countries allows a balance that eases some stress among new parents. Though unique, many aspects of Nordic parenting culture harness an unprecedented sense of adventure and independence in early childhood.
Carina Cole
Carina Cole is a Media Studies student with a Correlate in Creative Writing at Vassar College. She is an avid journalist and occasional flash fiction writer. Her passion for writing overlaps with environmentalism, feminism, social justice, and a desire to travel beyond the United States. When she’s not writing, you can find her meticulously curating playlists or picking up a paintbrush.
A 4-day Guide to Exploring Rome
Rome is a city full of must-see sites, but it can be overwhelming to plan for. Here is a 4-day itinerary to make sure you see all the top spots, while getting the atmosphere of a unique European summer.
Rome, Italy. @Bert Kaufmann. CC BY-SA 2.0
“A European Summer” is now the aesthetic of the season, spurred on by Gen Z and Millennial creators on TikTok. It’s a fashion statement, and young American women are obsessed with flowing white dresses, gold jewelry, maxi skirts, and more. The romanticization of European cities is a perfect escape from the monotonous urban environment Stateside.
Over the past month I was lucky enough to travel to Rome, Italy and experience a taste of the European summer that influencers have been talking about nonstop. But a trip to the Eternal City takes a lot of planning and, while it was only my first time exploring the history-rich city, I feel as though I know enough to compose an ideal 4-day itinerary — so travelers can experience every aspect of the European summer.
Day 1
As your feet touch the streets of Rome, it’s important to keep two things in mind: firstly, your primary means of transportation will be by walking, especially if your hotel accommodations are in the heart of the city itself, something I definitely recommend. So, pack footwear accordingly. Second, temperatures will be soaring. Expect around 100 degrees Fahrenheit, particularly in mid-summer.
Trevi Fountain. @NikonZ711. CC BY-SA 4.0
I recommend getting familiar with the main tourist sites on the first day. These include the Spanish Steps and Trevi Fountain, which are located relatively close to one another. Both are beautiful in the daylight and won’t eat up too much of your time. Throughout the streets it’s common to find small stores that sell gelato or souvenirs — pop into one and notice that prices are surprisingly cheap, especially compared to costs in the US.
One of the things I enjoyed about my time in Rome was the vibrant nightlife, so make sure to take advantage of all the city has to offer when the sun sets. The temperatures are much more bearable and the streets are filled with small, lively alleyways that offer restaurants and more stores. Live music is usually always playing, especially in places where tourists are likely to flock. If you’re looking for an opportunity to wear that white flowy dress you bought just for the sake of fitting the Italian summer aesthetic, now’s the time.
Enjoy the unique scenery and environment, and make sure to visit the Spanish Steps once more — while a great place to visit in the daytime, this tourist site comes to life at night and brings that perfect feeling of that “European Summer” the TikToks show so often.
Day 2
Hopefully you got a full night’s rest, because day two is the perfect day to visit Vatican City — a landlocked independent country within the borders of Rome itself. It’s important to dedicate an entire day to this because, while you’ll most likely only spend a few hours exploring, the exhaustion will set in quickly.
If interested in the Vatican Museums, I strongly recommend buying tickets weeks beforehand and selecting an earlier time. The tourists that were hoping to get tickets on the day of had to wait in line for hours on end in the burning heat. Make sure to arrive early, since the museum is a little further than expected from the main entrance to Vatican City.
Vatican City. @Diliff. CC BY-SA 3.0
Once in the museum, you can either follow your tour guide or explore at your own pace, depending on the ticket you bought. You’ll get a glimpse of St. Peter’s Basilica — a famous church built in Renaissance style — from a viewing platform and get to visit the Sistine Chapel, a Catholic church located inside the Vatican Museums home to some of Michelangelo’s finest work.
Because Vatican City is a Theocratic city-state, most websites will advise you to wear a certain type of outfit. But because it’s so hot in the summer months, it’s alright to push the rules a little. Showing up in shorts and a T-shirt is completely acceptable.
Take the rest of the day to recharge. Walking to, from and around Vatican City can get very tiring, especially if it’s hot out. Stay close to your hotel for dinner, and day two will shoot past in the blink of an eye.
Day 3
Depending on whether or not you’re fascinated by Roman culture, Day 3 is dedicated to the rest of the places you weren’t able to see. For me, this included the Pantheon and Piazza Navona, which are both very close to one another. Shopping in Rome was also a pleasant experience, with such cheap prices, so I recommend it if you’re able to fit it in.
Pantheon. @laszlo-photo. CC BY 2.0
For dinner, venture on over to Trastevere — a neighborhood filled with authentic Italian restaurants, located just across the Tiber River. The pasta and pizza is, of course, something every visitor should try. Paired with a drink of your choice, it’s hard to question why Rome is a city that attracts so many people from all over the world. The constant chatter of customers, the lights hung up as decoration, and the comfortable temperature combine to make a perfect getaway.
Day 4
Your last day in Rome should be dedicated to doing whatever you want. After three full days of so much walking, your body is bound to be tired, so just take this day as a time to relax and soak this experience in.
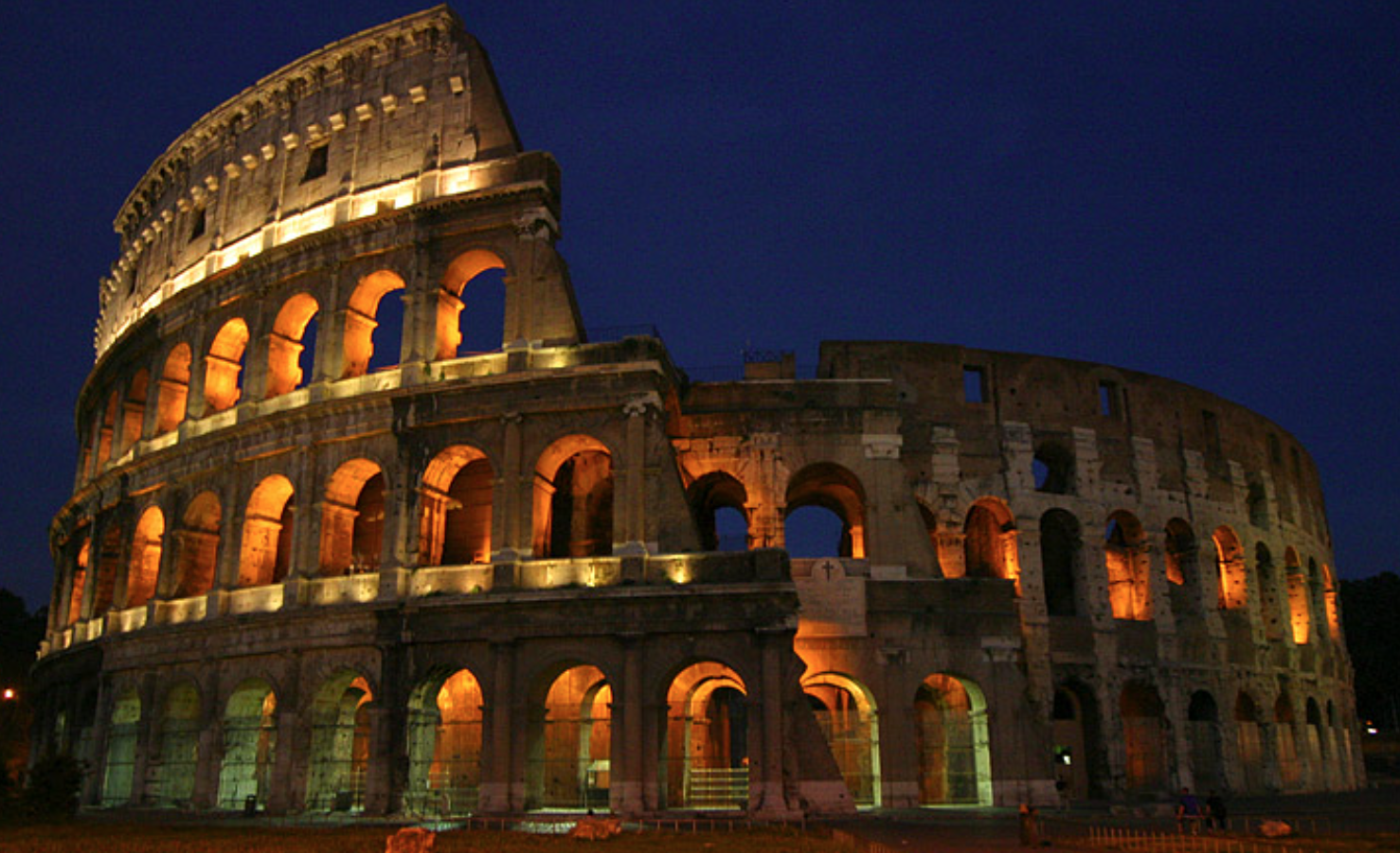
I know I haven’t mentioned the Colosseum — and it isn’t because it’s been forgotten. During my trip, I visited the Colosseum at night on my last full day in Rome, and it was the right decision. Of course, depending on the kind of traveler you are, this might not be your ideal itinerary but I loved seeing one of the most iconic landmarks in the world at night. I didn’t have to worry about the heat, and there is something so special about seeing the Colosseum lit up with hundreds of lights as it towers above you. It’s a great image to part Rome with, and along the road you’ll most likely pass the Roman Forum, which is impossible to miss.
