Since the fall of communism, Český Krumlov has transformed from relic to hotspot—but has it lost its authentic appeal along the way?
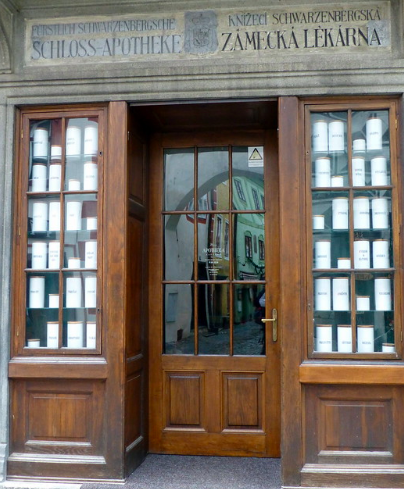
The Czech capital of Prague is known the world over for its storybook beauty, manifesting most dramatically in the towering gothic facade of the St. Vitus Cathedral and the sprawling tableau of red rooftops visible from atop Petřín Hill. Yet just over 100 miles away is another sparkling jewel in the Czech Republic’s crown: Český Krumlov, a city of only 13,000 residents whose 13th-century castle and picturesque riverbanks have brought it not only recognition as a UNESCO World Heritage site but also an increasing influx of tourists that now threatens its very identity.
Former Czechoslovakia’s communist regime, which lasted from 1948 to 1989 before it was ushered out by the Velvet Revolution, left much of Český Krumlov in disrepair. Yet the city’s neglected state lent it a sense of mystery and charm. In the years since, Krumlov—much like the country’s capital, Prague—has been transformed into a tourist wonderland, with historic buildings being renovated and revitalized and ensuing increases in tourist income bolstering the city’s economy.
City streets. Hindol Bhattacharya. CC BY-SA 2.0
As the city has changed, so have the demographics of its visitors. In an interview with Radio Praha, Krumlov’s mayor, Dalibor Carda, explained that an initial boom of Austrian and German tourists after 1989 gave way to an influx of Americans, many of whom settled in the city indefinitely. Today, for locals—whether native-born or transplants—the off-season is a thing of the past, with tour groups flooding the city on a year-round basis. “[I]f you want to have a pristine Krumlov,” writes Jan Velinger in a piece for Radio Praha, “you have to get up very early to ever have its romantic streets, or overlooking castle, ramparts to yourself.” Fed up with the unrelenting crowds, locals have largely migrated to the outskirts of the city, resulting in an exodus of local businesses: Bakeries, hardware stores, and family-owned shops are now difficult to find, having been replaced with bars, restaurants, and hostels catering to short-term visitors.
One of Český Krumlov’s bars, popular among tourists. kellerabteil. CC BY-NC 2.0
In some respects, Český Krumlov has moved to mitigate the encroaching tendrils of tourism, notes reporter Chris Johnstone, pointing to a ban on advertising and the exclusion of cars and buses from the city center. Moreover, just this June, the city established a tariff on buses in an effort to regulate the influx—up to 20,000—arriving each year. The plan is the first of its kind in the Czech Republic, although Salzburg and other Austrian cities have imposed similar measures. Now, all buses rolling into Krumlov must book in advance, navigate to one of two designated stops, and pay the toll of CZK 625, approximately $28.
Tourism has inspired not only legislative changes, but also works of art—as in the case of “UNES-CO,” a 2018 project by renowned conceptual artist Kateřina Šedá. Responding to the profound impact of visitors on the distribution of local populations, Šedá conceived of a work that involved relocating a group of individuals and families to the heart of Český Krumlov for three months at the height of the tourist season. The participants were provided with starter apartments and jobs “on the basis of what Krumlov most needs,” which Šedá deemed to be “the pursuit of normal life.” The title played on the city’s status as a UNESCO World Heritage site and on the Czech words “unést” and “co,” meaning “take away” and “what,” as in “What do visitors get out of this place?” Šedá, whose work often involves social themes and who is famed for relocating an entire Czech village to London’s Tate Modern in 2011, stressed that the project was not intended to be a show for tourists, but rather a social experiment.
Houses along the banks of the Vltava River. P. N. CC BY-SA 2.0
On the opposite side of the artistic spectrum, Huawei—the Chinese electronics behemoth currently facing scrutiny from the U.S. for potential security issues—announced in January that it would build an exact facsimile of Český Krumlov at its headquarters. The Huawei campus, which lies just outside of Shenzhen in the city of Dongguan, will also count Granada, Verona, Paris, Budapest, and Bruges among its plethora of reconstructed European cities. “I heard about it when they started preparing it,” commented Cardo. “The fact that they [are] building it without at least contacting the city does not sit well with me.”
The Krumlov replica may well draw more Chinese tourists, who already represent the largest segment of visitors to the historic city. Yet for embittered locals, the mini-city could be a grimly apt representation of what their home has become: a mere palimpsest of its original iteration, and a cautionary tale depicting how capitalism and tourism can spur unwelcome transformation.
Talya Phelps
Talya hails from the wilds of upstate New York, but dreams of exploring the globe. As former editor-in-chief at the student newspaper of her alma mater, Vassar College, and the daughter of a journalist, she hopes to follow her passion for writing and editing for many years to come. Contact her if you're looking for a spirited debate on the merits of the em dash vs. the hyphen.