A night view of the Colosseum. @Aaron Logan. CC BY 1.0
Personally, this 4-day itinerary helped me get the feel of every aspect of the “European Summer” — from its nightlife to its famous sites, it didn’t disappoint. Depending on the type of person you are, this itinerary is bound to change but as someone who loves spontaneity and surprises, I followed this rough guide and was able to soak in all the wonders of this eternally beloved city.
Michelle Tian
Michelle is a senior at Boston University, majoring in journalism and minoring in philosophy. Her parents are first-generation immigrants from China, so her love for different cultures and traveling came naturally at a young age. After graduation, she hopes to continue sharing important messages through her work.
Pathways and Pilgrimages: Exploring The Camino de Santiago
This pilgrimage to the Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela in Spain has been a centerpiece of Christian spiritual life for thousands of years, and a destination for travelers around the world.
The Santiago de Compostela. Dafydd Parri. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
The Camino de Santiago, also known as the Way of St. James, marks a pilgrimage to the Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela in Galicia, an autonomous community in northwestern Spain. Extending roughly 500 miles and taking about 30 to 35 days to complete at an average of around 15 miles per day, the Camino is known today both as a center for Christian spiritual life and a hiking haven for travelers looking to submerge themselves in nature with affordable accommodations and opportunities to adventure through local villages along the way.
Today, around 300,000 travelers make their way through the Camino every year, and those who complete the journey earn a Compostela Pilgrims Certificate. According to measurements from 2021, 45% of travelers reported walking the Camino for “religious and other reasons” while 30% reported walking the Camino strictly for religious reasons and 24% said they had no religious reasons for the pilgrimage. The growing popularity of the Camino as a secular travel experience as well as a religious one is aided by its accessibility. While daily expenditures on the Camino depend largely on the town one is stopping in, travelers can plan to budget for about $30 a day to cover the cost of food. Albergues, or hostels specifically made for pilgrims, are also a reliable and affordable option for accommodations along the Camino, with municipal albergues typically costing between $5 to $10 per person, while private albergues range between $12 and $15 per person. Via Lusitana helps connect travelers to albergues along the Camino Portugues.
While there is no exact starting point to the Camino, there are a handful of popular routes to choose from including Camino del Norte, Camino Primitivo, and Camino Ingles. The two most popular routes are that of the Camino Frances, which begins in Saint-Jean-Pied-de-Port in southwest France, and the Camino Portuguese which starts from Portugal’s coastal city of Porto. While the Camino Frances covers 500 miles, the Camino Portuguese offers two distinct routes: the Camino Portuguese Central route which is 385 miles and the Camino Portuguese Coastal route which is 175 miles.
The Camino became a UNESCO World Heritage site in 1993 and was recognized as the first European Cultural Route in 1987, however its history is one that dates back to the 9th century, when remains of the apostle James were believed to be found in Galicia. Saint James preached in the Iberian peninsula before returning to Jerusalem, where he was beheaded by the king Herod Agrippa I in 44 AD. The legend surrounding St. James details how his body was transported from Jerusalem to Spain via a boat and was buried by his followers in Galicia in what is now the city of Santiago de Compostela.
The tomb was discovered in the 9th century by the bishop Theodomir. Upon its discovery the King of Asturia, Alfonso II, widely considered the first pilgrim to the Santiago de Compostela, traveled to the site and ordered that a church be built at the place of burial. Construction began in 1075 and the church was consecrated in 1211.
To accommodate an increase of pilgrimages through the Camino in the Middle Ages, bridges and other infrastructure were built along the route to aid travelers. Between the 11th and 13th century, the Camino’s rising popularity gave rise to a network of housing options and medical services along the route, including hospitals chartered by European kings.
The Camino’s many routes were created by early travelers who shared information amongst themselves regarding the safest travel conditions, which nearby towns to stop in, and where to source food and water throughout the journey. Though lacking official infrastructure, these paths became well defined by the pilgrims who traveled them for hundreds of years. It was not until the 1980s that Father Elías Valiña Sampedro, a priest of a neighboring Galician village, added yellow arrows along the path in an attempt to prevent travelers from getting lost.
Camino Frances
El Alto del Perdón. Rocco Rossi. CC BY 2.0.
As the most popular route, the Camino Frances sees around 55% of all travelers on the Camino de Santiago. Embarking on the French Way is one of the most social options to experience the Camino, and those who do so are sure to run into fellow pilgrims and have opportunities to build connections and a sense of camaraderie along the way.
The entire Camino Frances starts at St Jean Pied de Port, a commune in southwest France, and extends roughly 500 miles and takes about 30 to 34 days to complete with an average of about 15 miles per day. However, the most popular starting point for travelers along the Camino is found at the last 60 miles of the pilgrimage, in the city of Sarria. This last stretch of the Camino takes approximately 7 days and passes through the towns of Portomarin, Melide and Arzua.
Travelers embarking on the Camino Frances will move through the Pyrenees mountain range and into the La Rioja region of Northern Spain. Travelers interested in enjoying the region’s world famous vineyards can explore a variety of wine tours showcasing the region’s diverse earthly flavors.
Other notable traveling stops along the Camino Frances include the Spanish city of Pamplona, whose yearly San Fermín Festival every July features the country’s world-famous bull runs. When the festival is not happening, the Pamplona remains a popular resting spot for travelers along the Camino to explore Gothic and Renaissance art at the Museum of Navarra and the historic Plaza del Castillo where cafes and bars such as Cafe Iruna served as prominent landmarks in American novelist Ernest Hemmingway’s life and writing.
Another highlight along the Camino Frances is the sculpture of El Alto del Perdon, which shows metal silhouettes representing pilgrims traveling through the Camino on foot and horseback. The art piece is located near the town of Puente de la Reina, a historical meeting point for early pilgrims traveling the Camino through a variety of routes along the Pyrenees. The town’s current architecture derives from attempts to accommodate pilgrims during the Middle Ages, including the bridge constructed under Queen Muniadona to assist pilgrims in their travels. The bridge is responsible for the town’s namesake, with Puente de la Reina translating to “the queen’s bridge.”
Camino Portugues
Travelers on El Camino. Staffan Andersson. CC0 1.0.
An alternative to the Camino Frances, the Camino Portugues begins in Portugal and moves the coastline up to Galicia as the second most popular path for the Camino de Santiago pilgrimage. The route gained popularity in the 12th century after Portugal gained its independence when Queen Isabel of Portugal, known as the “Holy Queen,” made the pilgrimage herself in the 14th century. Today, the Camino Portugues sees about 25% of all travelers embarking on the pilgrimage.
There are three main routes that travelers embarking on the Camino Portugues can choose from: the Central Route, which takes around 12 days, the Coastal Route, which takes between 12-14 days, and the Litoral Route, which follows the Coastal Route in large part while also incorporating pathways onto the beach. All routes meet in the Spanish town of Redondela before reaching Santiago de Compostela.
Each route carries its own advantages and disadvantages. The Central Route has more infrastructure and access to towns and accommodations, however it is also the busiest route, seeing 70% of all travelers on the Camino Portugues. Comparatively, only about 30% of travelers opt for the Coastal Route, making it a quieter experience with less built-in tourism.
Those starting the Camino Portugues from Porto will get to enjoy the city’s famous local port wine, the Baroque style Porto Cathedral — or Se do Porto — and the boat tours of the stunning Douro River.
Vigo is a popular starting point for those who want to experience the last 60 miles of the Camino, and the city offers a variety of activities including fish markets and a coastline overlooking the Cies Islands.
Services such as Pilgrim help travelers create a personal guide for their trip, curated towards each individual’s preferred route and transportation type — including walking, cycling and completing the Camino on horseback or with pets. Pilgrim also helps connect travelers to special services while on the road, including the options to order bike gear, rent a car and transport personal luggage.
Online guides are another helpful tool for travelers when it comes to finding rest stops and maps of nearby towns to explore along the Camino
Jessica Blatt
Jessica Blatt graduated from Barnard College with a degree in English. Along with journalism, she is passionate about creative writing and storytelling that inspires readers to engage with the world around them. She hopes to share her love for travel and learning about new cultures through her work.
Hagia Sophia: Istanbul’s Oldest Building
Having served as a church, mosque and museum, Hagia Sophia represents both religion and history in Istanbul.
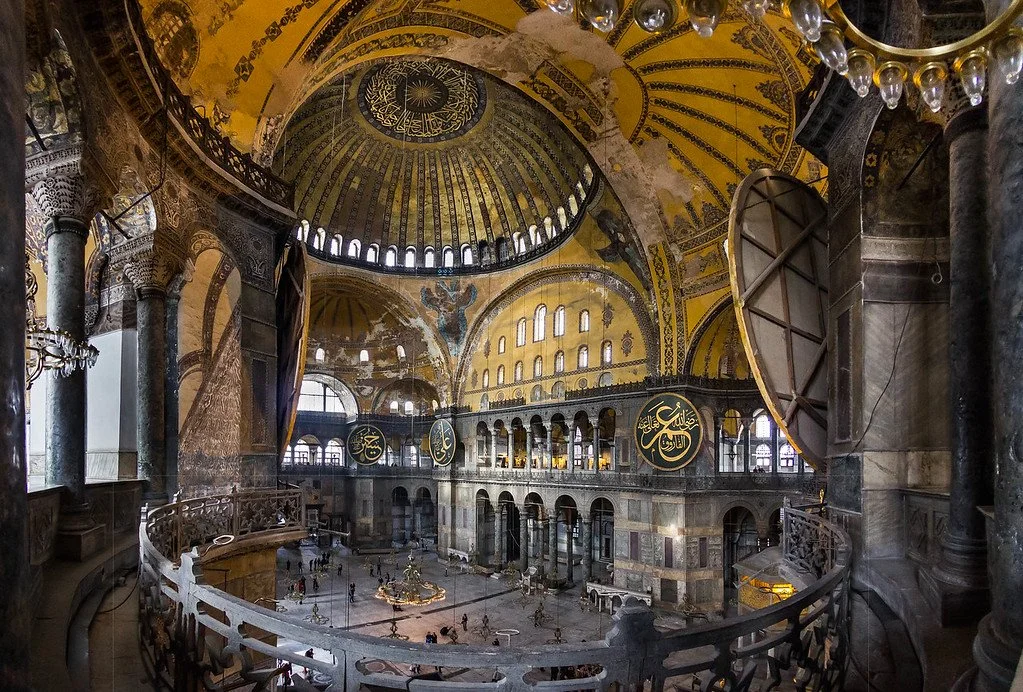
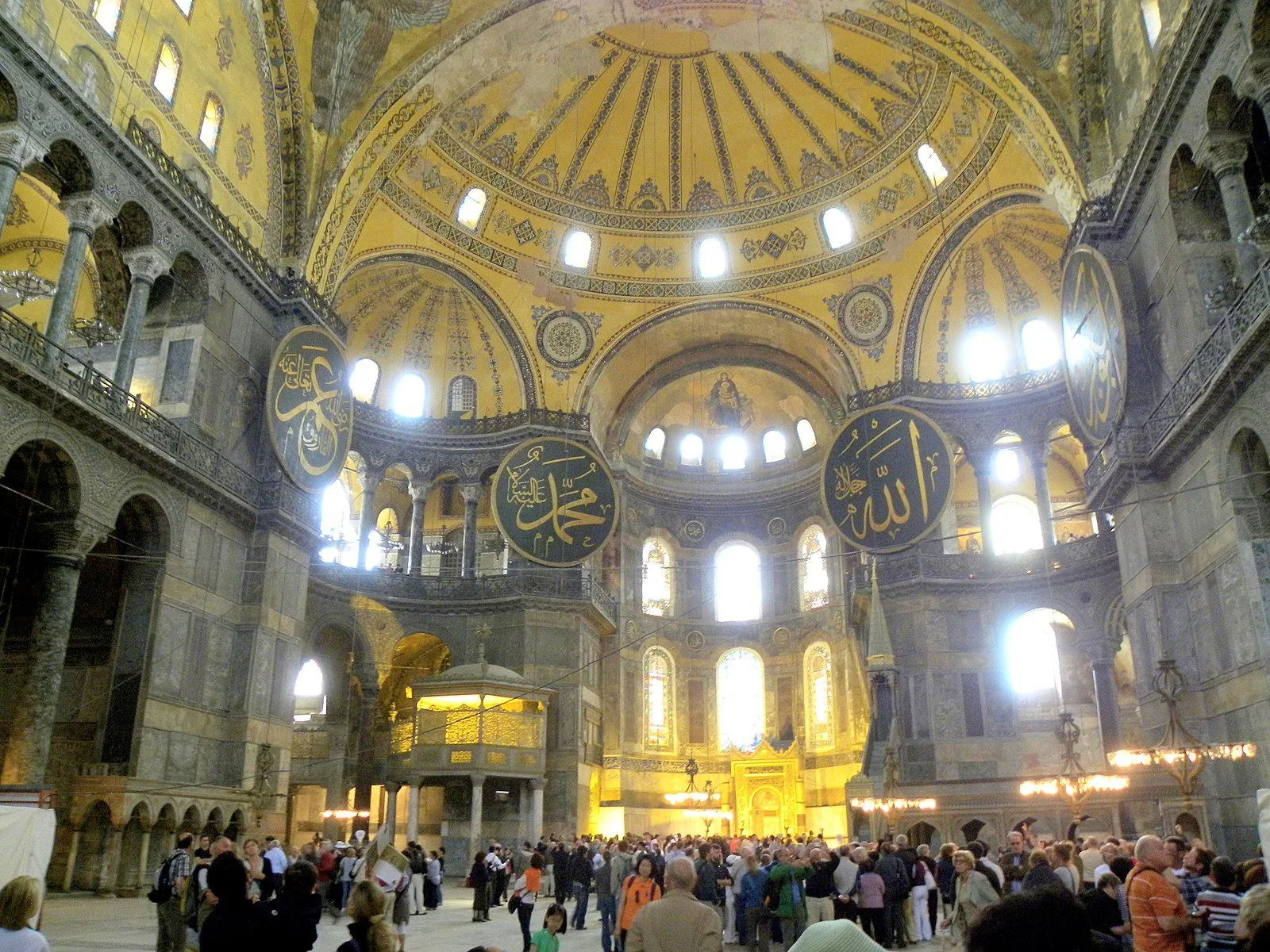
Hagia Sophia. Adli WahidCC BY-SA 3.0.
Built in the 6th Century, Hagia Sophia is the oldest building in Istanbul, Turkey. This ancient structure has been an important spiritual center for both Christians and Muslims, and its history is shown through its architectural features. Here is a deep-dive into the creation of Hagia Sophia, its meaning to different cultures, and how to visit it today.
History
Interior of Hagia Sophia. Wolfgang Guelcker. CC BY 3.0.
Originally named “Megale Ekklesia,” or “Great Church,” Hagia Sophia was built in 360 under Emperor Constantius. After the church was destroyed by riots in 404, it was rebuilt by Emperor Theodosius in 415. During this period, the church received its current name, “Hagia Sophia,” or “Holy Wisdom.” After being burned down during a revolt in 532, the final structure of Hagia Sophia was resurrected under Emperor Justinian I in 537, with some restorations in the 14th century. This version of the church was known as the Cathedral of the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople, which was a spiritual center of the Eastern Orthodox Church. After the Ottoman Empire took over Constintinople in 1453, Sultan Mehmet II repurposed Hagia Sophia, which served as a mosque until becoming a museum in 1935. In 1985, Hagia Sophia became a UNESCO World Heritage site, giving official recognition its long cherished cultural value.
Controversy
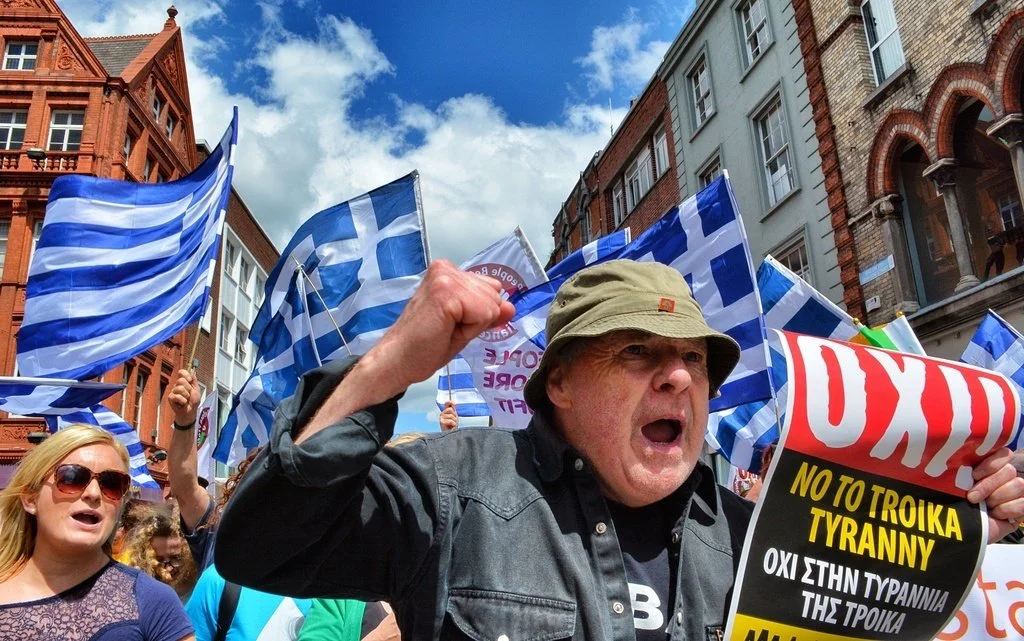
Greek protest against Turkey. Des Byrne. CC BY 2.0.
In 2020, Hagia Sophia was renamed a mosque under the Turkish government. This decision created controversy between Turkey and other nations, as repurposing it as a mosque draws away from the entirety of the structure’s history and the mutual respect between religions. This also strengthened existing tensions between Turkey and Greece, as Hagia Sophia was once part of the Greek Orthodox Church.
Architecture
Dome
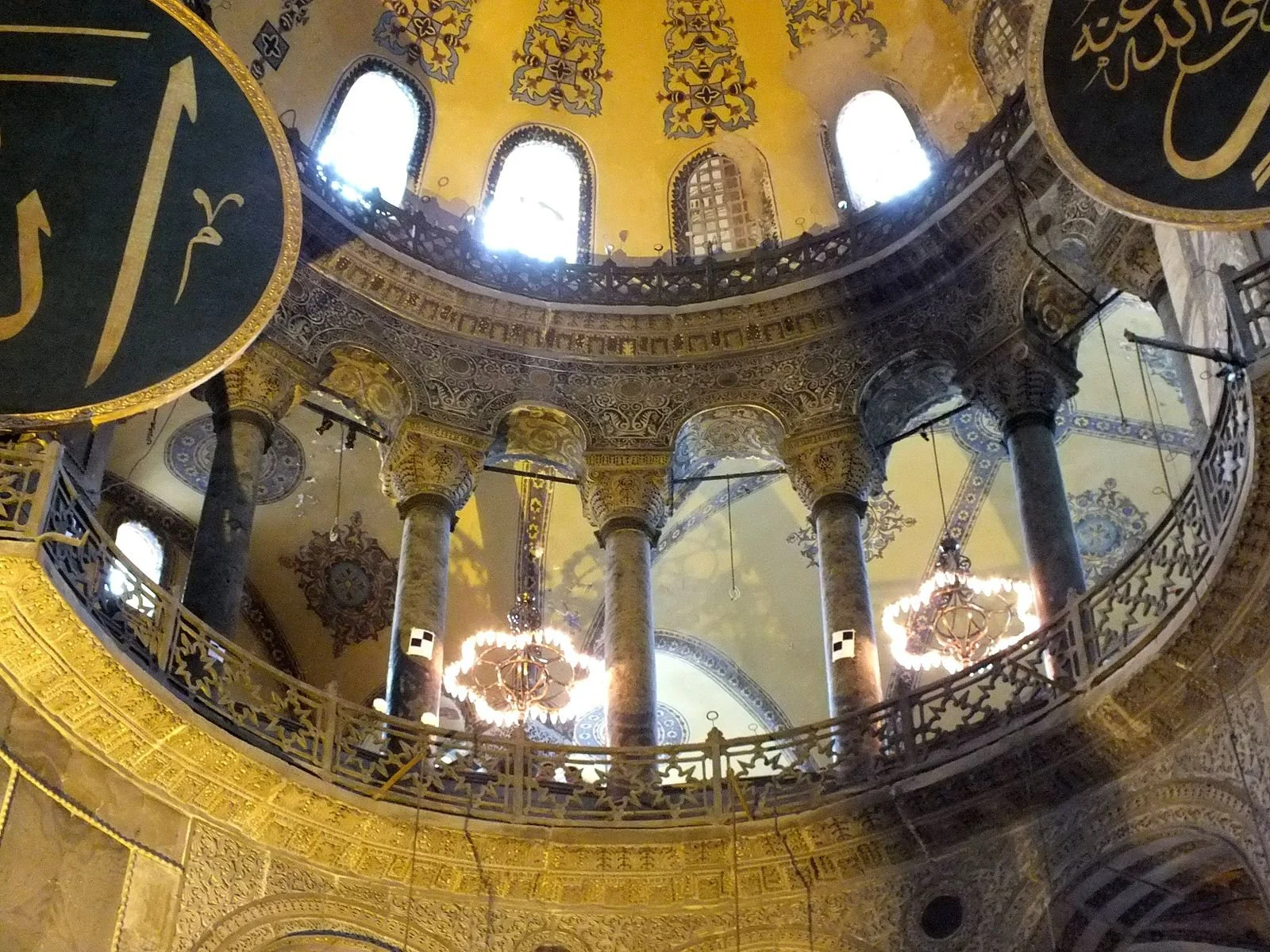
Main dome of Hagia Sophia. Osama Shukir Muhammed Amin. CC BY-SA 4.0.
Following St. Peter’s Basilica in Rome, Hagia Sophia is home to the second largest pendentive dome in the world. The main dome of the structure has a diameter of 107 feet and is supported by 4 pendentives, which are large triangular arches that meet in the middle of a structure. These structures are one of the earliestlarge pendentives to ever be made. There are also two semi-domes on each side of the main one, supported by columns.
Columns
Columns in Hagia Sophia. Serafita. CC BY-SA 4.0.
Hagia Sophia has 140 columns, all from different parts of the world. For example, the purple columns supporting the semi-domes of the structure originated in Egypt. There are also green columns from the Artemis Temple in Ephesus, an ancient Greek city. The most prominent columns are made of Verde Antique stone, which was mined from quarries in the city of Larissa, Greece during the Byzantine empire. These columns are 34 feet tall, and its material was used frequently during the 6th century.
Mosaics
Mosaic of the Virgin Mary and Jesus. World History Encyclopaedia. CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.
Originally, Hagia Sophia displayed many Christian mosaics, but these images were covered during the Ottoman Empire. Some of these mosaics depict angels and praise Jesus and the Virgin Mary, while others take the form of emperors such as Justinian and Constantine. One of the most iconic mosaics shows the Virgin Mary holding baby Jesus, and this image remains uncovered today. Created in the 860s, this is the oldest mosaic in Hagia Sophia.
How to Visit
People visiting Hagia Sophia. Magnus Manske. CC BY 2.0.
Though it has reverted to a mosque, Hagia Sophia is still open to the public. Visitors are required to remove their shoes before walking its carpets. Hagia Sophia is open to the public every day of the week, but closes to non-worshipping visitors during prayer hours. Guided tours of Hagia Sophia are also offered through different websites, usually for a fee.
Click here for more Hagia Sophia visitation guidelines.
Alexandra Copeland
Alexandra is a student at The College of New Jersey studying psychology and journalism. She is a lover of coffee, dancing, and visiting new places. Being raised with her Greek culture has inspired her interest in cultural customs around the world. She is a passionate writer and hopes that her work will make an impact in the future.
Going at it Alone: The Highs and Lows of Solo Travel
Though riddled with its own challenges, solo travel provides unparalleled opportunity to build confidence and create friendships on the road.
Read More7 Books by LatinX Authors to Read This Hispanic Heritage Month
From literary classics to modern favorites, here is a list of must-read titles by LatinX authors in celebration of Hispanic Heritage Month.
A traditional dancer performs at a Hispanic Heritage Month festival. GPA Photo Archive. CC0
With an incredibly rich history and huge variety of cultures, it is no surprise that Latin America has consistently produced world famous and award winning authors for decades. From historical fiction about the continent’s troubled colonial past to light-hearted stories about colorful local traditions, the diversity of Latin American literature spans time and space to offer incredible insights into life for bookworms and the average fiction reader alike. In celebration of September as LatinX Heritage Month, here are seven incredible books by LatinX authors to add to your reading list.
“Violeta” - Isabel Allende
Multi-award winner Isabel Allende’s most recent novel follows the titular character from her birth to her death over a tumultuous century. Violeta is born during the Spanish Flu in 1920 and lives through the Great Depression, World War II and all the changes brought by the turn of the twenty-first century, while navigating family, romance and her own desires. Allende, arguably the first internationally successful female Chilean author, is known for writing in the “magic realism” style, weaving history with fiction and myth with reality to create engaging plotlines that find their roots in Hispanic culture, society, and politics. This novel is no different, and Violeta’s story, written in the form of a letter to the one person she loves the most, recounts 100 years of Chilean history through the eyes of a determined, humorous woman who, above all else, carries a deep love life.
“Solito” - Javier Zamora
A poet by trade, Salvadoran writer and activist Javier Zamora has collected his fair share of accolades, and is currently a Radcliffe Fellow at Harvard University. The New York Times bestseller “Solito” is his latest project having been published in 2022 and tells the heart wrenching story of Zamora’s perilous journey from El Salvador to the United States at only nine years of age. Leaving his extended family and childhood home behind, Javier travels almost entirely alone to reunite with his parents who had fled the country years earlier. He has no way of knowing about the seemingly insurmountable obstacles that will stand in his way, or the group of kind-hearted strangers who will come to treat him like one of their own. This biographical memoir is unlike either of Zamora’s earlier published works, and provides an incredible and intimate account of a story shared by millions of Central American migrants who have no choice but to flee their homes due to violence and political unrest.
“A Little Luck” - Claudia Piñero
After the success of her earlier novel “Elena Knows,” Argentine novelist and finalist for the 2022 International Booker Prize Claudia Piñero has astounded her readers once again with this 2015 novel which has only recently been translated to English. Piñero has an incredible talent for exploring the depths of unbelievably tragedy and pain while offering her audiences brief moments of hope, and “A Little Luck” is no different. The novel follows Mary Lohan, a woman who fled the suburbs of Buenos Aires after an accident but has finally returned two decades later. While on the outside she in no way resembles her past self, she is very much still the same Mary, and as the past starts to resurface her present begins to crumble. “A Little Luck” is a beautifully crafted story about love, lies, unforgettable places, uninvited people, and most of all, the inescapable power of fate.
“The Brief Wondrous Life of Oscar Wao” - Junot Díaz
Originally published in 2007, this novel won the Pulitzer Prize for Fiction in 2008, along with a host of other awards. Dominican-American author Junot Díaz penned this novel, during his time at MIT, where he continues to teach in the Creative Writing department. Díaz wrote several works while attending the prestigious university, but “The Brief Wondrous Life of Oscar Wao” remains his most well-known and celebrated title to this day. The novel follows the titular character, a lovable and overweight Dominican teenager living in New Jersey with his mother and sister. He wants nothing more than to become a world famous author, except for maybe finding true love, a dream that feels far out of reach given the curse that has afflicted his family for generations and has resulted in only ill-fated romances. With an incredibly skilled hand, Díaz guides his readers through the life of Oscar and his family, both past and present, while also touching on the brutal reign of Dominican dictator Rafael Trujillo.
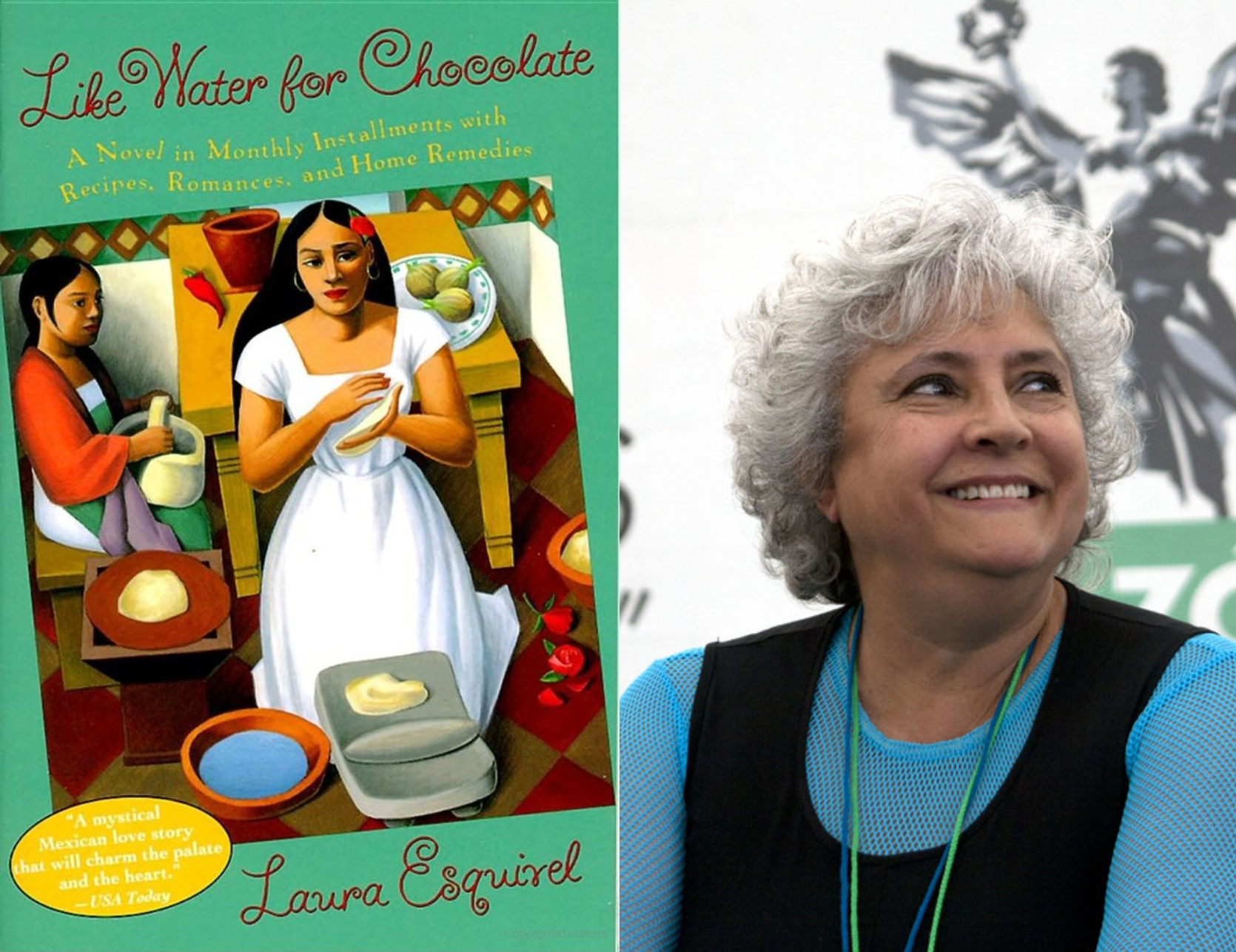
“Like Water for Chocolate” - Laura Esquivel
This 1989 novel was translated into English in 1992, and immediately became a modern classic in the pantheon of Latin American literature. The title comes from a common idiom in Spanish-speaking countries, “como agua para chocolate,” which refers to an intense state of emotion, whether it be anger, excitement or even arousal. Mexican author and screenwriter Laura Esquivel chose this for the title of her first novel because of the many references to food and culinary culture throughout the story, which add to her detailed description of family life at the turn of the century in Mexico. The novel makes use of humor and magic to explore a bittersweet love story both relatable and fantastical, as well as its impact on the families at the center of the drama. Each chapter begins with a recipe filled with cleverly chosen words and descriptions which allude to upcoming character and plot developments, an aspect that was unfortunately largely lost when Esquivel wrote the screenplay for the 1992 movie adaptation.
“In the Time of the Butterflies” - Julia Alvarez
Julia Alvarez is a Dominican-American essayist, poet, and novelist who is known for her ability to weave fact with fiction and craft irresistible plotlines that detail political and social events through the eyes of colorful and relatable characters. “In the Time of the Butterflies” is a perfect example of this, as a work of historical fiction with its foundations in the very real story of the Mirabal sisters, four young women who tirelessly fought for their country’s freedom under the dictatorship of Rafael Trujillo in the Dominican Republic during the 1900s. Known by Dominicans as “las mariposas” or “the butterflies,” the sisters were unfortunately assassinated in 1960 for their efforts to overthrow the government. Alvarez gives these characters a new life by imagining their time as teenagers, and how they came to be involved with revolutionary efforts before falling victim to the destructive regime. Through the voice of each sister, the story of their political involvement, victimization and deep love for each other slowly but surely come to light.
“100 Years of Solitude” - Gabriel García Márquez
No list of Latin American literature is complete with this 1982 Nobel Prize-winning classic, and what many consider to be Gabriel García Márquez’s best work. The late Colombian novelist published this novel in 1967, chronicling seven generations of the Buendía family and the rural town of Macondo they built in Colombia between the 1820s and the 1920s. While separated from the rest of Colombian society by an imposing mountain range, Macondo is a microcosm of larger society with its troubles and its magic, although the key to all of the town’s secrets remain hidden in a coded book. Through its delicate blend of magic, reality, history, and tradition, Márquez presents an allegorical insight into the turbulent social and political atmosphere in Colombia during the post-colonial times, and the country’s development over the following century.
Tanaya Vohra
Tanaya is an undergraduate student pursuing a major in Public Health at the University of Chicago. She's lived in Asia, Europe and North America and wants to share her love of travel and exploring new cultures through her writing.
Island Hopping Off The Grid: 5 Filipino Islands You’ve Never Heard Of
From unspoilt beaches and heritage sites to surfing hotspots and sunset views, there is plenty to choose from in the Philippines without running into massive crowds.
Read MoreColombia Unveiled: My Journey from Mountainous Bogota to Caribbean Cartagena
From palm forests to quaint towns to the scenic Caribbean, Colombia defies stereotypes and should be a must-visit destination on your South American travels.
Read MoreOff The Beaten Path in Shanghai
From cultural collections to ancient architecture, here are 6 of Shanghai’s esoteric sites.
Read MoreVisual Protest: The History and Legacy of the Berlin Wall Art
The Berlin Wall spent decades as a symbol for ideological division, but has become an outlet for personal expression.
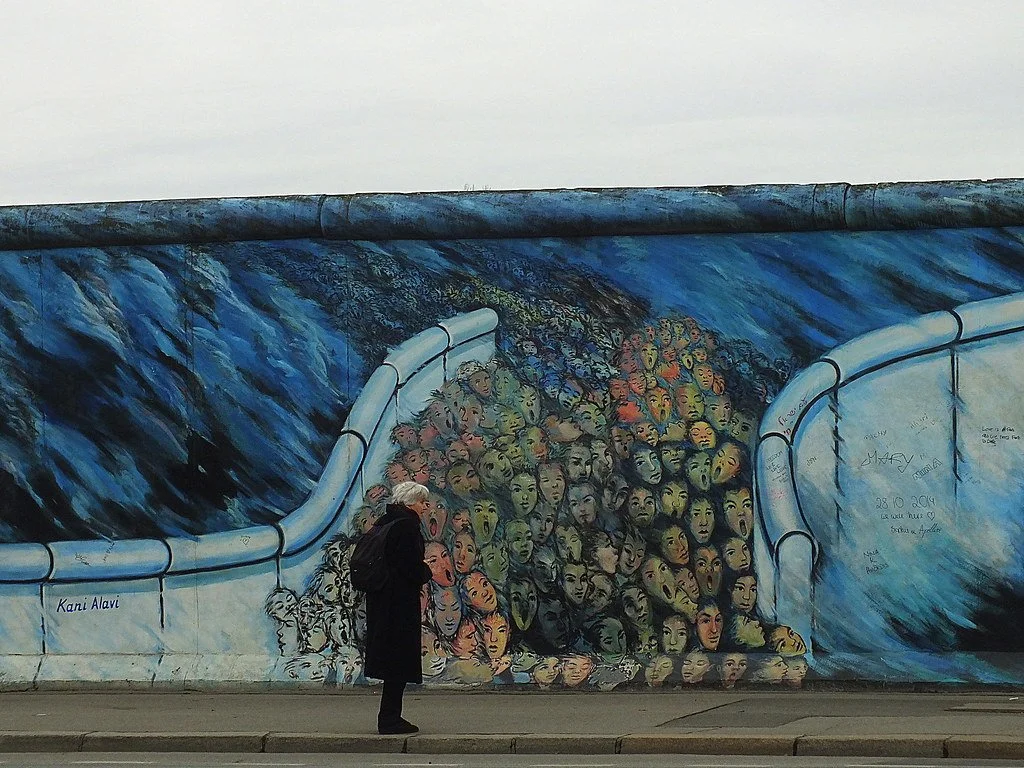
Thierry Noir’s heads at the East Side Gallery. Paul VanDerWerf. CC by 2.0.
Visually, the East Side Gallery in Berlin, Germany is a vast edifice of technicolor concrete. Although only fragments of the original 96 mile (155 kilometer) wall remain, the sections that still stand are striking. From the flashes of aquamarine and mustard yellow featured in Thierry Noir’s iconic cartoon heads to the dark spray paint outlining miscellaneous graffiti, the murals are simultaneously imposing and welcoming. But the gallery's importance runs deeper than its appearance; decades of history and political turbulence echo through its fallen walls.
When fully intact from 1961 until 1989, the Berlin Wall separated East Berlin from West Berlin; both halves were located well within East German territory, making West Berlin a NATO exclave in the Eastern Bloc. Prior to the wall's construction, emigration to West Germany by skilled workers, professionals, and intellectuals threatened East Germany’s economy. A few years after World War II, East Germany was constituted as a communist state controlled by the Soviet Union, while West Germany was formed out of the French, British and American occupation zones. The wall became a physical symbol of the Cold War: a division not only of Europe geographically, but also the global ideological divide between communism and democracy.
In the midst of longstanding Soviet de facto control of East Berlin, in 1985 then-Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev introduced the reform policies of glasnost (“openness”) and perestroika (“restructuring”), referring primarily to freedom of expression and economic reform, respectively. This decision, coupled with the growing number of protests sweeping across multiple Soviet republics, created a breaking point that eventually erupted into mass action. On November 9th, 1989, East German spokesman Günter Schabowski announced that East Germans would be free to travel into West Germany, starting immediately. In reality, travel was supposed to commence the following day, with regulations to prevent complete freedom of movement. But it was too late for regulations, and the crowds of people from East Germany immediately began to climb and even physically break down the wall.
The fall of the Berlin Wall, 1989. Gavin Stewart. CC by 2.0.
Because of the long period of repression associated with the barrier, one might assume that civilians who had lived on either side would want nothing to do with it ever again. But in 1990, just months after the Wall fell, some of the most famous murals of the Berlin Wall were painted (some of the preserved graffiti, including Thierry Noir’s brightly-colored heads, was created even before the Wall fell). With a newfound sense of freedom, people found their voice through art and created pointed political, social and cultural commentary.
Arguably the most famous of these works is Dmitri Vrubel’s “My God, Help Me to Survive this Deadly Love.” Commonly referred to as “Fraternal Kiss,” Vrubel’s piece depicts East German leader Erich Honecker and Soviet leader Leonid Brezhnev kissing. The kiss between the two socialist leaders was a rare, but not unknown greeting — often socialist leaders would kiss each other thrice on each cheek after embracing and, at special events, would kiss on the mouth to demonstrate solidarity and brotherhood.
The Brezhnev-Honecker mural was based on a real photograph of the event taken by Regis Bossu eleven years earlier, in 1979. The kiss took place after an economic agreement between the USSR and German Democratic Republic (the formal name of communist East Germany). The image was famous when it was originally taken, but Vrubel’s artistic rendering took its notoriety to new, unforeseen heights.
“My God, Please Help Me Survive this Deadly Love.” Andy Hay. CC by 2.0.
Although Vrubel’s iconic piece is perhaps the most recognizable mural, much of Berlin’s wall art would not have been painted without the help of Kani Alavi. Alavi was an organizer of the East Side Gallery, which invited artists from around the world to paint and express their reflections on the Cold War ideological divide and personal experiences. Alavi’s own visual contribution, “It Happened in November,” is a synthesis of personal experience and political commentary. The Berlin Wall consisted of two distinct walls separated by a gap for maximum security, and Alavi’s mural depicts thousands of faces walking between them on the day it came down. Alavi had viewed this scene personally from his apartment overlooking Checkpoint Charlie, which was the best-known border crossing between East and West Berlin.
“It Happened in November.” Fraser Mummery. CC by 2.0.
Alavi also directly helped inspire another of the most notable murals, the “Berlin Wall Trabant” by artist Birgit Kinder. Supposedly, Alavi told Kinder to paint anything she wanted on the wall, but she hesitated for a moment. It was only when she looked at her East-German manufactured Trabant car that she felt inspired. She began painting her car forcefully bursting through the wall, symbolizing the city’s escape from Soviet rule. Close observers will note that the license plate reads “Nov 9-89,” which is the day the Berlin Wall fell.
“Berlin Wall Trabant.” Judith. CC BY-NC 2.0.
When the wall fell, and the Soviet grip on East Germany loosened, creativity flowed. Artists visually translated their newfound freedom onto a canvas that had once held them captive. Their murals symbolized the reclamation of power by East Berlin’s formerly oppressed inhabitants. And with this somewhat-unlikely canvas they were able to recount their lived experience and depict the conflict and compromise of the world around them, concretely living in vivid color, forever.
Carina Cole
Carina Cole is a Media Studies student with a Correlate in Creative Writing at Vassar College. She is an avid journalist and occasional flash fiction writer. Her passion for writing overlaps with environmentalism, feminism, social justice, and a desire to travel beyond the United States. When she’s not writing, you can find her meticulously curating playlists or picking up a paintbrush.
Manaus: Capital of the Amazon
My visit to the Amazon’s largest and most contradictory city.
City of Manaus. Dennis Jarvis. CC BY-SA 2.0
My first guide in Manaus explained that when people think about a city in the middle of the Amazon, they expect the city to be wild and see snakes crossing the streets. The reality of the Amazon’s largest city, located in Brazil’s Amazonas Province, is completely different. This past May I spent one of the most memorable weeks of my life in this province. During that time, I did go deep into the Amazon, where I saw a tree Boa, a large snake. But, I also visited a beautiful pink opera house, a fish market, antique bookstores, fancy restaurants, the Presidente Figueiredo Waterfalls, and even the Ponta Negra Beach, which was lined with tall buildings that seemed to be hotels, just like any beach town you’d find in the US.
Me, in the Amazon outside of Manaus. Jeremy Giles
This city of over two million people borders both the Rio Negro and the Amazon River, and is the access point to reach many communities deeper within the Amazon jungle. It is also one of Brazil’s largest industrial centers, including businesses that have nothing to do with the rainforest it borders. In my experience, Manaus is a city unlike any other, and thrives off defying expectations.
The History
Manáos, Eduardo Ribeiro Avenue in 1909. National Library of Brazil, public domain.
Manaus was originally founded in 1669 as a Portuguese fort. By 1832, the fort grew into a town, and received its modern name, Manaus, meaning “mother of the gods,” from the indigenous Manaós tribe. Only 16 years later Manaus expanded into a city. Two years after that, it was officially declared the capital of the Amazonas province.
After the invention of cars in the late 1800s, Manaus became the center of the rubber boom due to the almost complete South American monopoly of rubber trees, which are native to the Amazon basin. This completely changed the city, as it became viewed as the gateway to the Amazon, and became home to many incredibly wealthy rubber barons. These ridiculously rich families had more money than things to spend it on, and began to focus on architecture, shipping materials all the way from Europe to build huge beautiful masterpieces, many of which still exist today.
By the early to mid 1900s the rubber boom had almost completely left Brazil, being replaced by rubber trees brought to Southeast Asia. This spelled financial ruin for Manaus, which sank into desperation. This poverty continued until 1967, when Manaus was named a duty free zone, making it cheap for companies to move there. This allowed Manaus to grow into the economic hub it is today, currently being a Brazilian access point for over 600 global companies.
The Amazonas Theatre
Amazon Theatre in Manaus. Rafael Zart. CC BY 2.0.
The Amazonas Theatre opened in 1897, carrying with it Manaus’ nickname “the Paris of the Tropics.” The opera theater was built almost entirely using materials imported from Europe, topped with a beautiful dome of Brazil’s flag.
At the time of its opening, the opera theater was in many ways a sign of all that was wrong in Manaus. It was built for Manaus’ uber-wealthy, using the money they made by exploiting the local population to harvest the rubber they sold abroad. Moreover, even the few who could enter the opera house valued the status it brought them more than the opera itself. The most expensive seats in the opera house were those that were the most visible to the public. Ironically, these spots actually had the worst view of the stage itself.
Today, the opera house, which remains a top opera house in the world, has come a long way from its imperialistic origins. Most performances at the theater are free, and those that aren’t are very affordable. The performances feature both local artists and acts from around the world. Moreover, to encourage all to join, a large screen is often set up in the plaza in front of the opera house, allowing as many people to see the performances as possible.
The Ports
Manaus market from the river. archer10 (Dennis). CC BY-SA 2.0.
In many ways, the center of Manaus is its ports. Manaus is bordered by both the Rio Negro and the Amazon River, allowing for a large number of ships and ferries, both for tourists and locals. These boats can take you deeper into the Amazon or out of it entirely, allowing ocean freight ships to transport goods directly to Manaus.
In addition, much of Manaus’ culture and nature revolves around the ports. A little over a half hour by boat from Manaus’ ports is the meeting of the waters, a line where the Rio Negro meets the Amazon River. This line is clearly visible with the water looking different and being a clearly different temperature on either side of the line.
On land, about a five minute walk from Manaus’ largest port is an amazing market “Mercado Municipal” that, every morning, is filled with different fresh fish, including some of the biggest fish in the world. My personal favorite of these huge fish is Tambaqui, a cousin of the Piranha and one of the most delicious meals I’ve ever had. The fish is so big that its ribs are visible and alone big enough for a meal. In fact, I’d go even further to say that, to me at least, the ribs are the best part.
Amazon Rainforest
The Amazon Rainforest, a few hours from Manaus. Jeremy Giles
While Manaus itself is a big city, much of the land around it is still forested and filled with natural wonders. If you go an hour or two downstream on the Rio Negro, you will be greeted by intensely green trees on both sides which, in the right conditions, are perfectly reflected by the black water below you. In the wet season this water will rise several meters, causing many of the trees to jut out of the water itself. Just to note, climate change has caused the water to rise more now than in the past, however, the water rising multiple meters is a natural phenomenon and one that actually helps the trees survive.
When you’re surrounded by the trees you may start to be greeted by animals almost immediately. Howler and spider monkeys can be seen leaping from tree to tree, sometimes carrying their babies, and boas can be found curled up on branches. The water itself is dotted with caiman and different kinds of fish. The lucky will get to see pink river dolphins breaching the water’s surface.
A waterfall at El Presidente Figueiredo. Jeremy Giles
There is plenty to see around Manaus and in Manaus on land as well. Most notably, about an hour and a half drive from Manaus are the Presidente Figueiredo waterfalls. These waterfalls are all stunning to look it, with fast moving water from the Rio Negro. However, they do vary in size. The first waterfall I was unable to approach because it was too big. The second one was small enough that I was able to climb behind it.
The Rio Negro, or Black River in English, gets its color from the decaying vegetation that falls into it. Beyond giving the river a wondrous dark hue, this decay causes the river to be relatively acidic. While it is perfectly okay for humans to swim in the water, the same cannot be said for mosquitoes, who almost completely avoid the river. This is amazing for Manaus, which borders the Rio Negro, as the city has relatively few mosquitos despite being in the middle of the Amazon.
The Technology Industry
President Lula visiting a motorcycle factory in Manaus. Brasil em Mapas Brazilmaps. CC BY 2.0
While much of Manaus’ economy does revolve around the Amazon, the tech industry is actually one of the city’s largest. Brazil’s largest research and development Institute, the Sidia Institute of Science and Technology, is based in Manaus. Moreover, Manaus is known for its extensive motorcycle industry, producing over 1.4 million motorcycles in 2022.
Manauara Shopping Center. Naldo Arruda. CC BY 2.0
I’ve spent the past few days trying to think of what, out of everything I saw, best represents Manaus. I believe I’ve found it, but, like everything else with the city, it’s not what you would expect.
The Manauara Shopping mall is a huge and beautiful structure, with big glass windows lining the outside, seeming to connect the building to the world beyond its walls. It has more than 200 stores, which range from those selling wooden crafts and acai from the Amazon to big brands on national and international levels. The moment I remember most is when, after exploring the first three levels of the mall, my family decided to visit the basement food court. Going down the escalator, we saw the same glass windows from the front of the building, except this time, they were facing inwards. We walked towards a door under the hulking glass and through it outside into open space. I looked up and spiraling branches blanketed with green leaves towered above me, almost blocking my view of the night sky. I breathed in the air deeply, letting go of a tension I didn’t know I was holding. Looking back, in this moment, in a rainforest in the middle of a mall, I truly experienced Manaus most.
Jeremy Giles
Jeremy is a Writing Seminars and International Studies major at Johns Hopkins University. He is an avid writer and the Co-Founder of Writers’ Warehouse, Johns Hopkins’ first creative writing group. He is an advocate for Indigenous rights, and studies how Indigenous philosophies can be used to help prevent climate change. Using his writing, he hopes to bring attention to underrepresented voices in today’s world.
On the Table: Sharing food Around the World
The tradition of sharing meals is a custom that transcends national borders and bridges generational divides.
Marketplace in Seychelles. UN Women. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
Breaking bread has long served as a sacred means of creating community and connection. In the 18th century, the term for a “good friend” in Dutch translated to a “table friend.” Today, such an exchange of friendship is still an elemental ingredient to mealtimes. The settings vary across the globe, from pre-set dinner tables to park picnic benches, floor mats to swiveling bar stools. About a quarter of the world’s population does not sit nightly at a table, but rather gathers around a mat or stands balancing on a wooden plank in the midst of the mud in a market. But, no matter the gathering space, one aspect remains core to nearly all eating traditions: the manner in which food is shared is a ritual that celebrates the communal over the individual.
Sharing small bits of food is a human habit that anthropologists believe connects to a primal need to forge alliances through a sense of communal equality. Such a need has led to a kind of communal snacking culture, in which groups share nibbles of food. From spreads of hummus and babaganoush, to tapas of cheese and olives, to steamed buns of dim sum, communal eating habits around the world exemplify how the best meals are always shared.
Ethiopia
An Ethiopian dish. Malingering. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
Communal eating is a central part of Ethiopian food culture and is aided with the use of Injera, a thin sourdough-risen flatbread with a spongy texture. Most Ethiopian meals are eaten with one’s hands and from a communal plate placed in the middle of the table. The left hand is considered unclean, and so the right hand is used for eating and ripping apart pieces of Injera to scoop up food. Traditionally, meals begin with the oldest at the table taking the first bite, a custom to indicate respect to elders.
The communal significance of food in Ethiopia is represented through a practice called the gursha: a form of hand-feeding, in which one will place a small morsel of food into another’s mouth. The gesture is usually first given to elders or guests at the meal and signifies a sign of respect, hospitality, and friendship.
Foods to try
Kitfo is a native Ethiopian dish made with raw beef. Similar to an American hamburger, kitfo uses Injera rather than a bun. The dish originates from the Gurage region of Ethiopia and is believed to have emerged from the Orthodox Christian tradition as a means of eating meat to break the fast after Lent.
France
French bakery. Hannah Wilson. CC BY-ND 2.0
French food culture is defined by a sense of intention and relaxation, with meals often lasting for hours at a time. The care characteristic of French culinary culture is exemplified in its “gastronomic meal.” The meal, which became a part of UNESCO’s List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity, refers to a kind of dining tradition in which a large meal is prepared to bring family together. Elements of the gastronomic meal include its use of fresh local ingredients, its careful selection of dishes that represent a diverse spread of the country’s regional cuisines, an emphasis on food and wine pairings, an aesthetic table setting, and group conversation throughout the dinner. The meal is often a foundational element to birthday and wedding celebrations and follows a set structure. Starting drinks, or apéritif, begin the meal, followed by up to four courses including a starter, a main dish of fish or meat with vegetables, and a sweet dessert paired with cheese. The meal typically ends with a drink referred to as digestif. Digestifs are characterized by a high alcohol content and rich flavor, and include liquors such as Génépi, Cognac, Armagnac, and Calvados.
Foods to try
While French food is popularly characterized by its flaky baguettes, croissants, and delicate pastries, cuisine varies significantly depending on the region. Cheese and ciders are a popular part of dinners in Normandy, while ratatouille is a family staple in the country’s Mediterranean south.
The Loire Valley boasts bountiful grapes, cherries and berries that are used to make rich liquors and sweet fruit tarts, while the Basque Country pairs fish and meats with spicy herbs and sauces.
Mexico
Mexican meal. VisitPlano. CC BY 2.0
In Mexico, community plays a central role in both the production and consumption of food. In an interview, renowned Mexican chef Margarita Carrillo Arronte described Mexican food as “a women's thing.” Arronte’s statement highlights a cultural tradition in which communal cooking and the sharing of recipes serve as a means of bringing women together, and a conduit for intergenerational knowledge. Dating back to pre-colonial times, the majority of cooks in Mexico have been women. After the arrival of the Spanish in the 16th century, a mix of indigenous, African, and Spanish cooks worked in conquistadors’ kitchens, where they developed a unique culinary blend. Today, some of the top Mexican restaurants have been opened and run by women chefs, the likes of which include Alicia Gironella de Angeli, Patricia Quintana, Monica Patiño, Martha Ortiz Chapa and Carmen 'Titita' Degollado. The State of Michoacán is especially known for its rich culinary life that centers the talents of indigenous female cooks, a status that got the state selected as the host for the upcoming VII Gastronomy Forum, in October 2023.
In 2010, Mexican food was inscribed on UNESCO’s Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity, and recognized for its sense of community and collective participation. Local’s use of the milpa system allows for more sustainable farming practices. The system uses intercropping to allow for multiple species to grow in the same place. When it comes to eating practices, singular utensils such as grinding stones and mortars are used rather than forks and knives.
Foods to try
Corn is a prime ingredient of Mexican food, and serves as a base for a diverse range of dishes. Elote, or corn on the cob, is a typical Mexican street food drizzled in mayonnaise and lime juice, while atole uses corn as its base for a hot beverage that can be sweetened with vanilla, cinnamon, and guava. Mexican tamales which date back to the Aztecs, use corn masa as a dough that can be filled with beans, meats, chillies, or vegetables. The most popular use of corn comes in the form of tortillas, a thin pancake shaped flatbread that serves as a base for beans, meats, and fresh vegetables.
Korea
Kimchi. Hyunwoo Sun. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
The philosophy of yak sik dong won, or “food is medicine,” lies at the heart of Korean cooking. Korean food culture revolves around a key sense of community and an appreciation of food as nourishment for the soul as well as the body. The sharing of banchan, or side dishes, serves as a key example of a communal eating culture. Banchan side dishes include vegetables, seafood, eggs, meats, and kimchi. Rich in fiber and probiotics, kimchi captures Korean culture’s understanding of food as medicine. The dish consists of fermented vegetables including cabbage and radish, mixed with seasonings such as ginger, garlic and spring onions.
Korean meals draw upon the concept of bapsang: the idea that a table is set up for shared enjoyment. Balance plays a key role in Korean meals, and spicy foods are often paired with more delicate and nuanced flavors, such as broths and rice.
Foods to try
Mandu is a popular Korean snack with traditional roots. Now a common example of Korean street food, the dumpling’s origins date back to the 14th century. It is believed that the Korean royal court frequently ate mandu that mimicked the shape of sea cucumbers as a way to represent the bounty of nature. The philosophy at the core of Mandu’s origins extends to its modern use as a staple of the Lunar New Year to represent future prosperity. The preparation of Mandu also incorporates the communal elements of Korean cooking, as families join together to fold the dough into craftful pouches for meats and vegetables.
Jessica Blatt
Jessica graduated from Barnard College with a degree in English. Along with journalism, she is passionate about creative writing and storytelling that inspires readers to engage with the world around them. She hopes to share her love for travel and learning about new cultures through her work.
Frozen Glory: Inside the Eskimo-Indian Olympics
From cultural preservation to sheer athletic spectacle, the World Eskimo-Indian Olympics are a highlight of the Native Alaskan calendar.
An athlete competes in the blanket toss event at the WEIO. KNOM Radio. CC BY-SA 2.0
In the early 1960s, two non-Indigenous pilots who regularly made trips over Alaska’s rural communities kept observing the celebration of an interesting cultural event. This sporting event, as they later came to realize it was, dated back far beyond living memory and honored strength, resilience and endurance through a series of events meant to test the skills necessary to live in such an unforgiving environment. Given that Alaska had just recently become an American state in 1959, the early 60s saw the gradual encroachment of mainstream American culture into its more remote outlying communities, posing a serious threat to local traditions and practices. After the pilots shared their concerns with various groups in Fairbanks, the World Eskimo-Indian Olympics (WEIO) was officially born in 1961 and drew Native participants and spectators from around the Fairbanks area to participate on the banks of the Chena River.
The WEIO has grown significantly since then, with thousands of people traveling to watch the best of Alaska’s Indigenous athletes compete in the Big Dipper Ice Arena for four days each July. Aside from a minimum age limit of 12 years, there are no age categories for any of the events, which means that several generations of the same family can be seen competing against each other. It is also common for older and more experienced competitors to coach and advise the younger athletes during the competition: rather than trying to beat one’s opponents, the larger goal is to compete against and better oneself.
Athletes Sean O’Brien (left) and Chris Kalmakoff (right) compete in the Eskimo stick pull event. Erich Engman. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
Many of the events, however, are still extremely competitive, and involve intimate face-offs between athletes. The Indian Stick Pull, for example, calls for athletes to wrench a short greased stick from their opponent, an event meant to replicate the grip strength necessary when trying to keep hold of a freshly caught fish by its tail. The Ear Pull is a contest of stamina to demonstrate the athletes’ ability to withstand pain, a valued trait in the often cruel conditions of the Alaskan North. In this event, string is looped around the opposite ears of two athletes as they face each other as they pull away in a tug-of-war with their ears until one cedes the match.
Other events are competed individually, but with just as much rigor and excitement. The Greased Pole Walk, as its name suggests, tests the balance needed for crossing creeks on slippery logs by having contestants walk as far as they can barefoot along a greased wooden pole. A favorite among both competitors and spectators alike, the Two-Foot High Kick requires competitors to jump vertically and kick a suspended ball with both feet before landing and maintaining their balance. Hundreds of years ago, villages along the coast would perform these kicks as a way to communicate to the village that a whale or some other game had been caught, and to prepare themselves to assist the hunters upon their return.
Athlete Ezra Elissoff competes in the Two-Foot High Kick final at the 2021 WEIO. Jeff Chen. CC BY-SA 2.0
Despite the popularity of basketball and ice hockey, the traditional sports seem to be gaining popularity among young children and teenagers, and are also contributing to the difficult task of preserving and passing on Native Alaskan culture. Miley Kakaruk, a 15-year-old athlete of the Inupiaq tribe of Northwestern Alaska, says that she imagines her ancestors competing in the same events centuries ago, vying to be chosen for their village’s next hunting party. Because each event is so heavily rooted in their history, younger competitors are able to learn the customs and stories that so heavily influence the culture and lifestyle of their people.
Equally important is the power of these games to forge a connection between athletes and society. Historically, studies have shown that Native Alaskans suffer from some of the highest rates of alcoholism and drug abuse in the US. A number of the people that the WEIO Board works with and recruits are young adults who are at risk of or actively battling addiction. According to Gina Kalloch, a board member and ex-athlete, discovering their culture through such a fondly practiced social tradition has allowed many of these people to develop a sense of pride in themselves and their culture, and helped to reorient their lives.
Native Alaskan women compete in the Miss WEIO Cultural Pageant alongside the athletic events each year. Danny Martin. CC BY-SA 2.0
While this year’s edition of the Olympics already took place between July 12 and 15, highlights of both the sporting events and the accompanying Miss WEIO Cultural Pageant are freely available on the internet.
Tanaya Vohra
Tanaya is an undergraduate student pursuing a major in Public Health at the University of Chicago. She's lived in Asia, Europe and North America and wants to share her love of travel and exploring new cultures through her writing.